Effect of heat treatment process on microstructure and properties of titanium alloy tubing
-
摘要: 通过光学显微镜、扫描电镜、拉伸试验机、冲击试验机等手段研究了不同热处理工艺对钛合金油管组织和性能的影响。结果表明:固溶温度对钛合金油管的晶粒形态和各相占比产生较大的影响。在α+β两相区固溶处理,随着固溶温度的升高,α相的占比下降;在850 ℃固溶1 h水冷+550 ℃时效2 h空冷热处理工艺下获得了双态组织,可实现钛合金油管的高强韧性匹配,综合性能优异,满足SY/T 6896.3标准对110ksi钢级钛合金油管的要求。Abstract: The effect of heat treatment process on the microstructure and properties of titanium alloy oil well tubes was studied by means of optical microscope, scanning electron microscope, tensile testing machine and impact testing machine. The results show that the solid solution temperature has a great influence on the grain morphology and phase proportion of titanium alloy tubing. In the α+β two-phase region, the proportion of α phase decreases with increase of the solution temperature. Bimodal structure of titanium alloy can be obtained at 850 ℃ of solid solution for 1 h followed by water cooling and 550 ℃ aging for 2 h followed by air cooling, which can realize the matching of high strength and toughness of titanium alloy oil well tubes. And it has excellent comprehensive properties, meeting the requirements of SY/T 6896.3 standard for 110ksi steel grade titanium alloy oil well tubes.
-
0. 引言
随着油气井井深及开采难度的不断增加,井下的温度和压力升高,H2S、CO2、S、Cl−含量很高,因此,对于油井管的材料和技术要求更为严格。常用碳钢、不锈钢管材已无法满足开采需求,高合金化的镍基耐蚀合金在石油勘探和工况苛刻的油气井上得到了广泛应用,然而,镍基合金价格高、密度大、镍资源稀少,且高温下强度衰减严重[1-2]。钛及钛合金是一种相对较为年轻的金属材料,于20世纪50年代发展起来,其具有密度小,比强度高,抗腐蚀性能、高温力学性能、抗疲劳和蠕变性能等优良的综合性能,在航空航天、海洋勘探、能源化工、生物医疗和其他一些领域得到广泛的应用[3-8]。钛合金具有优良的抗疲劳性能和极强的抗CO2+H2S+Cl−腐蚀能力等优点,近年来在高温高压及高腐蚀恶劣环境下油气井钻杆、油套管、连续管和海洋隔水管等石油管材中得到应用及推广,并逐步替代现用镍基合金管材[9-16]。钛合金的强度和韧性与它的微观组织形貌有着密不可分的关系,钛合金的微观组织首先取决于材料中各种元素的含量,稍有差别就会导致微观组织的差异。相同材料采用不同的热处理工艺可得到不同的微观组织,进而得到不同的强度和韧性匹配。目前,国内钛合金油井管的强度满足设计要求,但韧性指标相对较低。笔者以新设计的一种钛合金油管为研究对象,探讨不同热处理工艺对该钛合金油管显微组织及力学性能的影响,开发高强韧性匹配的钛合金油管产品,以满足油田现场应用需求。
1. 试验材料及方法
试验材料采用国内某钛合金厂家提供的Φ101.6 mm×10.54 mm冷轧钛合金管坯,经金相法测得该钛合金的相变点为950 ℃,其化学成分如表1所示。钛合金管坯的热处理试验在箱式电阻炉中进行,固溶温度取相变温度以下50~150 ℃的α+β两相区进行固溶处理,分别取800、850、900 ℃固溶1 h,固溶后进行水冷处理;随后对水冷后钛合金管坯进行550 ℃时效2 h处理,再进行空冷至室温,具体热处理工艺如下:
表 1 钛合金油管的化学成分Table 1. Chemical compositions of titanium alloy tubing% Al V Fe C N H O Mo+Zr Ti 5.06 4.05 0.045 0.015 0.01 0.005 0.08 ≥3 Bal 工艺1:800 ℃固溶/1 h/水冷+550 ℃时效/2 h/空冷;
工艺2:850 ℃固溶/1 h/水冷+550 ℃时效/2 h/空冷;
工艺3:900 ℃固溶/1 h/水冷+550 ℃时效/2 h/空冷。
分别对热处理后钛合金油管各取3个拉伸试样、3个冲击试样及金相试样进行检测分析,拉伸性能试验采用Zwick/Roell 1 200 kN拉伸试验机,按GB/T 228.1—2010《金属材料拉伸试验 第1部分:室温试验方法》标准进行;冲击性能测试采用Zwick PSW 750型摆锤冲击试验机按GB/T 229—2007《金属材料 夏比摆锤冲击试验方法》进行;切取金相试样进行打磨抛光,用HF+HNO3+H2O(体积比1∶2∶5)腐蚀液腐蚀试样,在DMI 5000M光学显微镜(OM)下观察显微组织,采用日立S3700N扫描电镜(SEM)对拉伸断口及冲击断口进行分析。
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 显微组织
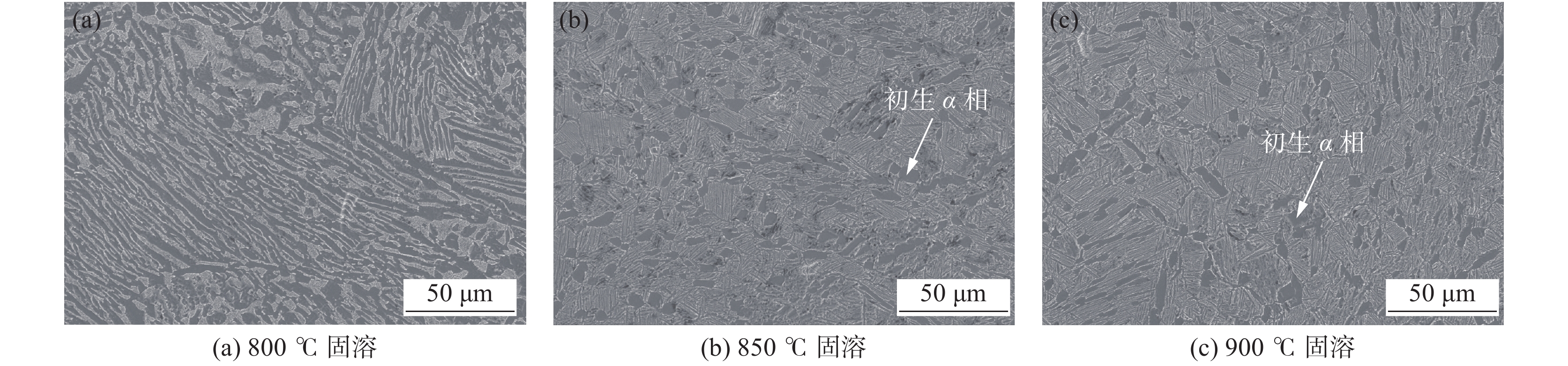
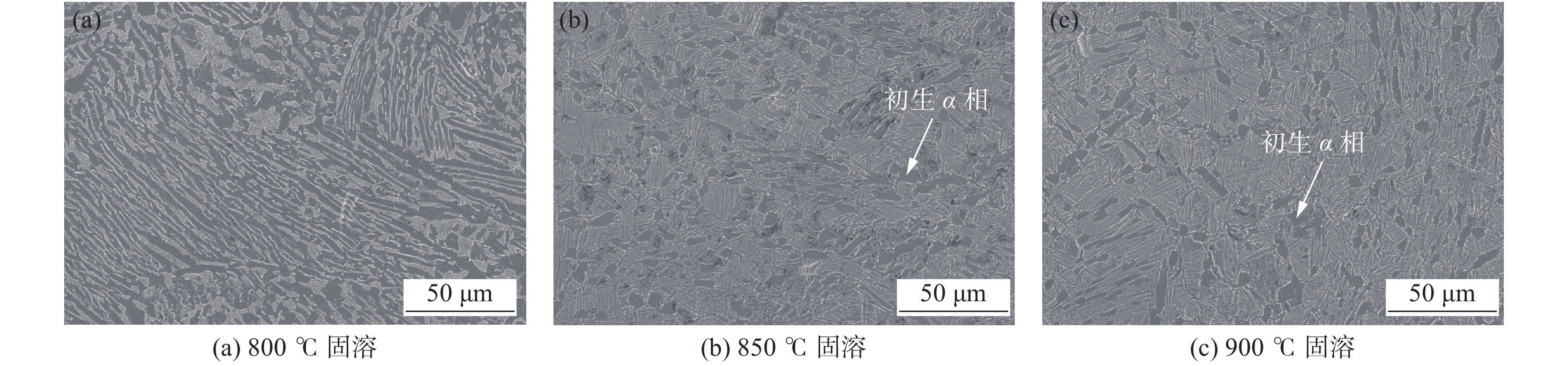
根据热处理过程中物相平衡所需的温度和时间等动力学条件,经预试验研究测定,该成分设计钛合金在α+β两相区固溶时,微观组织中初生α相占比逐渐减少。选取800、850、900 ℃三种固溶温度下固溶1 h处理,对固溶处理后金相组织扫描电镜(SEM)照片(图1)分析可以看出,该钛合金油管在α+β两相区固溶时,随着固溶温度的升高,组织中的初生α相含量占比逐渐减少。800 ℃固溶温度下,由于固溶温度较低,初生α相溶解进入β相动力条件弱,轧制组织中弯曲流线依旧可见,统计测量初生α相占比约为50%左右;900 ℃固溶温度时,元素扩散的动力学条件较优,初生α相溶解进入β相越多,测量统计初生α相占比最低约15%左右;在 850 ℃固溶温度下,初生α相溶解进入β相介于两者之间,由图1(b)测量统计微观组织中初生α相占比约25%左右。
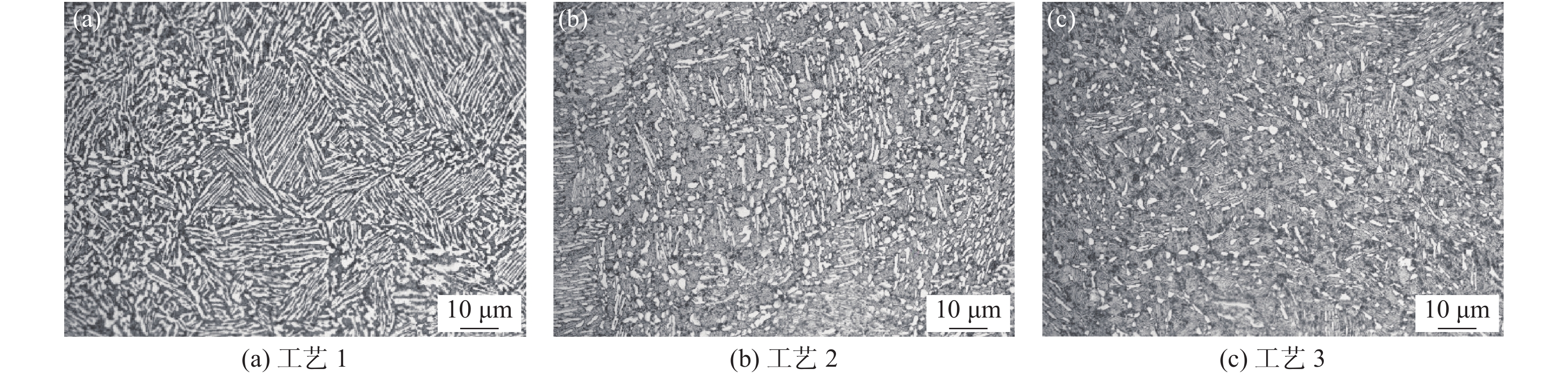
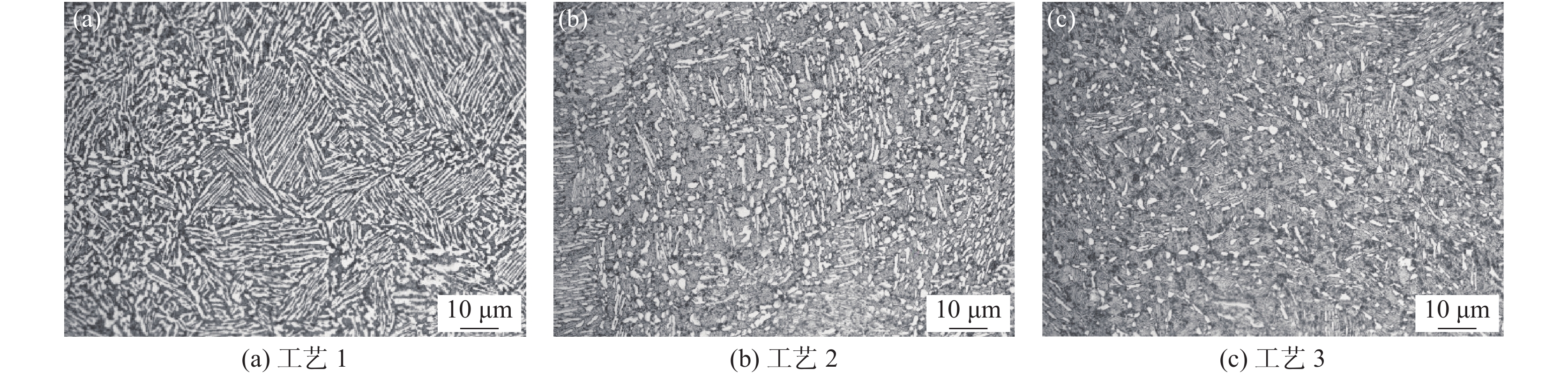
不同热处理工艺试验后,对钛合金油管进行微观组织分析,工艺 1的微观组织如图2(a)所示,观察到显微组织为α+β的等轴组织,无明显的原始β晶界,转变的β基体上为等轴态的初生α相;工艺 2的微观组织见图2(b),组织为α+β双态组织,初生α相及少量拉长的次生α相;工艺 3的微观组织见图2(c),组织为α+β双态组织,少量的初生α相及次生片状α相。
2.2 力学性能
对热处理后钛合金油管进行拉伸性能检测,每种热处理工艺下,沿钛合金油管周向取三个拉伸试样进行检测,不同热处理工艺下的钛合金油管的力学性能如表2所示。
通过表2可以看出,热处理工艺 1的屈服强度在805~825 MPa,抗拉强度在915 ~925 MPa,满足强度要求,但伸长率在10.5%~12.0%,不满足标准要求最低伸长率12%;热处理工艺2、工艺3的屈服强度、抗拉强度、伸长率均满足标准要求。表明:随着固溶温度的升高,屈服强度逐步升高,在800~850 ℃区间,屈服强度升高的幅度大于在850~900 ℃升高的幅度,当在850 ℃固溶×1 h水冷+550 ℃时效×2 h 空冷热处理工艺下,该钛合金油管的综合力学性能最优。
表 2 不同热处理钛合金油管的力学性能Table 2. Mechanical properties of titanium alloy tubing with different heat treatment parameters工艺 试样号 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 延伸率A /% 1 1-1 805 915 12.0 1-2 825 920 10.5 1-3 815 925 11.5 2 2-1 900 1000 15.5 2-2 895 1010 15.0 2-3 915 1035 15.5 3 3-1 930 1040 12.0 3-2 925 1030 12.5 3-3 920 1025 13.5 SY/T 6896.3标准对
110ksi钢级要求758~965 ≥862 ≥12 2.3 拉伸断口SEM 分析
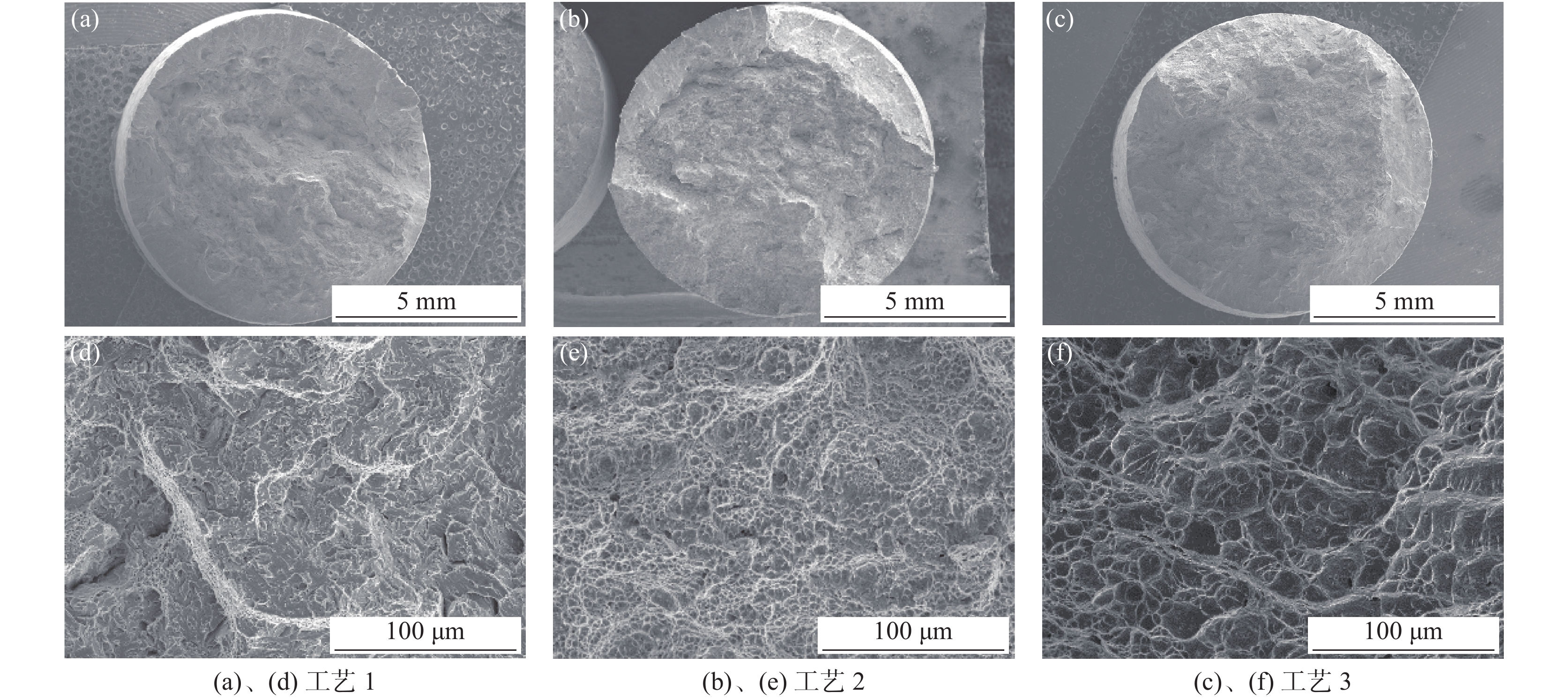
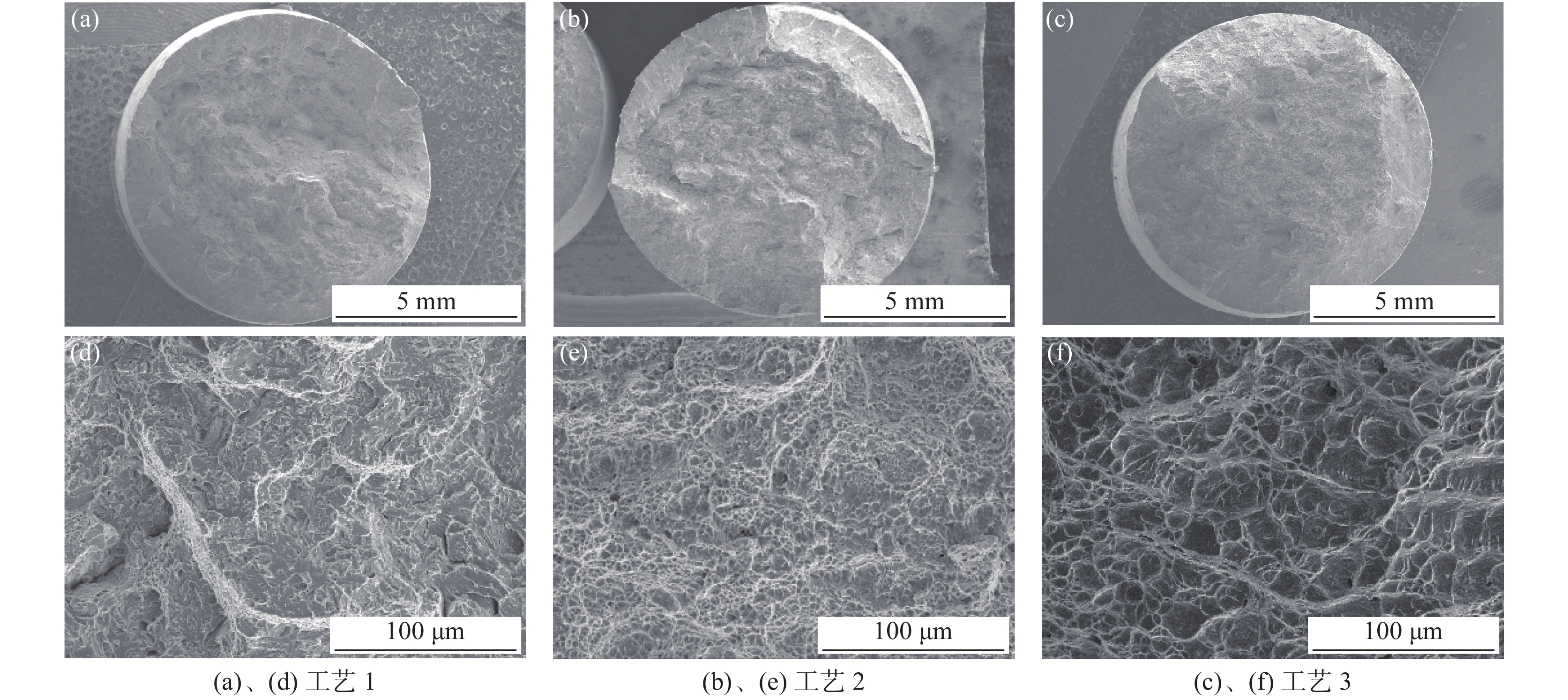
为了研究不同热处理工艺所得钛合金的断裂机理,对拉伸断口作SEM分析,断口形貌如图3所示。从图3(a)和(d)可得,工艺 1对应的宏观断口未观察到轻微的缩颈现象,为韧性断口,韧窝小而浅,还存在少量解理面,说明其塑性相对较差;从图3(b)、(e)、(c)、(f)可得,宏观断口出现颈缩现象,断面存在明显的纤维区、放射区及剪切唇三种韧性断裂的典型特征,表明工艺2和工艺3热处理后的钛合金油管的断裂韧性相对较好。
2.4 冲击断口分析
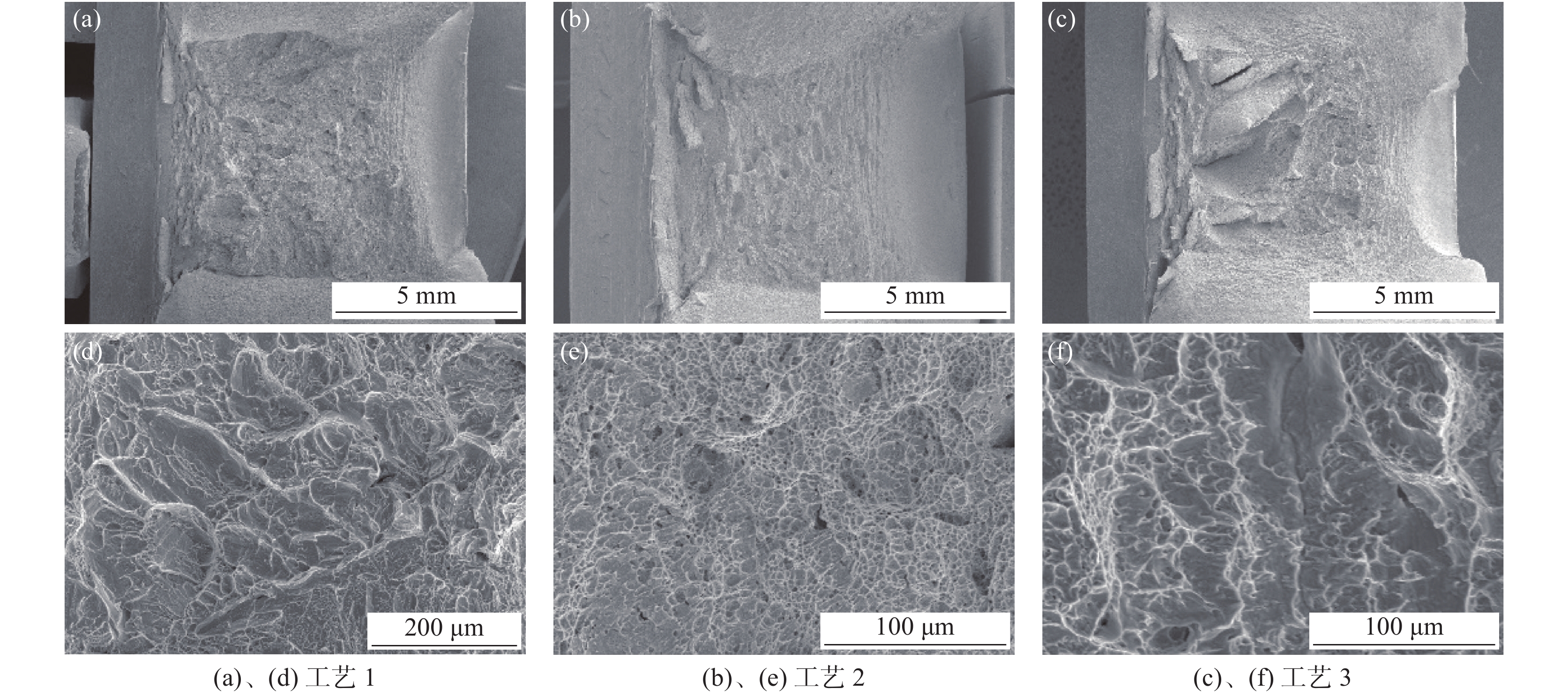
为了研究该钛合金油管热处理后塑性断裂特征及断裂方式与组织性能之间的关系,以便对该钛合金材料不同状态下的塑性作出判断,对工艺 1、工艺 2及工艺 3热处理后的冲击断口做了SEM 断口分析,如图4、表3所示。
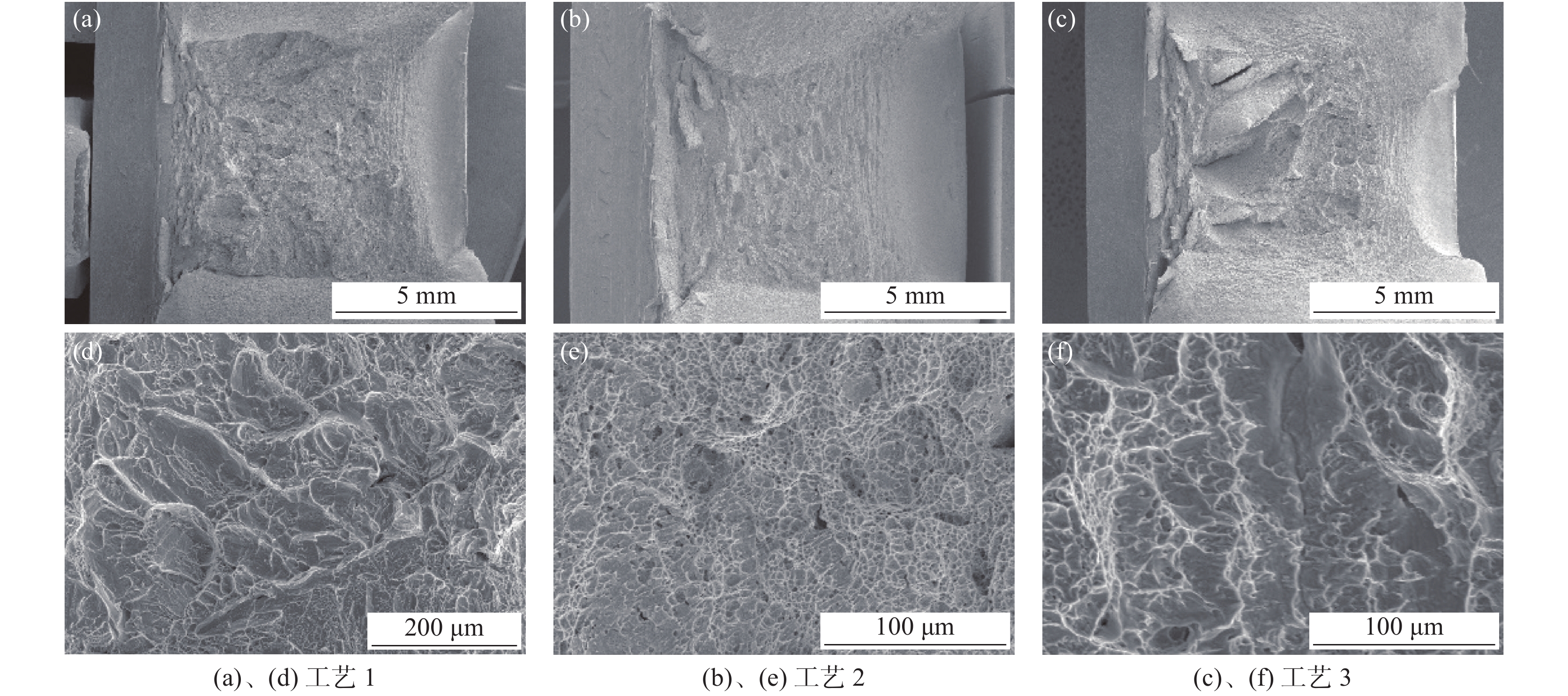
通过分析三种热处理工艺下钛合金油管的冲击断口的SEM照片可以看到,三种热处理工艺下冲击断口河流花样明显,均为韧性断裂,其中图4(e)中的韧窝深而多且分布均匀,韧性最好;图4(d)韧窝浅且平坦,韧性较差;图4(f)韧性值介于两者之中。
表 3 不同热处理钛合金油管的夏比冲击值Table 3. Charpy impact value of titanium alloy tubing with different heat treatment工艺 取样方向 冲击值(0 ℃)/J 测试值 平均值 1 纵向 36,38,40 38.0 2 纵向 68,69,64 67.0 3 纵向 38,45,43 42.0 注:冲击试样尺寸为10 mm×10 mm×55 mm。SY/T 6896.3标准对110ksi钢级要求:0 ℃纵向冲击值≥41 J。 3. 结论
1) 该钛合金油管在α+β两相区固溶,随着固溶温度升高,微观组织中等轴α相比例逐渐减少,β转变组织数量逐渐增加。
2)随固溶温度升高,该钛合金油管热处理后的屈服强度升高,850 ℃固溶时,屈服强度增幅最大;当微观组织中的初生α相占比约25%时,其夏比冲击值最高,0 ℃纵向冲击值达64~69 J。
3) 850 ℃固溶1 h水冷+550 ℃时效2 h空冷热处理工艺,为该钛合金油管的最优热处理制度,实现该钛合金油管强韧性匹配,获得综合性能优异钛合油管产品,满足110 ksi钢级钛合金油管性能要求。
-
表 1 钛合金油管的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of titanium alloy tubing
% Al V Fe C N H O Mo+Zr Ti 5.06 4.05 0.045 0.015 0.01 0.005 0.08 ≥3 Bal 表 2 不同热处理钛合金油管的力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of titanium alloy tubing with different heat treatment parameters
工艺 试样号 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 延伸率A /% 1 1-1 805 915 12.0 1-2 825 920 10.5 1-3 815 925 11.5 2 2-1 900 1000 15.5 2-2 895 1010 15.0 2-3 915 1035 15.5 3 3-1 930 1040 12.0 3-2 925 1030 12.5 3-3 920 1025 13.5 SY/T 6896.3标准对
110ksi钢级要求758~965 ≥862 ≥12 表 3 不同热处理钛合金油管的夏比冲击值
Table 3. Charpy impact value of titanium alloy tubing with different heat treatment
工艺 取样方向 冲击值(0 ℃)/J 测试值 平均值 1 纵向 36,38,40 38.0 2 纵向 68,69,64 67.0 3 纵向 38,45,43 42.0 注:冲击试样尺寸为10 mm×10 mm×55 mm。SY/T 6896.3标准对110ksi钢级要求:0 ℃纵向冲击值≥41 J。 -
[1] Xing Na, He Libo, Gao Zhenfeng, et al. Development status of Ni-based alloy tube and casing for high acidic corrosive cas fields[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2013,35(4):59−62. (邢娜, 何立波, 高真凤, 等. 高酸性腐蚀油气田用镍基合金油套管开发现状[J]. 上海金属, 2013,35(4):59−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2013.04.015 [2] Ishiguro Y, Miyata Y, Nakahashi T, et al. Enhanced corrosion-resistant stainless steel OCTG of 17Cr for sweet and sour environments[C]//USA 68th NACE Annual Conference, 2013. [3] Zhao Yongqing. Current situation and development trend of titanium alloys[J]. Materials China, 2010,29(5):1−8. (赵永庆. 国内外钛合金研究的发展现状及趋势[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010,29(5):1−8. [4] Fu Yanyan, Song Yueqing, Hui Songxiao, et al. Research and application of typical aerospace titanium alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2006,30(6):850−856. (付艳艳, 宋月清, 惠松骁, 等. 航空用钛合金的研究与应用进展[J]. 稀有金属, 2006,30(6):850−856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2006.06.028 [5] Zhu Zhishou. Recent research and development of titanium alloys for aviation application in China[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2014,34(4):44−50. (朱知寿. 我国航空用钛合金技术研究现状及发展[J]. 航空材料学报, 2014,34(4):44−50. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2014.4.004 [6] He Junli, Mao Xiaonan, Zhang Pengsheng. Effect of cycling temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2013,38(2):62−66. (何军利, 毛小南, 张鹏省. 循环热处理温度对TC4 钛合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2013,38(2):62−66. [7] Gu Xiaohui, Liu Jun, Shi Jihong. Influence of quenching and aging temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2011,36(2):29−33. (顾晓辉, 刘君, 石继红. 淬火、时效温度对TC4钛合金组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2011,36(2):29−33. [8] Vanderhasten M, Rabet L, Verlinden B. Ti6Al4V deformation map and modelisation of tensile behaviour[J]. Materials and Design, 2008,(29):1090−1098. [9] He Defu, Cao Zhiliang, Zhou Zhijiang, et al. A newly-developed pneumatic process for leak testing of stainless steel tube and titanium alloy tube[J]. Steel Pipe, 2012,41(4):63−67. (何德孚, 曹志樑, 周志江, 等. 不锈钢管和钛管的气动泄漏密实性试验新方法[J]. 钢管, 2012,41(4):63−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2311.2012.04.014 [10] Gonzalez Manuel, Maskos Krystian, Hargrave Robert, et al. Titanium alloy tubing for HPHT applications[C]//U K SPE International. Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2008. [11] Li Liang, Sun Jianke, Meng Xiangjun. Application state and prospects for titanium alloys[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2004,21(5):19−24. (李梁, 孙健科, 孟祥军. 钛合金的应用现状及发展前景[J]. 钛工业进展, 2004,21(5):19−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2004.05.005 [12] Kane D R, Craig B, Venkatesh A. Titanium alloys for oil and gas service: a review[C]. NACE International. Proceedings of International Conferce NACE Corrosion, 2009. [13] Wu Xinyuan, Zhang Heng, Xu Xuejun, et al. Application of titanium alloy in oil&gas exploration and development[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2016,35(11):105−108, 113. (吴欣袁, 张恒, 徐学军, 等. 钛合金在石油天然气勘探开发中的应用[J]. 石油化工应用, 2016,35(11):105−108, 113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2016.11.026 [14] Shi Xuezhi, Zhou Xiaohu. Status quo of research on properties of titanium alloy OCTG and relevant application evaluation[J]. Steel Pipe, 2015,44(1):10−14. (史雪枝, 周小虎. 钛合金油井管性能研究及应用评价现状[J]. 钢管, 2015,44(1):10−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2311.2015.01.002 [15] Yu Cunye. Development and application on corrosion resistant titamium alloys[J]. Total Corrosion Control, 2002,16(6):6−11. (余存烨. 耐蚀钛合金的发展与应用[J]. 全面腐蚀控制, 2002,16(6):6−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7818.2002.06.004 [16] Lü Xianghong, Shu Ying, Zhao Guoxian, et al. Research and application progress of Ti alloy oil country tubular goods[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014,43(6):1518−1524. (吕祥鸿, 舒滢, 赵国仙, 等. 钛合金石油管材的研究和应用进展[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2014,43(6):1518−1524. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 许玲玉,马博荣,李冲,宋德军,陈春阳,孙晓毅. 热处理工艺对TiB95合金石油管材微观组织与力学性能的影响. 材料开发与应用. 2024(02): 63-67+88 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 司玉杰. 功率对TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆改性的影响. 中国信息界. 2024(03): 212-214 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术