Study on inclusions and microstructure of 55SiCrA spring steel wire rod
-
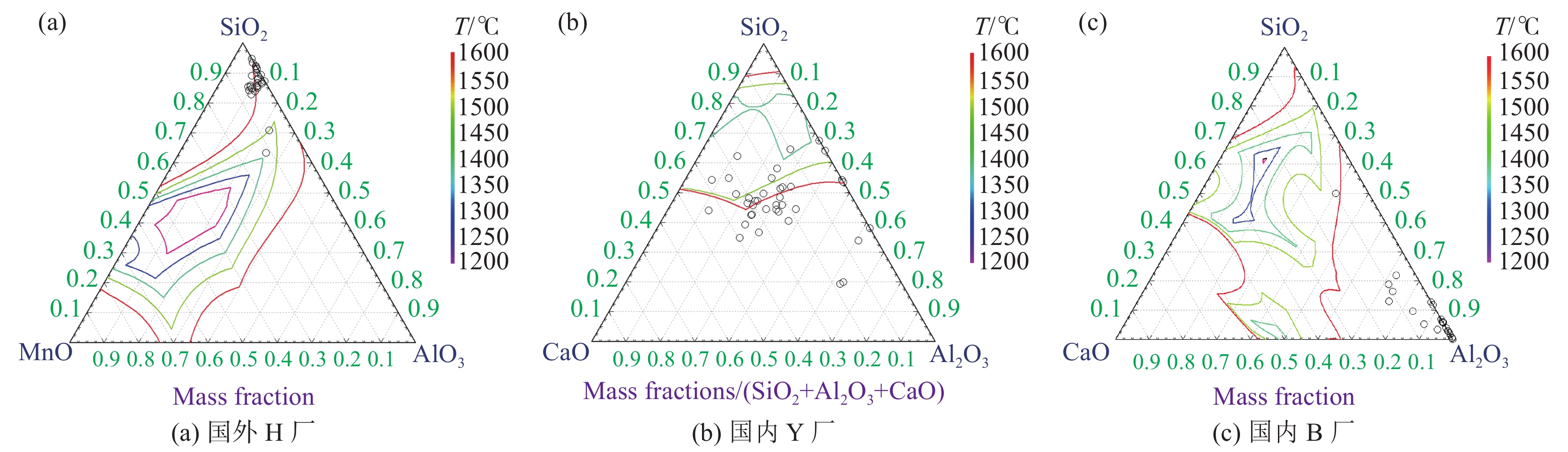
摘要: 利用光学显微镜(OM)、扫描电镜(SEM-EDS)以及Factsage热力学软件对国内外弹簧用线材夹杂物与组织进行了研究。结果表明:国内外3家钢厂弹簧钢线材在显微组织、中心偏析、脱碳层厚度、晶粒度等方面相差不大;国内Y厂弹簧钢线材中发现有1级D类夹杂物以及1.5级Ds类夹杂,而国外H厂和国内B厂相对较好,均未出现Ds类夹杂物。国外H厂弹簧钢夹杂物数量最少,尺寸最小,最大尺寸仅3.4 μm且可变形比例近100%;然而国内弹簧钢线材夹杂物数量多、尺寸大且不可变形。国内Y厂线材夹杂物平均Al2O3、MgO含量较高,国内B厂发现有纯Al2O3夹杂物。此外,国内钢厂需进一步合理控制钢水、精炼渣成分以及提高耐材质量并合理选用耐火材料,来强化夹杂物的改性和脱除。Abstract: Inclusions and microstructure of 55SiCrA spring steel wire rod were studied by means of OM, SEM-EDS and Factsage software. The results show that the microstructure, central segregation, thickness of decarburized layer and grain size of spring steel wire rod in the three plants at home and abroad are almost the same. Moreover, the level 1 D-type inclusions and the level 1.5 Ds-type inclusions are found in domestic steel Y (DSY), however, no Ds-type inclusions are found in foreign steel H (FSH) and domestic steel B (DSB). The number of inclusions in spring steel of FSH is the least and their size is the smallest, the maximum size is only 3.4 μm, and the deformable ratio is nearly 100%; however, the inclusions in spring steel wire rod of DSY and DSB are large in number and size, and are not deformable. The average contents of Al2O3 and MgO are higher in inclusions of DSY, and pure Al2O3 inclusions are found in the wire rod of DSB. In addition, for domestic steel mills it is necessary to further control the composition of molten steel and refined slag, improve the quality of refractory materials and select refractory materials reasonably to enhance the modification and removal of inclusions.
-
Key words:
- spring steel /
- wire rod /
- microstructure /
- inclusion
-
0. 引言
功率超声因其产生的空化效应可提高化学反应速率而广泛应用于冶金领域,Rayleigh建立的空化泡动力学模型为超声空化的研究提供了理论依据[1-3]。目前,空化泡在功率超声作用下的研究主要集中于水溶液模拟体系,以直观的方式观察空化泡运动过程中尺寸的变化,并不能定量描述空化泡尺寸的演变行为[4-5]。此外,目前关于空化泡的研究主要集中在常温下水溶液中,或功率超声作用下对钢液中夹杂物去除的影响,缺少功率超声对钢液中空化泡尺寸演变的影响的系统研究[5-6]。
由于空化泡不是规则的球形,且受力情况与能量的交换过程较为复杂,目前存在的方程难以准确描述空化泡尺寸的变化规律[7-8]。基于这一问题,笔者利用Matlab软件运用四阶龙格库塔算法[9],在R-P方程的基础上引入能量粘滞损耗及辐射阻尼项,对功率超声作用下钢液中单个空化泡尺寸的演变进行研究,分析声压幅值、频率、空化泡初始平衡半径和气体多变指数等因素对空化泡尺寸的影响,探究稳态空化及瞬态空化条件下的空化效应,旨在得出功率超声参数对钢液中空化泡尺寸演变行为的影响规律,为探究功率超声产生的空化效应对钢液中流动及传质行为提供理论依据。
1. 模型建立
1.1 基本假设
功率超声在钢液中传播产生的空化泡发生膨胀与收缩,为了简化计算做以下假设[10-11]:
1)钢液为不可压缩流体,忽略温度与密度的变化;
2)空化泡为球形,且仅做径向运动,运动只与径向轴有关;
3)空化泡的半径远小于距钢包壁的距离;
4)不考虑重力和浮力对空化泡的影响;
5)不考虑空化泡外液体边界层的化学反应。
1.2 控制方程
Rayleigh-Plesset方程:
$$ R\frac{{{\partial ^2}R}}{{\partial {t^2}}} + 3/2{\frac{{{\rm{d}}R}}{{{\rm{d}}t}}^2} + \left(4{v_{\rm{l}}}\frac{{{\rm{d}}R}}{{{\rm{d}}t}}\right)/R + \frac{{2\sigma }}{{{\rho _{\rm{l}}}R}} = ({P_{\rm{B}}}(t) - {P_\infty }(t))/{\rho _i} $$ (1) 功率超声作用下钢液与蒸气处于相对平衡状态,则:
$$ P(R) = \left(R + \frac{{2\sigma }}{{{R_0}}}\right){\left(\frac{{{R_0}}}{R}\right)^{3k}} + {P_v} - \frac{{2\sigma }}{R} $$ (2) 由于空化泡演变过程中存在能量粘滞损耗及辐射阻尼,则:
$$ \begin{split} & R\left(\frac{{\left({{\rm{d}}^2}R\right)}}{{\left({\rm{d}}{t^2}\right)}}\right) + 3/2{\left(\frac{{{\rm{d}}R}}{{{\rm{d}}t}}\right)^2} = 1/\rho \left[\left({P_0} + 2\rho /{R_0}\right){\left(\frac{{{R_0}}}{R}\right)^3}n -\right. \\ & \left.{P_{\rm{A}}} - {P_0} - 2\frac{\rho }{R}\right] - \frac{{4\mu }}{{\rho R}}\frac{{{\rm{d}}R}}{{{\rm{d}}t}} + \frac{R}{{\rho c}}\frac{{\rm{d}}}{{{\rm{d}}x}}\left[\left({P_0} + \frac{{2\sigma }}{{{R_0}}}\right){\left(\frac{{{R_0}}}{R}\right)^{3n}} - {P_{\rm{A}}} \right] \end{split} $$ (3) 功率超声作用在空化泡壁上的压力:
$$ {P_{\rm{A}}} = {P_a}\sin \omega t $$ (4) $$ \omega = 2{\text{π}} f $$ (5) 功率超声周期T:
$$ T = 1/f $$ (6) 式中,μ为粘滞系数,Pa·s;R为空化泡瞬时半径,μm;R0为空化泡初始平衡半径,μm;νl为液相运动粘度,取值0.0067 m2/s;σ为表面张力系数,取值1.4 N/m;P0为静压力,取值101325 Pa;PB(t)为空化泡内压力,取值6 Pa;P∞(t)为无穷远处压力,Pa;PA为超声波声压幅值,Pa;Pv为饱和蒸汽压,Pa;ρl为液相密度,取值7000 kg/m3;t为功率超声作用时间,s;T为功率超声作用周期,s;k为气体多变指数;ω为功率超声角频率,rad/s;f为频率,kHz。
1.3 计算求解
R-P方程为非线性二阶常微分方程,常规方法无法求解此方程的数值解,采用四阶龙格库塔法进行迭代求解[4]。
$$ y = \mathop R\limits^ \bullet $$ (7) $$ \begin{split} &\mathop y\limits^ \bullet = \mathop R\limits^{ \bullet \bullet } = \\ & \frac{1}{{\rho R}}\left[ {\left( {{P_0} + \frac{{2\sigma }}{{{R_0}}}} \right){{\left( {\frac{{{R_0}}}{R}} \right)}^{3\gamma }} - \frac{{2\sigma }}{R} - \frac{{4\mu \mathop R\limits^ \bullet }}{R} - {P_0} + {P_v} + {P_{\rm{A}}}} \right] \end{split}$$ (8) 假设时间步长为h,四阶龙格库塔法计算所涉及的方程如下。
$$ {y_{n + 1}} = {y_n} + h{{\mathop R\limits^ \bullet} _n} + \frac{h}{6}\left( {{k_1} + 2{k_{{}_2}} + 2{k_3} + {k_4}} \right) $$ (9) $$ \mathop {{y_{n + 1}}}\limits^ \bullet = \mathop {{y_n}}\limits^ \bullet + \frac{h}{6}\left( {{k_1} + 2{k_{{}_2}} + 2{k_3} + {k_4}} \right) $$ (10) 其中:
$$ {k_1} = f\left( {{x_n},{y_n}} \right) $$ (11) $$ {k_2} = f\left({x_n} + \frac{h}{2},{y_n} + \frac{h}{2}{k_1}\right) $$ (12) $$ {k_3} = f\left( {{x_n} + \frac{h}{2},{y_n} + \frac{h}{2}{k_2}} \right) $$ (13) $$ {k_4} = f\left( {{x_n} + h,{y_n} + {k_3}} \right) $$ (14) 1.4 研究方案
通过改变声压幅值、频率、空化泡初始平衡半径及气体多变指数考察功率超声参数对钢液中空化泡半径的影响,以空化泡半径的大小为指标评价空化效应的强弱。通过方程(7)与方程(8)可以得到空化泡半径,以R/R0值表述空化泡尺寸的变化规律。
所涉及的参数及初始条件取值为:声压幅值PA取值范围是1~100P0;超声频率f的取值范围是20~80 kHz;空化泡初始平衡半径R0的取值范围为1~50 μm;气体多变指数k的取值范围为1~1.65。其中,气体多变指数定义为:在实际热力内平衡过程中,如果P乘以v的n次方为一个定值,则称这个过程为多变过程,以k描述气体多变指数。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 声压幅值对钢液中空化泡半径演变过程的影响
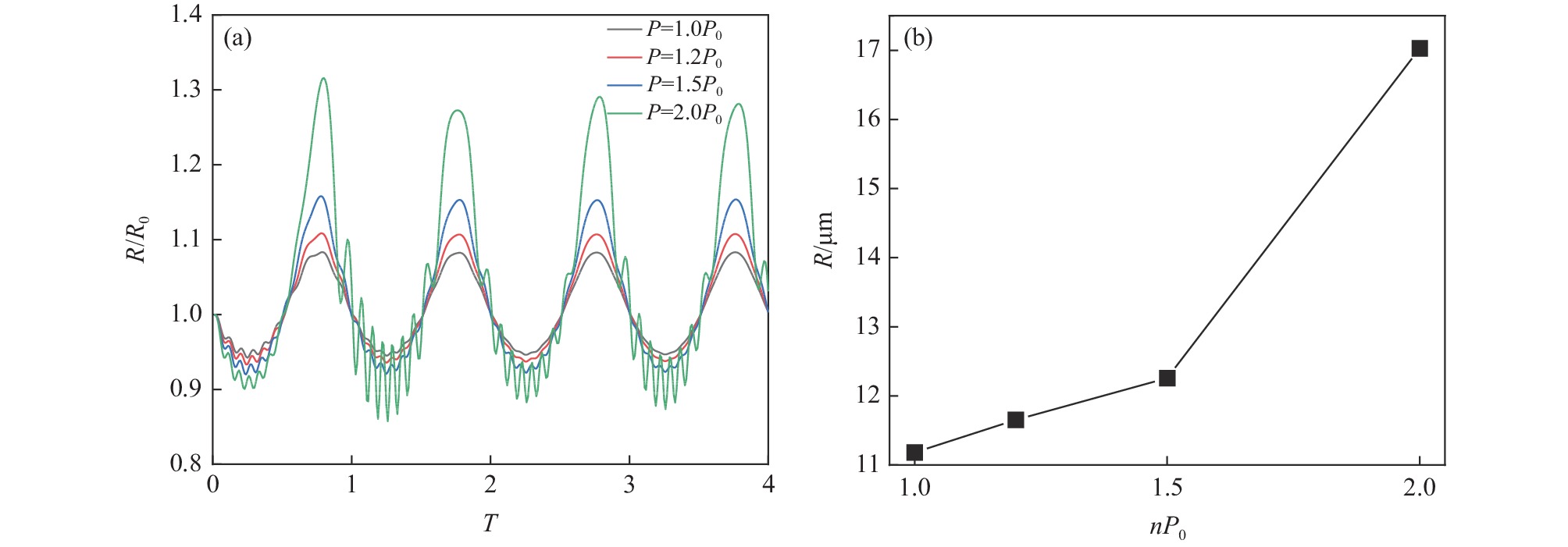
在频率为24 kHz,空化泡初始平衡半径为10 μm,气体多变指数为1.35条件下,探究声压幅值对空化泡半径演变的影响。利用Matlab软件计算得到的空化泡半径与初始平衡半径的比值(R/R0)随声压幅值变化的曲线如图1和图2所示。
由图1(a)可见,声压幅值在1~1.5P0范围内变化时,钢液中空化泡半径变化趋势为正弦曲线,随着声压幅值的增加,空化泡的半径变化幅度增强。当声压幅值为2P0时,在nT/2周期内,空化泡半径的演变仅表现为振动幅度明显增强,但在(n+1)T/2周期内,空化泡半径演变的过程中出现振荡现象,但空化泡未发生崩溃,为稳态空化。声压幅值在1~2P0范围内,空化泡半径做周期性振荡,由于声压幅值的增加,空化效应对空化泡的作用增强,表现为负压区功率超声对空化泡的拉伸作用增强,空化泡的半径增大;在正压区功率超声对空化泡的压缩作用增强,空化泡的半径减小。空化泡的峰值半径随声压幅值的变化如图1(b)所示,声压幅值由1P0增加至1.5P0时,空化泡的峰值半径由11.18 μm增加至12.26 μm。当声压幅值由1.5P0增加至2P0时,空化泡的峰值半径增加至17.03 μm,且斜率增加,表明空化泡的峰值半径急剧增加,而空化泡半径的剧烈变化易使空化现象由稳态空化向瞬态空化转变。因此有利于稳态空化的声压幅值为1.5P0。另外,稳态空化时产生的空化泡振荡周期较长,持续上浮,可在钢液钙处理过程中有效促进夹杂物上浮[10]。
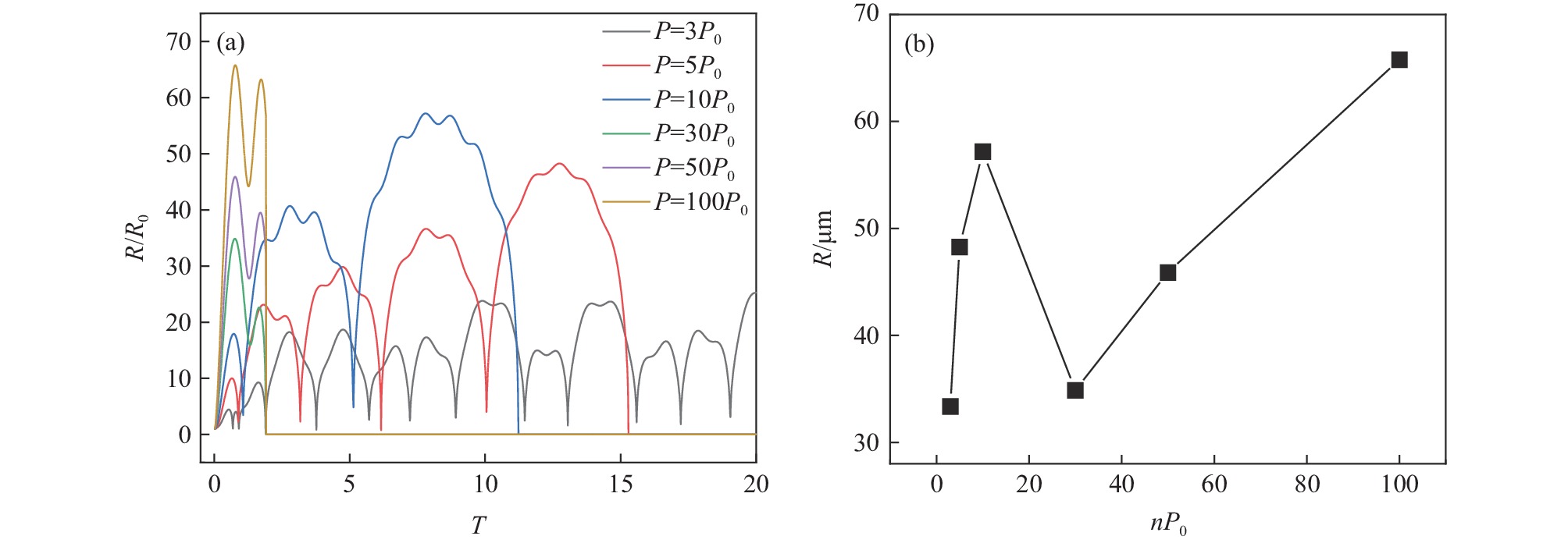
由图2(a)可见,声压幅值在3~100P0范围变化时,随着声压幅值的增加,空化泡半径与初始平衡半径的比值增加,空化效应增强。空化泡振动周期缩短,空化泡的半径变化趋势为非正弦曲线,空化泡经历若干次膨胀与收缩过程后发生崩溃,为瞬态空化。另外,随着声压幅值的增大,空化泡经历的膨胀与收缩至崩溃次数逐渐减小,当声压幅值为10P0时,空化泡经历3次膨胀与收缩后发生崩溃,而当声压幅值大于30P0时,空化泡在经历2次膨胀与收缩过程后发生崩溃。空化泡崩溃前膨胀与收缩过程的减少亦表明空化效应的增强。由图2(b)可见,声压幅值在3~30P0范围内,空化泡的峰值半径先增加后减小,在声压幅值由3P0增加至10P0时,空化泡的峰值半径由33.37 μm增加至57.18 μm,当声压幅值增加至30P0时,空化泡的峰值半径减小为34.86 μm。随后,当声压幅值由30P0增加至100P0时,空化泡的峰值半径增加至65.78 μm。空化泡峰值半径的增加有利于产生瞬态空化,但过高的声压幅值脱离工业实际操作过程。且声压幅值为10P0与80P0条件下所对应的空化泡峰值半径分别为57.18 μm与58.02 μm,这表明10P0与80P0条件下所产生的空化效应强度基本一致,考虑工业实际应用,瞬态空化适宜的声压幅值为10P0。另外,由于瞬态空化条件下空化泡产生至崩溃所持续的时间较短,且较高的声压幅值可加速空化泡的运动,可有效提高钢液内的传质速率。
2.2 稳态空化(1.5P0)条件下各参数对钢液中空化泡半径的影响
2.2.1 初始平衡半径对钢液中空化泡半径的影响
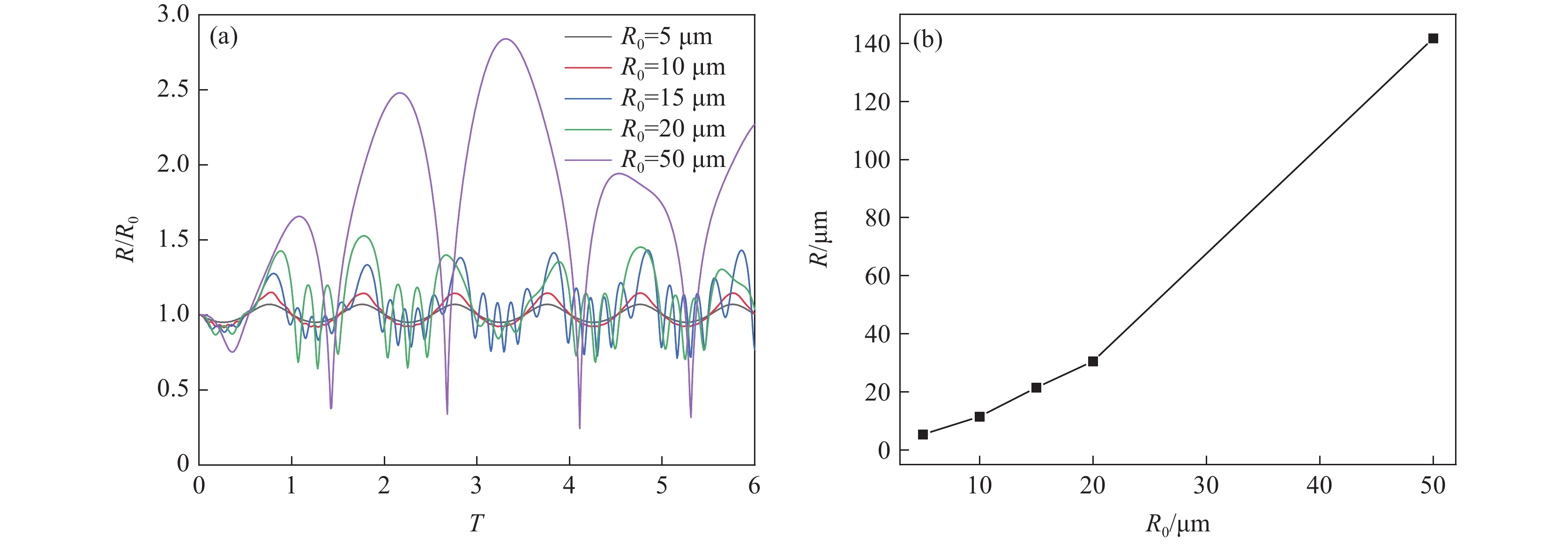
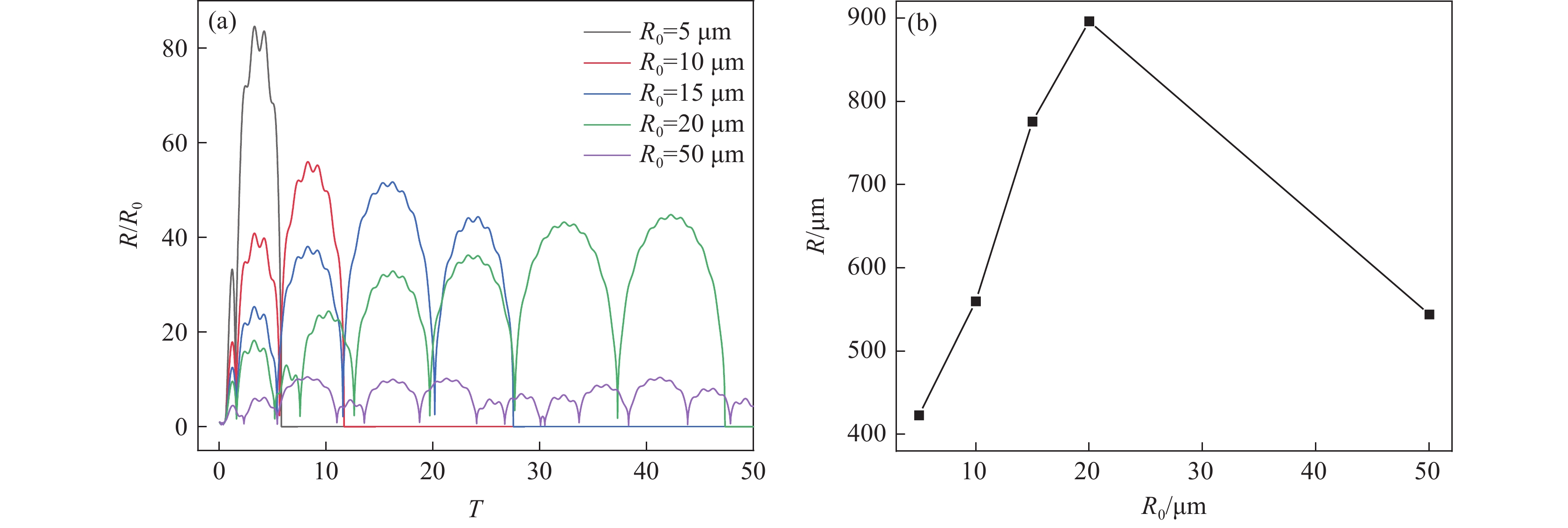
由图3(a)可见,空化泡初始平衡半径在5~50 μm的范围内变化时,随着空化泡初始平衡半径增大,空化泡膨胀与收缩的程度增强。这是由于初始平衡半径增大,可提高空化泡与钢液的接触面积,促进空化泡对周围能量的吸收,导致空化泡的峰值半径增大。当空化泡初始平衡半径为50 μm时,空化泡半径变化周期延长,这是由于空化泡初始平衡半径较大时,需要更充足的时间吸收能量,导致空化泡膨胀与收缩周期增加。由图3(b)可见,随着空化泡半径的增加,空化泡的峰值半径增加,当空化泡初始平衡半径由5 μm增加至50 μm时,空化泡的峰值半径由5.35 μm增加至141.75 μm,与空化泡初始平衡半径相比,空化泡的峰值半径分别增加了0.35 μm和91.75 μm。因此,为提高稳态空化条件下的空化效果,空化泡初始平衡半径应控制在50 μm。
2.2.2 频率对钢液中空化泡半径的影响
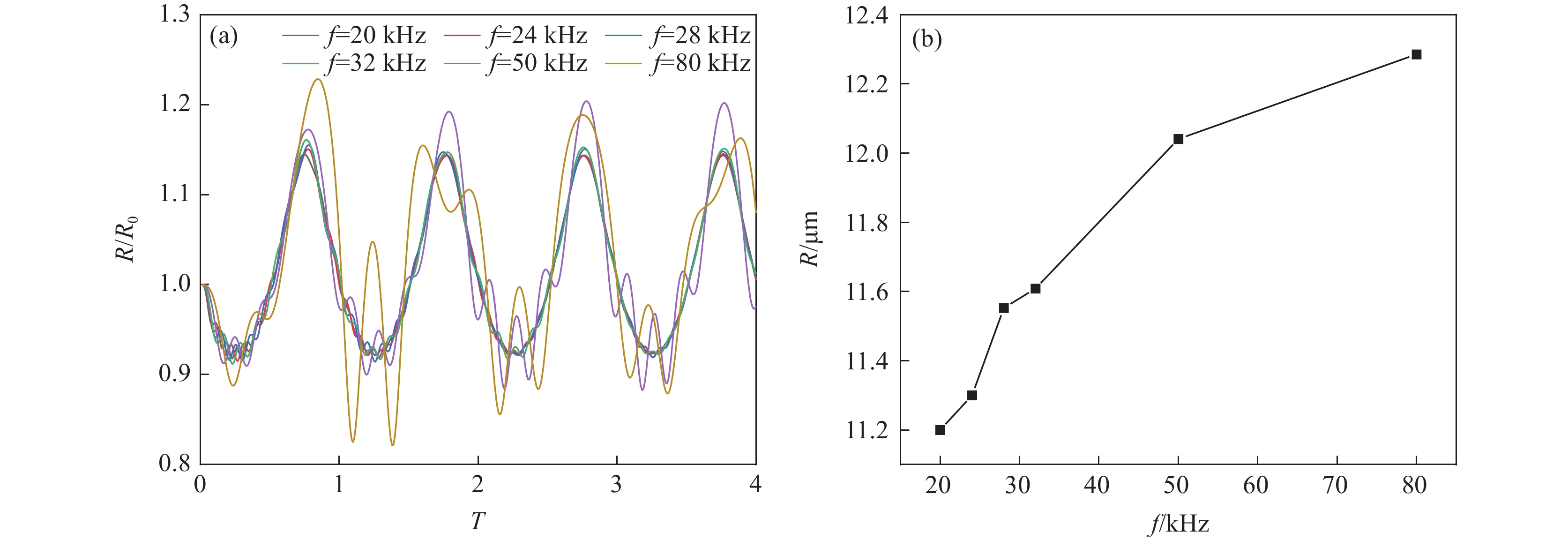
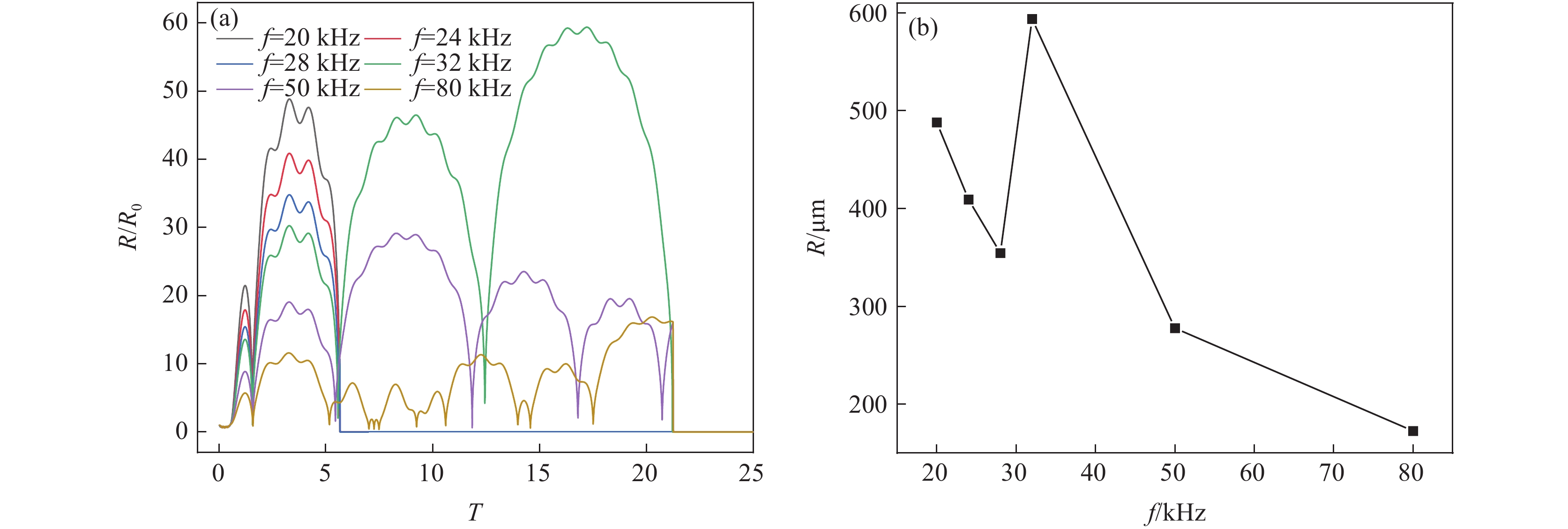
由图4(a)可见,频率在20~32 kHz范围内变化时,空化泡半径变化趋势基本一致,此频率范围内对空化泡半径的影响较小。当频率为50 kHz和80 kHz时,空化泡半径的振荡幅度提高,表明较高的频率可提高空化泡的半径,且在一个周期内空化泡半径出现多次振荡。图4(b)可见,随着功率超声频率的增加,空化泡的峰值半径增大。当功率超声的频率由20 kHz增加至80 kHz时,空化泡的峰值半径由11.21 μm增加至12.29 μm,与功率超声频率增加60 kHz的幅度相比,空化泡的峰值半径仅增加了1.08 μm。说明功率超声的频率对空化泡半径演变的影响较小。
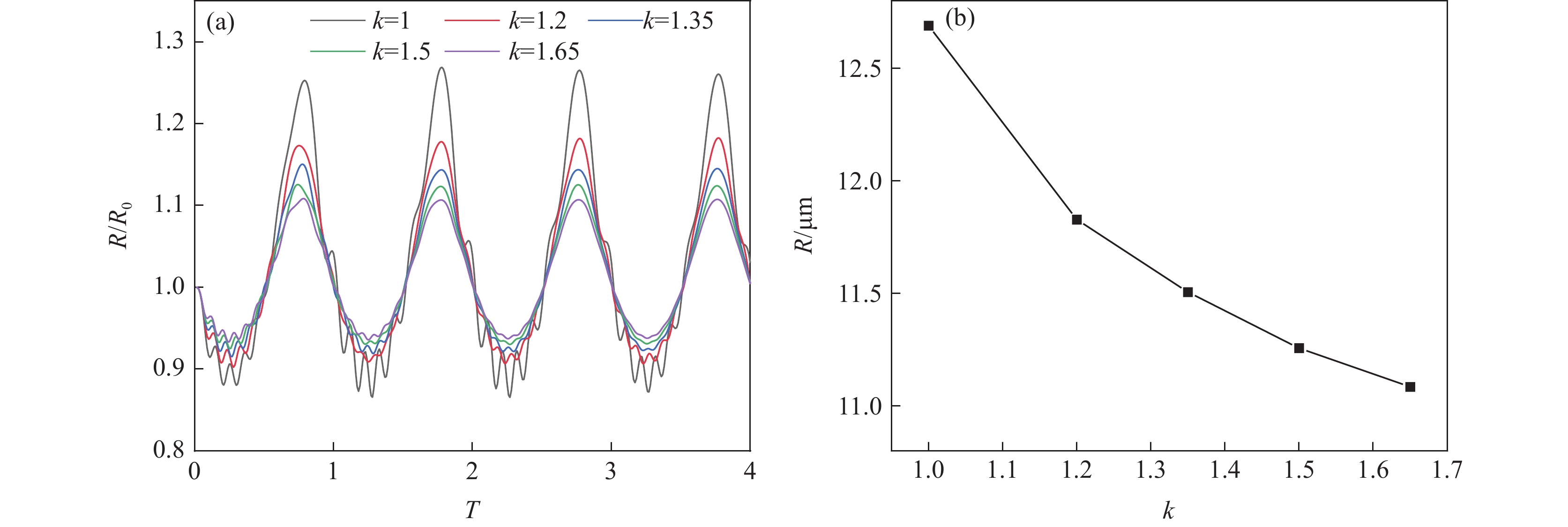
2.2.3 气体多变指数对钢液中空化泡半径的影响
由图5(a)可见,随着气体多变指数k的增加,空化泡膨胀与收缩的周期基本保持一致,空化泡半径的振荡幅度逐渐降低,且同一周期内的振荡次数逐渐减少,说明气体多变指数的增加对空化泡半径产生负面影响。由图5(b)可见,随着k值的增加,空化泡的峰值半径逐渐减小。当气体多变指数由1增加至1.65时,空化泡的峰值半径由12.68 μm减小至11.08 μm,表明增加气体多变指数将削弱功率超声的空化强度。主要原因在于单原子气体空化泡的峰值半径大于多原子气体,且振荡周期基本一致。上述结论与多变指数较小的单原子气体的空化效应优于多原子气体的结论相吻合[6]。
2.3 瞬态空化(10P0)条件下各参数对钢液中空化泡半径的影响
2.3.1 初始平衡半径对钢液中空化泡半径的影响
由图6(a)可见,与稳态空化条件下空化泡半径的变化曲线相比,空化泡半径变化幅度明显提高。当空化泡初始平衡半径为5 μm时,空化泡仅经历2次膨胀与收缩的过程后发生崩溃。而空化泡初始平衡半径为10、15和20 μm时,空化泡膨胀与收缩次数增加,分别为3、5和8次膨胀与收缩过程后发生崩溃。当空化泡初始平衡半径为50 μm时,空化泡经历13次膨胀与收缩过程后发生崩溃,且空化泡膨胀幅度明显减小,表明随着空化泡初始平衡半径的增加,空化效应减弱。另外,空化泡初始平衡半径为5 μm时,空化泡发生崩溃时峰值半径达到423.01 μm,空化泡最大半径膨胀率为846%,而崩溃时膨胀率越大,释放的能量越多,空化效应增强。由图6(b)可见,空化泡的峰值半径随着初始平衡半径的增加先增大后减小。当空化泡初始平衡半径由5 μm增加至20 μm时,空化泡的峰值半径由423.01 μm增加至896.12 μm,此时的膨胀率为448%;当初始平衡半径增加至50 μm时,空化泡的峰值半径减小到544.16 μm,此时空化泡膨胀率为108.8%。半径由5 μm增大至20 μm过程中峰值半径不断增加,但发生崩溃时的膨胀率由846%降低为448%,瞬态空化效应减弱。因此,空化泡初始平衡半径为5 μm时有利于发生瞬态空化。
2.3.2 频率对钢液中空化泡半径的影响
由图7(a)可见,频率在20~28 kHz范围内变化时,空化泡经历2次膨胀与收缩的过程后发生崩溃,且发生崩溃时空化泡半径的膨胀率逐渐减小。频率为32、50和80 kHz时,空化泡分别经历4、5和8次膨胀与收缩过程后崩溃。瞬态空化过程中,发生崩溃所经历的膨胀与收缩次数越多,其空化强度越弱。由图7(b)可见,在低频率20~28 kHz范围内,随着频率的增加,空化泡的峰值半径由488.05 μm减小至354.43 μm;当频率为32 kHz时,空化泡的峰值半径为593.78 μm,为各频率条件下半径最大值,但其膨胀与收缩次数较多,空化泡崩溃时间较长,空化效应减弱。当频率为80 kHz时,空化泡的峰值半径减小至172.65 μm。表明高频率的条件下空化泡膨胀与收缩时间延长,空化核未能及时发生崩溃,空化效应减弱。因此,为提高超声的瞬态空化强度,功率超声的频率应选择为20 kHz。
2.3.3 气体多变指数对钢液中空化泡半径的影响
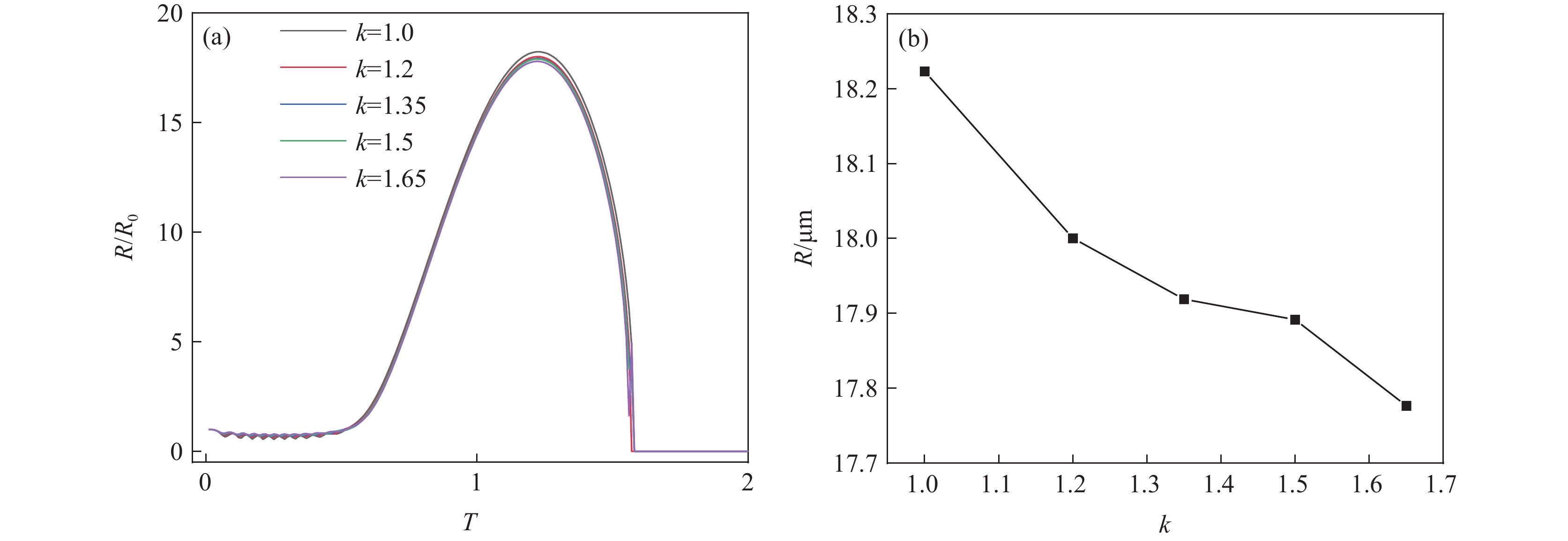
图8(a)可见,瞬态空化条件下,空化泡仅经历1次膨胀与收缩过程即发生崩溃,且随着气体多变指数k的增加,空化泡崩溃所经历的周期基本一致,表明瞬态空化条件下气体多变指数对空化泡膨胀与收缩过程影响较小。主要原因在于瞬态空化频率高、能量大,空化泡崩溃过程中单原子及多原子气体的作用性能减弱,对空化效应强弱的影响并不明显。由图8(b)可见,随着气体多变指数的增加,空化泡的峰值半径逐渐减小。当气体多变指数由1增加至1.65时,空化泡的峰值半径由18.22 μm减小至17.87 μm,仅减小了0.35 μm,亦表明气体多变指数对瞬态空化强弱的影响较小。但考虑能量的吸收与释放过程,多变指数较低的单原子气体有利于产生瞬态空化。
3. 结论与展望
1)功率超声作用下引起钢液中空化泡的膨胀与收缩,不同声压幅值可产生不同的空化效应。声压幅值在1~2P0的范围内产生稳态空化,可促进夹杂物上浮过程;声压幅值在3~100P0的范围内产生瞬态空化,可加速钢液内的传质过程。
2)稳态空化条件下,随着频率和初始平衡半径的增加,空化泡的峰值半径增大。初始平衡半径由5 μm增加至50 μm时,空化泡的峰值半径由5.35 μm增加至141.75 μm;频率由20 kHz增加至80 kHz时,空化泡的峰值半径由11.45 μm增加至12.29 μm。
3)瞬态空化条件下,频率为20 kHz时,空化泡经历2次膨胀与收缩过程后崩溃,对应空化泡的峰值半径为488.05 μm。初始平衡半径对空化泡尺寸的影响显著,由5 μm增加至20 μm时,空化泡的峰值半径由423.01 μm增加至896.12 μm,当初始平衡半径增加至50 μm时,空化泡的峰值半径减小至544.16 μm。
4)气体多变指数对稳态和瞬态空化条件下空化泡尺寸的影响较小,但气体多变指数较小的单原子气体产生的空化效应优于多原子气体。当气体多变指数由1增加至1.65时,空化泡的峰值半径仅由18.22 μm减小至17.87 μm。
5)本研究成果可为探究功率超声产生的空化效应对钢液中流动及传质行为提供理论依据,但空化泡的体积、密度及空化泡之间的作用对空化泡膨胀与收缩产生影响,后续需进一步修正空化泡的尺寸变化方程,并结合实际设计试验,对模拟结果进行验证。
-
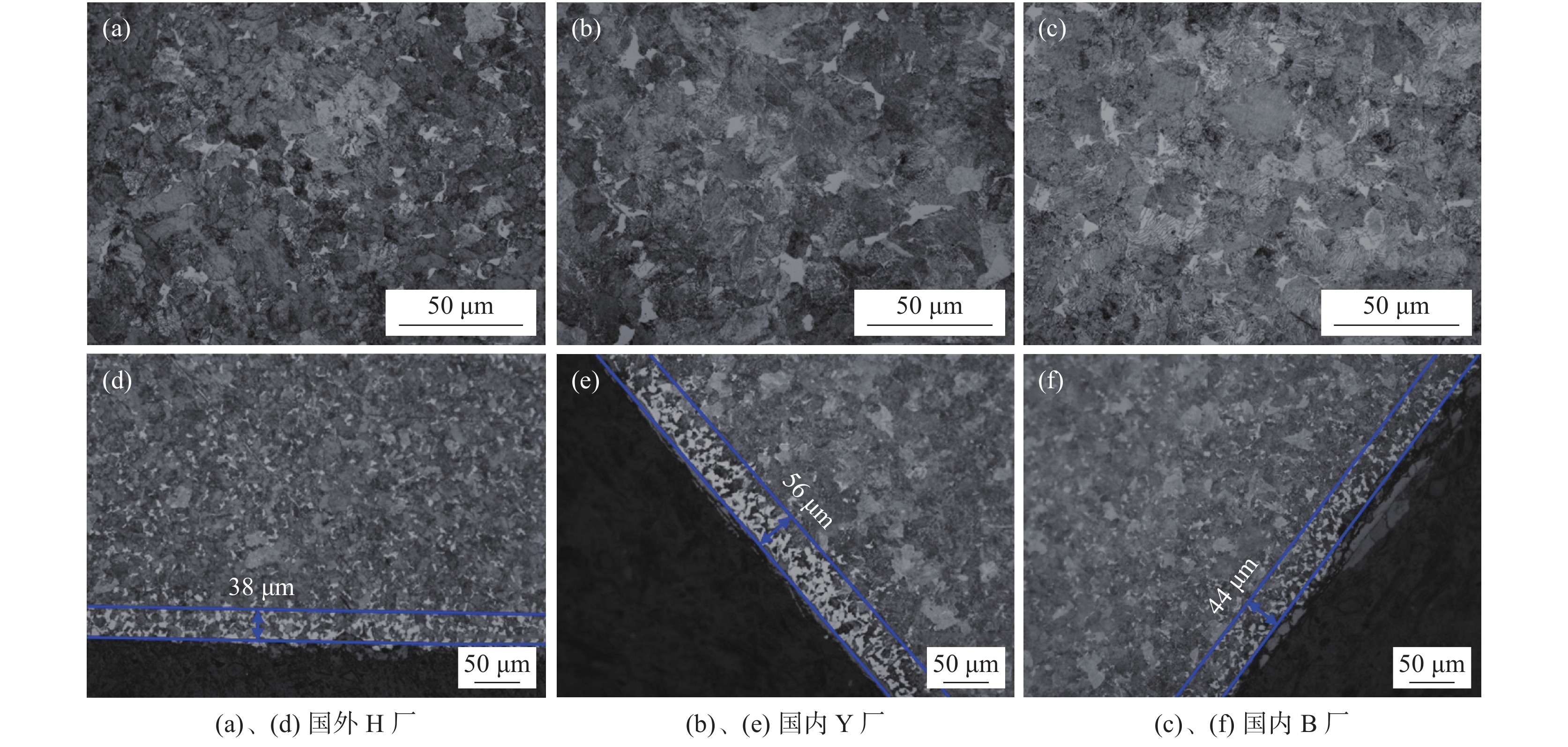
表 1 弹簧钢的夹杂物级别与显微组织
Table 1. Inclusion grading and microstructure of the tested spring steel
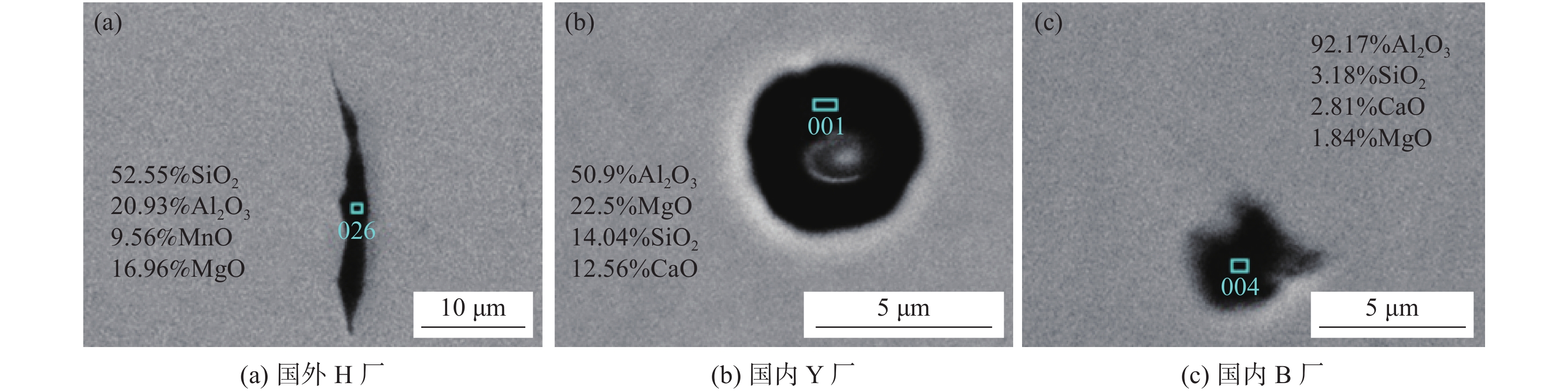
厂家 显微组织 中心偏析 脱碳层厚度/μm 晶粒度级别 夹杂物级别 全脱碳层 总脱碳层 国外H厂 S+P+F 0 0 38 7 A0.5,B0.5,C1,D0.5 国内Y厂 S+P+F 0 0 56 8 A0.5,B0.5,C0.5,D1,DS1.5 国内B厂 S+P+F 0 0 44 8 A0.5,B0.5,C0.5,D0.5e 表 2 弹簧钢线材夹杂物成分、尺寸、类型及盘条酸溶铝含量
Table 2. Inclusion composition, size, type and acid soluble aluminum content of the tested spring steel
编号 夹杂物成分/% 平均Al2O3
含量/%平均MgO
含量/%夹杂物尺寸
(长×宽)/μm夹杂物
类型盘条Als
含量×106Al2O3 MgO SiO2 MnO CaO 国外H厂 20.93 16.96 52.55 9.56 11.8 0.5 23.3×2.5 MnO-SiO2-Al2O3 (-MgO) 3 国内Y厂 50.9 22.5 14.04 12.56 23.6 24.5 4.7×4.7 CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO 23 国内B厂 92.17 1.84 3.18 2.81 89.6 4.4 4.1×3.1 Al2O3-SiO2-CaO (-MgO) 10 -
[1] Canale L C F, Penha R N, Totten G E, et al. Overview of factors contributing to steel spring performance and failure[J]. International Journal of Microstructure and Materials Properties, 2007,2(3−4):262−309. [2] Lyu S, Ma X, Huang Z, et al. Inclusion characterization and formation mechanisms in spring steel deoxidized by silicon[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2019,50(2):732−747. doi: 10.1007/s11663-019-01505-3 [3] Wu Xuexing, Sun Haibo, Yu Dahua. Production practice of high quality automobile suspension spring steel 55SiCr[J]. Jiangxi Metallurgy, 2016,36(2):13−16. (吴学兴, 孙海波, 余大华. 高品质汽车悬架弹簧钢55SiCr生产工艺实践[J]. 江西冶金, 2016,36(2):13−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2777.2016.02.004 [4] Meng Yaoqing, Guo Xiaopei, Zhao Lei, et al. Study on exogenous inclusions in rotary bending fatigue fracture of Si-killed spring steel 55SiCr[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2018,30(12):977−982. (孟耀青, 郭晓培, 赵垒, 等. 硅脱氧弹簧钢55SiCr旋转弯曲疲劳断口中外来夹杂物的研究[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2018,30(12):977−982. [5] Meng Yaoqing, Wang Kunpeng, Zheng Yongrui. Analysis of sources of inclusions induced fatigue failure in 1950 MPa-grade spring steel 55SiCrA[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017,29(10):859−864. (孟耀青, 王昆鹏, 郑永瑞. 1950 MPa级弹簧钢55SiCrA疲劳断口夹杂物来源分析[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2017,29(10):859−864. [6] (殷瑞钰. 钢的质量现代进展[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1995.)Ying Ruiyu.Progress of quality of steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1995. [7] Hu Yang, Chen Weiqing, Han Huaibin, et al. Quality contrast of domestic and overseas spring steel wire rod for valve spring[J]. Steelmaking, 2015,31(6):47−52. (胡阳, 陈伟庆, 韩怀宾, 等. 国内外气门簧用弹簧钢线材质量对比[J]. 炼钢, 2015,31(6):47−52. [8] Cui Huaizhou, Chen Weiqing, Cao Changfa. Analysis of banded structure in wire rod for tire cord steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2011,36(6):41−45. (崔怀周, 陈伟庆, 曹长法. 帘线钢盘条带状组织的分析[J]. 金属热处理, 2011,36(6):41−45. [9] Karihara K. Production technology of wire rod for high tensile strength steel cord[J]. Kobelco Technology Review, 2011,30:62−65. [10] Maede S, Soejima T, Saito T, et al. Shape Control of inclusions in wire rods for high tensile cord by refining with synthetic slag[C]//Steelmaking Conference Proceedings.Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society of USA, 1989, 77: 379−385. [11] (殷雪. 汽车悬架弹簧钢非金属夹杂物塑性化控制研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2018.)Yin Xue. Investigation on non-metallic inclusion plasticization control for automotive suspension spring steel[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018. [12] Peng Hongbing, Tang Yao. Quality comparison of the domestic and foreign high carbon steel cord wire[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019,44(12):44−48. (彭红兵, 唐尧. 国内外帘线用高碳钢线材质量对比[J]. 金属热处理, 2019,44(12):44−48. [13] Wang Kunpeng, Jiang Min, Wang Xinhua, et al. Progress of control technology of inclusions in steel for tyre cord and saw wire[J]. Special Steel, 2016,37(2):26−31. (王昆鹏, 姜敏, 王新华, 等. 钢帘线和切割丝用钢夹杂物控制技术的进展[J]. 特殊钢, 2016,37(2):26−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2016.02.008 -





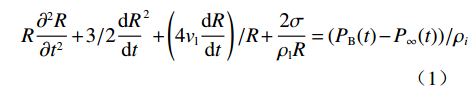
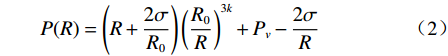





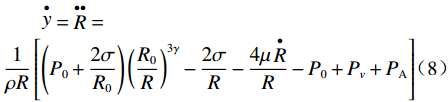

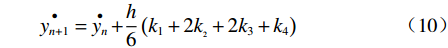

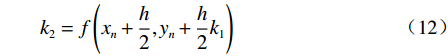



 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载: