Analysis on split-head cracking of Y1Cr13 stainless rolled bar
-
摘要: 针对某厂生产的Y1Cr13不锈钢在轧制过程产生劈头开裂的问题,采用金相显微镜、扫描电子显微镜、小样电解等分析检测方法,从夹杂物微观形貌角度对钢劈头开裂样中硫化物的微观形貌特征进行了表征分析,并探究了Y1Cr13不锈钢轧制时劈头开裂形成的原因。结果表明:该不锈钢轧材存在大量长条状硫化物,硫化物长宽比较大,长宽比分布在3以内的夹杂物占比为65.4%,长宽比大于3的夹杂物占比为34.6%,硫化物的国标评级为:粗系4.5级,细系5.5级,德标评级为3-3级;钢中过多的热脆细长条状硫化锰和锰铁硫化物是劈头开裂的主要原因。采用镁、碲等新工艺可对硫化物形态进行改质,将其控制为球形或纺锤形,并提高硫化物硬度,轧制时不易变形;通过适当减少钢中的[S]含量以及提高钢中Mn/S等措施可减少钢中的(Mn,Fe)硫化物。Abstract: In order to find out the causes of split-head cracking of Y1Cr13 stainless steel in the rolling process, the splitting samples of steel were analyzed and characterized from the view of inclusions microstructure with a metallographic microscope, a scanning electron microscope and the method of electrolytic etching. Also, the causes of split-head crackingof Y1Cr13 stainless steel during the rolling process were explored. The results show that there exist a lot of long strip sulfides in rolled steel, and the ratio of length/width of sulfides is large. The proportion of the inclusions with length/width ratio below 3 is 65.4%. The proportion of the inclusions with length/width ratio above 3 is 34.6%. The standard ratings of sulfides are 4.5 for coarse series, 5.5 for fine series, and 3-3 for German standard. A large number of long strip hot shortness manganese sulfides and ferromanganese sulfides are the main causes of split-head cracking of Y1Cr13 rolled bar. Such as magnesium and tellurium can be used to modify the form of sulfide into a spherical or spindle shape, and increase the hardness of the sulfide, making it difficult to deform during rolling. The (Mn, Fe) sulfide in steel can be reduced by properly reducing [S] content and increasing Mn/S in steel.
-
Key words:
- Y1Cr13 stainless steel /
- split-head /
- cracking /
- manganesesulfide /
- ferromanganesesulfide
-
0. 引言
Y1Cr13不锈钢属马氏体不锈钢,是在马氏体不锈钢1Cr13成分基础上增加硫形成,含碳量低,耐腐蚀性能好,主要用于电磁阀、微特电机和电气等元件的生产[1-2]。然而,国内部分钢厂在热轧生产Y1Cr13钢的过程中会发生劈头开裂,严重时裂纹始自轴心部位,并延伸至边缘致使钢坯开裂,断口平整,同时还存在自边缘向内部扩展的贯穿裂纹,成坯和成材率均较低。通常地,有效控制钢中硫化物形态是防止钢头部开裂或劈头的有效手段。因此,对钢中硫化物形态研究尤为重要。
马宝国等人[3]对BT303CuS易切削不锈钢轧件劈头进行了研究,发现轧件劈头与钢中硫化物的形态有关。王维宁[4]的研究表明,Y1Cr13钢轧制温度在1000~1200 ℃范围时,显著的硫热脆性影响和大量脆性硅酸盐夹杂的存在是造成钢坯开裂的主要诱因。张宇[1]分析了Y1Cr13钢轧制开裂产生的原因,认为高硫使钢的热加工塑性降低是造成轧制开裂的原因。郝世风等人[5]的研究表明,M7钢轧制劈头开裂的主要原因是碳化物组织分解破碎不充分。然而目前较少文献对Y1Cr13不锈钢劈头开裂从硫化物夹杂微观形貌(二维、三维形貌)角度进行研究,以及对比不同显微夹杂物的形貌特征。
因此,笔者对某厂Y1Cr13不锈钢劈头开裂样进行分析,通过金相显微镜、扫描电子显微镜、小样电解等分析检测方法从夹杂物微观形貌角度对钢劈头开裂样中硫化物的微观形貌特征进行了表征分析,探究了Y1Cr13不锈钢轧制时劈头开裂形成的原因,并提出了解决劈头开裂问题的建议。
1. 试验材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
某厂(A厂)生产Y1Cr13不锈钢采用的生产工艺为:40 t EAF→40 t AOD→模铸→热轧→退火。为了对比该厂硫化物的控制水平,将它与国内两家企业(B厂和C厂)生产相同工艺的Y1Cr13轧材作对比研究。试验钢主要化学成分如表1所示。从表1可以看出,Y1Cr13不锈钢中硫含量较高,属于高硫不锈钢。三种钢中锰和铬含量大致相同。
1.2 试样制备
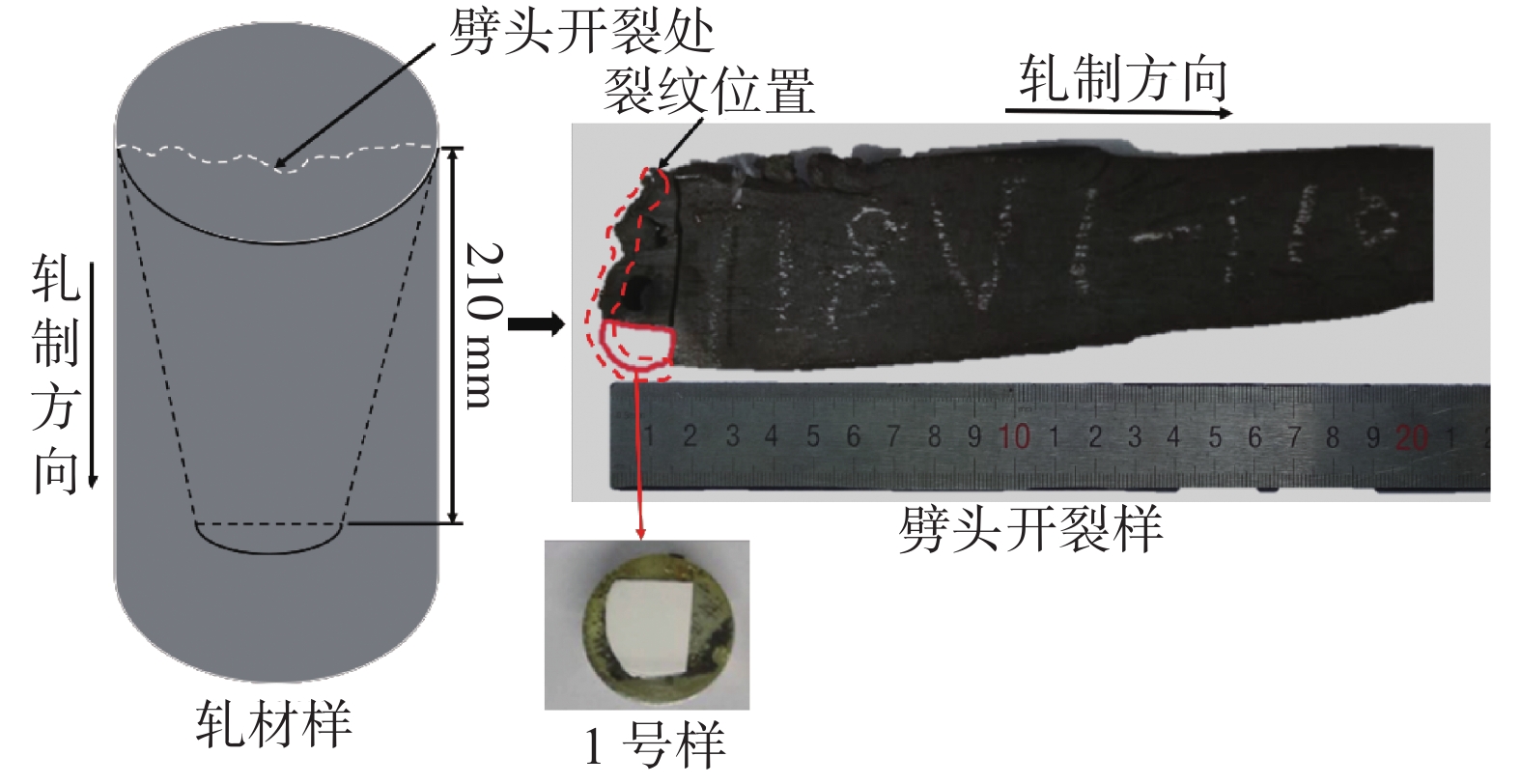
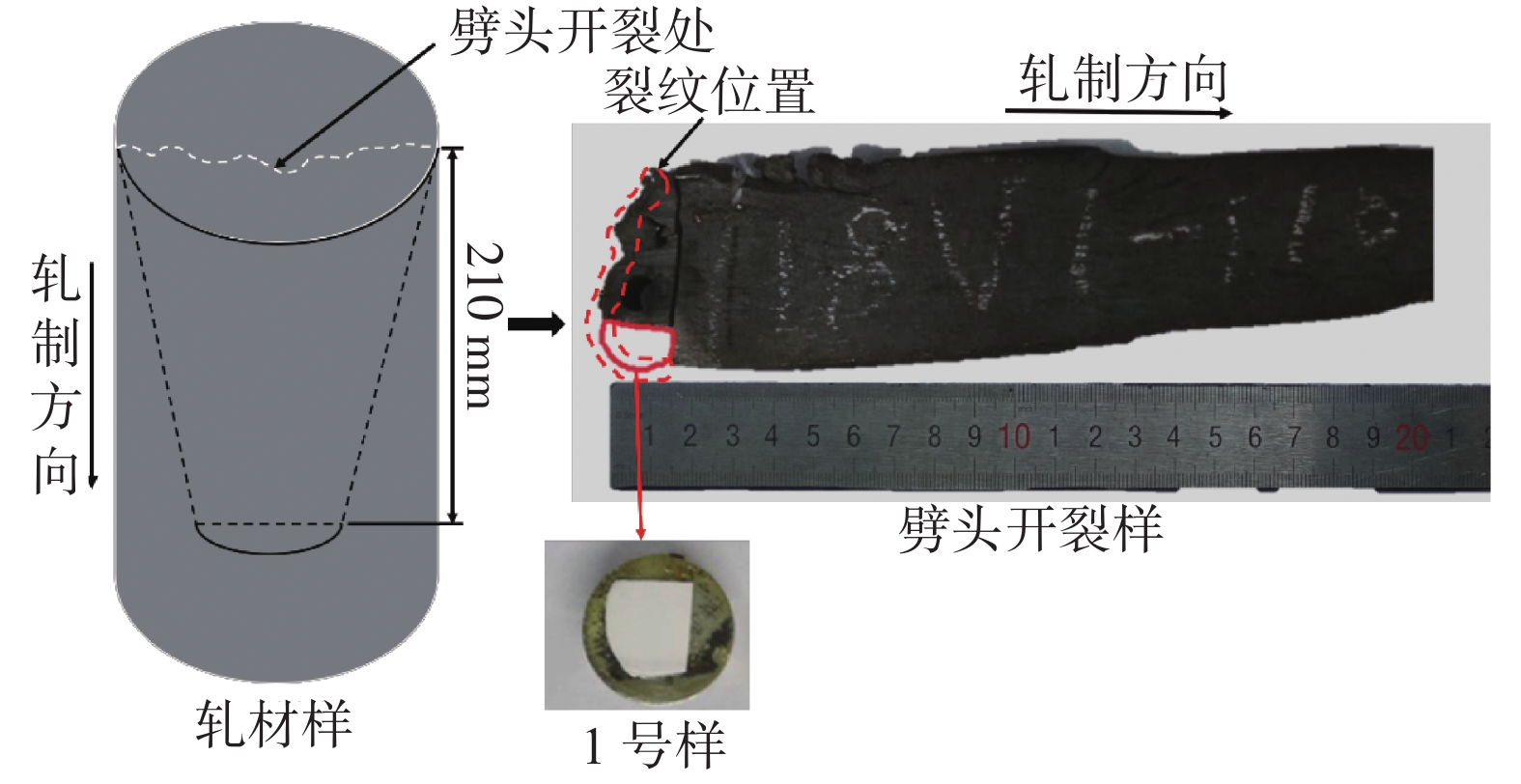
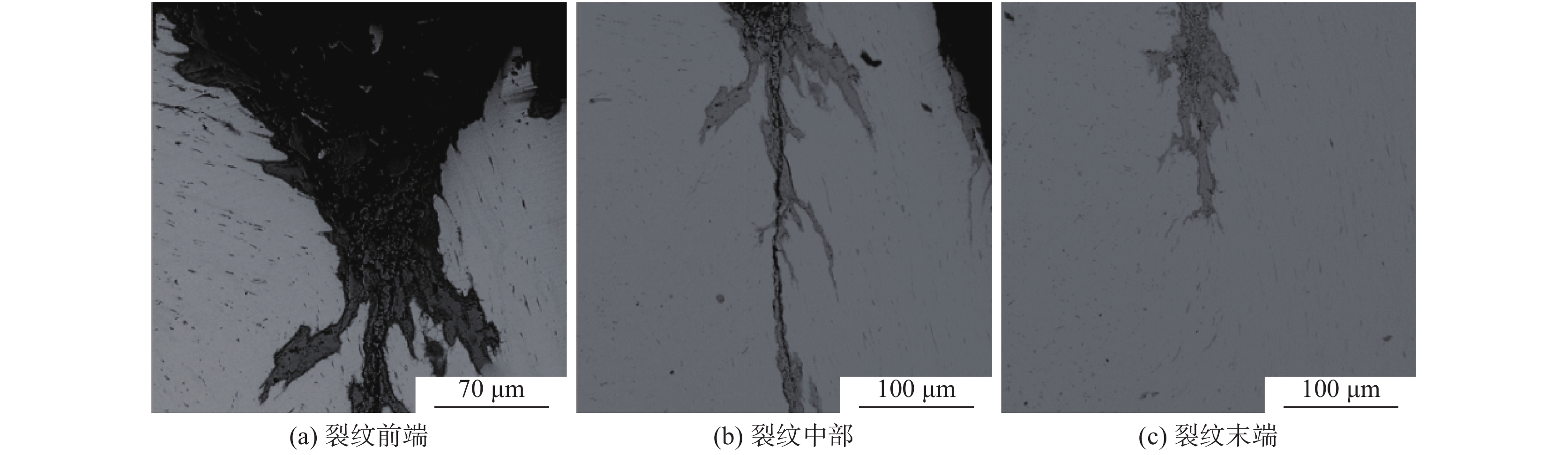
首先,由于劈头开裂试样表面有油污和部分铁锈,同时为了保证试样表面裂纹不被破坏,将试样放入10%的柠檬酸溶液中,然后一起放入超声波清洗机内清洗掉裂纹表面的铁锈和油污;接着用酒精清洗柠檬酸浸泡过的试样,除去表面的柠檬酸,之后烘干。经清理后的试样按图1中的实线标记区域位置用线切割的方法进行取样,标记为1号样,此处为劈头开裂处,存在表面裂纹,并对1号样进行镶嵌;2号样依照GBT 10516—2005取轧材样四分之一中心位置,便于分析钢样内部夹杂物的形态控制情况。1号样和2号样都以沿轧制方向的轧材面为观察面。对1号和2号试样分别进行磨抛处理后,利用蔡司光学显微镜(Zeiss AVxo)和扫描电子显微镜(Phenom Pro)分别对试样中的显微组织和硫化物形态进行观察。B厂和C厂试样取样方式为取轧材四分之一中心处沿轧制方向的轧材面为观察面。试样大小约为:10 mm×10 mm×10 mm。
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分Table 1. Main chemical compositions of experimental steels% 厂家 C Si Mn P S Cr Mo Ni A 0.13 0.54 1.15 0.027 0.31 12.89 0.04 B 0.122 0.229 0.957 0.026 0.350 12.300 0.105 C 0.120 0.430 1.160 0.018 0.270 12.790 0.260 2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 裂纹处显微分析
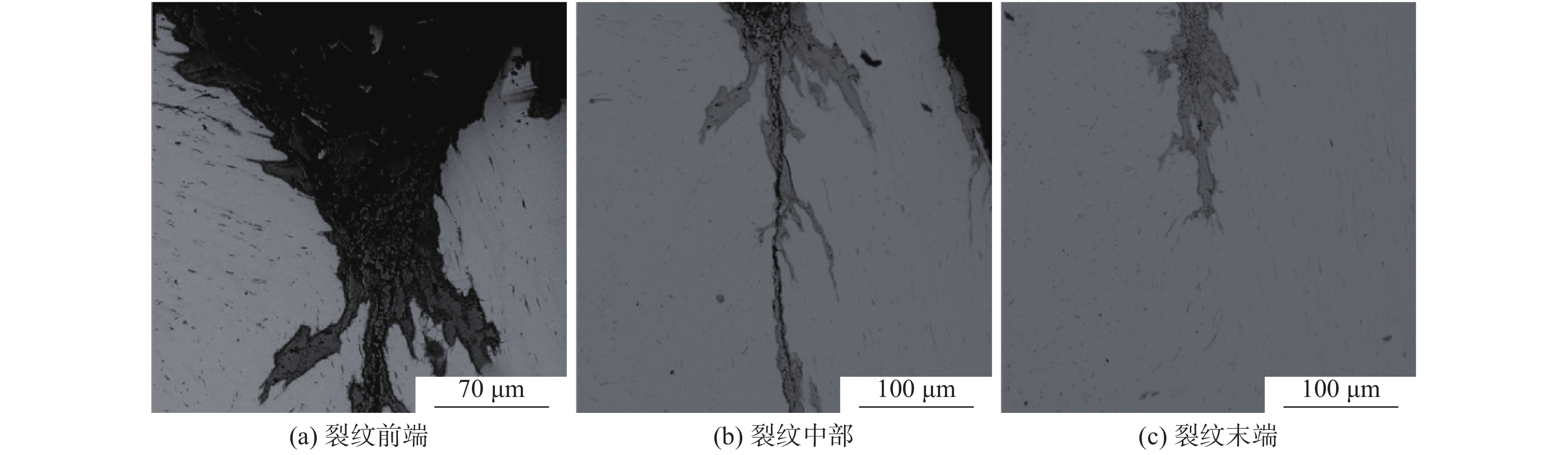
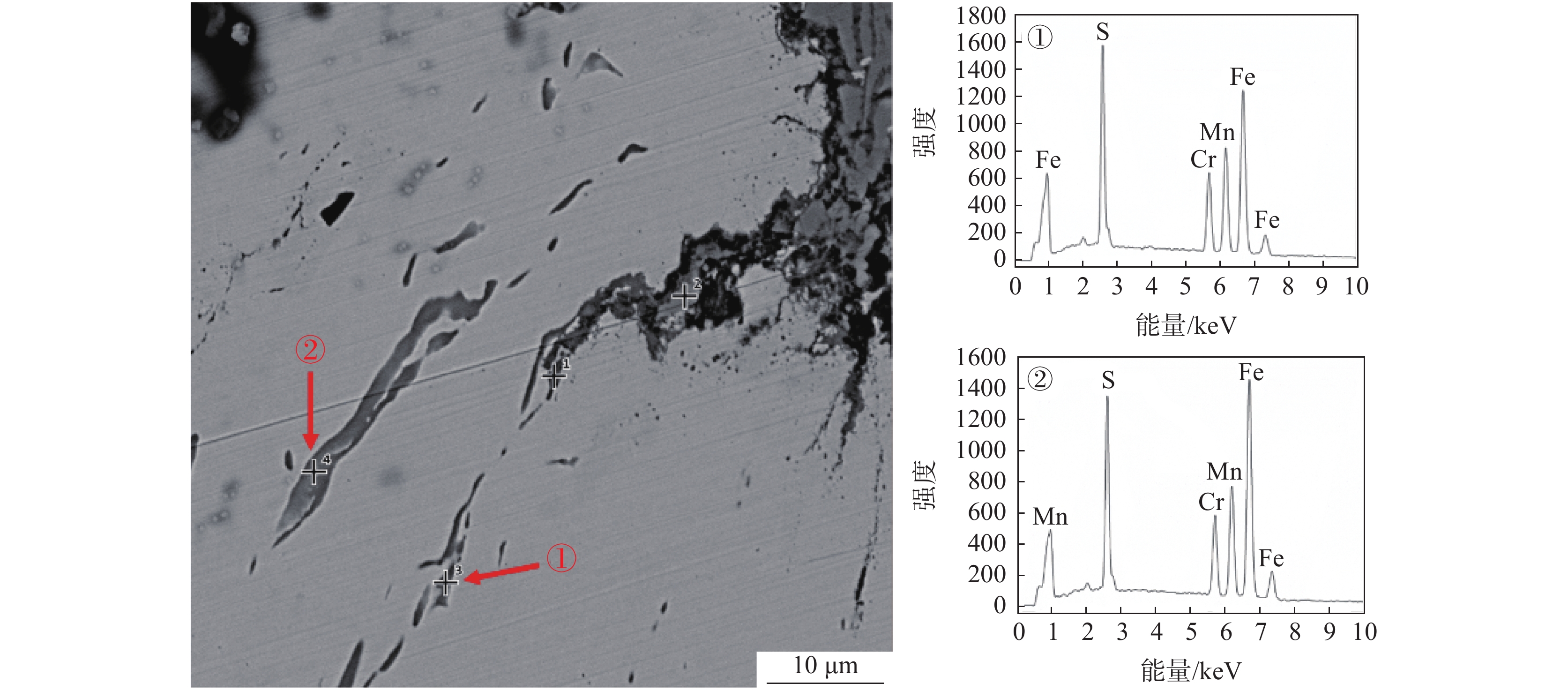
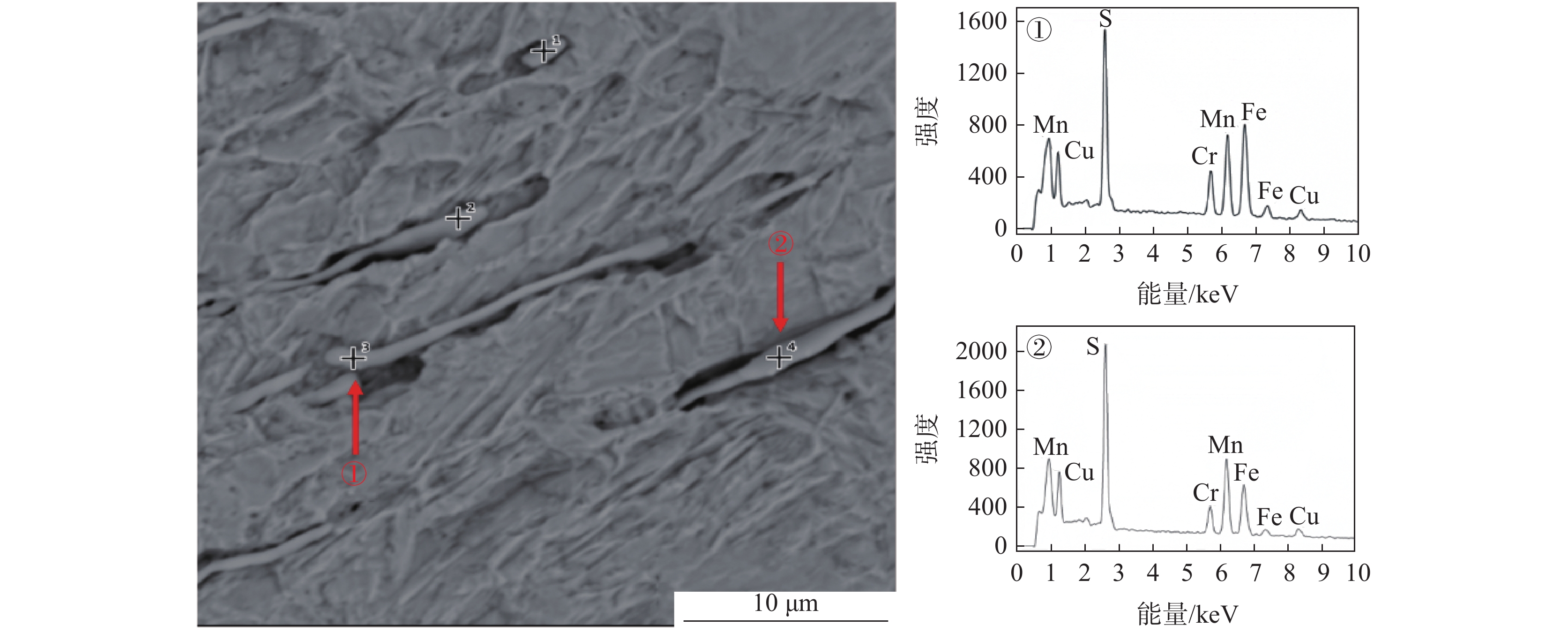
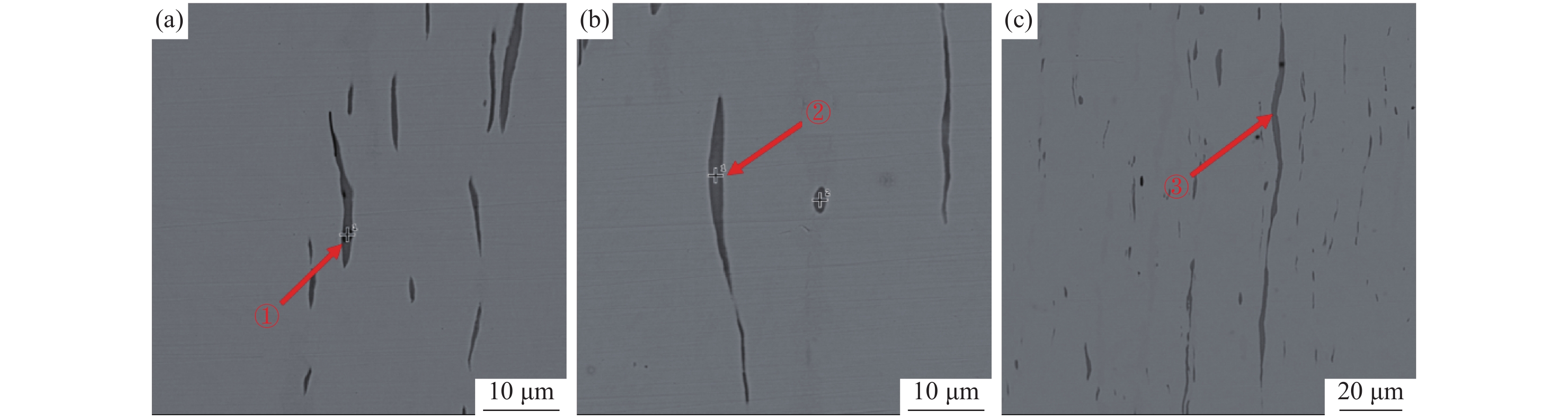
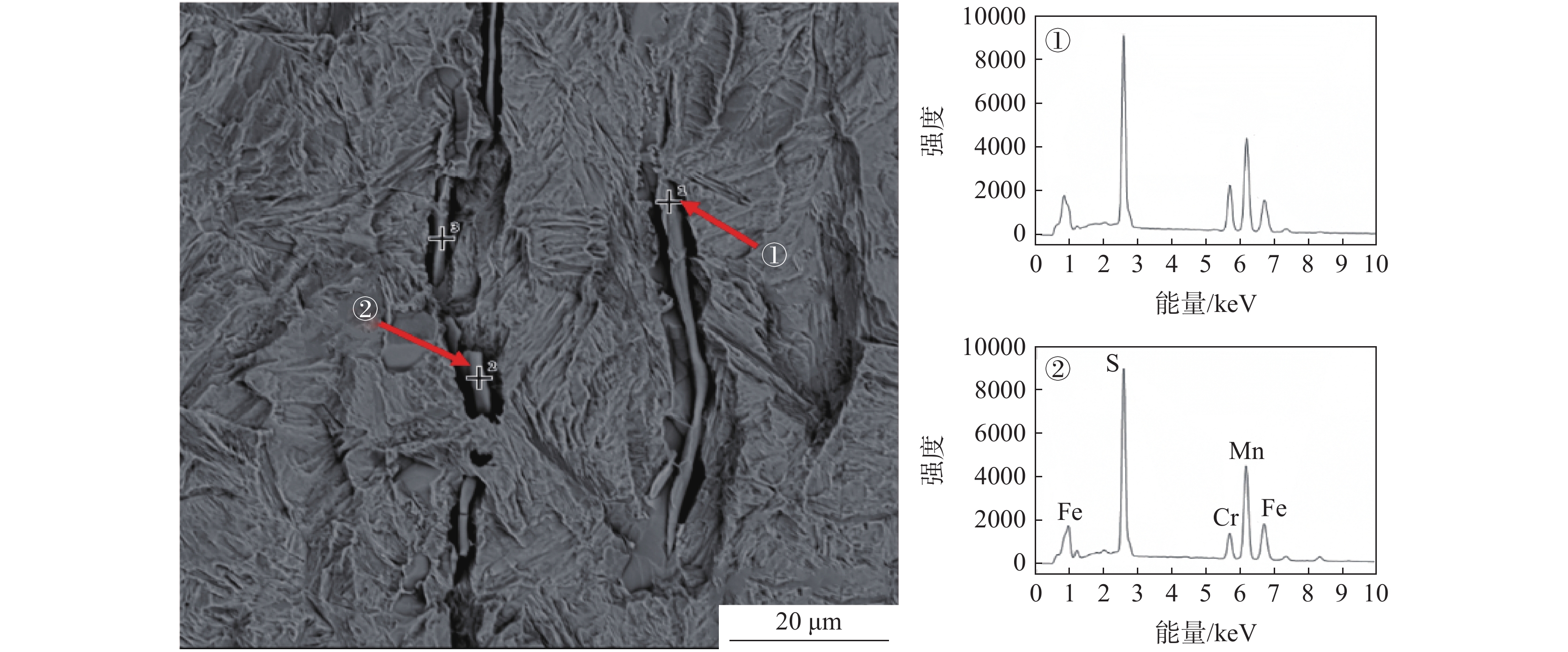
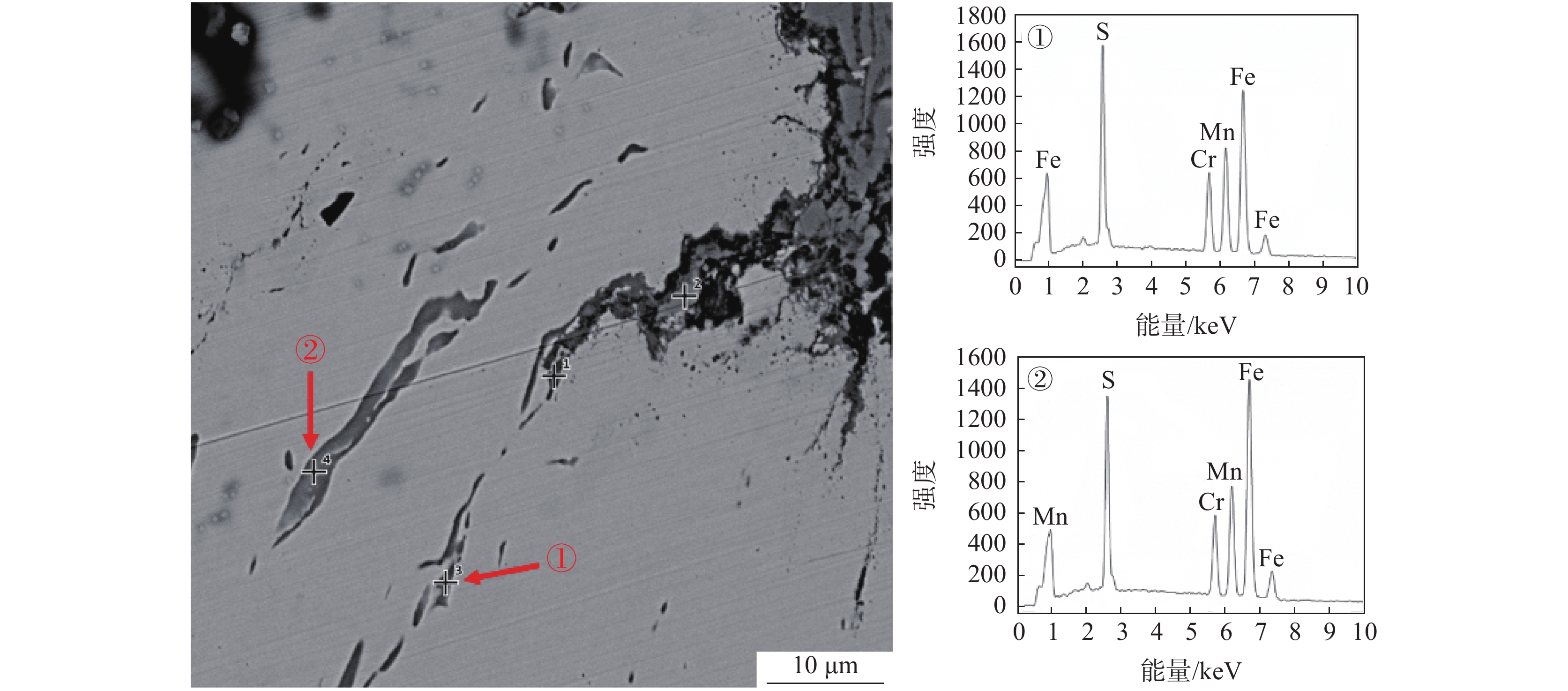
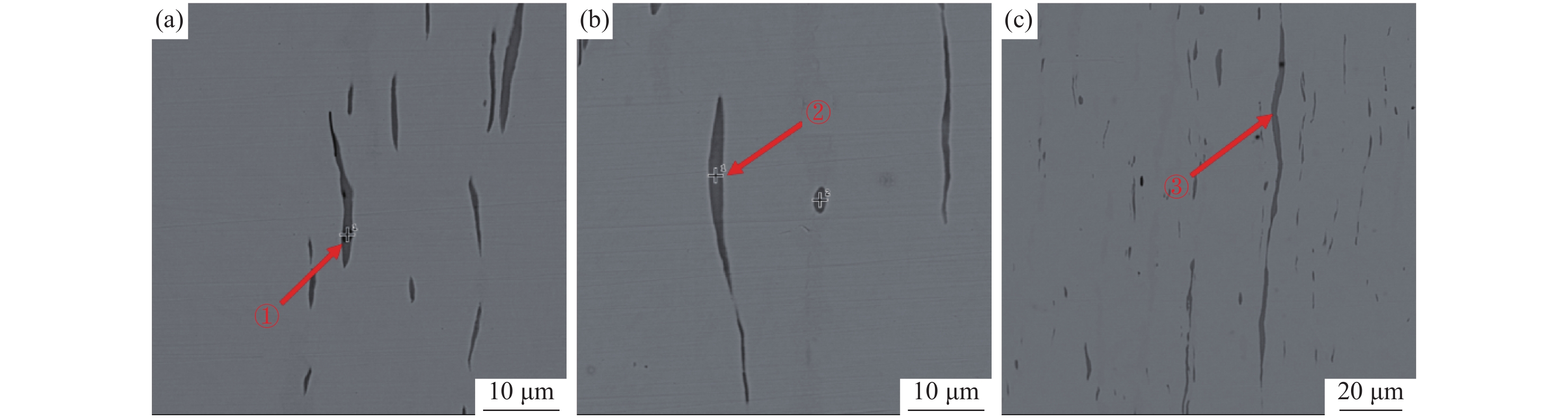
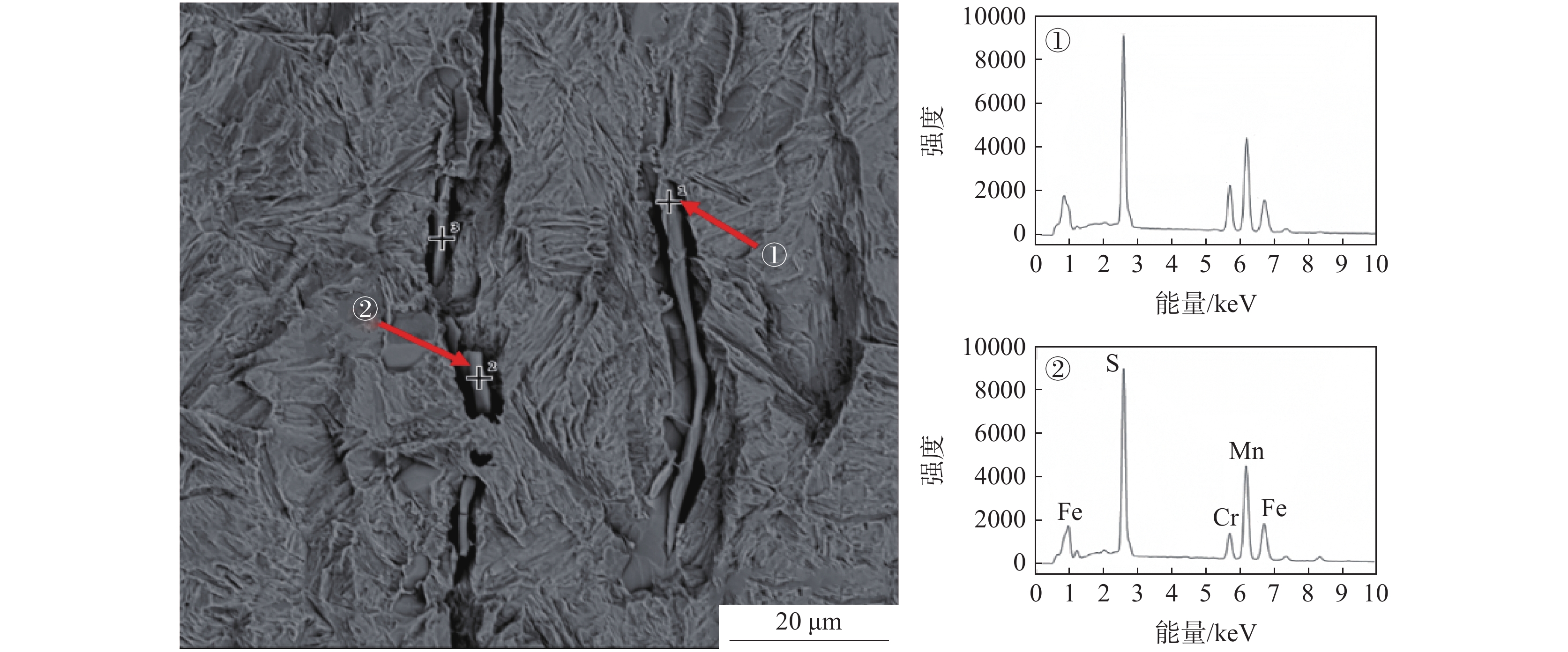
将清理制备的1号样放入扫描电镜下观察,如图2所示。从图2可以看出,在裂纹内部发现一层灰黑色填充物,出现与钢基体不一致的组织。对该组织进行能谱分析可知,主要为FeO,无明显其他异常物质。原因可能为试样在轧制时表面形成氧化铁皮,由拉拔过程导致裂纹扩展,氧化铁皮掉入裂纹缝隙处进而形成覆盖层。在裂纹边部和延展部发现细长条状硫化物,对其进行能谱分析,结果显示为MnS和(Mn,Fe)S,如图3所示。
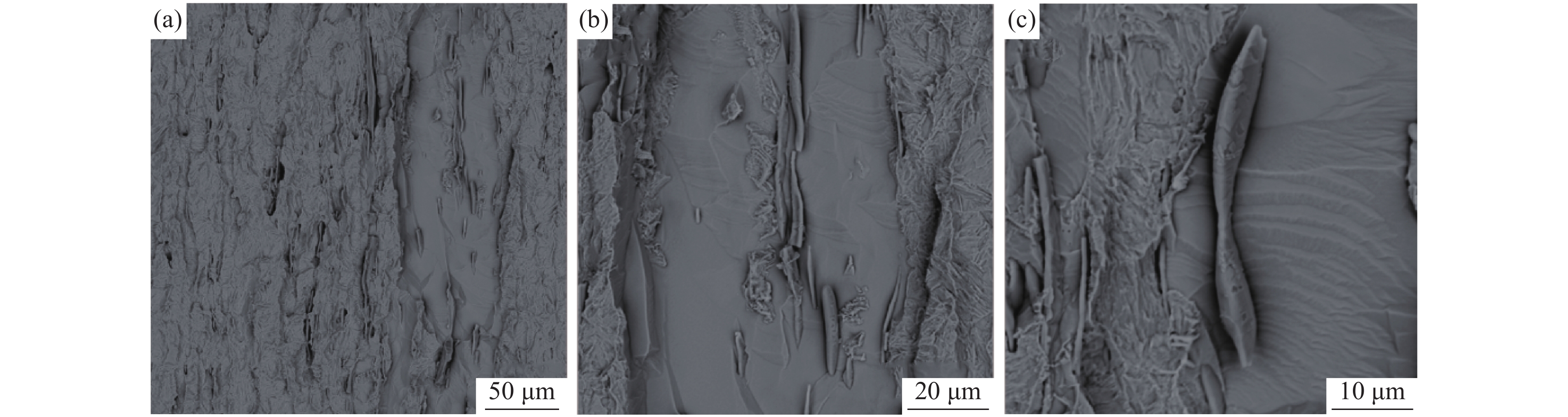
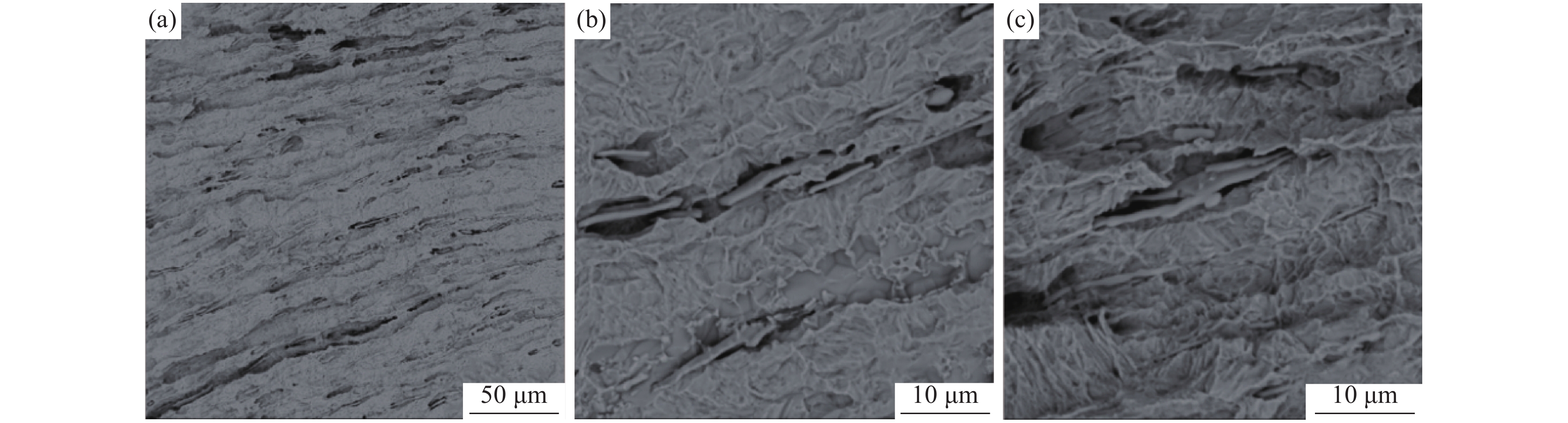
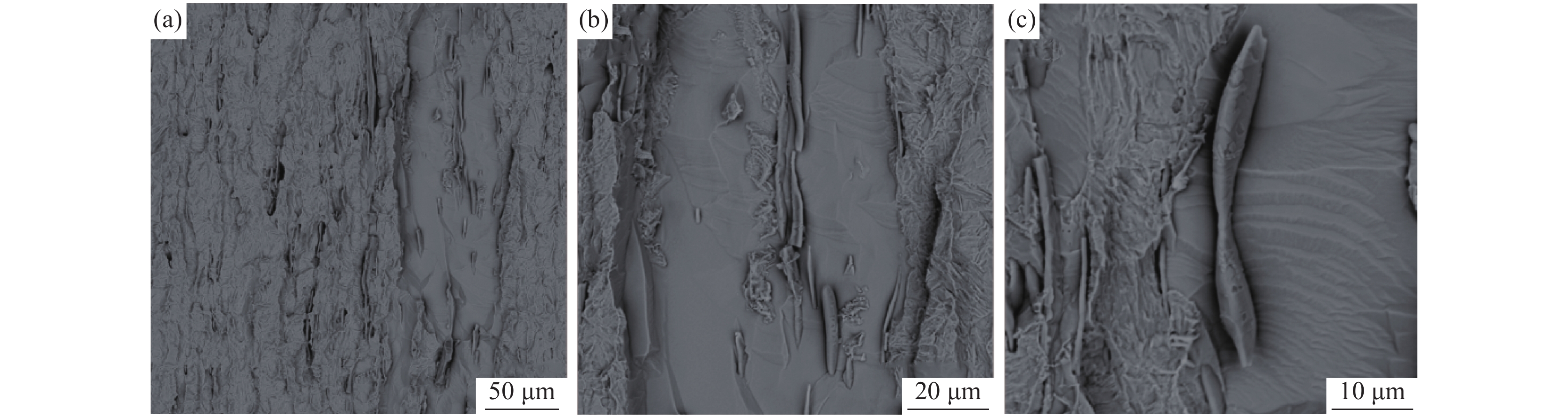
为了观察裂纹内壁的真实形貌,对1号样进行电解腐蚀。将试样作为电解阳极,不锈钢钢片作为电解阴极,在无水电解液(1%四甲基氯化铵-10%三乙醇胺-甲醇)中进行恒电流、低温电解腐蚀,获得裂纹内壁的形貌,并在扫描电镜下观察[6]。电解腐蚀后的扫描照片如图4所示。从图4可以看出:在电解腐蚀后裂纹中的FeO夹杂已基本消除,裂纹内壁的真实形貌得以裸露出来;裂纹内壁为凹凸不平的平面,有许多与轧制方向平行的细长条状夹杂物,尺寸约为20~60 μm,相对于基体夹杂物尺寸偏大,对图4中的细长条状夹杂物进行能谱分析,结果如图5所示,从能谱图中可以看出细长条状夹杂物为MnS和(Mn,Fe)S夹杂物。推测该厂Y1Cr13轧材劈头裂纹产生的原因是:硫化物形态控制较差,存在大量细长条状的MnS和(Mn,Fe)S夹杂物。
2.2 金相形貌分析
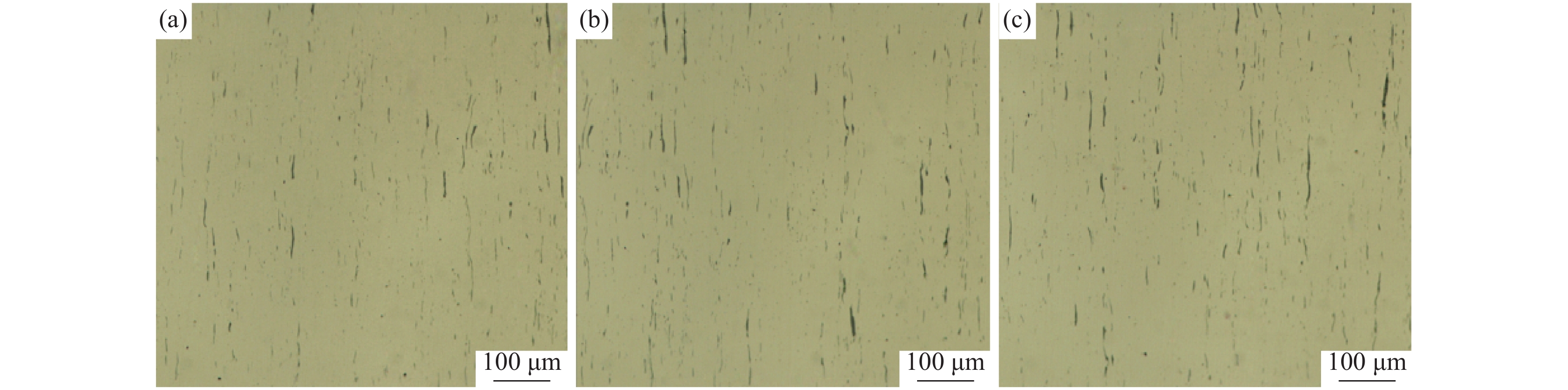
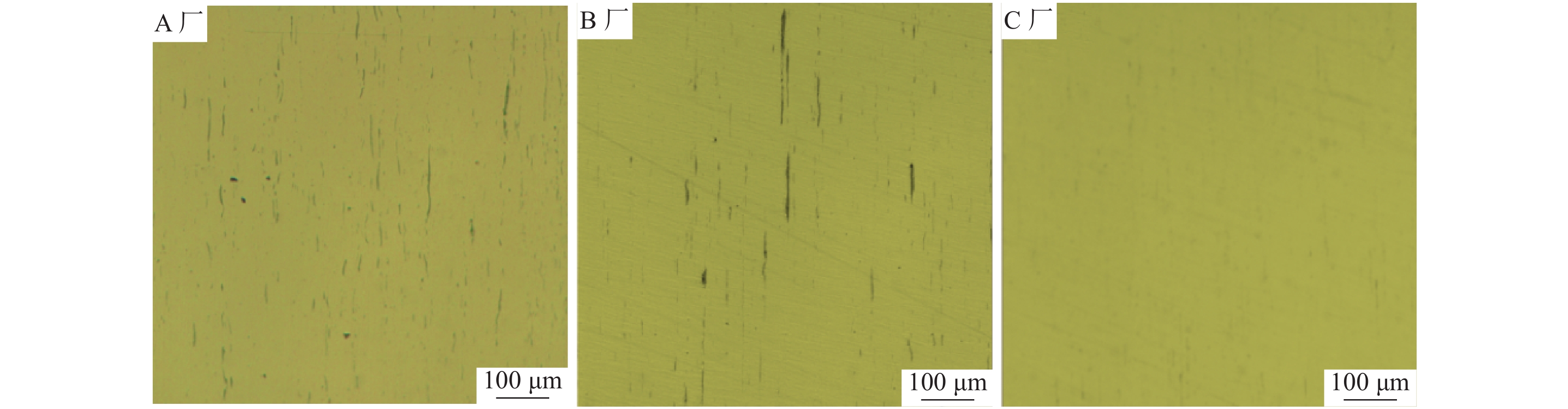
为了判断该厂Y1Cr13不锈钢中硫化物形态的控制水平,将制备的2号样在光学显微镜下(×100倍)选取多个典型视场进行观察,如图6所示。
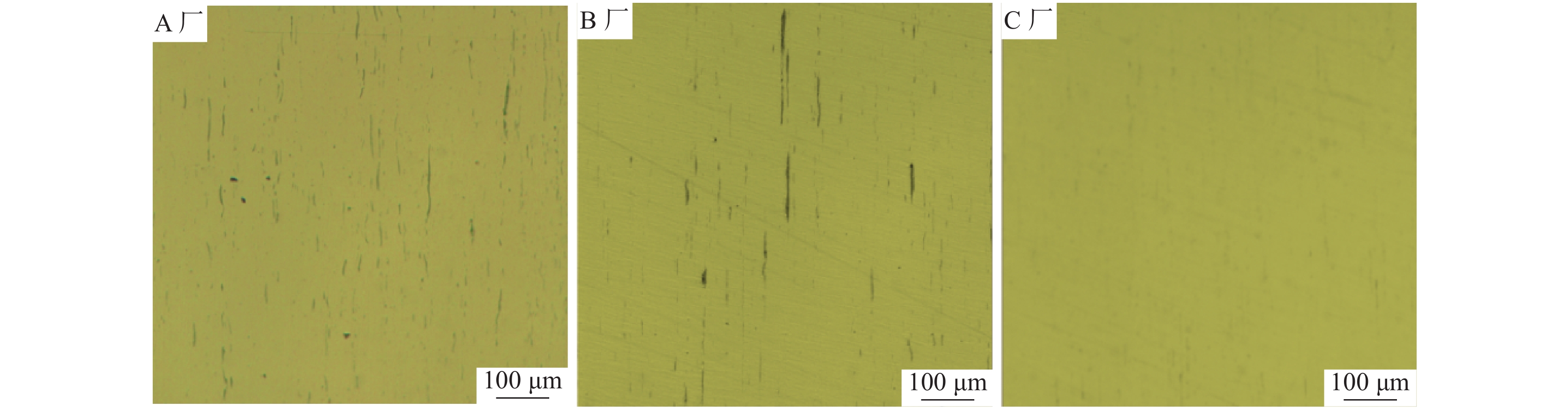
由图6可以看出,该厂的轧材中夹杂物主要为硫化物,且分布不均匀。大部分硫化物呈细长条状,少量为纺锤状、球状,硫化物形态控制较差。依据GBT 10516—2005附录,采用最恶劣视场法对该厂的A类夹杂物(硫化物)进行评级。评级结果为粗系4.5级,细系5.5级,粗系评级较高,说明存在大量长条状硫化物。然而与国内B厂和C厂轧材作相同评级对比发现,B厂和C厂的硫化物形态控制水平较好。B厂评级为:粗系3.0级,细系5.5级;C厂评级为:粗系1.5级,细系5.5级;按照德国高硫易切削钢SEP1572评级图谱,各钢厂的评级分别为:A厂3-3级,B厂2-3级,C厂2-2级,结果如表2所示。三厂试样中典型视场如图7所示。
从表2看出,A厂的硫化物夹杂控制水平较低,粗系硫化物劣于B厂和C厂,且其钢样中夹杂物的数量和分布都不如另外两厂理想,大型长条状硫化物夹杂较多,故硫化物形态控制相对较差,可能最终导致了劈头裂纹的产生。
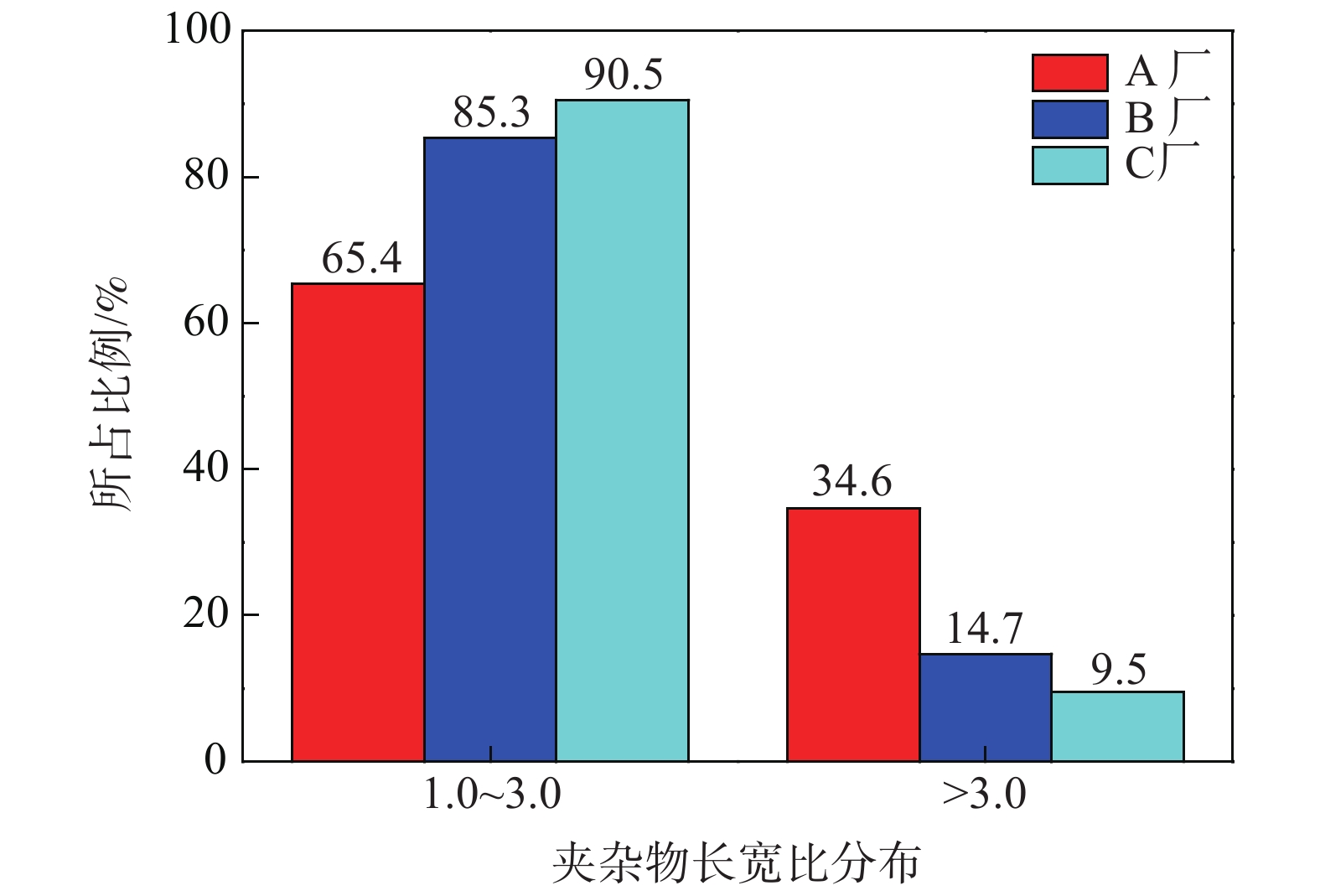
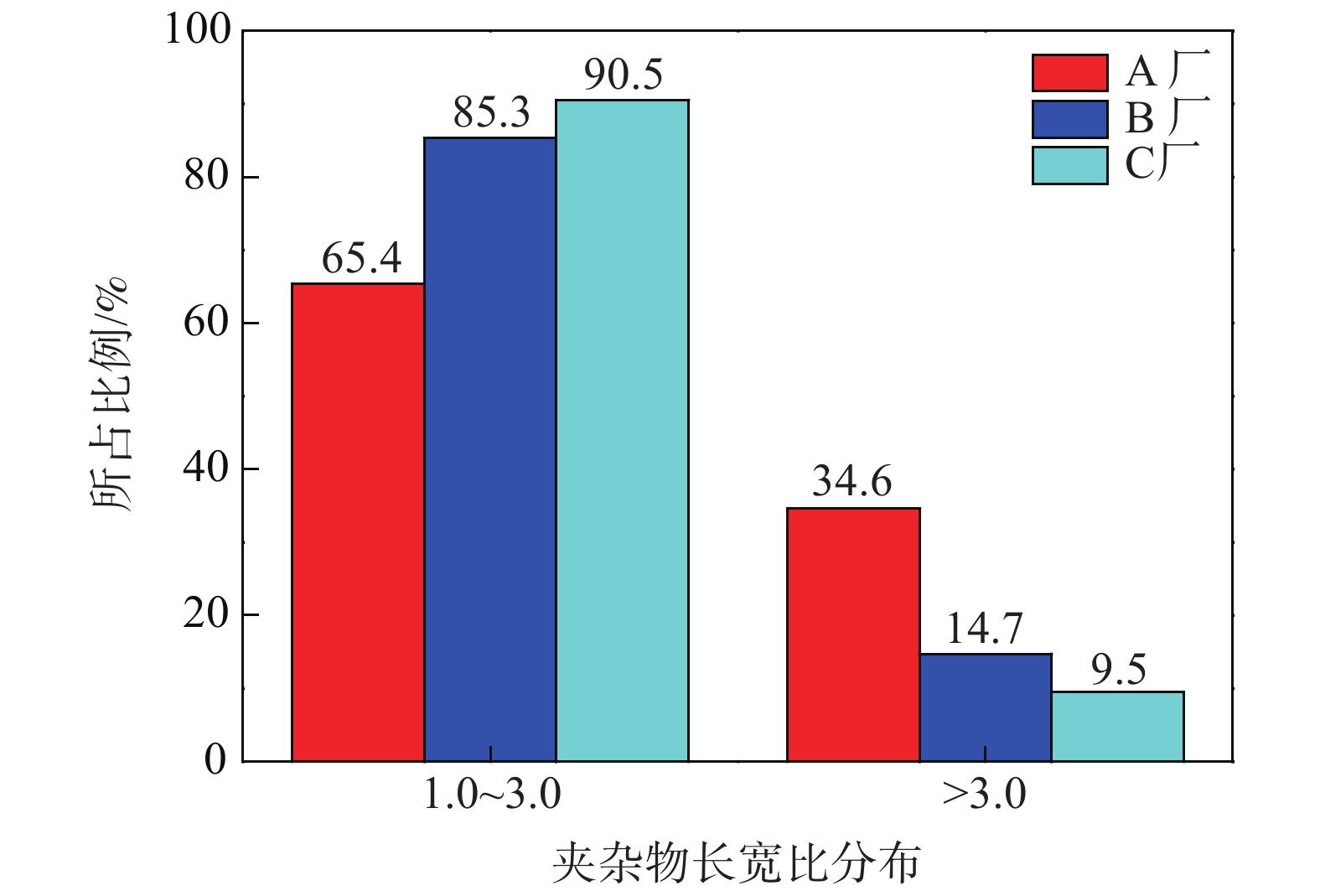
由于金相评级是在100倍照片下进行的,不能比较以上三厂硫化物的大小和数量,故进一步对以上三厂的硫化物在200倍金相照片下进行了统计。在光学显微镜下各选取10个视场对三厂的硫化物长宽比作对比,结果如图8所示。
表 2 三个厂硫化物评级对比Table 2. Comparison of inclusions rating of samples provided by three plants厂家 国标评级(GBT 10516—2005) 德标评级 A 粗系4.5级,细系5.5级 3-3级 B 粗系3.0级,细系5.5级 2-3级 C 粗系1.5级,细系5.5级 2-2级 从图8可以看出B厂和C厂钢样中硫化物长宽比主要分布在3以内,B厂和C厂长宽比小于3的夹杂物所占比例分别为85.3%和90.5%,形态趋于短粗条状;相比而言,国内A厂钢材中硫化物长宽比较大,其钢样中硫化物长宽比分布在3以内的夹杂物占比为65.4%,长宽比大于3的夹杂物占比为34.6%,较另外两厂多,可见该厂Y1Cr13钢中细长条状硫化物较多,硫化物形态控制较差。
2.3 夹杂物形貌与成分分析
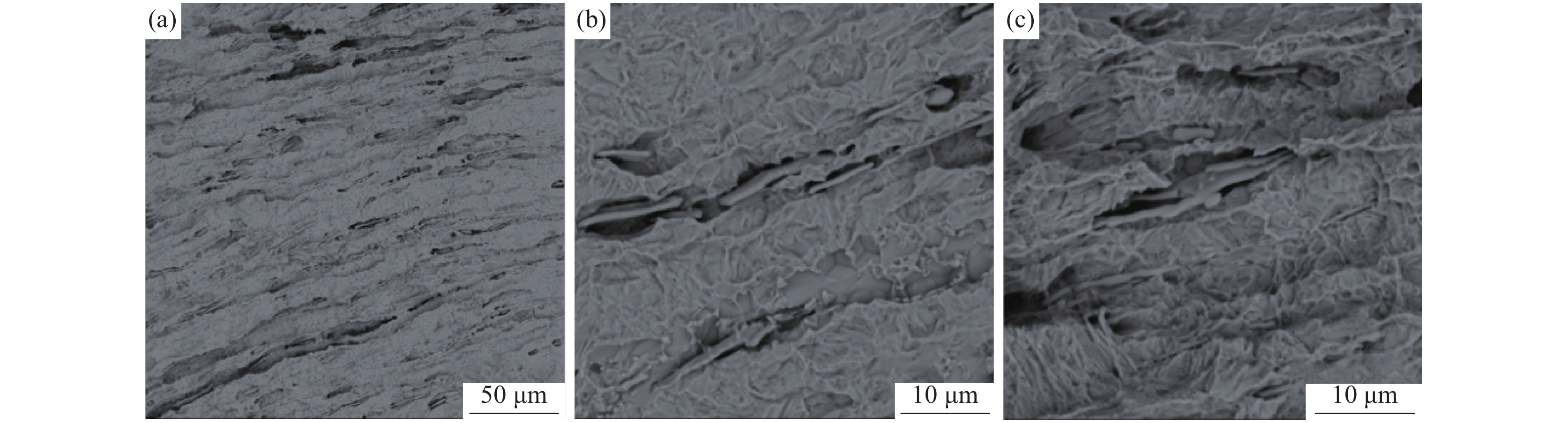
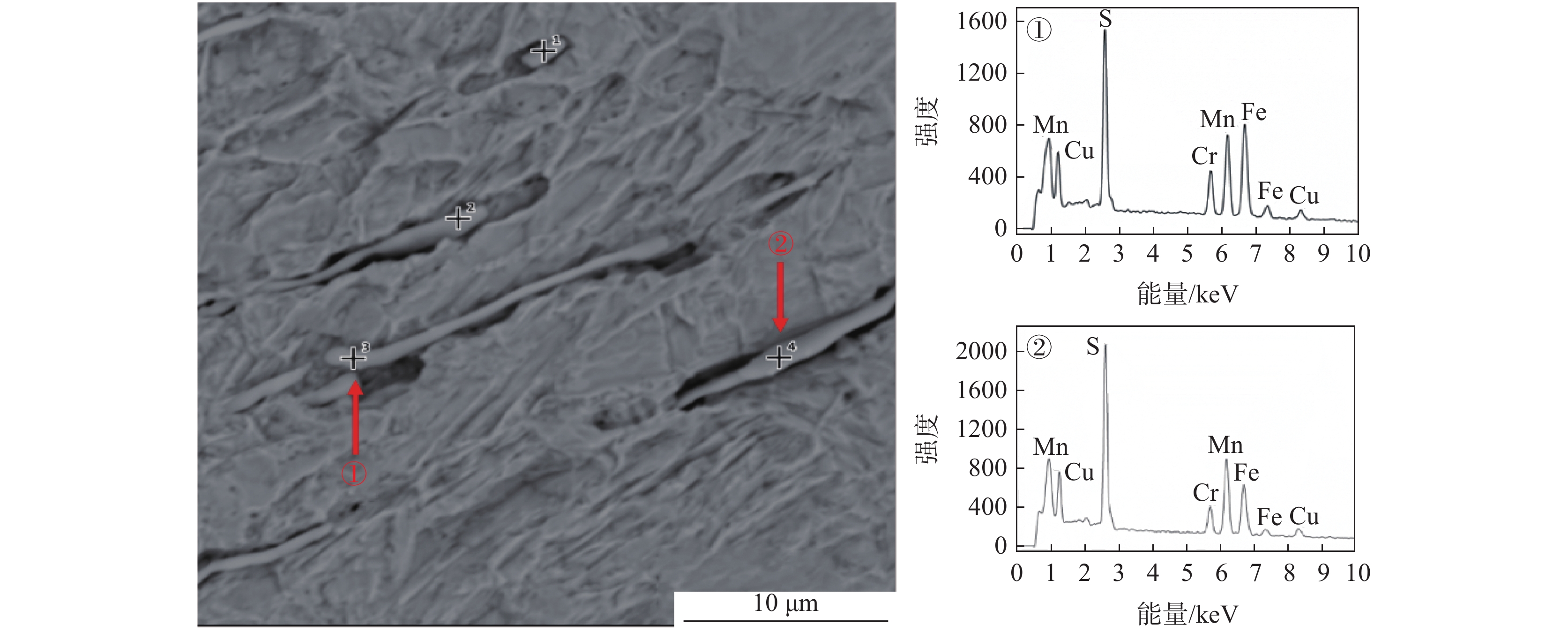
为了确定2号样中硫化物的成分,将清理制备的2号样放入扫描电镜下观察,如图9所示。从图9可以看出,劈头钢样内部存在大量浅灰色夹杂物,且夹杂物大都成细长条状分布,尺寸可达约60 μm,少量为纺锤状、球状,分布不均,此外,其中也存在一些特征夹杂物。对其进行能谱分析,结果如表3所示,可知:该浅灰色夹杂物为MnS和(Mn,Fe)S夹杂,这些特征夹杂物为Al2O3,而此类夹杂并不会直接导致轧材劈头开裂;另外也可以看出劈头钢样内部除部分MnS和(Mn,Fe)S夹杂物内部含有Al2O3夹杂外,绝大多数夹杂物为热脆性的纯MnS和(Mn,Fe)S,不存在异常形态或分布的夹杂物。
为了进一步观察硫化物的三维形貌,对2号样进行了电解腐蚀。电解腐蚀后的扫描照片如图10所示。从图10可以看出:硫化物多为细长条状,尺寸可达约60 μm;对其进行能谱分析,结果如图11所示。从能谱图中可以看出细长条状硫化物为MnS和(Mn,Fe)S。大量的热脆性长条状硫化物在轧制过程中随钢基体滑移形成的,长条状硫化物周围聚集着大量应力,一旦应力集中,高温轧制就会形成高温轧制裂纹。
2.4 结果讨论
由上述试验结果及分析可知,国内A厂Y1Cr13易切削不锈钢的劈头裂纹是由硫化物形态控制较差,细长条状硫化锰及锰铁硫化物所导致的。易切削不锈钢中细长的硫化物会显著降低钢的横向韧性和伸长性,而短粗状硫化物对钢的横向力学性能降低较少,一般来说,尺寸较大、形态为球形或纺锤形(即长宽比≤3)的硫化物夹杂,在热加工时变形较小,钢的横向力学性能降低得也少[7],因此,细长条状硫化物易导致轧制时产生劈头开裂现象。钢中MnS为软质相,在轧制过程容易沿轧制方向被拉长,变成长条状,而后期的热处理工艺也很难使之溶解[8]。长条状MnS夹杂对材料性能的危害最大[9]。由于夹杂物与金属基体的弹性模量和膨胀系数不同,在受力过程中容易在夹杂物的尖角处产生应力集中,甚至产生微裂纹[10-11]。当夹杂物大到一定的尺寸时,夹杂物与基体为非共格关系,与基体的结合力较低,容易成为裂纹扩展的通道[12]。(Mn,Fe)S也是钢中最常见的非金属夹杂物,纯MnS的熔点为1610 ℃,当硫化锰含硫化亚铁时,熔点就相对降低,FeS和MnS二元共晶温度为1110 ℃[13]。A厂Y1Cr13不锈钢中Mn/S较低(<4),钢中存在大量(Mn,Fe)S夹杂物,其为低熔点(1110 ℃)的固溶物,当在较高温度下轧制时,会有部分液化,液相沿着长条状硫化物分布,在受到轧制冲击力时会诱导开裂。因此,适当减少钢中的[S]含量并提高锰/硫比,有利于减少(Mn,Fe)S。
钢中的夹杂物的尺寸、成分、形状和自身的各种属性(如硬度、熔点等)的差异会对钢的成品组织和性能产生各种或好或坏的影响[14-15],针对该厂硫化物形态控制较差的问题,建议采用镁、碲等新工艺对硫化物形态进行改质[16-17]。改质剂在钢中的作用机理是:当镁添加入钢液后会优先与[Al]、[O]反应生成细小弥散的MgO·Al2O3和MgO;凝固末期诱导硫化物的包裹,形成“外软内硬”的复合夹杂物,故在后续轧制过程中硫化物不易变形。当碲添加到钢液后,一部分固溶到硫化锰中,另一部分在硫化锰周围析出,形成MnTe;固溶到硫化锰中的碲会使硫化锰硬度增加,以致轧制时硫化锰不易变形,在硫化锰周围析出的MnTe,会包裹住硫化锰,轧制时吸收轧制应力,导致轧制时硫化锰不易变形。
3. 结论
1)通过对Y1Cr13易切削不锈钢轧材劈头开裂样进行分析,发现裂纹边缘和延展部存在细长条状硫化锰和锰铁硫化物,硫化物的国标评级情况为:粗系4.5级,细系5.5级,德标评级为3-3级,且硫化物长宽比较大。
2)根据样品的分析检测结果推测:试样中硫化物形态控制相对较差,裂纹是由细长条状硫化锰和锰铁硫化物导致。
3)针对该厂硫化物形态控制较差问题,建议采用镁、碲等新工艺对硫化物形态进行改质;并可通过适当减少钢中的[S]含量以及提高钢中锰硫比等措施来减少钢中的(Mn,Fe)硫化物。
-
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of experimental steels
% 厂家 C Si Mn P S Cr Mo Ni A 0.13 0.54 1.15 0.027 0.31 12.89 0.04 B 0.122 0.229 0.957 0.026 0.350 12.300 0.105 C 0.120 0.430 1.160 0.018 0.270 12.790 0.260 表 2 三个厂硫化物评级对比
Table 2. Comparison of inclusions rating of samples provided by three plants
厂家 国标评级(GBT 10516—2005) 德标评级 A 粗系4.5级,细系5.5级 3-3级 B 粗系3.0级,细系5.5级 2-3级 C 粗系1.5级,细系5.5级 2-2级 -
[1] Zhang Yu. Analysis on the causes of rolling cracking of Y1Cr13[J]. Special Steel Technology, 2013,(3):17−19. (张宇. Y1Cr13轧制开裂原因浅析[J]. 特钢技术, 2013,(3):17−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0971.2013.03.005 [2] Fan Zhijin, Cheng Xiufeng. Crack analysis and process optimization of high sulfur stainless steel SUSY1Cr13 in hot working[J]. Special Steel, 1996,(5):42−44. (范植金, 程秀峰. 高硫不锈钢SUSY1Cr13热加工裂纹分析及其工艺优化[J]. 特殊钢, 1996,(5):42−44. [3] Ma Baoguo, Xu Songqian, Zhao Suwu, et al. Research on splitting head of BT303CuS free-cutting stainless steel rolling stock[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2010,31(3):381−384. (马宝国, 徐松乾, 赵肃武, 等. BT303CuS易切削不锈钢轧件劈头的研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2010,31(3):381−384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2010.03.020 [4] Wang Weining. Analysis of cracking causes of Y1Cr13 steel[J]. Special Steel Technology, 2010,16(4):23−26. (王维宁. Y1Cr13钢开裂原因浅析[J]. 特钢技术, 2010,16(4):23−26. [5] Hao Shifeng, You Xiaodong, He Ning. Analysis and process improvement of M7 steel rolling split[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 2015,(8):61−63. (郝世风, 尤晓东, 何宁. M7钢轧制劈头分析及工艺改进[J]. 河北冶金, 2015,(8):61−63. [6] Zhang D, Shen P, Xie J B, et al. A method for observing tridimensional morphology of sulfides by non-aqueous solution electrolytic etching[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2019,26(3):275−284. doi: 10.1007/s42243-018-0142-z [7] Deng Xiangyang, Li Jian, Xie Jianbo, et al. Comparative analysis of steel quality for C70S6 expanding connecting rod at home and abroad[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(1):148−154. (邓向阳, 李健, 谢剑波, 等. 国内外C70S6胀断连杆用钢质量对比分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(1):148−154. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.01.026 [8] Chen Yu, Liu Hongliang, Zheng Zhong, et al. Development of QStE series automotive structural steel products of bengang[J]. Science and Technology and Enterprise, 2014,10:299. (陈宇, 刘宏亮, 郑中, 等. 本钢QStE系列汽车结构用钢产品的开发[J]. 科技与企业, 2014,10:299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9207.2014.17.277 [9] Yang Wen, Yang Xiaogang, Zhang Lifeng, et al. Review of MnS inclusion control in steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2013,29(6):71−78. (杨文, 杨小刚, 张立峰, 等. 钢中MnS夹杂物控制综述[J]. 炼钢, 2013,29(6):71−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2013.06.017 [10] Zou Changfei, Yang Jieming, Wei Xianyi, et al. Microstructure characteristics of point segregation zone in 25CrMo ingot Steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2017,52(3):21−26. (邹长飞, 杨接明, 韦贤毅, 等. 25CrMo钢锭点状偏析区微观组织特点[J]. 钢铁, 2017,52(3):21−26. [11] Ma Yue, Pan Tao, Jiang Bo, et al. Study on the effect of S content on fracture toughness of high speed wheel steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2011,47(8):978−983. (马跃, 潘涛, 江波, 等. S含量对高速车轮钢断裂韧性影响的研究[J]. 金属学报, 2011,47(8):978−983. [12] Liu Yangbo, Tong Qian, Sun Qisong, et al. Effect of notch, short crack and inclusion on fatigue strength of high strength steel[J]. Shanghai Metal, 2017,39(4):69−74. (柳洋波, 佟倩, 孙齐松, 等. 缺口、短裂纹以及夹杂物对高强钢疲劳强度的影响[J]. 上海金属, 2017,39(4):69−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2017.04.014 [13] Li Hongsheng, Gao Hui. The form of manganese sulfide in steel and its effect on steel properties[J]. Yizhong Technology, 2004,(4):26−28. (李洪生, 高辉. 钢中硫化锰的形态及对钢性能的影响[J]. 一重技术, 2004,(4):26−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3355.2004.04.011 [14] Koseki T. Inclusion assisted microstructure control in C-Mn and low alloy steel welds[J]. Metals Science Technology, 2005,21(8):867−879. doi: 10.1179/174328405X51703 [15] Liu Z. Nucleation of acicular ferrite on sulfide inclusion during rapid solidification of low carbon steel[J]. CAMP-ISIJ, 2006,19(4):743. [16] Ai Kenan, Xie Jianbo, Zeng Zhiqi, et al. Effect of magnesium on microstructure and sulfide in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019,31(4):361−367. (艾克南, 谢剑波, 曾志崎, 等. 镁对非调质钢中组织及硫化物的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019,31(4):361−367. [17] Shen P, Yang QK, Zhang D, et al. The effect of tellurium on the formation of MnTe-MnS composite inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Metals, 2018,8(8):639−652. doi: 10.3390/met8080639 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 杨振,赵烁,薛余强,王建锋,孙晓林. 铸坯轧制过程中夹杂物变形行为研究进展. 钢铁研究学报. 2024(06): 707-716 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 朱强斌,季灯平,严道聪,李立,付建勋. Te对303Cu不锈钢硫化物及性能的影响. 钢铁钒钛. 2023(01): 188-196 .  本站查看
本站查看3. 张浩,王冬,伦明睿,付建勋,沈平. 国内外耐磨钢夹杂物控制水平分析. 铸造技术. 2023(04): 351-357 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 于吉鲲,贾华. 1Cr13半马氏体不锈钢短轴热处理后开裂的原因分析. 热加工工艺. 2023(18): 143-146 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 王高峰,钟亮美,周楠,张志明,付建勋. SAE1144易切削钢八角棒表面裂纹缺陷分析. 钢铁钒钛. 2022(01): 190-196 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(1)
-





 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术