Direct leaching of spent catalyst from acid production from flue gas
-
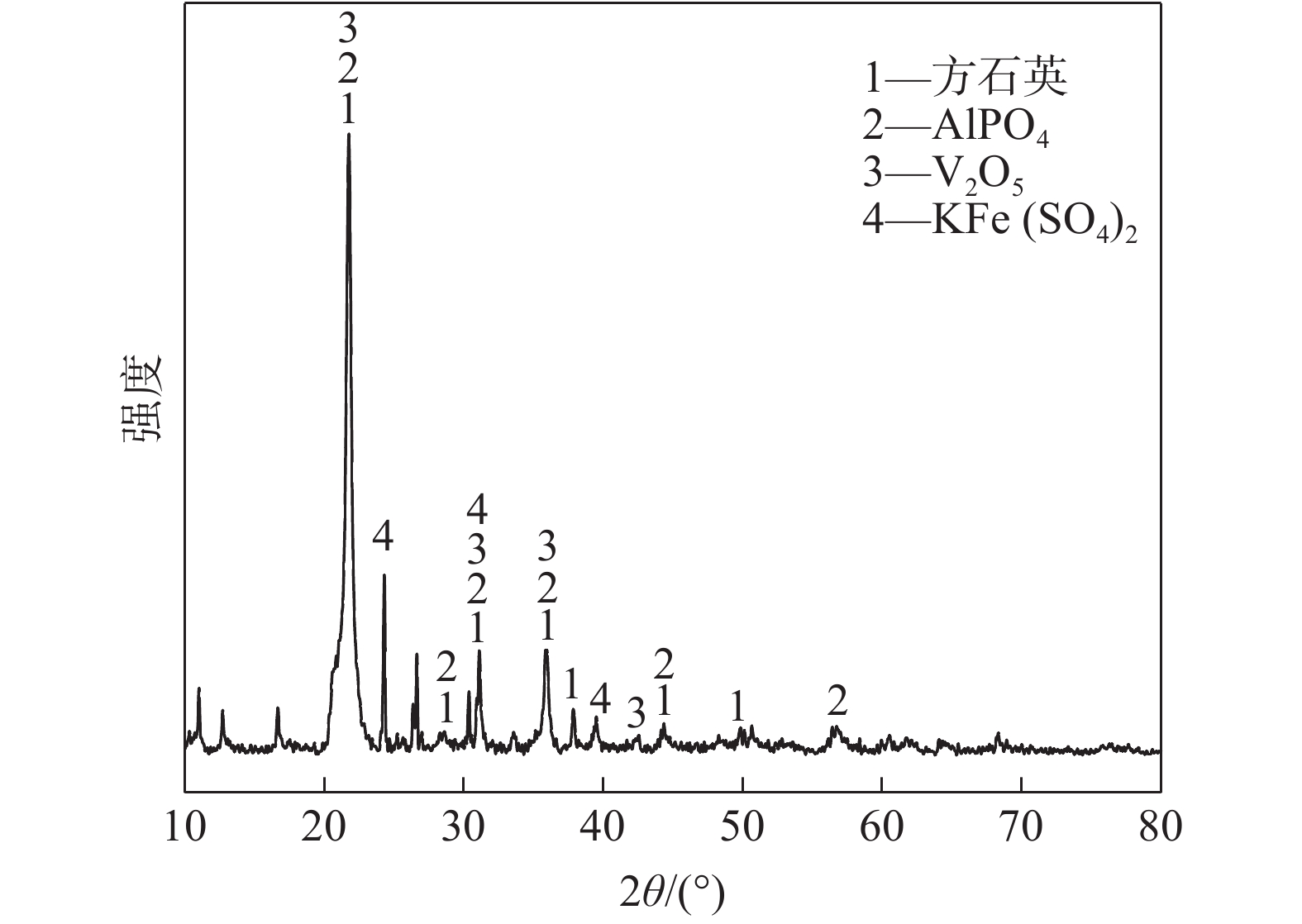
摘要: 重金属冶炼烟气制酸的废催化剂杂质组成相对复杂,为获得此类废催化剂综合回收钒、钾、锌工艺的优化条件,对直接湿法浸出工艺钒、钾、锌浸出率的影响因素进行了试验研究。通过单因素试验,系统研究了浸出剂质量分数、液固比、反应温度、反应时间对钒、钾、锌浸出率的影响,其次对废催化剂和浸出渣的化学成分及物相进行了分析对比。结果表明,浸出的最佳工艺条件为:硫酸质量分数8%、液固比2∶1、浸出温度70 ℃、浸出时间1.5 h,钒、钾、锌的浸出率分别达93.58%、85.43%、99.31%,优于传统焙烧法。Abstract: The waste catalyst from acid production from heavy metal smelting flue gas has relatively complex impurity compositions. In order to obtain the optimum conditions for comprehensive recovery of vanadium, potassium and zinc from the waste catalyst, a direct leaching process was proposed and the factors affecting the leaching rate of vanadium, potassium and zinc, e.g. the mass fraction of leaching agent, liquid-solid ratio, reaction temperature and time, were studied. The chemical and phase compositions of the waste catalyst and leaching residue were analyzed and compared. The optimum leaching conditions were determined at the sulfuric acid mass fraction of 8%, liquid-solid ratio of 2∶1, leaching temperature of 70 ℃ and leaching time of 1.5 h, with the leaching rates of vanadium, potassium and zinc at 93.58%, 85.43% and 99.31%, respectively. The proposed process is better than the traditional roasting method.
-
Key words:
- waste catalyst /
- smelting flue gas /
- acid production /
- acid leaching /
- vanadium /
- potassium /
- zinc /
- recovery rate
-
表 1 废催化剂的主要化学成分分析
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of the spent catalyst
% SiO2 SO3 K2O V2O5 Fe2O3 60.23 15.39 7.62 5.76 3.62 Al2O3 P2O5 Na2O ZnO 其余 2.00 1.94 0.920 0.784 1.736 表 2 酸浸渣的主要成分
Table 2. Main compositions of acid leaching residue
% SiO2 K2O V2O5 ZnO 其余 89.41 1.64 0.658 0.02 8.272 -
[1] Yang Shaoli, Peng Fuchang, Pan Fusheng, et al. Research and application of vanadium catalysts[J]. Materials Guide, 2008,(4):53−56. (杨绍利, 彭富昌, 潘复生, 等. 钒系催化剂的研究与应用[J]. 材料导报, 2008,(4):53−56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2008.04.014 [2] Xu Mao, Huang Xianfa, Gui Lin. New process for comprehensive recovery of spent vanadium catalyst[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbide, 2014,42(6):14−15, 60. (徐懋, 黄宪法, 桂林. 废钒催化剂的综合回收新工艺[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2014,42(6):14−15, 60. [3] Mazurek Krzysztof. Recovery of vanadium, potassium and iron from a spent vanadium catalyst by oxalic acid solution leaching, precipitation and ion exchange processes[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013,134-135:26−31. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.01.011 [4] Ji Chengqing, Shen Mingwei, Zhu Changluo, et al. Experimental study on direct wet sulfuric acid leaching of black shale type clay vanadium ore[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014,35(1):11−15. (冀成庆, 沈明伟, 朱昌洛, 等. 黑色页岩型黏土钒矿的硫酸直接湿法浸出试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014,35(1):11−15. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.01.003 [5] Xu Zhengzhen, Liang Jinglong, Li Hui, et al. Research status and prospect of vanadium recovery from vanadium containing waste[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020,(3):8−13. (徐正震, 梁精龙, 李慧, 等. 含钒废弃物中钒的回收研究现状及展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020,(3):8−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.03.002 [6] (李洪贵. 湿法冶金学[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2002.)Li Honggui. Hydrometallurgy [M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2002. [7] Lígia Fernanda Kaefer Mangini, Renata Bachmann Guimarães Valt, Maria José Jerônimo de Santana Ponte, et al. Vanadium removal from spent catalyst used in the manufacture of sulfuric acid by electrical potential application[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020,246:342. [8] Liu Bo, Tong Qingyun, Li Guoliang. Recovery of vanadium from waste vanadium catalyst by oxidation roasting method[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2002,(2):112−115. (刘波, 童庆云, 李国良. 氧化焙烧法回收废钒触媒中的钒[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2002,(2):112−115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3087.2002.02.028 [9] Wang Xinwen, Lei Zhaomin. Experimental study on recovery and purification of vanadium pentoxide from waste vanadium catalyst[J]. Sulphuric Acid Industry, 1998,(2):47−51. (王新文, 雷兆敏. 从废钒催化剂中回收精制五氧化二钒的试验研究[J]. 硫酸工业, 1998,(2):47−51. [10] Ye Guohua, He Wei, Tong Xiong, et al. Study on direct acid leaching of vanadium from clay vanadium ore without grinding and roasting[J]. Rare Metals, 2013,(4):621−627. (叶国华, 何伟, 童雄, 等. 粘土钒矿不磨不焙烧直接酸浸提钒的研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2013,(4):621−627. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2013.04.017 [11] Wang Chunqiong. Study on sulfuric acid leaching process of calcined vanadium bearing clinker[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(1):26−30, 36. (王春琼. 钙化焙烧含钒熟料硫酸浸出工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(1):26−30, 36. -





 下载:
下载: