Research on fatigue corrosion behavior of 22MnCrNiMo steel
-
摘要: 采用海水挂片试验和腐蚀疲劳试验对R4s (22MnCrNiMo)级钢的耐腐蚀机理和腐蚀疲劳性能进行了研究,腐蚀时间选择为30、60 、90 d。结果表明:腐蚀初期,22MnCrNiMo钢的腐蚀机理为点蚀的局部腐蚀,随着时间的增加转变为点蚀的均匀腐蚀。当腐蚀时间到90 d时,试样表面已完全被花状腐蚀产物覆盖,整个腐蚀过程中,22MnCrNiMo钢的腐蚀速率在0.035~0.045 g/(m2·h)。22MnCrNiMo钢腐蚀疲劳的幂函数表达式为:S=14 000.12×N −0.266 4,其疲劳极限约为190 MPa。在电化学效应和交变应力以及侵蚀性离子的作用下,试样的裂纹扩展速度增加,断裂时间提前。
-
关键词:
- 22MnCrNiMo钢 /
- 点蚀 /
- 耐蚀性 /
- 腐蚀疲劳
Abstract: In this paper, the corrosion resistance mechanism and corrosion fatigue performance of R4s (22MnCrNiMo) grade steel were studied by means of seawater coupon test and corrosion fatigue test. The choice of corrosion time was 30 d, 60 d and 90 d, respectively. The experimental results show that in the initial stage of corrosion, the corrosion mechanism of 22MnCrNiMo steel is localized corrosion of pitting corrosion, which changes into uniform corrosion of pitting corrosion as time extends. When the corrosion time reaches to 90 d, the surface of the sample is completely covered with flower-like corrosion products. During the entire corrosion process, the corrosion rate of 22MnCrNiMo steel is between 0.035~0.045 g/(m2·h). The power function expression of corrosion fatigue of 22MnCrNiMo steel is: S=14 000.12×N −0.266 4, and its fatigue limit is about 190 MPa. Subject to electrochemical effect, alternating stress and aggressive ions effects, the crack propagation speed of the sample increases, and the fracture occurs in advance.-
Key words:
- 22MnCrNiMo steel /
- pitting /
- corrosion resistance /
- corrosion fatigue
-
0. 引言
近年来,人类对各种自然资源的需求日益增加,而海洋便拥有大量丰富的自然资源,因此探索海洋吸引了许多工程学会的注意[1-3]。在海上进行探索和作业时,最重要的是依靠系泊系统[4];系泊链作为固定装置,其在恶劣的海洋环境中需要经受住各种复杂的考验;这就需要系泊链钢具有优良的强韧性、抗疲劳性以及耐蚀性等性能。
系泊链产品主要用于海洋石油生产、浮式生产、半潜式钻井平台等海上设施[5]。使用期间,链条会被海水浸没,在海洋这样的腐蚀环境中,对系泊链的要求往往比一般产业链、钢、矿用链等用钢的要求高,这就需要系泊链钢要具有高强度、高韧性及其他优良特性[6-8]。
系泊链在工作过程中,上与海面浮体相连,下与海底锚腿相接,通体基本浸入在海水中,受到周围环境主要是海水的腐蚀,而且随着海洋洋流的作用,受到海水的响应上下来回震动。由于其自身重力和海面浮体的拉力,使其承受了一定的应力作用,并且在震动过程中,链条还会受到交变载荷的作用,交变载荷和海水腐蚀共同作用导致了腐蚀疲劳。笔者对系泊链钢在海水腐蚀条件下腐蚀疲劳的S-N曲线进行了拟合,并通过对疲劳断口的微观组织分析,研究腐蚀疲劳裂纹萌生、扩展的机理[9]。
1. 试验过程
海水挂片试验的材料为R4s (22MnCrNiMo)级钢,具体化学成分如表1所示,试验的温度为室温,试验的过程中采用水浴法保持温度,浸泡时间分别为30、60 d和90 d。首先将焊缝区挂片试样装入盛有人工海水的烧杯中并密封,人工海水的具体成分如表2所示。为保证试验的真实性,每隔2 d将人工海水进行更换并对相关的试验现象进行记录。为减少试验误差,在浸泡前将试样的每一个面都进行抛光处理,随后用无水乙醇清洗烘干,最后在干燥皿中放置24 h后称重。腐蚀结束后,用硬毛刷对试样表面的腐蚀产物进行清理,经超声波无水酒精清洗干燥后,在干燥皿中放置24 h后称重。对试验获得的数据,采用失重法计算其腐蚀速率。
表 1 22MnCrNiMo钢的化学成分Table 1. Chemical compositions of the steel 22MnCrNiMo% C Si Mn P S Cr Ni 0.24~0.30 0.15~0.30 1.20~1.60 ≤0.025 ≤0.025 0.80~1.30 0.70~1.30 Cu Al Mo Nb [O] [N] [H] ≤0.20 0.020~0.050 0.40~0.80 0.02~0.06 ≤25 ×10−4 ≤90 ×10−4 ≤2 ×10−4 表 2 人工海水成分配比Table 2. Chemical compositions of artificial seawater名称 化学式 分子量 用量/( g·L−1) 无水硫酸钠 Na2SO4 142.04 4.00 氯化钠 NaCl 58.44 25.00 氯化镁 MgCl2·6H2O 203.30 11.00 氯化钙 CaCl2 111.00 1.20 疲劳试验的试样具体尺寸如图1所示,试验设备为SANTECH.20/G型全数控材料试验机。试验中应力比取R=0,指定疲劳寿命的循环次数取104~106,试验环境为人工海水,频率在10 Hz左右,载荷谱为三角波形下恒载荷的拉伸。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 海水挂片试验
采用失重法对海水挂片试验后的试样进行腐蚀研究,具体公式如下所示:
$${V_{ - W}} = ({W_0} - {W_1})/St$$ (1) 式中,V−W为腐蚀速度,g/(m2·h);W0为腐蚀前质量,g;W1为除蚀产物后质量,g;S为表面积,m2;t为腐蚀时间,h。
有研究表明[10-14]当介质中含有活性阴离子(如Cl−)时,较易在钢材表面一定点上产生腐蚀坑。如图2所示为海水挂片试验中试样的腐蚀速率图。可以看到,前30 d的腐蚀速率最快,这是因为腐蚀初期,试样本身就存在一定的组织缺陷,而缺陷部分的微区又容易产生电化学腐蚀,从而形成点蚀。随着点蚀的进行,腐蚀面积逐渐扩大,当腐蚀面积覆盖试样表面时,腐蚀速率达到最大。在30~60 d时,试样的腐蚀速率最低,此时试样的表面已被腐蚀产物覆盖,并产生了一定的隔离效果,腐蚀机制从点蚀的局部腐蚀转变成点蚀的均匀腐蚀,试样未被腐蚀的部分与海水的接触面积大大减小,腐蚀速率也随之下降。随着浸泡时间的增加,腐蚀产物表面产生微裂纹,隔绝效果有所下降,60 d以后,试样的腐蚀速率相较于30~60 d时有所增加,在0.035~0.045 g/(m2·h)。
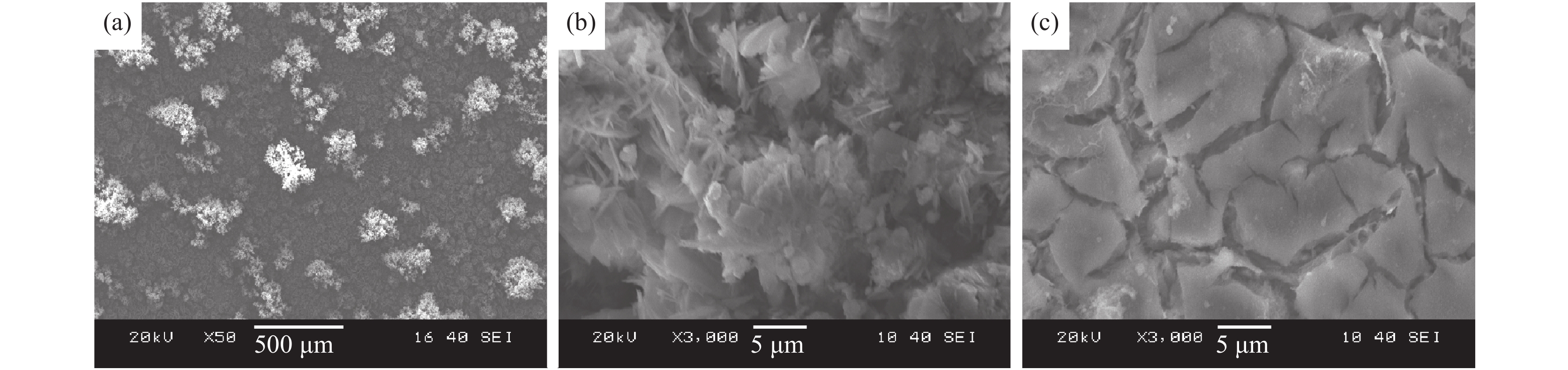
如图3所示为海水挂片试样浸泡30天的SEM形貌,可以看到,图3(a)中试样的表面出现了花状和泥状两种腐蚀产物。图3(b)为图3(a)中花状腐蚀产物的放大图,一般认为,花状腐蚀产物是由于发生了点蚀所产生的。发生点蚀时,反应较为激烈,产生的花状腐蚀产物结构较为松散,对底下的金属不能起到良好的隔离保护效果。图3(c)为图3(a)中泥纹花样腐蚀产物的放大图,这是电化学腐蚀所造成的,腐蚀过程较为缓慢,腐蚀产物也相对较少。
图4为海水挂片试样浸泡60 d的SEM形貌,可以看到,花状腐蚀产物较图3(a)明显增多,这是因为海水中有着大量Cl-存在,而Cl-的半径非常小,可以穿透氧化膜进而接触到试样的金属表面,造成试样表面点蚀程度的加深。此时,泥纹花样腐蚀产物有所减少,对金属的保护作用较差。
图5为海水挂片试样浸泡90 d的SEM形貌,此时试样表面已完全被花状腐蚀产物覆盖。图5(b)所示为花状腐蚀产物的EDS测试结果,可以看到腐蚀产物主要为Fe、Ca合金的氧化物,一般认为是Ca合金与金属表面的渗碳体形成了原电池,从而引起电化学腐蚀。腐蚀的过程较为平缓,泥状腐蚀产物较为致密,起到了良好的保护作用,该区域金属腐蚀进入钝化区。
2.2 腐蚀疲劳S-N曲线
一般来说,S-N曲线和Miner线性累积损伤理论是评估工程构件疲劳程度的常用方法,图6为试样的腐蚀疲劳S-N曲线[15]。从图6可以看出,随着载荷的增加,循环次数呈线性下降。这是因为随着载荷的增加,材料内部的缺陷也随之增加并且快速累积,使得缺陷累积的速度大大增加,最终造成破坏的提前到来。
以应力范围水平S及对应的循环次数N所得曲线表达式:
$$S = {\rm{a}} \cdot {N^{\rm{b}}}$$ (2) 式中a和b为试验所测。曲线表达式为:S=14 000.12×N−0.266 4,曲线如图7所示。从图7可以看到,循环次数在104~108,随着循环次数的增加,应力范围逐渐下降,但下降的速率有所减缓,最终与x轴平行。一般来说,当循环次数达到107时,此时材料仍能在对应的应力下保持不断裂,即可认为达到条件疲劳极限。从图中不难看出,其条件疲劳极限约为190 MPa。
2.3 腐蚀疲劳断裂行为
图8为试样腐蚀疲劳断裂断口的SEM形貌,其中图8(a)为宏观断口,图8(b)为试样腐蚀疲劳裂纹起始区断口SEM形貌。从图8(a)中可以看到,1、2和3处分别为裂纹的起始区、扩展区和瞬断区。断裂的具体过程如下:断口的裂纹首先在试样的表面产生,随后扩展,最终达到瞬断区,使得材料发生脆性断裂。换句话说,试样在人工海水的腐蚀条件下受到交变应力的作用,使得点蚀坑处产生应力集中,当应力值超过最大切应力后,发生局部滑移,此时裂纹产生。随着腐蚀和交变应力的进一步作用,产生的裂纹不断扩大,试样的有效断面面积不断减少,当有效断面断口无法承受外加交变应力时,材料发生脆断,形成瞬断区[16-17]。
从图8(b)中可以看到,裂纹在试样表面产生,随后慢慢扩展并汇集形成较大裂纹(如图中箭头所指)。造成这样的原因是:在腐蚀环境下,材料的表面会发生点蚀,随后在交变应力的作用下形成短裂纹,短裂纹在试样内部不断扩展并聚集,最终形成长裂纹,进而造成材料的断裂。
图9为裂纹扩展区和瞬断区的SEM形貌,其中图9(a)和(b)为扩展区,图9(c)为瞬断区。从图9(a)中可以看到,断口表现出锯齿状,并且与裂纹扩展的方向相同。当裂纹扩展达到第二阶段时,如图9(b)所示,断口表面出现了数量较多的台阶,这是由于不同平面的裂纹扩展并相遇所造成的。同时图9(b)中还能看到许多腐蚀产生的不同形状的疖瘤和裂纹向试样内部扩展产生的二次裂纹。从图9(c)中可以看到少量的韧窝和孔洞,这是因为瞬断时产生了较大的应力,对材料产生了一定的撕裂作用。此外,在断口的表面还可以看到泥状的腐蚀产物,为确定其成分,对其进行EDS测试,结果如图10所示。泥状腐蚀产物由Fe、C以及O元素组成。
2.4 断口分析讨论
众所周知,由于凝固的先后不同,金属材料内部和表面的物理化学性质并不是完全相同的,会存在各种缺陷,如第二相、金属杂家等。这些缺陷会使得材料自身的电化学性能不均匀,腐蚀的过程中极易形成点蚀坑。点蚀是由具有小阳极大阴极电池所引起的阳极区高度集中的腐蚀形式,多发生于表面存在氧化膜的合金。当处于特定的腐蚀环境时(如Cl−),点蚀产生的点蚀坑会集中于材料表面并产生自催化作用,在自催化作用下,点蚀坑会不断朝着金属内部深入,破坏力极大。另一方面,应力的作用也不可忽视,在应力的作用下,点蚀坑处易产生应力集中,加速了裂纹的形成。
当材料处于腐蚀环境时,材料表面的碳化物会和金属基体形成原电池,从而加速阳极金属基体的溶解,造成材料表面微裂纹的产生,加剧应力集中[18]。根据图9、10可以发现,附着在金属表面的腐蚀产物对金属基体可以产生暂时的保护作用,但是由于交变应力的存在,使得金属来回震动造成腐蚀产物的脱落,促进了金属的进一步腐蚀。此外,人工海水存在的大量Cl−可以直接穿透泥状腐蚀产物形成的保护膜,进而接触到金属基体,使得腐蚀产物的保护效果大大降低。同时,点蚀坑周围Cl−的聚集会降低金属原子间的亲和力[19],从而降低金属的表面能,加速裂纹的扩展。总而言之,对于22MnCrNiMo钢而言,疲劳腐蚀条件下的失效原因可归结为外加载荷和腐蚀环境的共同作用。
3. 结论
1)整个腐蚀过程中,22MnCrNiMo钢的腐蚀速率在0.035~0.045 g/(m2·h)。腐蚀开始时,腐蚀机理为点蚀的局部腐蚀,随着腐蚀的加剧,腐蚀产物覆盖材料表面,腐蚀机理转变为点蚀的均匀腐蚀。腐蚀90 d时,试样表面已完全被花状腐蚀产物覆盖,此时点蚀程度最大。
2)22MnCrNiMo钢的腐蚀疲劳幂函数曲线表达式为:S=14 000.12×N −0.266 4,其条件疲劳极限约为190 MPa。
3)点蚀和外加载荷产生的应力集中造成了裂纹的萌生;电化学效应、交变应力以及侵蚀性离子的共同作用,加速了裂纹的扩展,最终造成22MnCrNiMo钢的失效。
-
表 1 22MnCrNiMo钢的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of the steel 22MnCrNiMo
% C Si Mn P S Cr Ni 0.24~0.30 0.15~0.30 1.20~1.60 ≤0.025 ≤0.025 0.80~1.30 0.70~1.30 Cu Al Mo Nb [O] [N] [H] ≤0.20 0.020~0.050 0.40~0.80 0.02~0.06 ≤25 ×10−4 ≤90 ×10−4 ≤2 ×10−4 表 2 人工海水成分配比
Table 2. Chemical compositions of artificial seawater
名称 化学式 分子量 用量/( g·L−1) 无水硫酸钠 Na2SO4 142.04 4.00 氯化钠 NaCl 58.44 25.00 氯化镁 MgCl2·6H2O 203.30 11.00 氯化钙 CaCl2 111.00 1.20 -
[1] Zarandi E P, Skallerud B H. Cyclic behavior and strain energy-based fatigue damage analysis of mooring chains high strength steel[J]. Marine Structures, 2020,70:102703. doi: 10.1016/j.marstruc.2019.102703 [2] Dong Fang, Yan Ruijun, Yang Zongjia, et al. Effect of rare earth Ce on corrosion resistance properties of steel 22MnCrNiMo[J]. China Metallurgy, 2019,29(1):30−37. (董方, 闫瑞军, 杨宗佳, 等. 稀土铈对22MnCrNiMo钢耐腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 中国冶金, 2019,29(1):30−37. [3] Shen Yan, Liu Guixiang, Wang Hongxing. Preparation of composite coatings on 22MnCrNiMo steel for mooring rope[J]. Surface Technology, 2017,46(10):50−59. (沈雁, 刘桂香, 王红星. 系泊缆用22MnCrNiMo钢表面纳米复合镀层的制备[J]. 表面技术, 2017,46(10):50−59. [4] Fang Guangjin. Determination and analysis of CCT curves of R4(22MnCrNiMo) steel for mooring chain[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2020,45(3):208−211. (方光锦. 系泊链用R4(22MnCrNiMo)钢CCT曲线测定及分析[J]. 金属热处理, 2020,45(3):208−211. [5] An Liqiao, Liu Yubao, Liu Deyi, et al. Effect of practical decarburized depth on fatigue property of 60Si2CrVAT spring steel[J]. Journal of Dalian Jiaotong University, 2009,30(3):52−55. (安丽乔, 刘玉宝, 刘德义, 等. 脱碳深度对60Si2CrVAT弹簧钢疲劳性能的影响[J]. 大连交通大学学报, 2009,30(3):52−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9590.2009.03.013 [6] Yan Ruijun, Dong Fang, Ma Zheng, et al. Effect of rare earth Ce on structure and mechanical properties of steel 22MnCrNiMo[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, 2017,36(04):333−337. (闫瑞军, 董方, 马征,等. 稀土Ce对22MnCrNiMo钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 内蒙古科技大学学报, 2017,36(04):333−337. [7] Buzzatti D T, Chludzinki M, dos Santos R E, et al. Toughness properties of a friction hydro pillar processed offshore mooring chain steel[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019,8(3):2625−2637. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.04.002 [8] Zhang X, Hoogeland M. Influence of deformation on corrosion of mooring chain steel in seawater[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2019,70(6):962−972. doi: 10.1002/maco.201810766 [9] (冯国庆. 船舶结构疲劳强度评估方法研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2006.)Feng Guoqing. Research on fatigue strength assessment method of ship struetures[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2006. [10] Nakano T, Sakakibara T, Wakita M, et al. Development of high-strength suspension coil springs with improved corrosion fatigue strength[J]. Transactions of Japan Society for Spring Research, 2001,(46):7−12. [11] Kurihara Y, Takasaki S, Kobayashi M, et al. Corrosion fatigue behavior of automobile suspension spring steels[J]. Mitsubishi Steel Manuf. Tech. Rev., 1993,27(1):9−15. [12] Masataka Shimotsusa, Nobuhiko Ibarakl, Tatsuo Ikeda and Takenori Nakayma. Wire rod for suspension spring with excellent corrosion fatigue life[J]. Wire Journal International, 1998:78−83. [13] Gan Yang, Li Ying, Lin Haichao. Experimental studies on the pitting corrosion of low alloy steels in 3.5% NaCl[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2001,21(2):82−87. (甘阳, 李瑛, 林海潮. 海水中低合金钢局部腐蚀过程的试验室模拟[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2001,21(2):82−87. [14] (吴荫顺. 金属腐蚀研究方法[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1993: 24−28, 68−73.)Wu Yinshun. Metal corrosion research methods[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1993: 24−28, 68−73. [15] Shao Yunliang, Li Jian. Zhang Weixin, et al. Study on mooring chain fatigue performance in seawater[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2019,37(5):127−132. (邵云亮, 李剑, 张卫新, 等. 系泊链海水疲劳性能初步研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2019,37(5):127−132. [16] (王荣. 金属材料的腐蚀疲劳[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2001.)Wang Rong. Corrosion fatigue of metal materials[M]. Xi, an: Northwestern Polytechnical University Press,2001. [17] (曾春华, 邹十践编译. 疲劳分析方法及应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1991.)Zeng Chunhua, Zou Shijian Compile. Fatigue analysis methods and applications[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press. 1991. [18] (王放. 金属基复合材料循环响应和疲劳破坏的理论和模拟[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2007.)Wang Fang. Modelling and simulation of cyclic response and fatigue failure of fiber reinforced ductile composite[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2007. [19] (Suresh S, 王中光. 材料的疲劳[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1993.)Suresh S, Wang Zhongguang. Material fatigue[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1993. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 毛威昂,崔政,王瑞,刘广磊,王刘艳. 转炉生产矿用链23MnNiMoCr54钢的工艺实践及研究. 特钢技术. 2024(02): 17-21 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:













 下载:
下载:








 百度学术
百度学术











