Effect of self-induced magnetic field on liquid flow and segregation during VAR process for titanium alloys
-
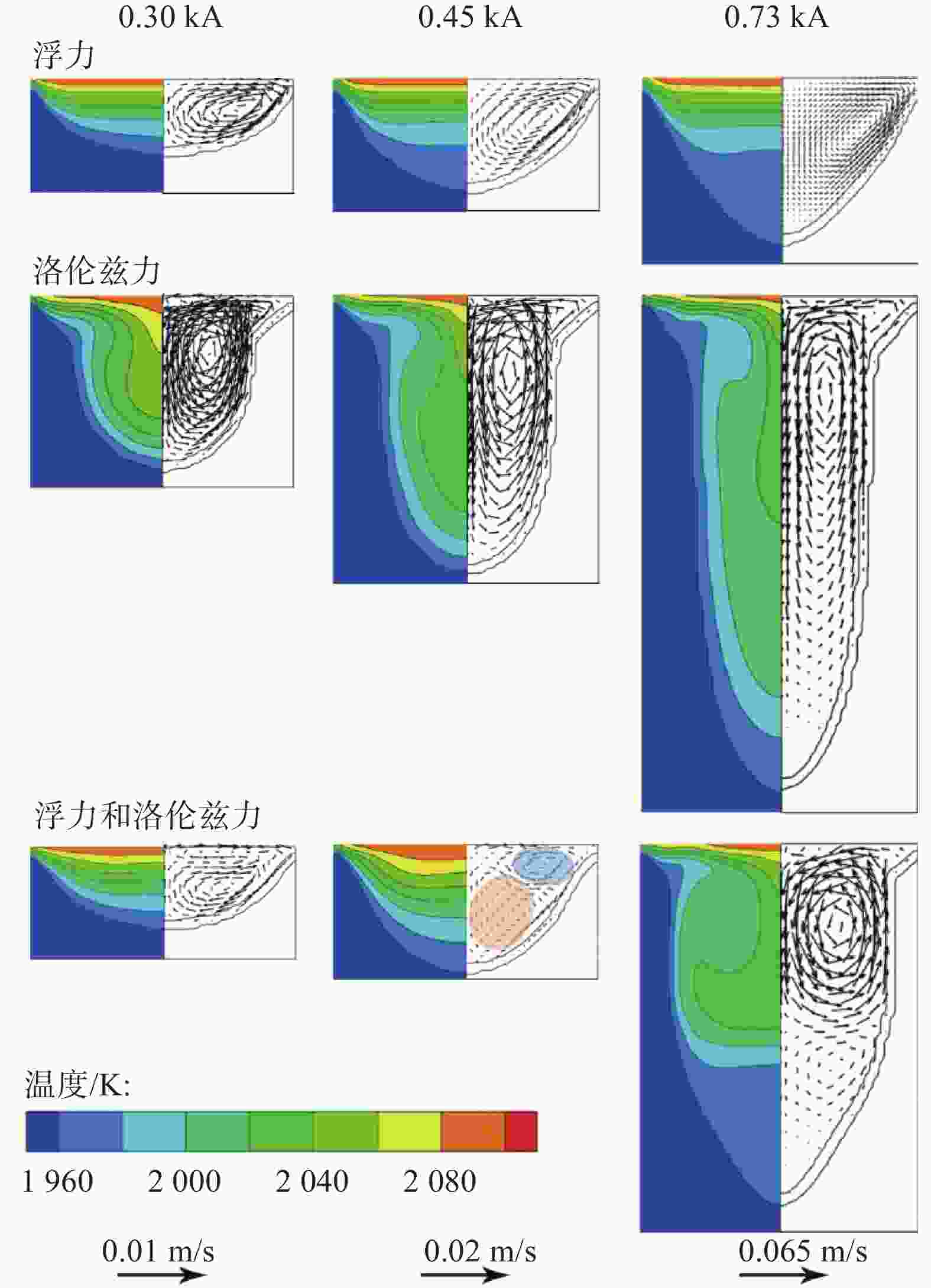
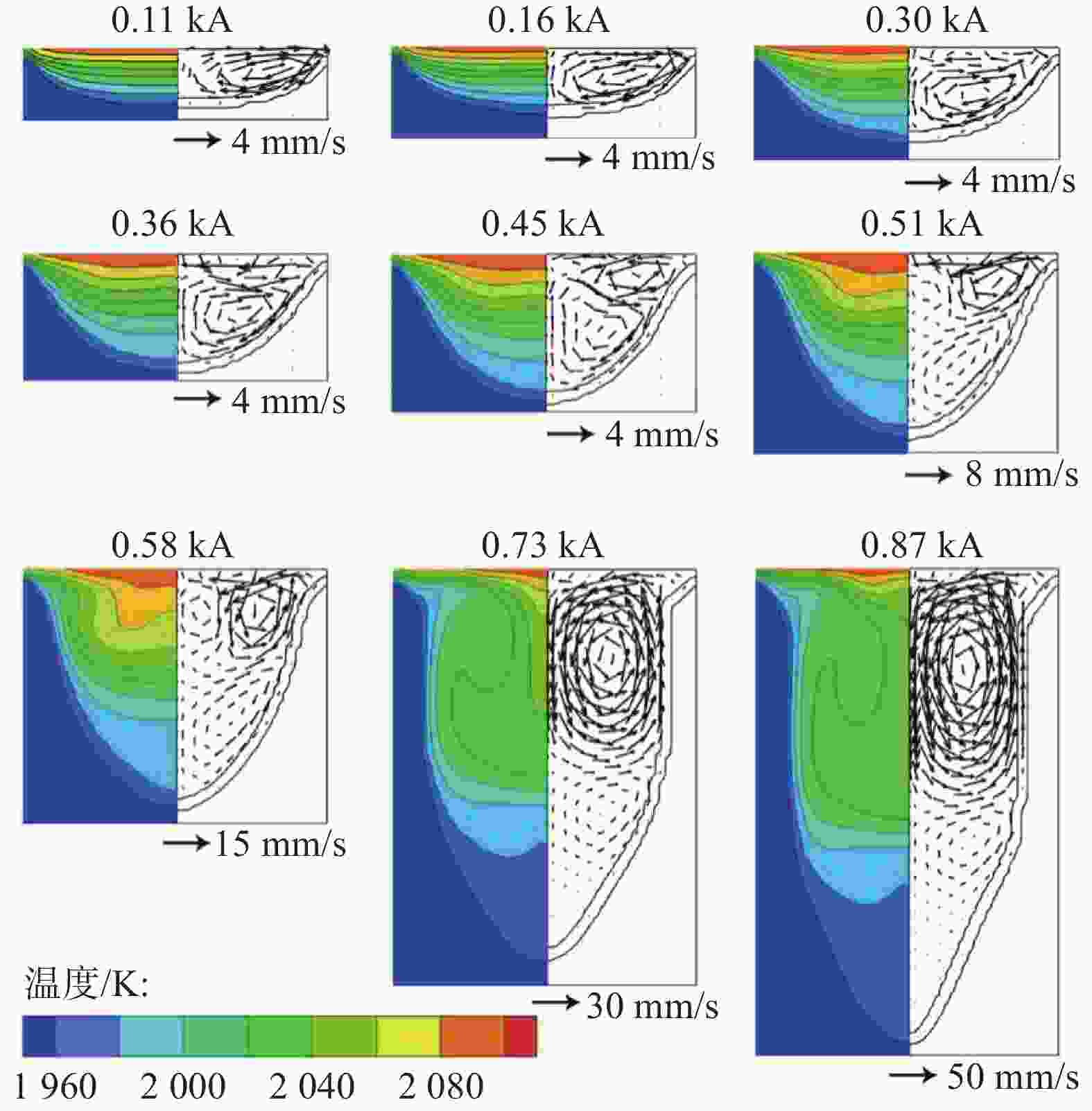
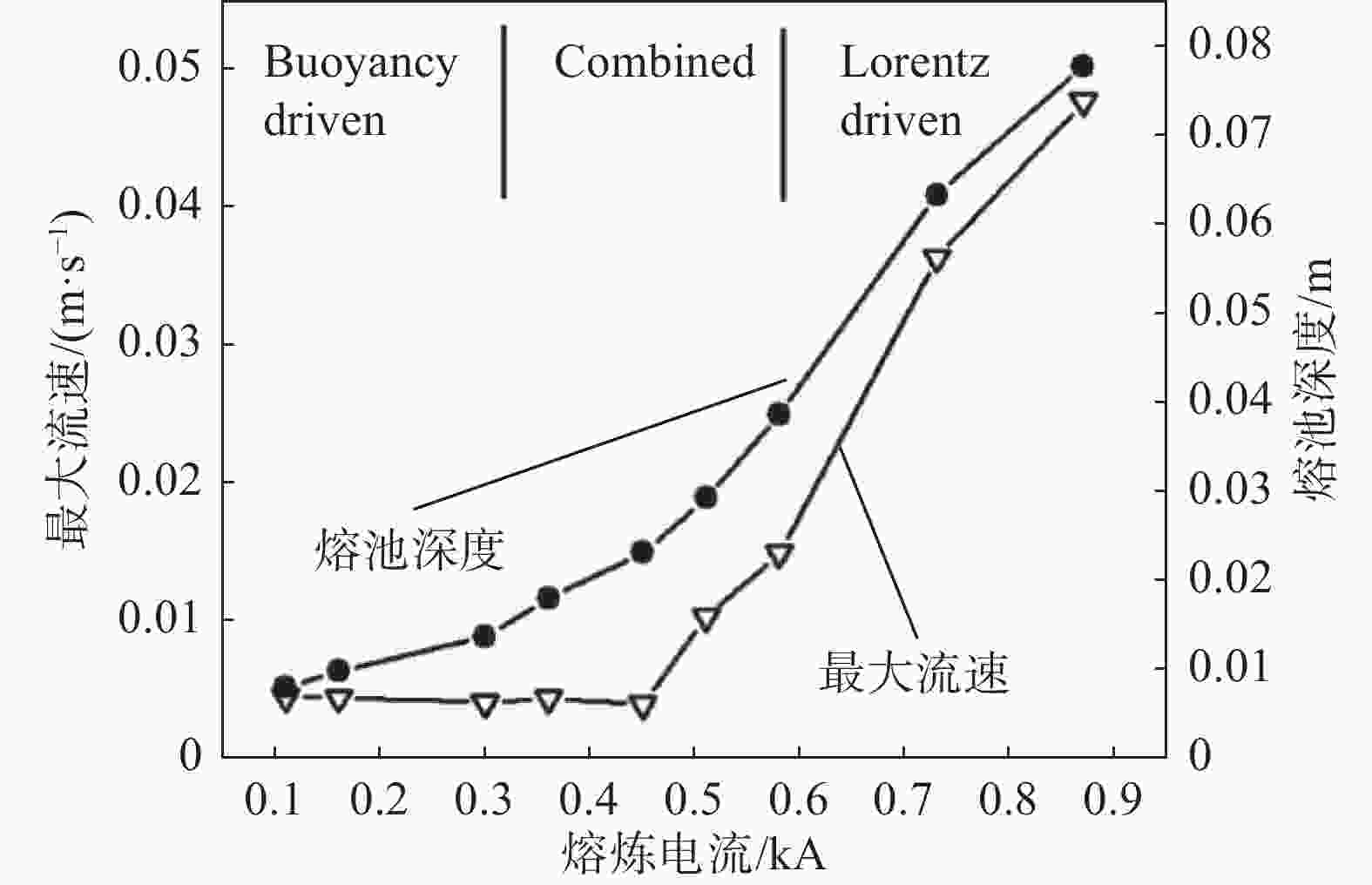
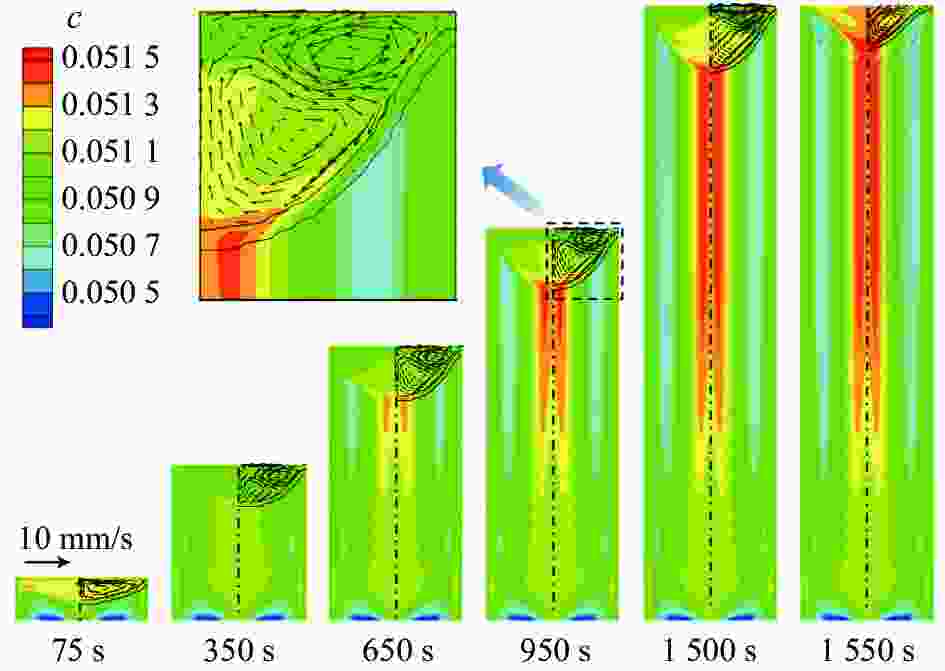
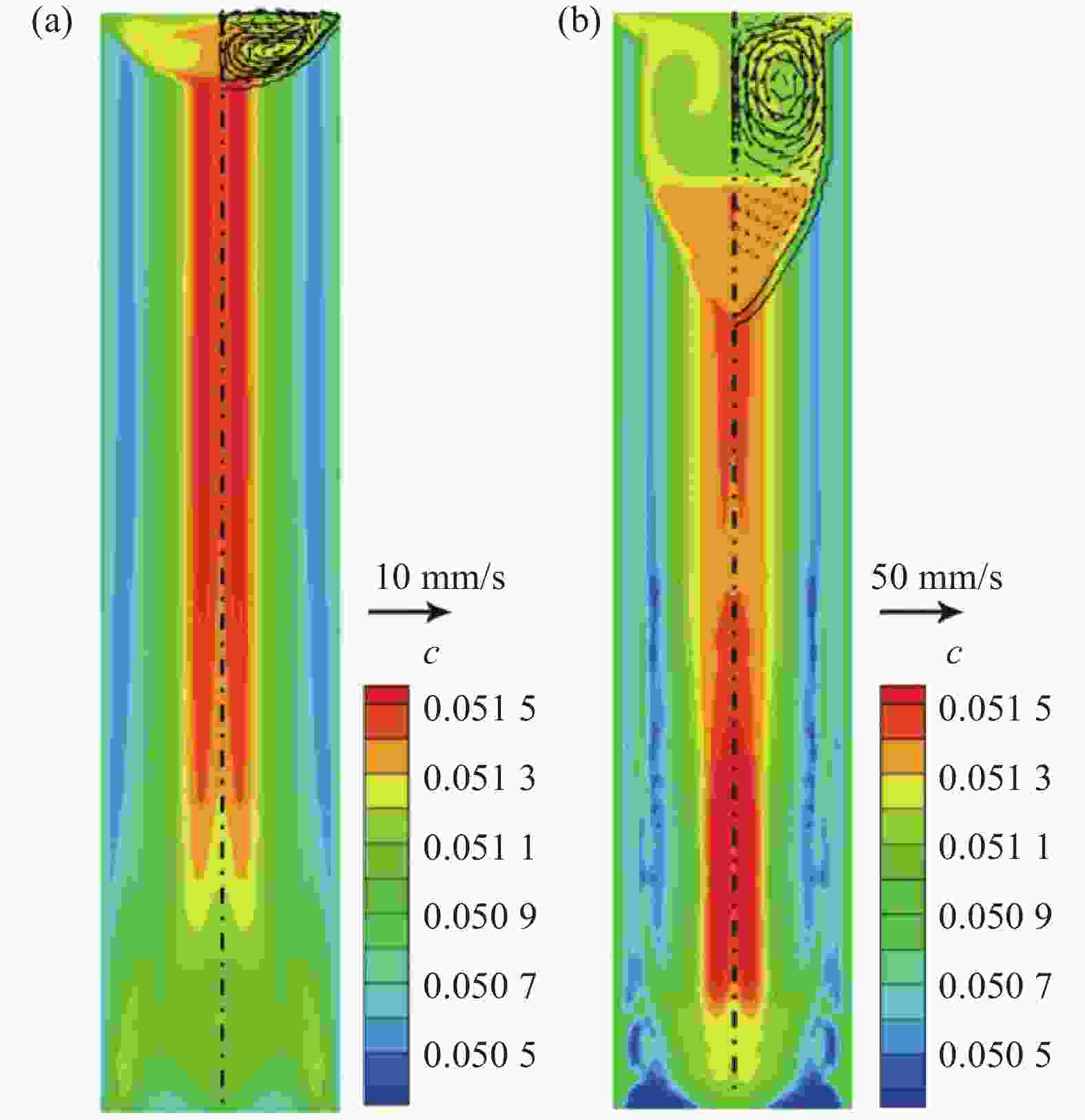
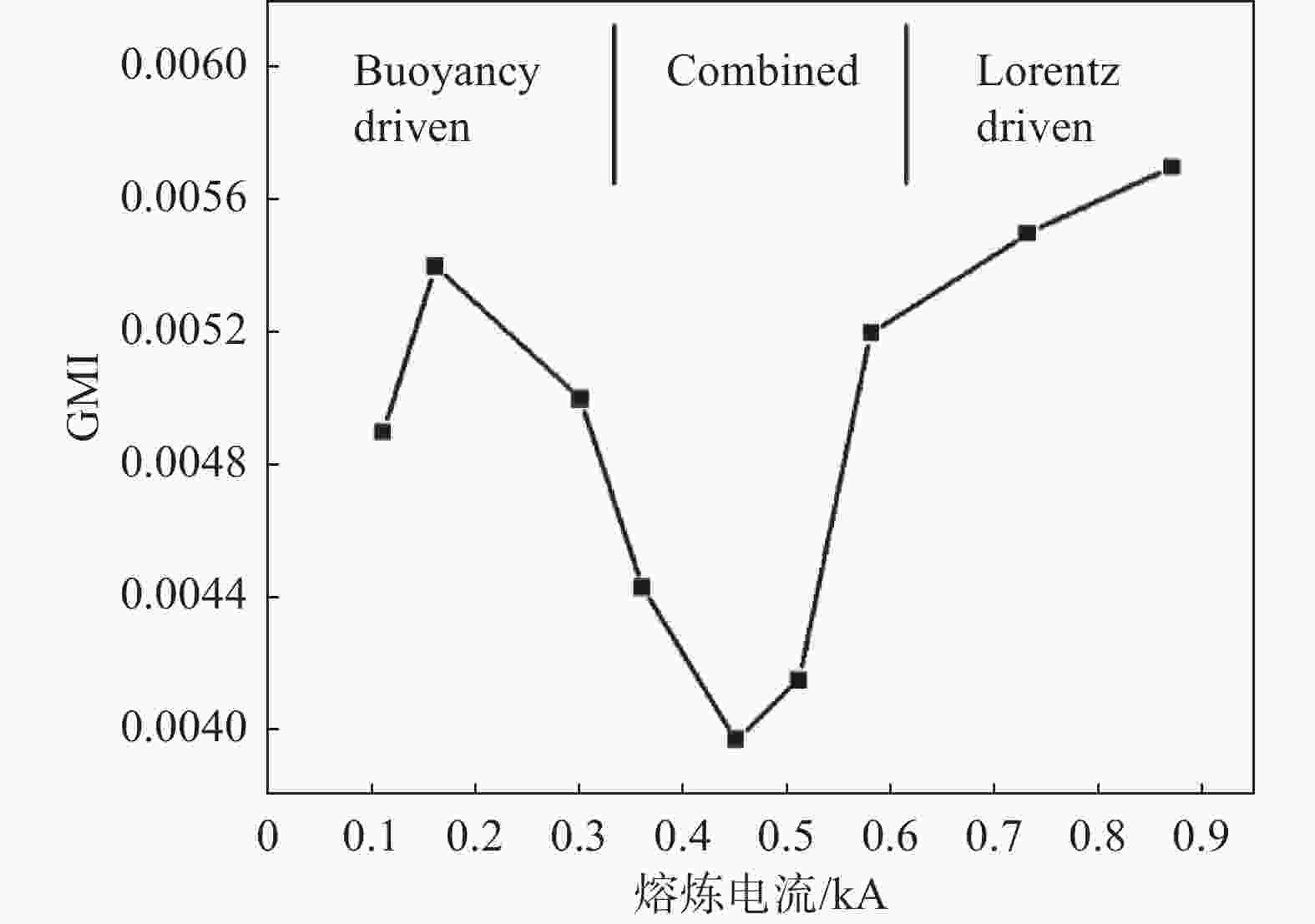
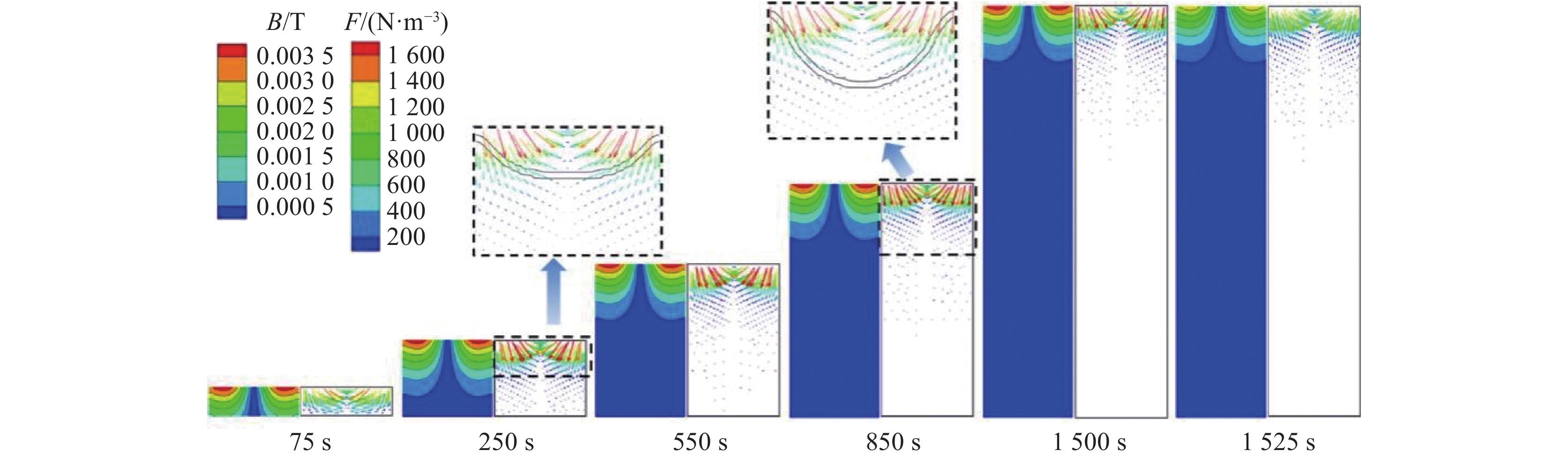
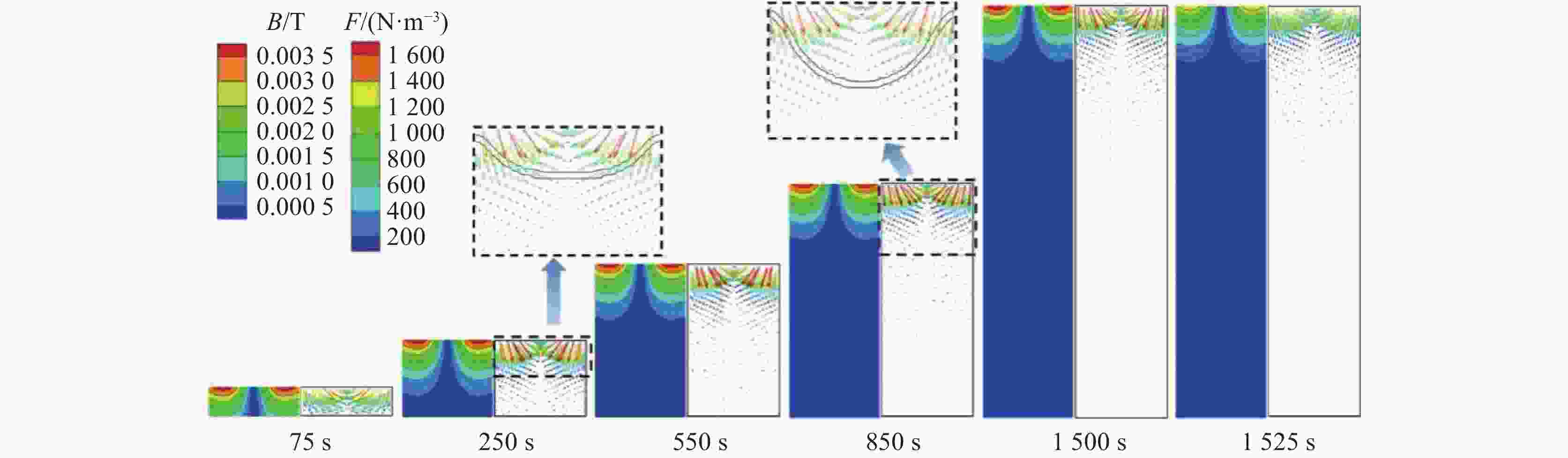
摘要: 采用合金凝固的连续介质模型,模拟了钛合金真空自耗电弧熔炼过程中温度场、溶质场、流场、自感电磁场的演化行为。通过对比浮力单独作用、自感电磁力单独作用以及二者共同作用下的熔池流动及成分偏析结果,揭示了熔炼过程中熔体流动和溶质偏析的形成机理。结果表明,0.3 kA小电流熔炼时,熔池内熔体流动由浮力主导,形成侧壁向下、中心向上的对流;0.73 kA大电流熔炼时,熔池内呈现由电磁力主导的反向对流,熔池最大流速为0.036 m/s;0.45 kA中等电流熔炼时,浮力和电磁力对熔体流动的作用均比较明显,熔池内形成两个流动方向相反的区域,且由于两者相互竞争制约,导致熔池中最大流速达到极低值0.004 m/s。铸锭整体宏观成分偏析随着熔炼电流的增加呈现先上升后下降再上升的变化规律,三阶段宏观偏析的极值分别为0.54%、0.39%与0.57%。当电磁力和浮力作用基本相当时,宏观偏析程度最轻。Abstract: A continuum model for alloy solidification was used to simulate the temperature evolution, solute distribution, liquid flow, and self-induced magnetic field during VAR process for titanium alloys. The work reveals the influence of self-induced magnetic force and/or buoyancy force on the melt flow and solute segregation by contrastively exerting the forces. When a small melting current of 0.3 kA is used, the melt flow is dominantly driven by the buoyancy force that the melt flows downward at the side of the melt pool and upward in the center of the melt pool. When a large melting current of 0.73 kA is used, the melt flow is dominantly driven by the self-induced magnetic force and the melt flows adversely, and the maximum velocity reaches 0.036 m/s. When a medium current of 0.45 kA is applied, both the two forces act evidently, forming two regions in the pool where the melt flow directions are opposite, and the maximum flow rate in the pool can reach a minimum value of 0.004 m/s due to their competition. With increasing the current, the total segregation of the ingot rises at begin, has a reduction stage after a peak, but then increase continuously again. The extreme values of the three stages are 0.54%, 0.39% and 0.57%, correspondingly. The minimum segregation can be obtained when the self-induced magnetic force and buoyancy force act equally.
-
Key words:
- titanium alloy /
- vacuum arc remelting /
- continuum model /
- self-induced magnetic field /
- liquid flow /
- macrosegregation
-
表 1 计算模型采用的物性参数[13]
Table 1. Physical parameters of the computational model
密度 / (kg·m−3) 扩散系数 / (m2·s−1) 熔化潜热 / (J·kg−1) V分配
系数液相线斜率 / (K·%−1) 热膨胀系
数 / %−1比热容 / (J·kg−1·K−1) 热导率 / (W·m−1·K−1) 流体粘度/ (kg·m−1·s−1) 电导率 / (S·m−1) 磁导率 / (H·m−1) 4170 4.0×10−9 3.77×105 0.95 −2.0 −0.35 975 32.7 3.1×10−3 1.0×106 1.26×10−6 -
[1] Li Xiong, Pang Kechang, Guo Hua, et al. Melting technology of wrought Ti and Ti alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010,20(S1):906−913. (李雄, 庞克昌, 郭华, 等. 变形钛及钛合金熔炼技术[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010,20(S1):906−913. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2010.s1.195Li Xiong, Pang Kechang, Guo Hua, et al. Melting technology of wrought Ti and Ti alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(S1): 906-913. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2010.s1.195 [2] Hayakawa H, Fukada N, Udagawa T, et al. Solidification structure and segregation in cast ingots of titanium alloy produced by vacuum arc consumable electrode method[J]. ISIJ International, 1991,31(8):775−784. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.31.775 [3] Mitchell A, Kawakami A, Cockcroft S L. Beta fleck and segregation in titanium alloy ingots[J]. High Temperature Materials Processes (London), 2006, 25(5-6): 337-349. [4] Liu Yingying, Chen Ziyong, Jin Tounan, et al. Present situation and prospect of 600 ℃ high-temperature titanium alloys[J]. Materials Reports, 2018,32(11):1863−1869,1883. (刘莹莹, 陈子勇, 金头男, 等. 600 ℃高温钛合金发展现状与展望[J]. 材料导报, 2018,32(11):1863−1869,1883. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.11.013Liu Yingying, Chen Ziyong, Jin Tounan, et al. Present situation and prospect of 600 ℃ high-temperature titanium alloys[J]. Materials Reports, 2018, 32(11): 1863-1869+1883. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.11.013 [5] Dobatkin V I, Anoshkin N F. Comparison of macrosegregation in titanium and aluminium alloy ingots[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999,263(2):224−229. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01152-6 [6] Zhao Yongqing, Liu Junlin, Zhou Lian. Analysis on the segregation of typical β alloying elements of Cu, Fe and Cr in Ti alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005,34(4):531−538. (赵永庆, 刘军林, 周廉. 典型β型钛合金元素Cu, Fe和Cr的偏析规律[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005,34(4):531−538.Zhao Yongqing, Liu Junlin, Zhou Lian. Analysis on the segregation of typical β alloying elements of Cu, Fe and Cr in Ti alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(4): 531-538. [7] Liu Junling, Zhao Yongqing, Zhou Lian. Segregation of Ti-2.5Cu, Ti-3Fe and Ti-3Cr alloy ingots[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004,33(7):731−735. (刘军林, 赵永庆, 周廉. Ti-2.5Cu, Ti-3Fe, Ti-3Cr合金铸锭的偏析[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004,33(7):731−735. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.07.014Liu Junling, Zhao Yongqing, Zhou Lian. Segregation of Ti-2.5 Cu, Ti-3 Fe and Ti-3 Cr alloy ingots[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004, 33(7): 731-735. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.07.014 [8] Davidson P A, He X, Lowe A J. Flow transitions in vacuum arc remelting[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2000,16(6):699−711. doi: 10.1179/026708300101508306 [9] Kondrashov E N, Musatov M I, Maksimov A Yu, et al. Calculation of the molten pool depth in vacuum arc remelting of alloy VT3-1[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2007,16(1):19−25. doi: 10.1134/S1810232807010031 [10] Xiao Cong. Simulation and industrial validation of molten pool morphology and solidification structure of pure titanium during VAR process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(2):44−49,83. (肖聪. 纯钛VAR熔池形貌和凝固组织模拟及其工业验证[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(2):44−49,83.Xiao Cong. Simulation and industrial validation of molten pool morphology and solidification structure of pure titanium during VAR process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016, 37(2): 44-49+83. [11] Fan Kai, Wu Lincai, Li Junjie, et al. Numerical simulation of macrosegregation caused by buoyancy driven flow during VAR process for titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020,49(3):871−877. (樊凯, 吴林财, 李俊杰, 等. 钛合金VAR过程中自然对流下的宏观偏析行为模拟[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2020,49(3):871−877.Fan Kai, Wu Lincai, Li Junjie, et al. Numerical simulation of macrosegregation caused by buoyancy driven flow during VAR process for titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020, 49(3): 871-877. [12] Kou H, Zhang Y, Yang Z, et al. Liquid metal flow behavior during vacuum consumable arc remelting process for titanium[J]. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 2014,12(1):50. [13] 吴京洋. 钛合金VAR过程中熔体流动及宏观偏析行为的数值模拟[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2021.Wu Jingyang. Numerical simulation of liquid flow and macrosegregation behavior during VAR process for titanium alloys[D]. Xi, an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2021 . [14] Yao Jingshen, Cao Jianhua. Iron segregation in Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al alloy ingot[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 1992,16(4):267−270. (姚锦声, 曹建华. Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al合金锭中的铁偏析[J]. 稀有金属, 1992,16(4):267−270.Yao Jingshen, Cao Jianhua. Iron segregation in Ti-10 V-2 Fe-3 Al alloy ingot[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 1992, 16(4): 267-270. [15] Xue Xiangyi, Meng Xiangwei, Fu Baoquan, et al. Influence of arc current on solidification microstructure of Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al under vacuum arc melting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009,19(10):1772−1776. (薛祥义, 孟祥炜, 付宝全, 等. 真空自耗电弧熔炼电流对Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al铸锭凝固组织的影响[J]. 中国有色 金属学报, 2009,19(10):1772−1776.Xue Xiangyi, Meng Xiangwei, Fu Baoquan, et al. Influence of arc current on solidification microstructure of Ti-10 V-2 Fe-3 Al under vacuum arc melting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(10): 1772-1776. -




 下载:
下载: