Recovery and regeneration of waste electrolyte from all-vanadium redox flow battery
-
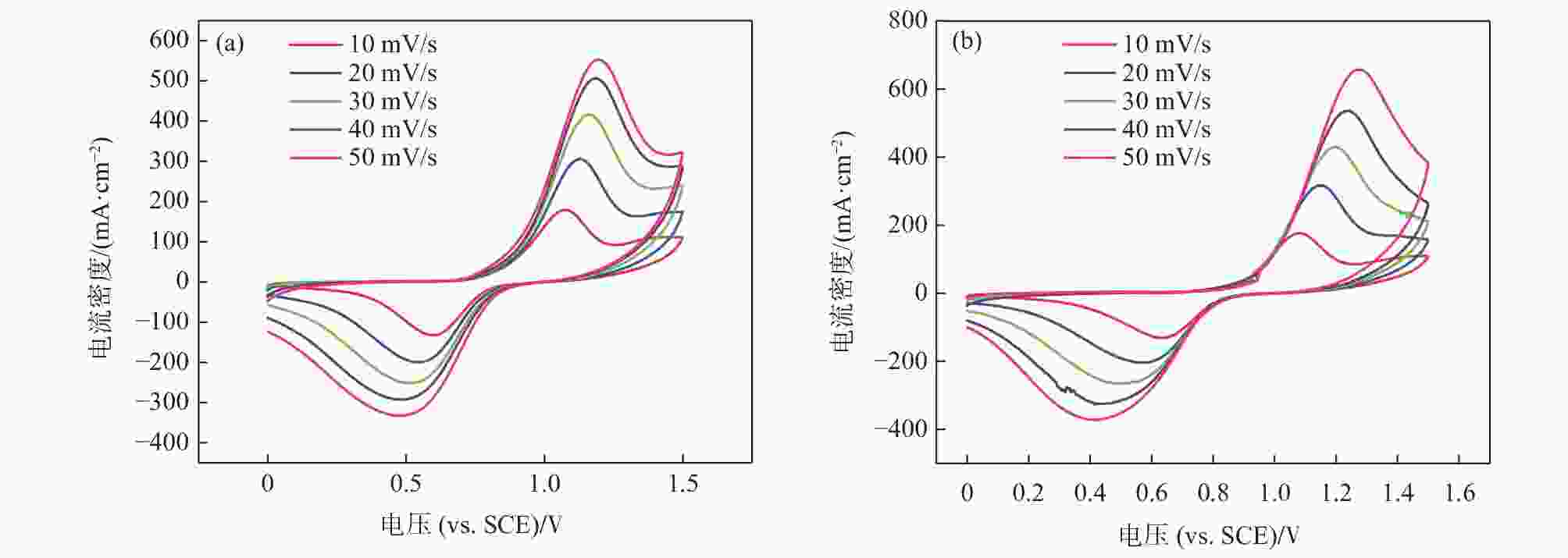
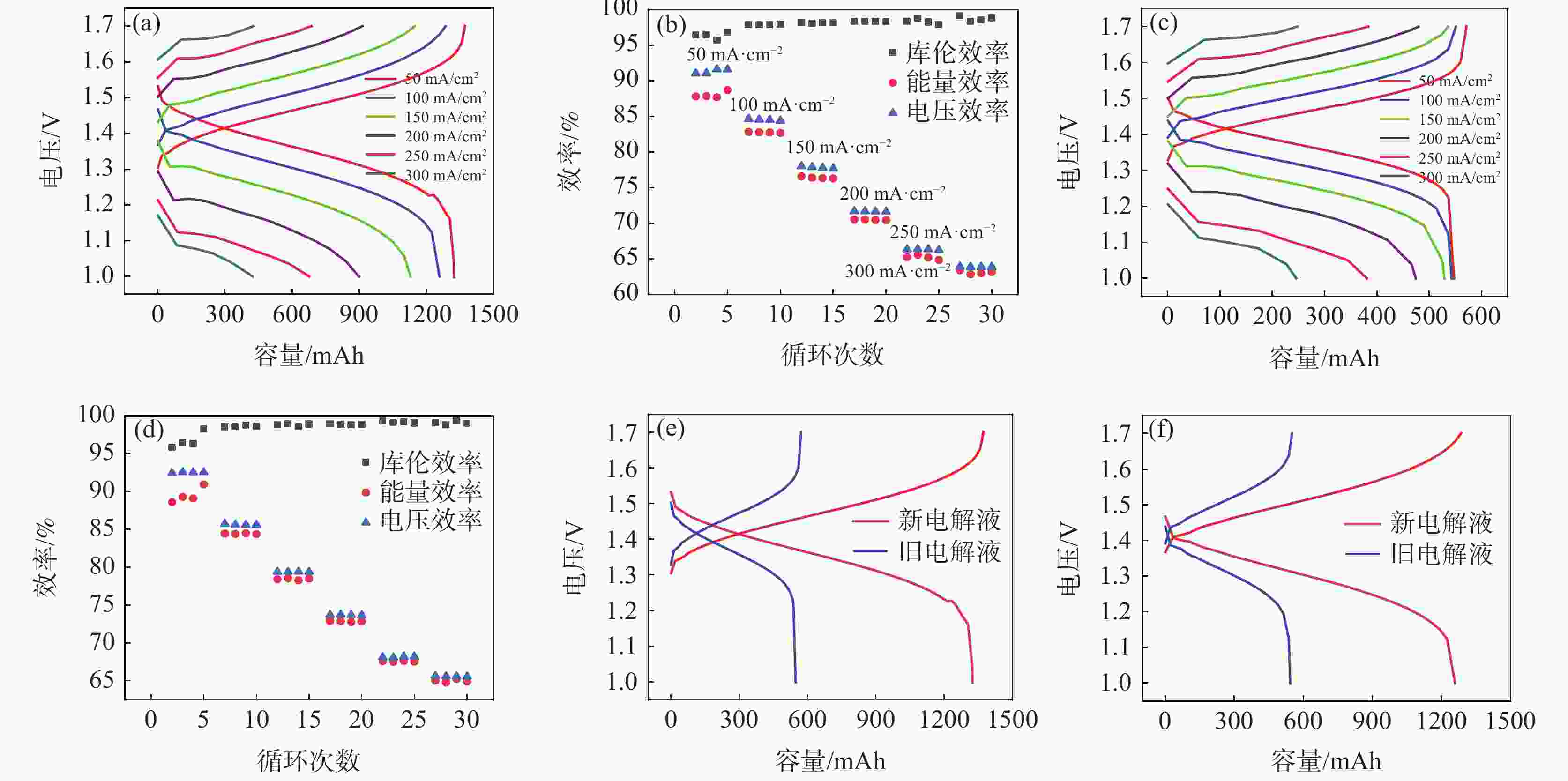
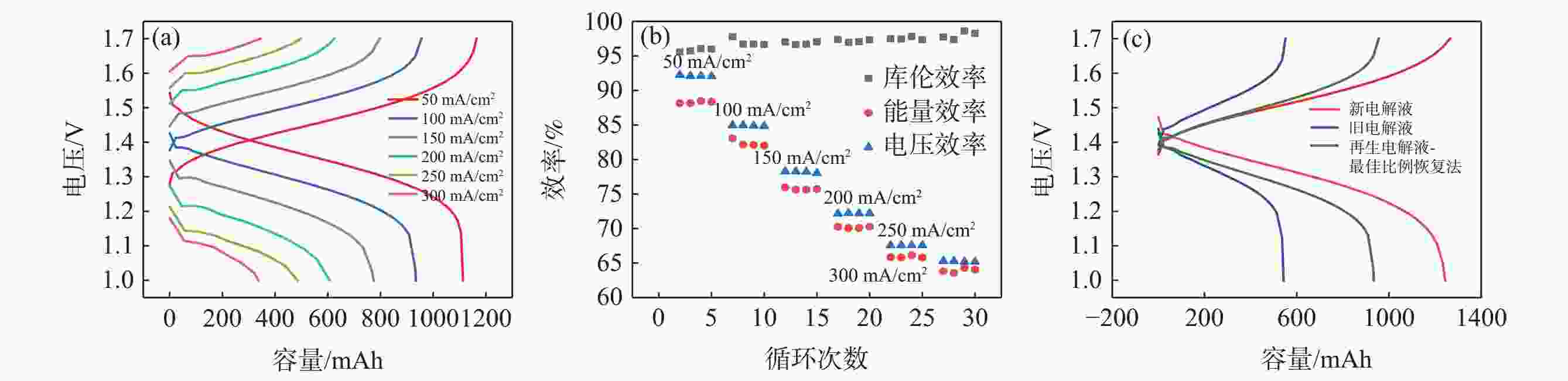
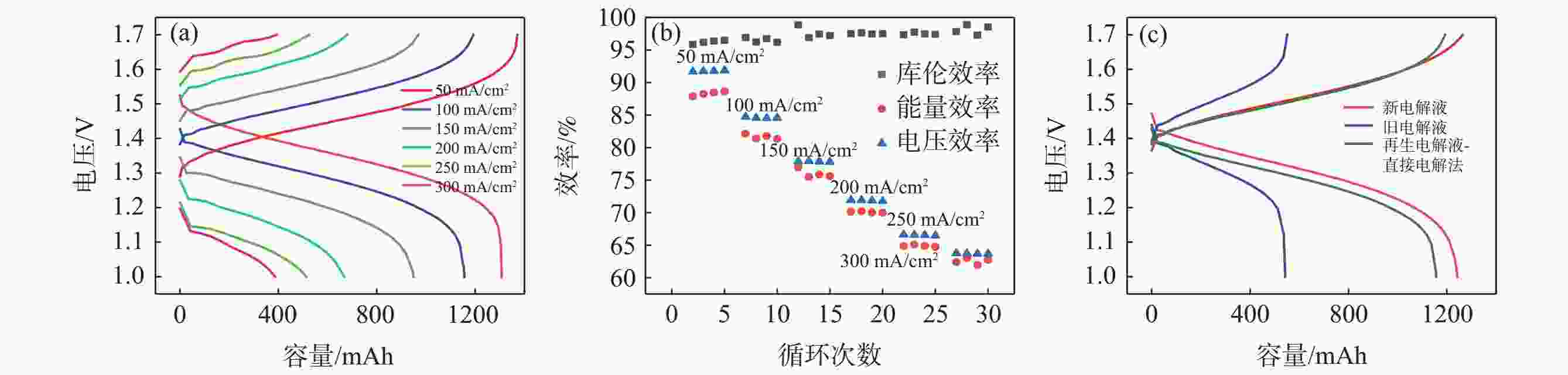
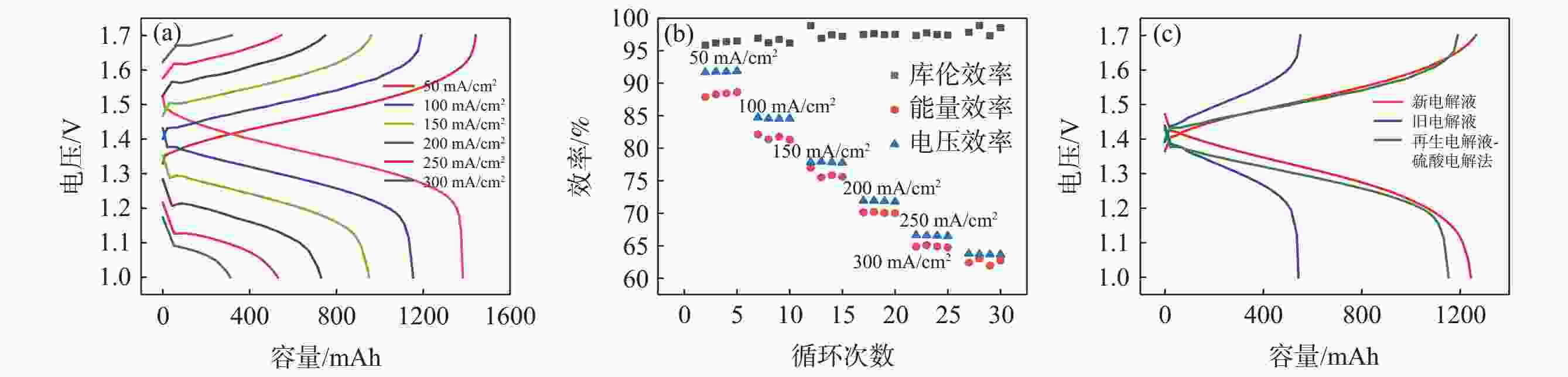
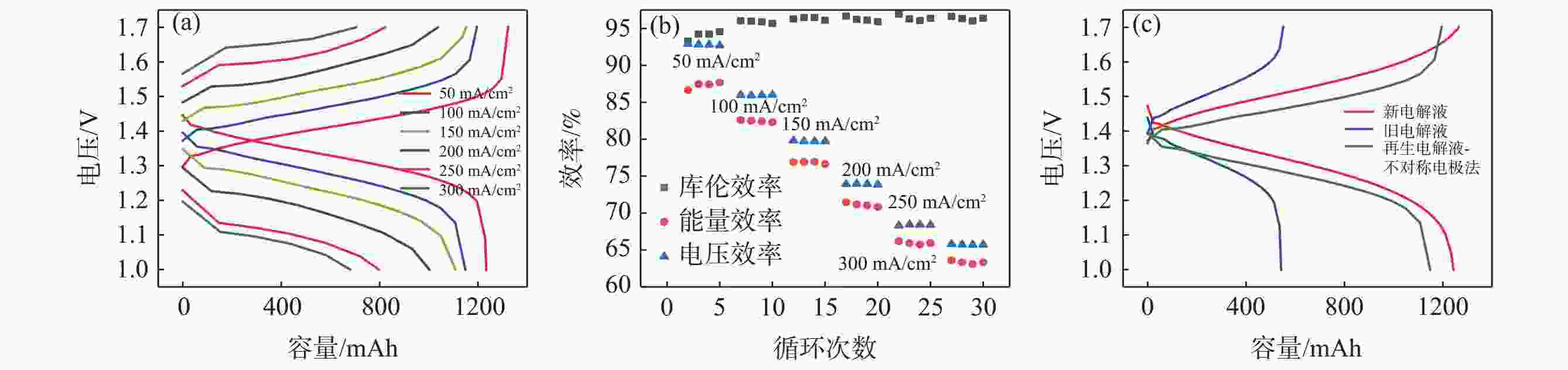
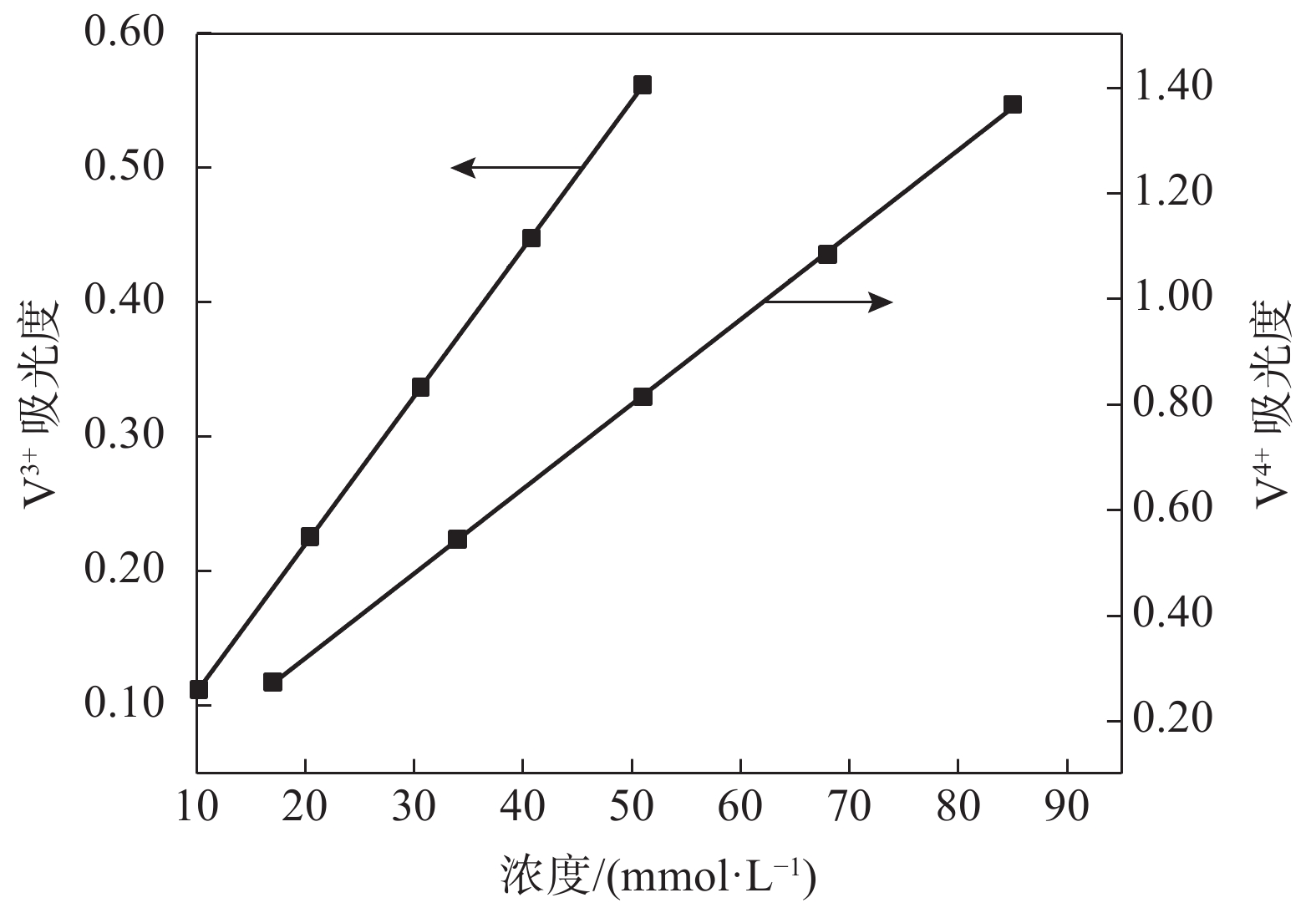
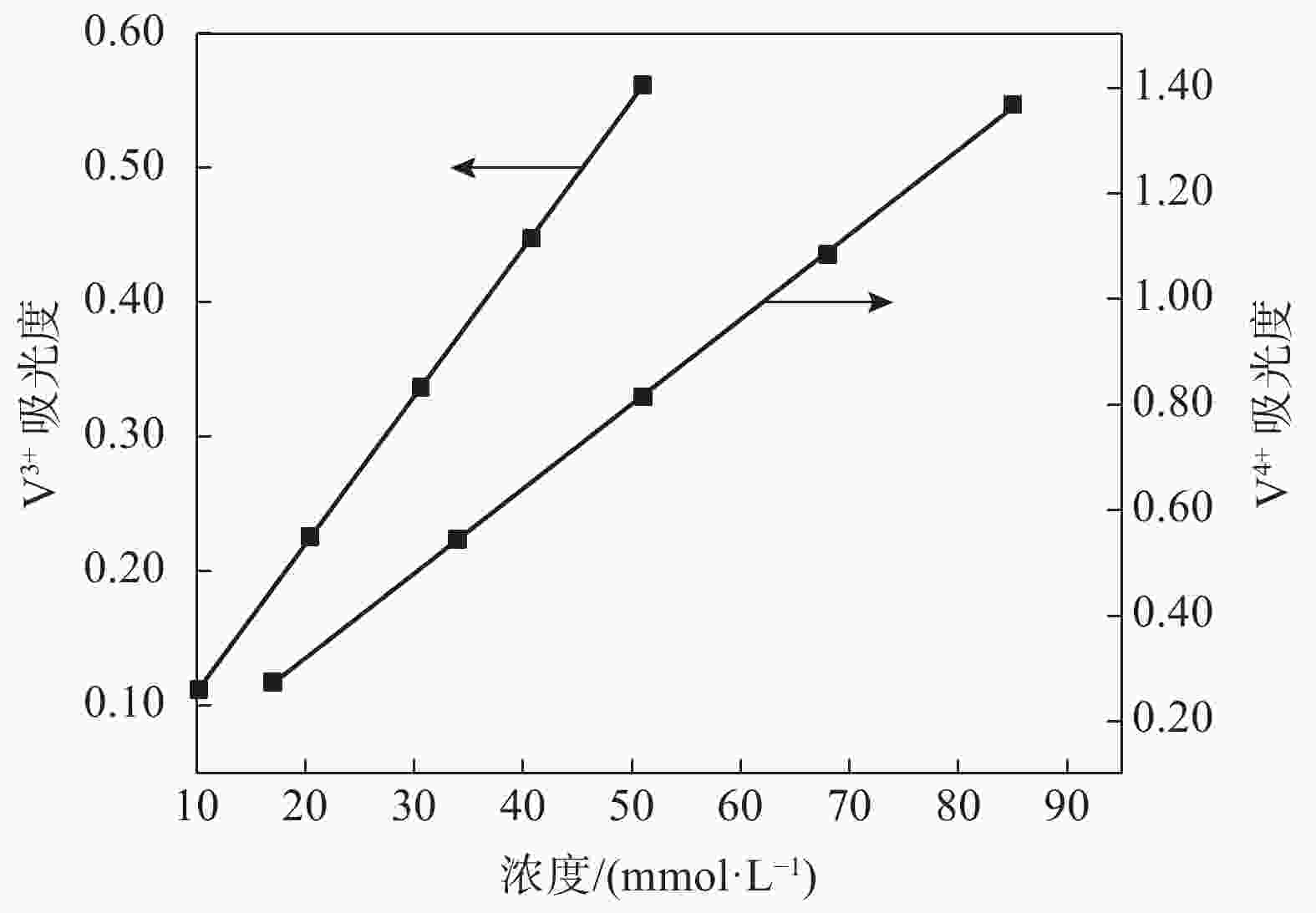
摘要: 全钒氧化还原液流电池是一种电化学储能装置,由于将能量存储于电解液中,功率和容量相互独立,在大规模储能领域具有突出优势,但电池废旧电解液的回收处理是一个难题。电化学测试和电解液成分分析表明:废旧电解液的活性并未明显下降,恢复的着眼点应是电解液价态的综合调节。提出四种电解液恢复方法,最佳比例恢复法、直接电解法、硫酸电解法和不对称电极法分别将电解液容量恢复至初始状态的75%、92%、93%、92%,并且电池库伦效率保持在95%~98%,表现出良好的充放电性能。该研究有利于促进钒资源的综合利用,并对全钒液流电池的应用和运行维护具有重要指导意义。Abstract: Vanadium flow battery is an electrochemical energy storage device. As energy is stored in the electrolyte, power and capacity are independent of each other, which has outstanding advantages in the field of large-scale energy storage. However, the recovery and treatment of the used electrolyte of the battery is a challenge. Electrochemical tests and electrolyte composition analysis showed that the activity of the waste electrolyte did not decrease significantly, and the focus of recovery should be the comprehensive adjustment of the electrolyte valence state. This paper proposes four electrolyte recovery methods, the optimal proportion recovery method, direct electrolysis method, sulfuric acid electrolysis method and asymmetric electrode method, which can restore the electrolyte capacity to 75%, 92%, 93%, 92% of the initial state, respectively, and the coulombic efficiency of the battery is maintained at 95%~98%, showing good charge and discharge performance. This study is conducive to promoting the comprehensive utilization of vanadium resources and has important guiding significance for the application and operation maintenance of vanadium flow batteries.
-
表 1 充电程序
Table 1. Charging program
步骤 工步名称 电流密度/(mA·cm−2) 截止电压/V 步骤1 搁置 步骤2 恒流充电 200 1.7 恒流充电 100 1.7 恒流充电 50 1.7 恒流充电 25 1.7 恒流充电 7.15 1.7 恒流充电 3.57 1.7 步骤3 停止 表 2 四种恢复方法各自优缺点
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of four recovery methods
恢复方法 优点 缺点 最佳比例恢复法 方法简便,无需分析旧电解液原始价态构成 容量恢复率较低 直接电解法 恢复效果好 恢复负极电解液的同时,正极电解液价态升高,
无法将全部电解液进行恢复硫酸电解法 恢复效果好,且由于正极采用电解液,可将全部电解液进行恢复 恢复过程正极大量析氧,容易腐蚀集流体 不对称电极法 恢复效果好,可将全部电解液进行恢复,不腐蚀集流体和其他电池材料 效率不高;恢复时间长 -
[1] Lv Y, Han C, Zhu Y, et al. Recent advances in metals and metal oxides as catalysts for vanadium redox flow battery: Properties, structures, and perspectives[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021,75:96−109. [2] Sanchez-Diez E, Ventosa E, Guarnieri M, et al. Redox flow batteries: Status and perspective towards sustainable stationary energy storage[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021,481:228804. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228804 [3] Lourenssen K, Williams J, Ahmadpour F, et al. Vanadium redox flow batteries: A comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2019,25:100844. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2019.100844 [4] Liu T, Li X, Zhang H, et al. Progress on the electrode materials towards vanadium flow batteries (VFBs) with improved power density[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2018,27:1292−1303. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2018.07.003 [5] Yuan Zhizhang, Liu Zonghao, Li Xianfeng. Research progress of flow battery energy storage technology[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022,11:2944−2958. (袁治章, 刘宗浩, 李先锋. 液流电池储能技术研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022,11:2944−2958.Yuan Zhizhang, Liu Zonghao, Li Xianfeng. Research progress of flow battery energy storage technology[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11: 2944−2958. [6] Wandschneider F, Röhm S, Fischer P, et al. A multi-stack simulation of shunt currents in vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014,261:64−74. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.03.054 [7] Puleston T, Clemente A, Costa-Castello R, et al. Modelling and estimation of vanadium redox flow batteries: a review[J]. Batteries-Basel, 2023,8:121. [8] Cui Xumei, Ding Hubiao. Research progress of electrolyte for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Xihua University(Natural Science Edition), 2018,37(5):15−19. (崔旭梅, 丁虎标. 钒液流电池电解液研究综述[J]. 西华大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,37(5):15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-159X.2018.05.004Cui Xumei, Ding Hubiao. Research progress of electrolyte for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Xihua University(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 37(5): 15−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-159X.2018.05.004 [9] Xu Zhengzhen , Liang Jinglong, Li Hui, et al. Research status and prospects of vanadium recovery in vanadium containing wastes[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 3: 8−13. (徐正震, 梁精龙, 李慧, 等. 含钒废弃物中钒的回收研究现状及展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020, 3: 8−13.Xu Zhengzhen , Liang Jinglong, Li Hui, et al. Research status and prospects of vanadium recovery in vanadium containing wastes[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 3: 8−13. [10] Wang K, Liu L, Xi J, et al. Reduction of capacity decay in vanadium flow batteries by an electrolyte-reflow method[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017,338:17−25. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.11.031 [11] Zhang Y, Liu L, Xi J, et al. The benefits and limitations of electrolyte mixing in vanadium flow batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2017,204:373−381. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.07.049 [12] Yang Mingping, Wang Yuanwang. Study on the preparation technology of ammonium metavanadate with vanadium recycled from spent vanadium electrolyte solutions[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016,35(9):2982−2986. (杨明平, 王远望. 利用失效钒电解液回收钒制备偏钒酸铵工艺[J]. 化工进展, 2016,35(9):2982−2986.Yang Mingping, Wang Yuanwang. Study on the preparation technology of ammonium metavanadate with vanadium recycled from spent vanadium electrolyte solutions[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016, 35(9): 2982−2986. [13] Ding Hubiao, Cui Xumei, Chen Xiao’e. Preparation of vanadium pentoxide from vanadium battery failure electrolyte[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2017,41(2):272−273. (丁虎标, 崔旭梅, 陈孝娥. 钒电池失效电解液制备五氧化二钒[J]. 电源技术, 2017,41(2):272−273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2017.02.030Ding Hubiao, Cui Xumei, Chen Xiao’e. Preparation of vanadium pentoxide from vanadium battery failure electrolyte[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 41(2): 272−273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2017.02.030 [14] Qin Ye, Zhang Bo, Wang Lijuan, et al. Method for preparing vanadium pentoxide from waste vanadium battery electrolyte: China, CN102983379A[P]. 2013-03-20. (秦野, 张博, 王丽娟, 等. 利用失效的钒电池用电解液制取五氧化二钒的方法: 中国, CN102983379A[P]. 2013-03-20.Qin Ye, Zhang Bo, Wang Lijuan, et al. Method for preparing vanadium pentoxide from waste vanadium battery electrolyte: China, CN102983379A[P]. 2013-03-20. [15] Peng Ronghua. Technological study on vanadium recovery from waste electrolyte solutions of vanadium redox-flow battery to prepare vanadium pentoxide[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2016,36(10):64−68. (彭荣华. 从钒电池废电解液中回收钒制备五氧化二钒的工艺研究[J]. 现代化工, 2016,36(10):64−68.Peng Ronghua. Technological study on vanadium recovery from waste electrolyte solutions of vanadium redox-flow battery to prepare vanadium pentoxide[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2016, 36(10): 64−68. [16] Wang Yuanwang, Guan Qing. Method for preparing vanadium oxysulfate from waste vanadium battery electrolyte: China, CN105406098A[P]. 2018-01-05. (王远望, 官清. 利用失效钒电池电解液制备硫酸氧钒的方法: 中国, CN105406098A[P]. 2018-01-05.Wang Yuanwang, Guan Qing. Method for preparing vanadium oxysulfate from waste vanadium battery electrolyte: China, CN105406098A[P]. 2018-01-05. -




 下载:
下载: