Comparative study of dispersion performance of the zinc and aluminum salt treated rutile titanium dioxides
-
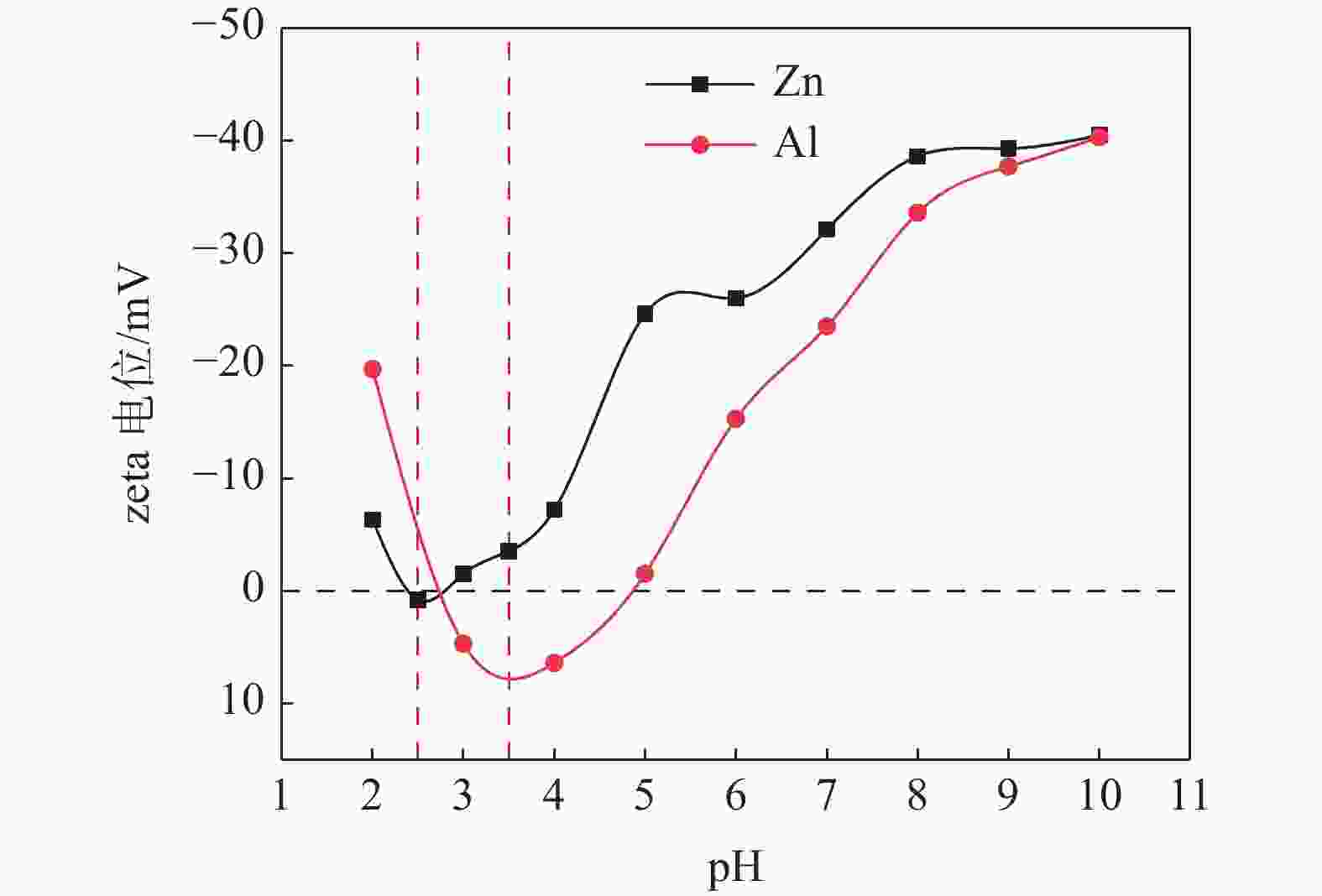
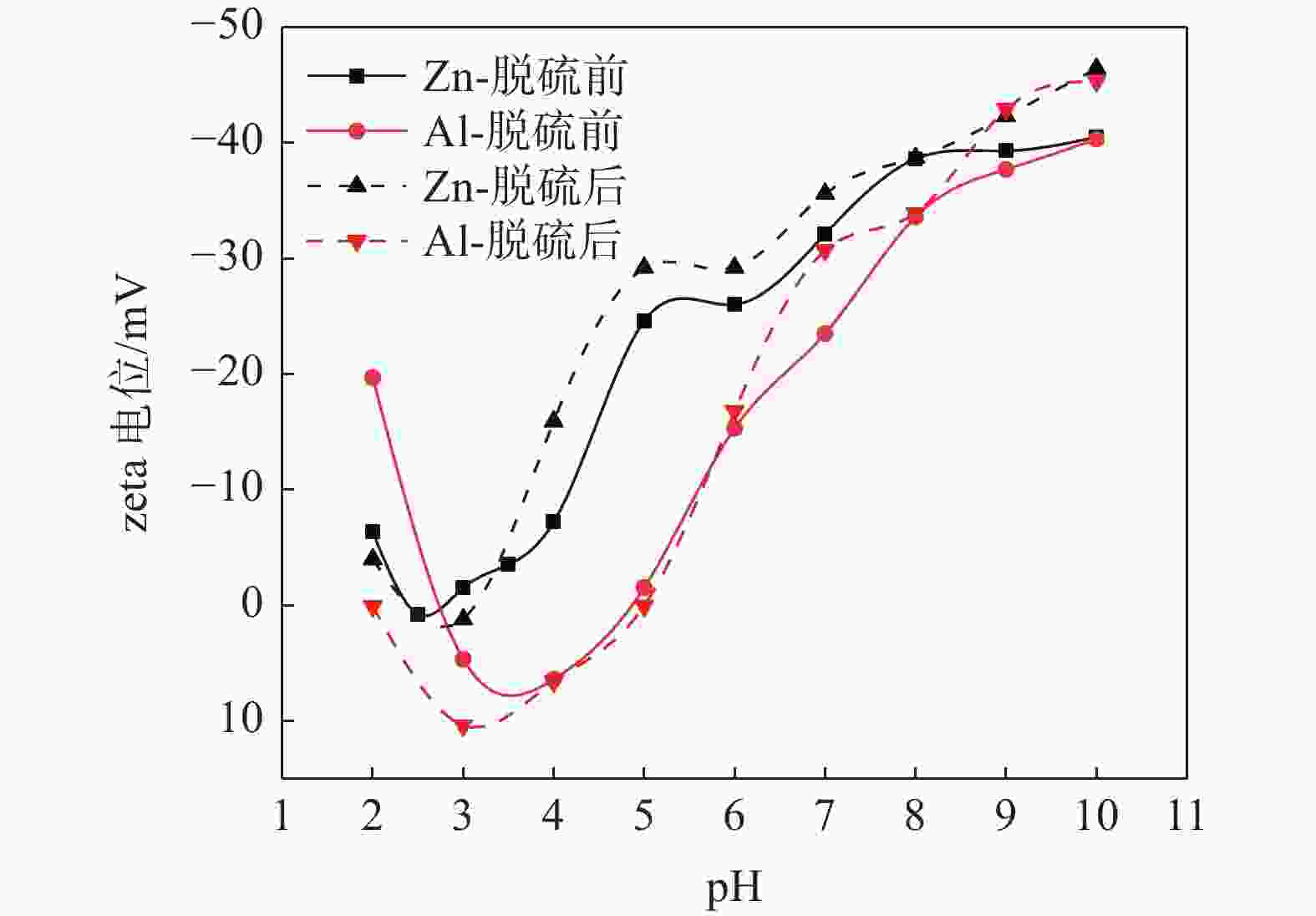
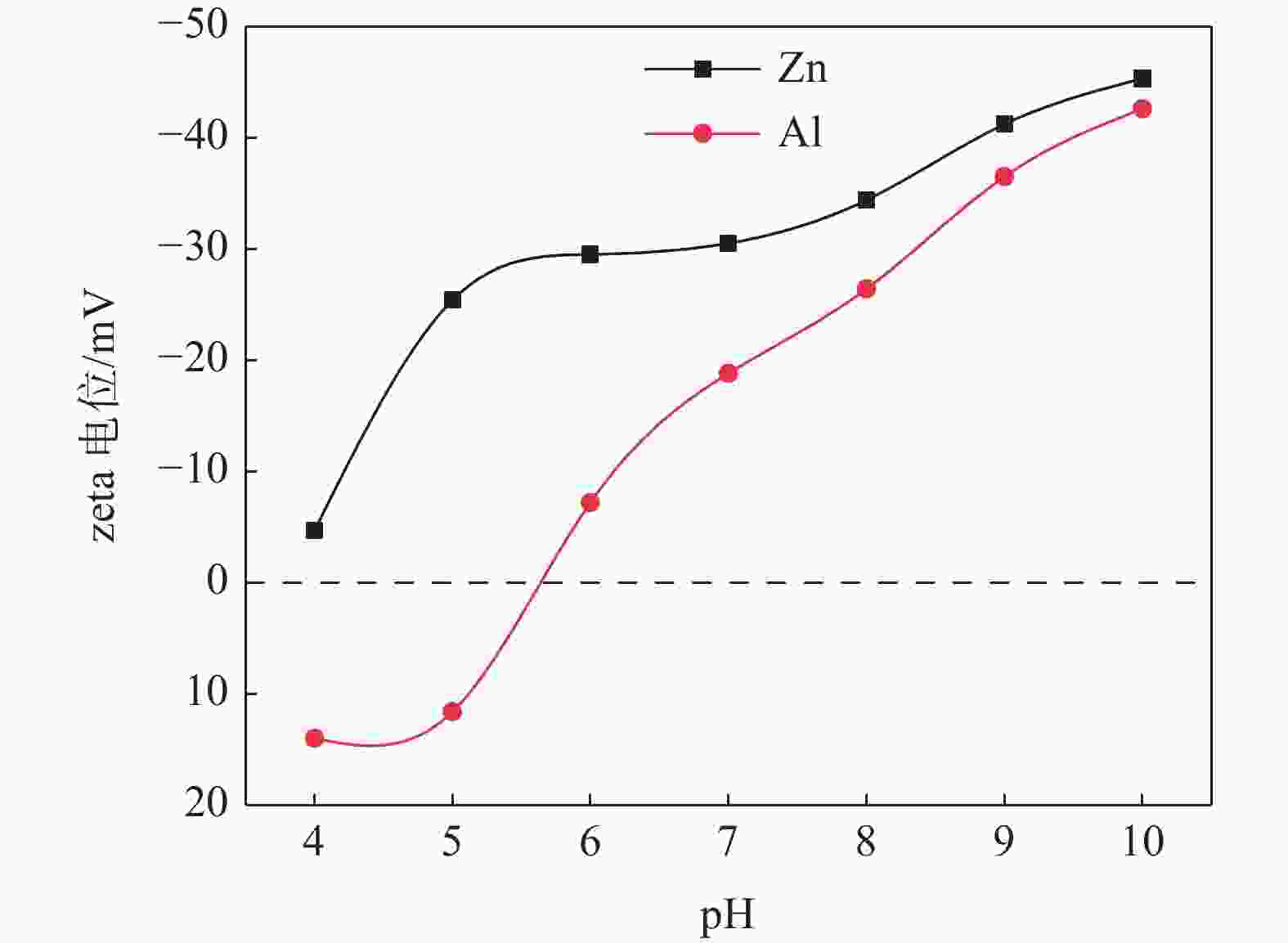
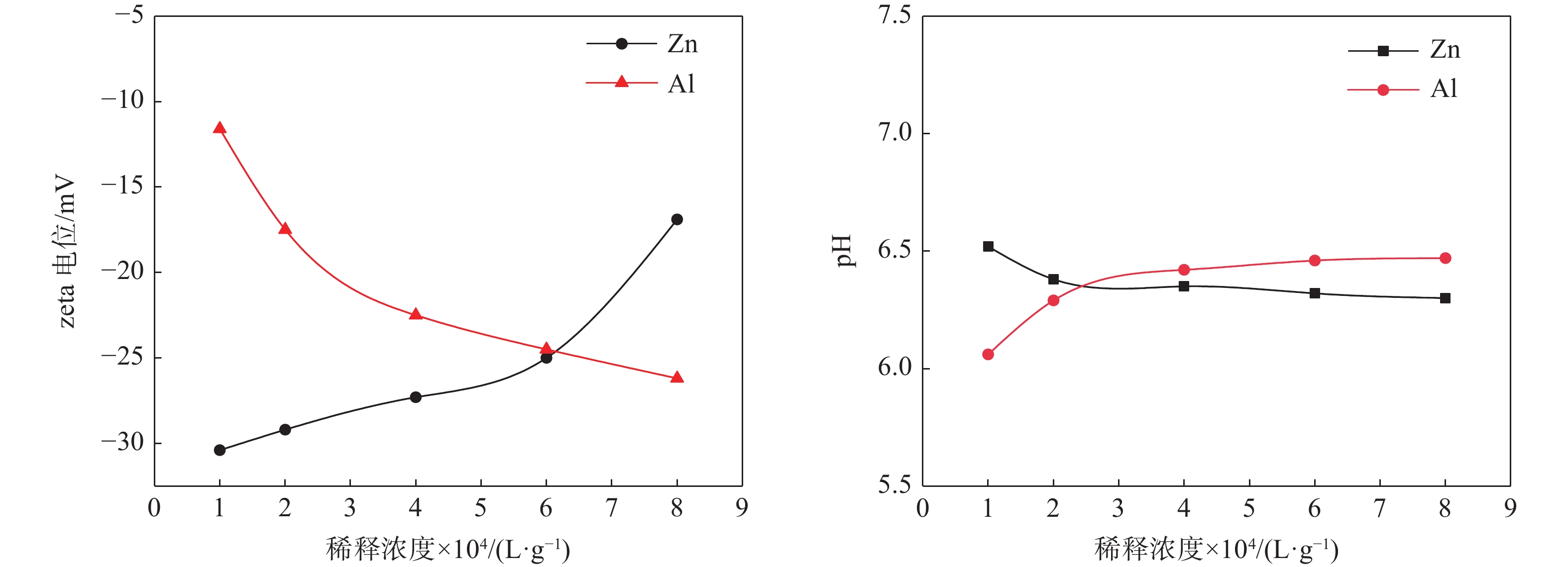
摘要: 选取某硫酸法钛白厂生产的锌系和铝系盐处理金红石初品作为试验原料,系统研究TiO2浓度、分散体系pH和表面吸附的化学成分等因素的变化对锌、铝两系初品悬浊液zeta电位的影响规律,对比分析了锌系和铝系初品分散稳定性的差异。结果表明,随着稀释浓度增高,铝系初品分散越来越稳定,而锌系则逐渐失稳;分散液pH从4.0升至10.0,铝系初品zeta电位较锌系更为显著,即铝系初品更易分散稳定;初品表面脱硫和脱羟基后,铝、锌两系初品的zeta电位随pH的变化规律没有改变,证明了表面吸附的化学成分并非构成两系初品分散差异性的原因。通过实验室单一盐处理-煅烧试验,进一步证明了Zn2+和Al3+掺杂是导致初品分散稳定性差异的根本原因,煅烧温度对初品表面电荷的变化有显著影响,对铝系初品的影响更显著。Abstract: In this paper, the effects of TiO2 concentration, pH of the dispersion system and surface adsorbed chemical ingredients on the zeta potential of the zinc and aluminum salt treated rutile titanium dioxides produced by the manufacturer were systematically studied. The differences of the dispersion stability of the zinc and aluminum salt treated rutile titanium dioxides were compared and analyzed. The results show that with the increase of dilution concentration, the dispersion of aluminum series becomes more and more stable, while that of zinc series becomes unstable. The pH of the dispersion solution increased from 4.0 to 10.0, and the zeta potential of the aluminum series primary product was more significant than that of the zinc series primary product, that is, the aluminum primary product was more easily dispersed and stable. After surface desulphurization and dehydroxylation of primary products, the variation of zeta potential of aluminum and zinc series primary products with pH did not change, which proved that the surface adsorbed chemical ingredients were not the fundamental influencing factors of differences of dispersion of the two series primary products. It was further proved that Zn2+ or Al3+ doping was the root cause of the difference of dispersion stability of the two series primary products through the single salt treatment and calcination test in the laboratory. Moreover, the calcination temperature had a significant effect on the surface charge of the primary products, and the effect on the aluminum series primary product was more significant.
-
Key words:
- titanium dioxide primer /
- zinc series /
- aluminium series /
- dispersion property /
- zeta potential
-
表 1 仪器设备
Table 1. Instruments and equipments
名称 型号 厂家 pH计 PHSJ-3F 雷磁 扫描电镜 JSM-7001F Thermal Field Emission X射线荧光光谱仪 S8 TIGER BRUKER 碳硫仪 CS2000 ELTRA ICP-AES光谱仪 IRIS Intrepid Thermo Fisher Scientific zeta电位仪 Nano-ZS90 Malvern 表 2 锌系/铝系盐处理的产线初品不同pH条件下离子溶出结果
Table 2. Ion dissolution data of the on-site Al/Zn-doped TiO2 particles under different pH conditions
初品 pH w(Zn2+)/% w(K+)/% w(Al3+)/% 锌系 2.00 1.800 4.11 6.81 0.001 3.00 铝系 3.01 3.79 0.003 8.89 2.53 <0.001 表 3 产线锌系和铝系初品的团聚粒径检测结果
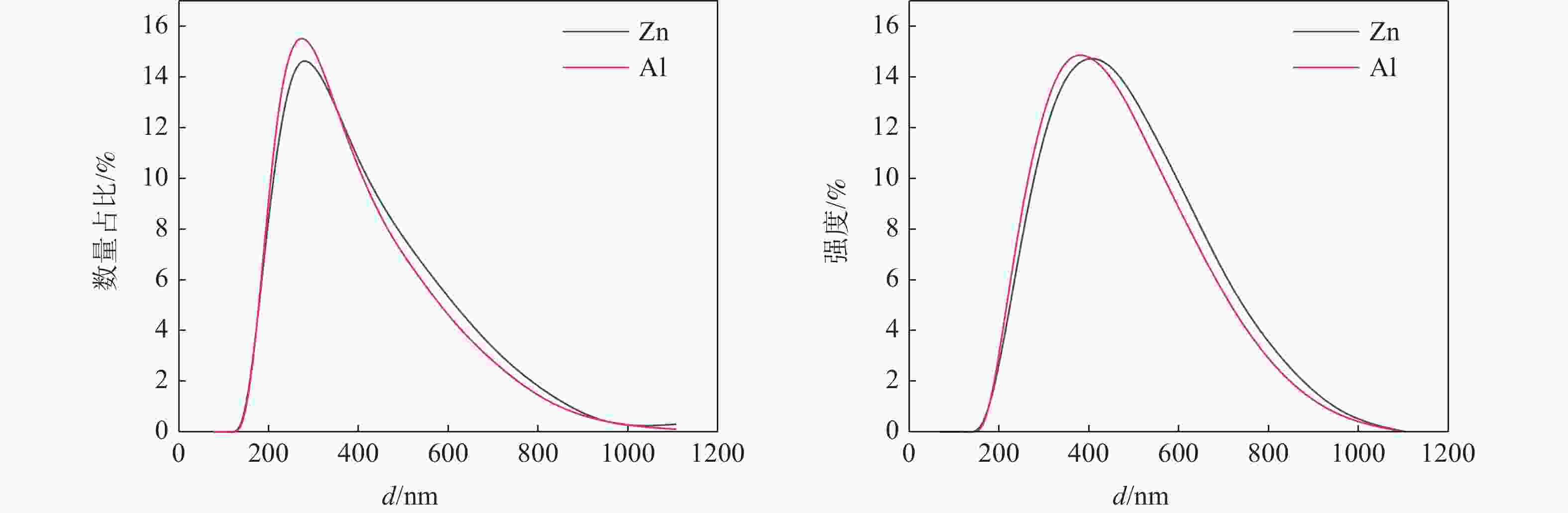
Table 3. Aggregate particle size data of on-site Al/Zn-doped TiO2 particles
初品 ZP/mV Z-Ave/nm Pk 1 Mean Int/nm Pk 1 Area Int/% 锌系 –63.5 365.4 435.3 100 铝系 –61.6 370 421.1 100 表 4 实验室锌/铝单一盐处理初品zeta电位与pH的线性拟合结果
Table 4. Linear fitting results of in dispersion of Al/Zn single-doped TiO2 particles from the laboratory
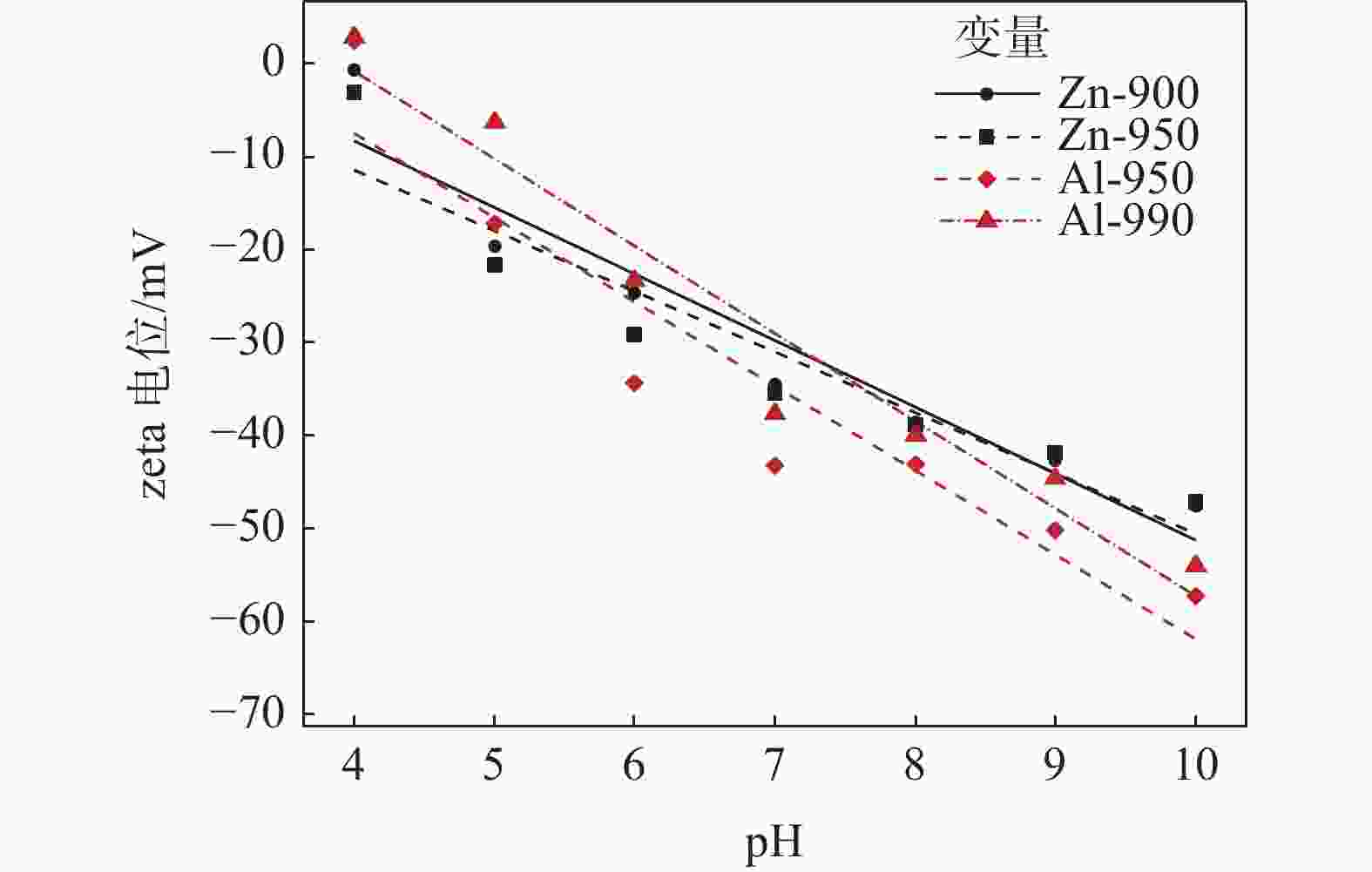
盐处理剂 加量/% 煅烧温度/℃ 金红石含量/% 拟合公式 R-Sq/% ZnO 0.10 900 99.43 Zn-900 = 20.44–7.165pH 92.22 950 99.47 Zn-950 = 14.56–6.510pH 89.15 Al2O3 0.30 950 98.67 Al-950 = 28.90–9.085pH 89.16 990 99.24 Al-990 = 36.98–9.421pH 94.70 -
[1] Bi Sheng. Development and analysis on 2022 titanium dioxide industry in China[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(1):1−3. (毕胜. 2022年中国钛白粉行业发展及分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(1):1−3. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.01.001Bi Sheng. Development and analysis on 2022 titanium dioxide industry in China[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(1): 1−3. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.01.001 [2] Dolganov, Aleksei Bishop, Matthew T Chen, et al. Rheological study and printability investigation of titania inks for direct ink writing process[J]. Ceramics International, 2021,47(9):12020−12027. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.045 [3] Kumarjyoti Roy, Swapan Kumar Mandal, Md Najib Alam, et al. A comparison between polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polypropylene glycol (PPG) treatment on the properties of nano-titanium dioxide (TiO2) based natural rubber (NR) nanocomposites[J]. Polym. Bull, 2016,73(11):3065−3079. doi: 10.1007/s00289-016-1641-3 [4] Zhang Y, Yin H, Wang A, et al. Evolution of zirconia coating layer on rutile TiO2 surface and the pigmentary property[J]. Journal of Physics & Chemistry of Solids, 2010,71(10):1458−1466. [5] Karlsson M C F, Abbas Z, Bordes R, et al. Characterisation of silicon, zirconium and aluminium coated titanium dioxide pigments recovered from paint waste[J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2019,162:145−152. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2018.06.028 [6] Diebold U. The surfacescience of titanium dioxide[J]. Surface Science Reports, 2003,48(5):53−229. [7] Vargas W, Greenwood P, Otterstedt J , et al. Light scattering in pigmented coatings: experiments and theory[J]. Solar Energy, 2000, 68(6): 553−561. [8] Sun Sijia, Ding Hao, Luo Qin. Research on preparation of silica-TiO2 composite particles through mechanical grinding method and their pigment property[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2015,21(4):76−79,88. (孙思佳, 丁浩, 罗琴. 机械研磨法制备白炭黑-TiO2复合粉体及颜料性能研究[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2015,21(4):76−79,88.Sun Sijia, Ding Hao, Luo Qin. Research on preparation of silica-TiO2 composite particles through mechanical grinding method and their pigment property[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2015, 21(4): 76−79,88. [9] Wu Wangchao, Cui Jian, Jiang Hao, et al. Preparation of single particle dispersed titanium dioxide by wet grinding and its influencing factors[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2018,24(2):60−64,80. (吴王超, 崔健, 江浩, 等. 湿法研磨制备单颗粒分散二氧化钛及其影响因素[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2018,24(2):60−64,80. doi: 10.13732/j.issn.1008-5548.2018.02.010Wu Wangchao, Cui Jian, Jiang Hao, et al. Preparation of single particle dispersed titanium dioxide by wet grinding and its influencing factors[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2018, 24(2): 60−64,80. doi: 10.13732/j.issn.1008-5548.2018.02.010 [10] Elmehasseb I, Kandil S, Elgendy K. Advanced visible-light applications utilizing modified Zn-doped TiO2 nanoparticles via non-metal in situ dual doping for wastewater detoxification[J]. Optik, 2020,213:164654. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164654 [11] Hatta K, Higuchi M, Takahashi J, et al. Floating zone growth and characterization of aluminum-doped rutile single crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1996,163(3):279−284. doi: 10.1016/0022-0248(95)00972-8 [12] Wu Jianchun, Lu Ruifang, Ma Weiping. Analysis of difference between zinc salt and aluminum salt treated titanium dioxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(2):29−32. (吴健春, 路瑞芳, 马维平. 锌系与铝系盐处理钛白差异分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(2):29−32. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.02.006Wu Jianchun, Lu Ruifang, Ma Weiping. Analysis of difference between zinc salt and aluminum salt treated titanium dioxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(2): 29−32. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.02.006 [13] Chen X, Burda C. The electronic origin of the visible-light absorption properties of C-, N- and S-doped TiO2 nanomaterials[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008,130(15):5018−5019. doi: 10.1021/ja711023z [14] Asahi R, Morikawa T, Ohwaki T, et al. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides[J]. Science, 2001,293(5528):269−271. doi: 10.1126/science.1061051 [15] Kobayashi T. Pigment dispersion in water-reducible paints[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 1996,28:79−87. doi: 10.1016/0300-9440(95)00608-7 [16] Wang Haibo, Li Li, Luo Zhiqiang, et al. Research on slurry viscosity of zinc salt initial titanium dioxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(2):61−65. (王海波, 李礼, 罗志强, 等. 锌盐类钛白初品浆料黏度研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(2):61−65. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.02.010Wang Haibo, Li Li, Luo Zhiqiang, et al. Research on slurry viscosity of zinc salt initial titanium dioxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019, 40(2): 61−65. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.02.010 [17] Yang Cheng, Wu Jizhong. Applied research on dispersion of titanium dioxide in hydrosolvents[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2010,42(3):28−30. (杨成, 吴继忠. 钛白初品在水溶剂中的分散性应用研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2010,42(3):28−30.Yang Cheng, Wu Jizhong. Applied research on dispersion of titanium dioxide in hydrosolvents[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2010, 42(3): 28−30. [18] Wang Yongshan, Dou Jun, Miao Weiran, et al. Analysis of post-treatment technology of rutile titunium dioxide[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2021(10):123−124. (王永珊, 豆君, 苗委然, 等. 金红石型钛白粉后处理工艺技术分析[J]. 当代化工研究, 2021(10):123−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2021.10.061Wang Yongshan, Dou Jun, Miao Weiran, et al. Analysis of post-treatment technology of rutile titunium dioxide[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2021(10): 123−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2021.10.061 [19] Liu Rulin. Study of electronic structure and transportation behavior of defects in rutile TiO2[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2018. (刘汝霖. 金红石型二氧化钛中缺陷的电子结构及其输运性质研究[D]. 北京: 国防科技大学, 2018.Liu Rulin. Study of electronic structure and transportation behavior of defects in rutile TiO2[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2018. -




 下载:
下载: