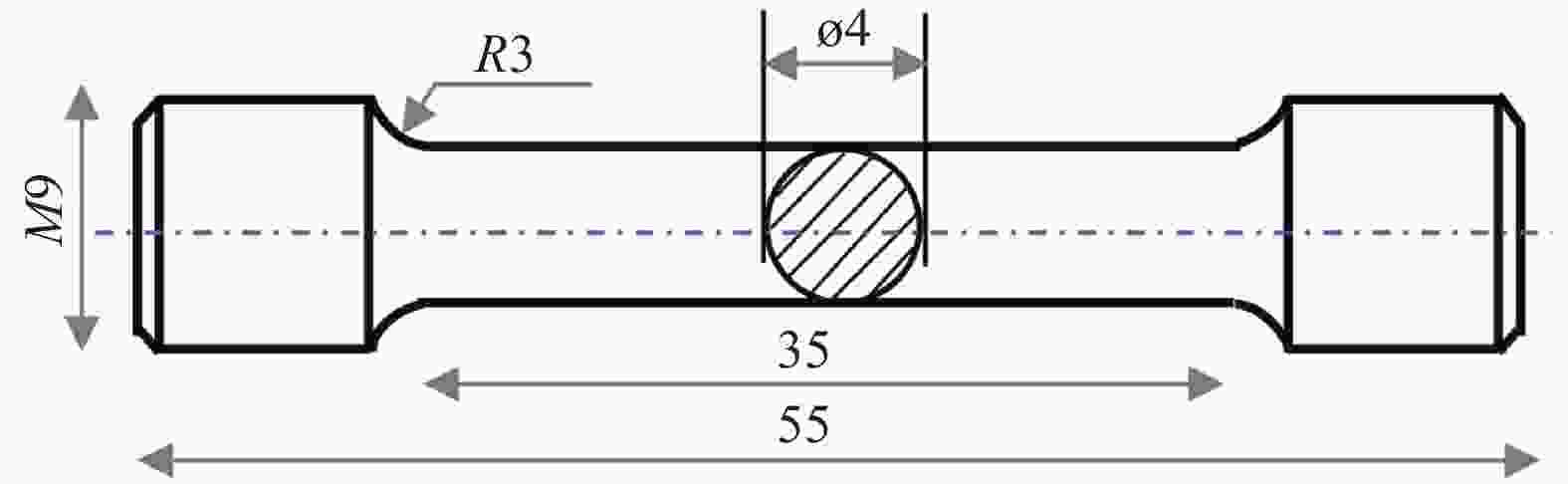
Optimization of the investment casting process and defect control for variable cross−section components of TC4 alloy
-
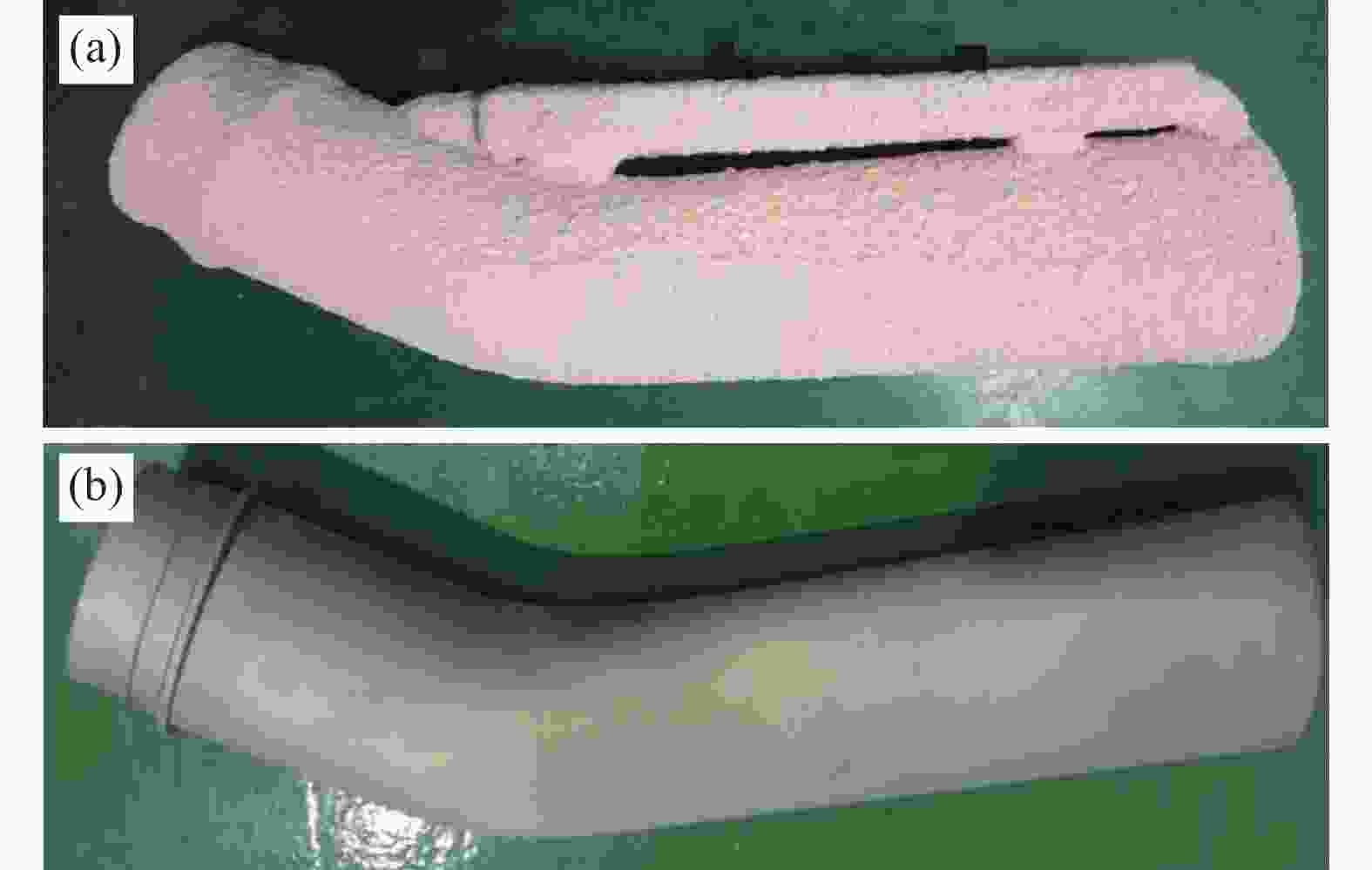
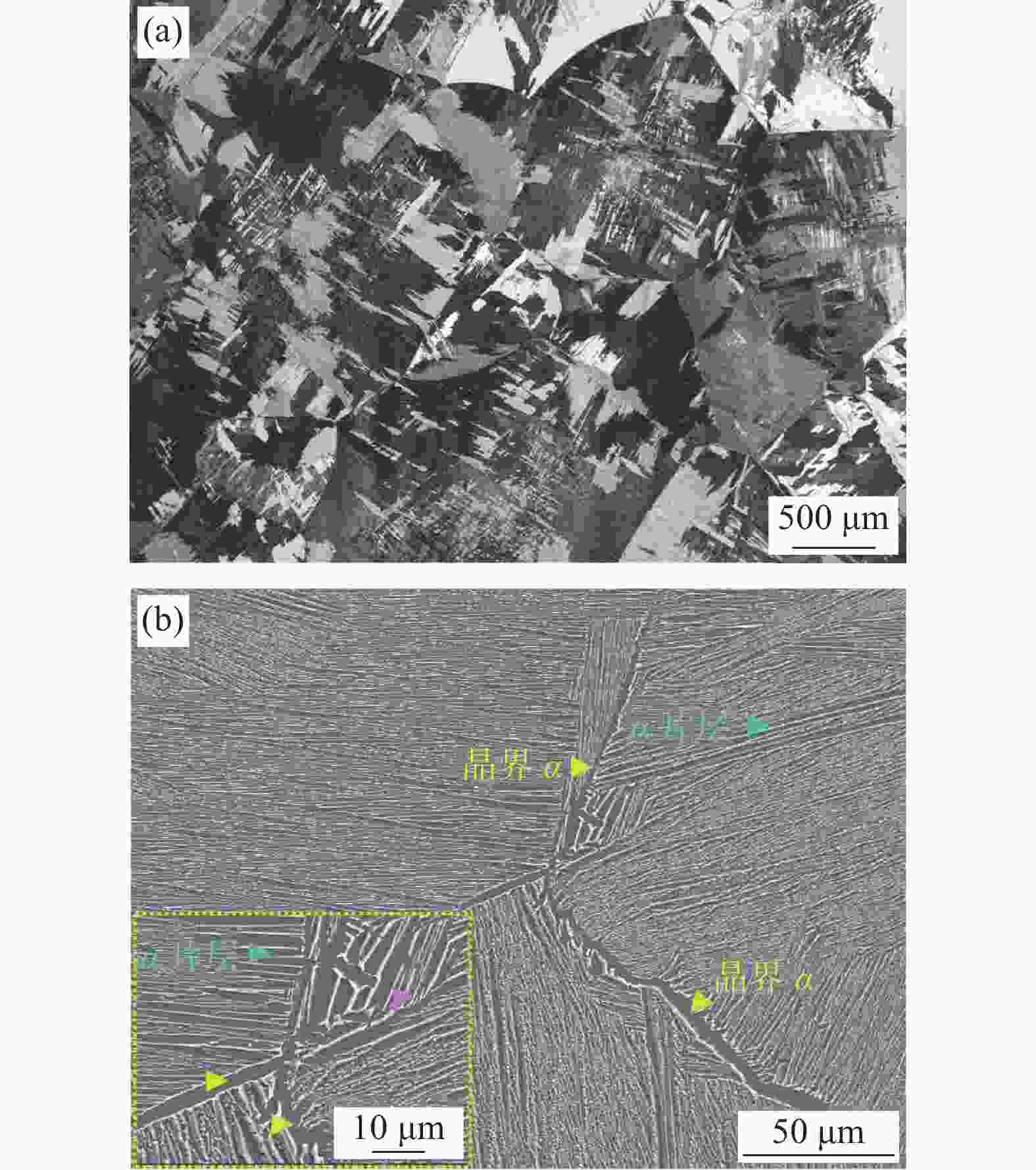
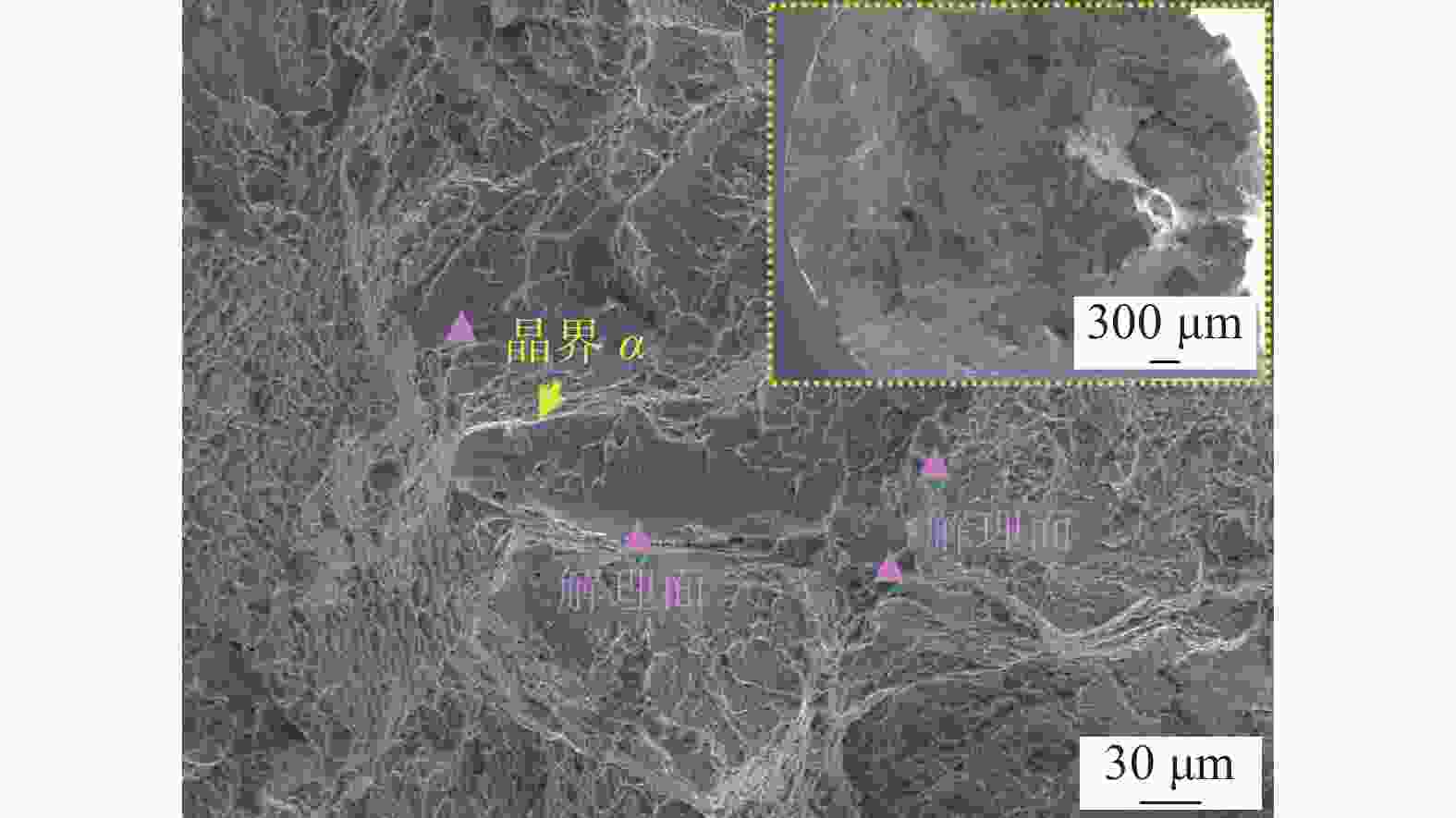
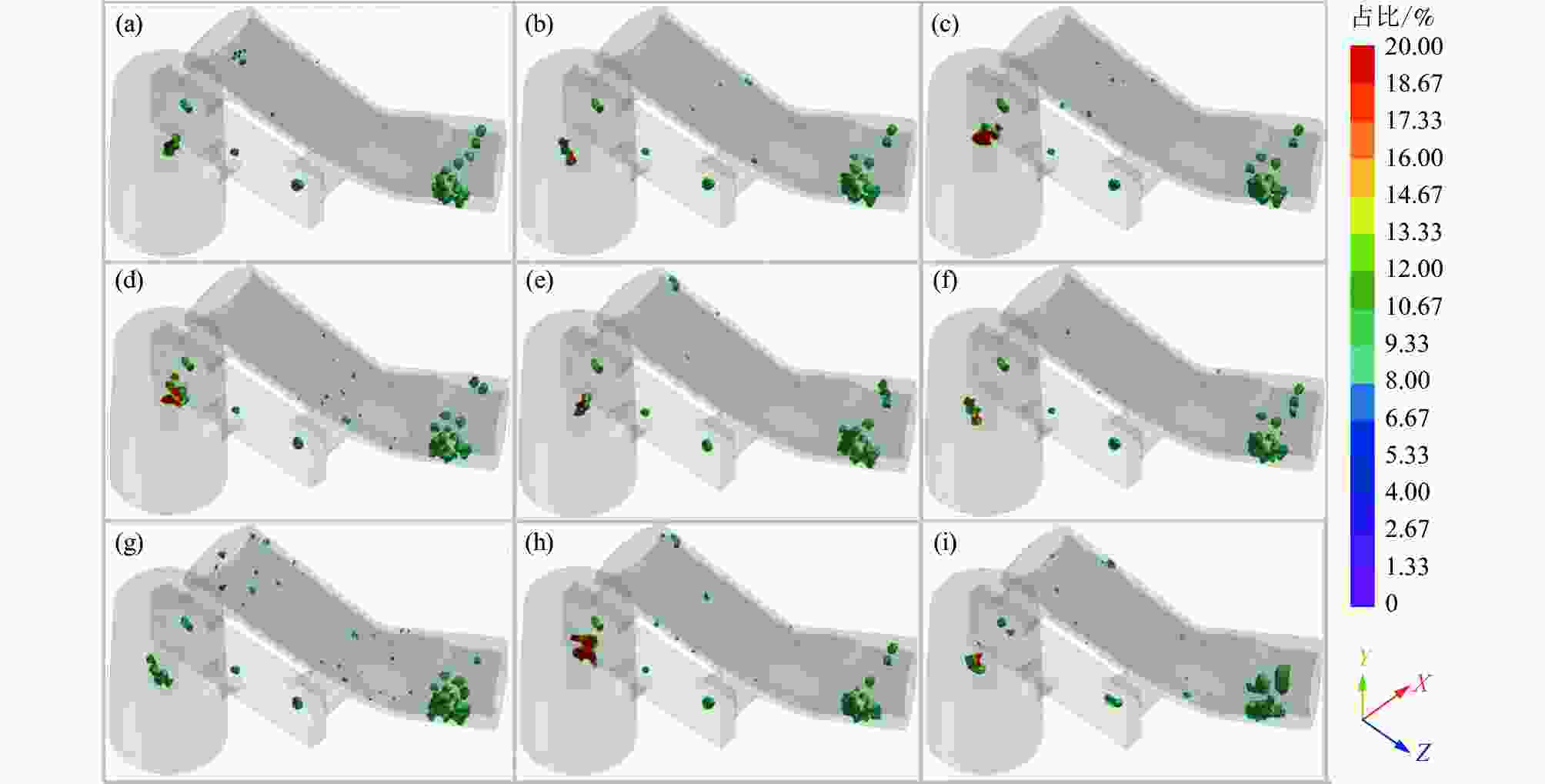
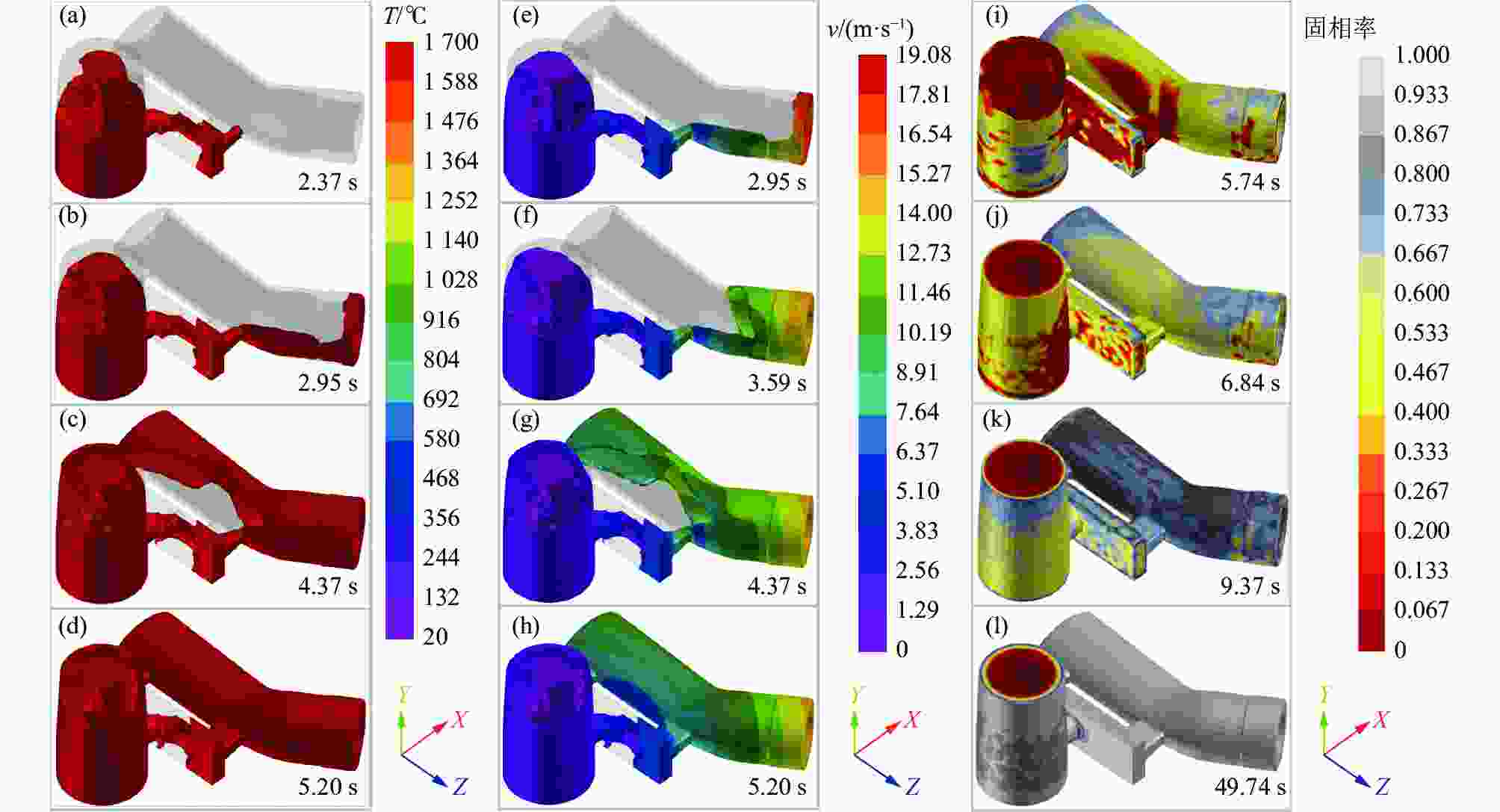
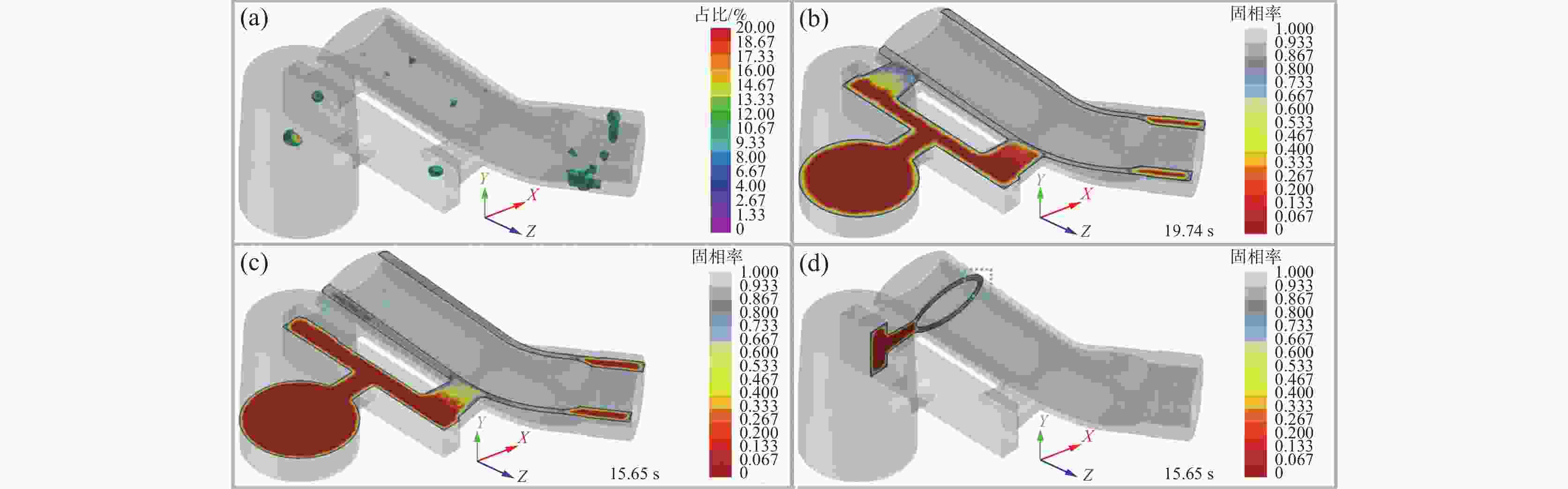
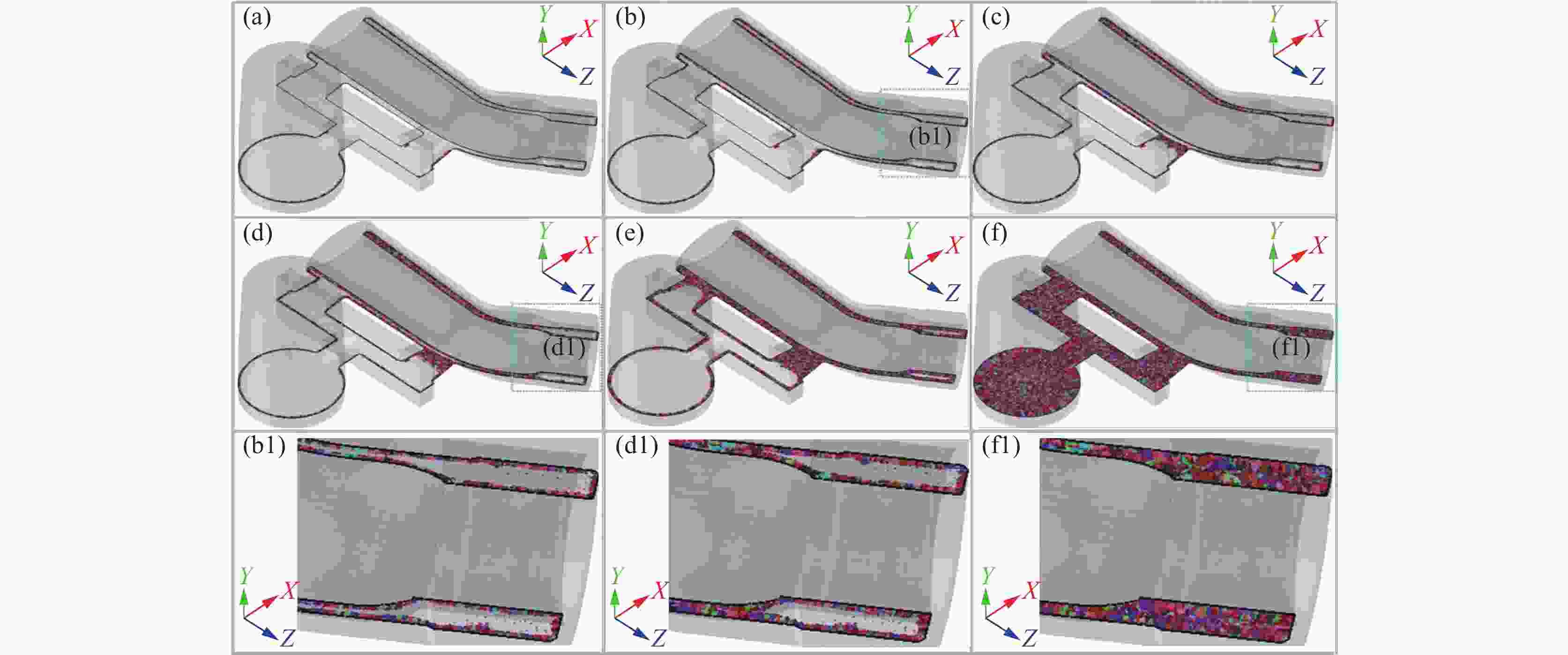
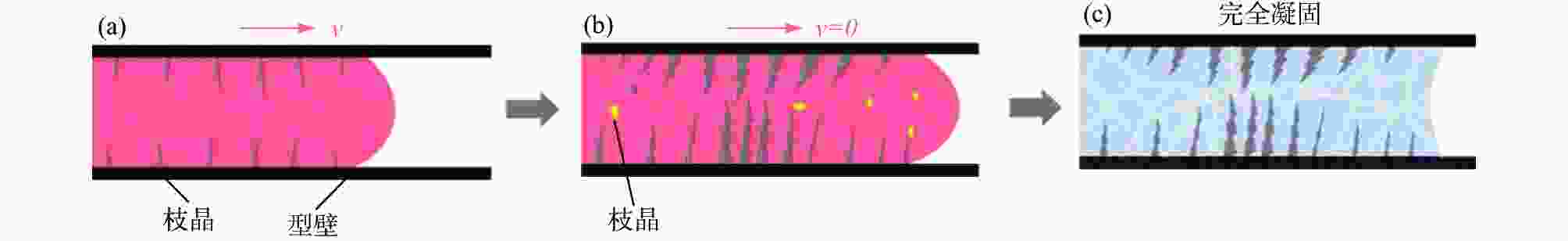
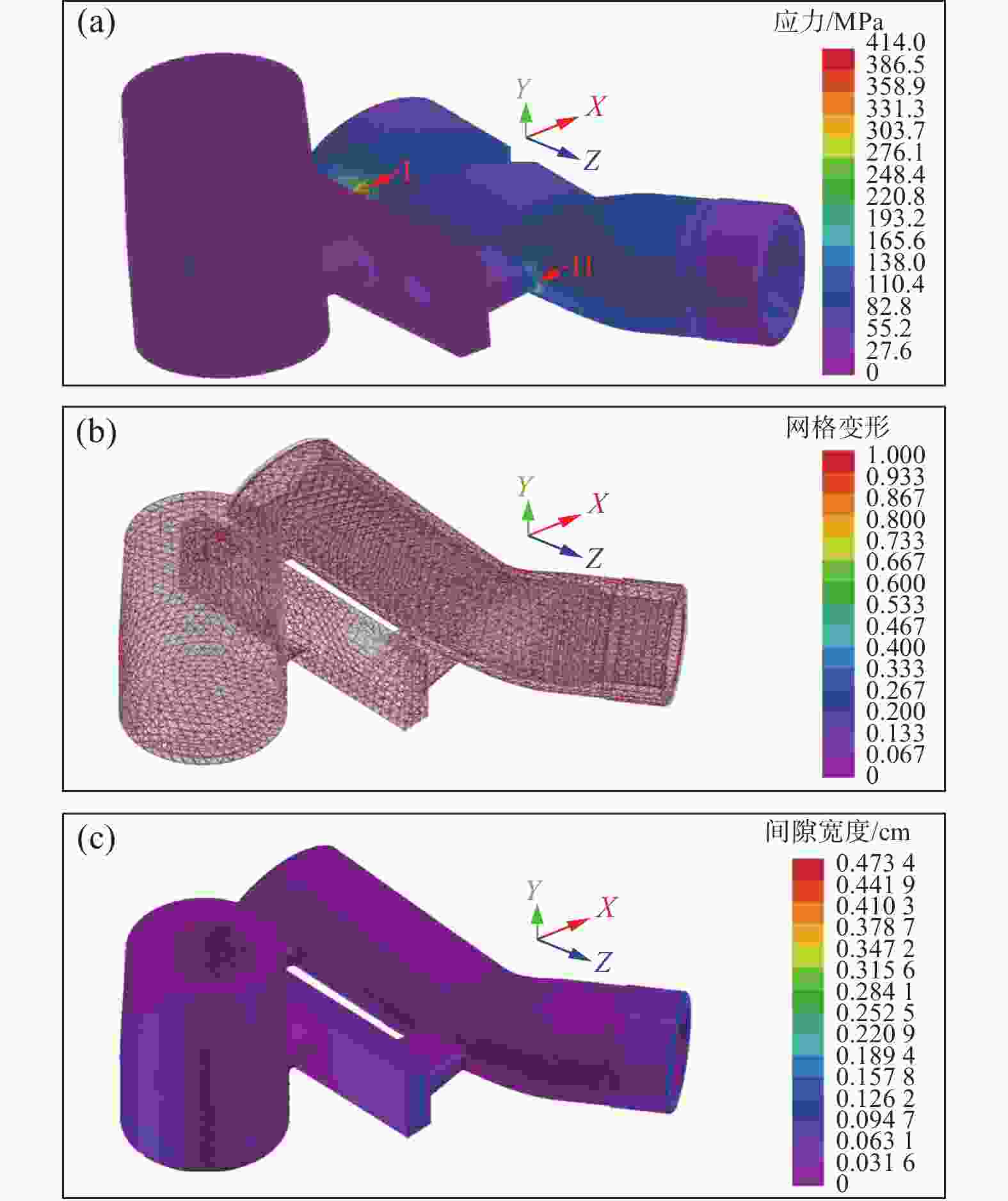
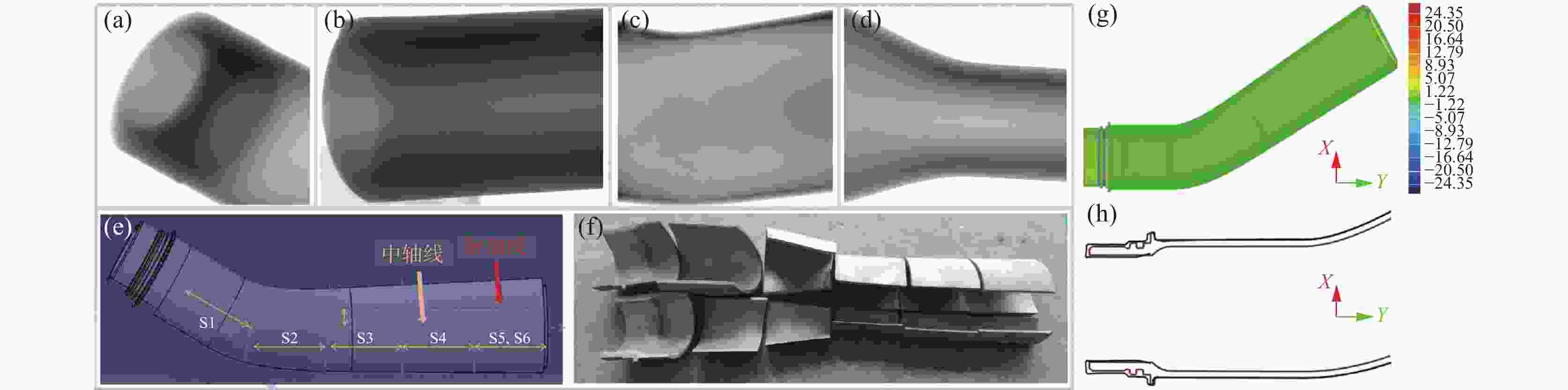
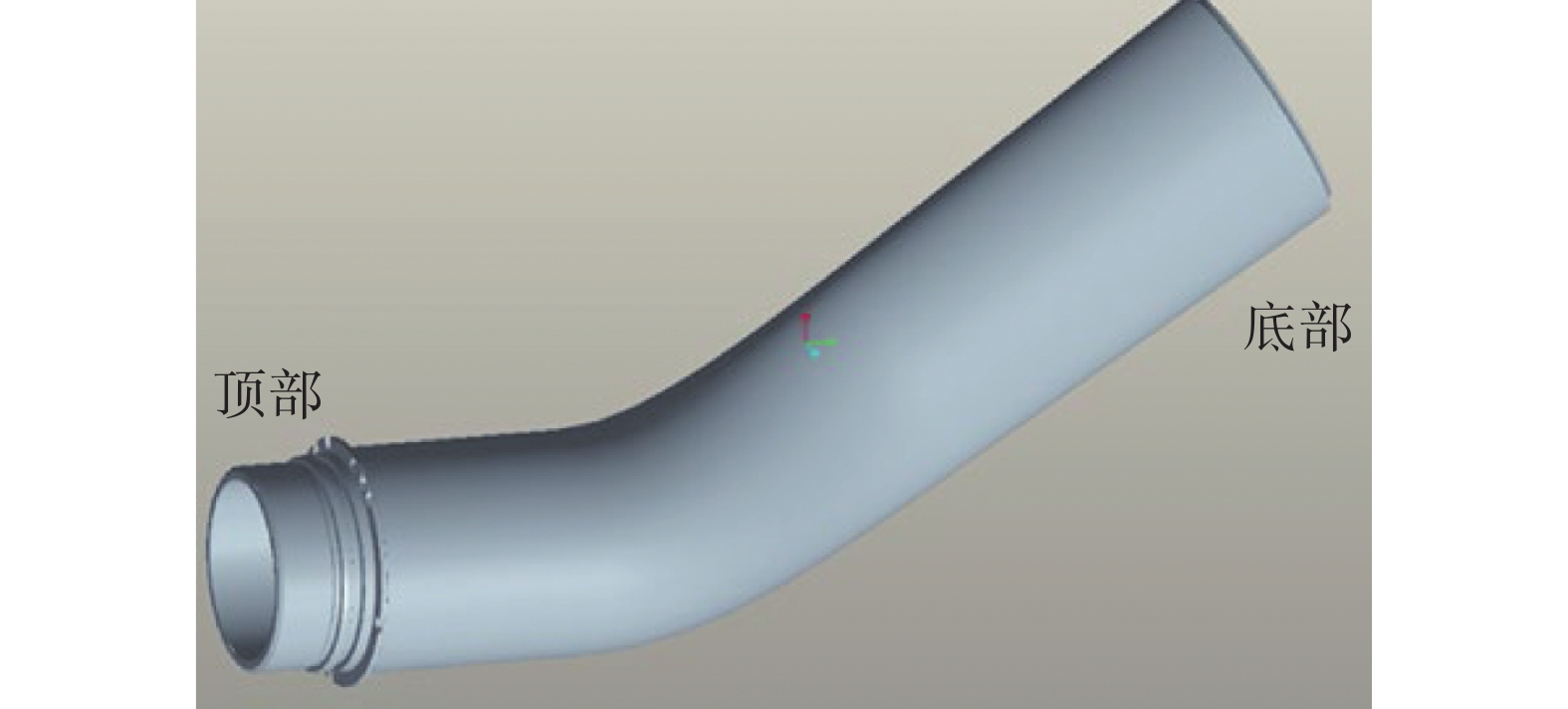
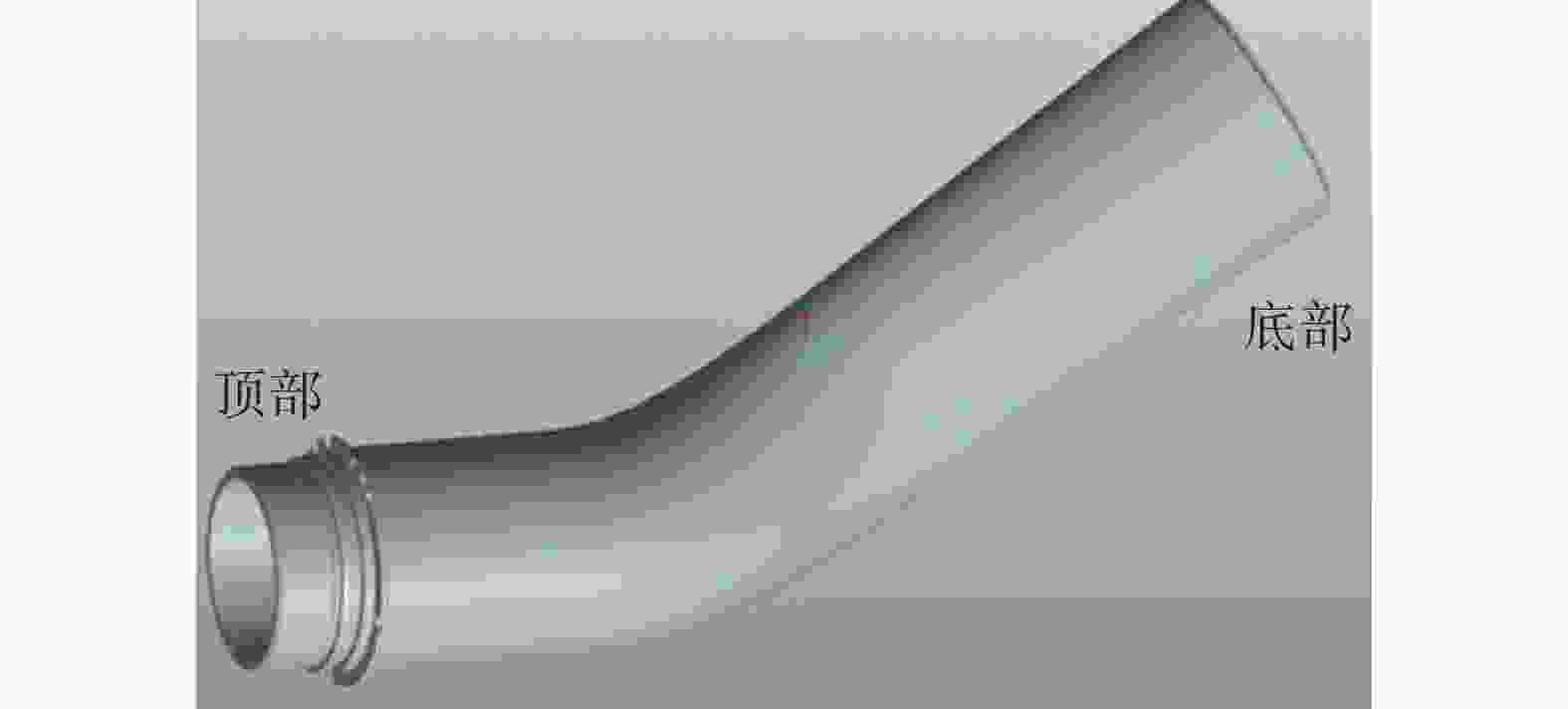
摘要: 以TC4合金变截面构件为研究对象,基于正交试验设计,采用ProCAST软件对铸件的离心熔模铸造工艺进行了优化。同时,对铸件的充型与凝固行为进行了数值分析,并对铸件质量及力学性能进行了表征。结果表明,缩松缩孔集中分布在铸件顶部,少量缩松缩孔离散分布在铸件中部或底部,孤立液相区是导致缩松缩孔形成的主要原因,熔体流动停止表现出窄结晶温度范围合金特征;应力集中主要发生在内浇道与铸件连接处,较大的结构变化是诱使应力集中产生的主要原因。对铸件内部质量及尺寸进行表征分析,发现铸件内部无缩松缩孔存在,铸件尺寸可以较好地满足设计要求,未发生明显变形。热等静压态铸件的室温抗拉强度为953.5 MPa、屈服强度为835.0 MPa、断后伸长率为10.0%,可以较好地满足实际服役要求。
-
关键词:
- TC4合金 /
- 变截面构件 /
- 熔模铸造 /
- ProCAST数值分析 /
- 缺陷控制
Abstract: In this study, the centrifugal investment casting process was optimized using ProCAST software based on an orthogonal experiment for TC4 alloy variable cross−section components. Simultaneously, the mold filling and solidification behaviors of the castings were investigated in detail, and the quality and mechanical properties of the castings were characterized. The results show that a small amount of shrinkage porosity is discretely distributed in the middle and bottom of the casting, while a large concentration is discretely distributed at the top. The formation of isolated liquid phase zones is the main reason for the shrinkage porosity, and the termination of melt metal flow exhibits the characteristics of a narrow crystallization temperature range. At the same time, the stress concentration mainly occurs at the connection between the inner sprue and the casting, and the major cause of it is the large structural change. The internal quality and dimensions of the casting were characterized, and it was discovered that there is no shrinkage porosity, the casting dimensions better satisfy the design requirements, and there is no visible deformation. The room-temperature tensile strength (UTS) of the hot isostatic pressing (HIPed) castings is 953.5 MPa, the yield strength (YS) is 835.0 MPa, and the elongation (EL) is 10.0%, which can better meet the actual service demands. -
表 1 正交试验设计
Table 1. Orthogonal experimental design
序号 A / ℃ B / ℃ C /(kg·s−1) D/ (r·min−1) 方案 1 1680 300 3 350 A1B1C1D1 2 1680 350 5 450 A1B2C2D2 3 1680 400 7 550 A1B3C3D3 4 1700 300 5 550 A2B1C2D3 5 1700 350 7 350 A2B2C3D1 6 1700 400 3 450 A2B3C1D2 7 1750 300 7 450 A3B1C3D2 8 1750 350 3 550 A3B2C1D3 9 1750 400 5 350 A3B3C2D1 A代表浇注温度(℃);B代表型壳预热温度 (℃);C代表浇注速率(kg/s);D代表离心转速(r/min)。 表 2 正交试验直观分析
Table 2. Intuitive analysis table of orthogonal experiment
序号 A/℃ B/℃ C/ (kg·s−1) D/(r·min−1) 方案 缩松缩孔
/cm31 1680 300 3 350 A1B1C1D1 5.1081 2 1680 350 5 450 A1B2C2D2 5.1409 3 1680 400 7 550 A1B3C3D3 5.2849 4 1700 300 5 550 A2B1C2D3 5.5014 5 1700 350 7 350 A2B2C3D1 5.4112 6 1700 400 3 450 A2B3C1D2 5.1672 7 1750 300 7 450 A3B1C3D2 6.1459 8 1750 350 3 550 A3B2C1D3 5.3232 9 1750 400 5 350 A3B3C2D1 5.4044 K1 15.5339 16.7554 15.5985 15.9237 K2 16.0798 15.8753 16.0467 16.4540 K3 16.8735 15.8565 16.8420 16.1095 R 1.3396 0.8989 1.2435 0.5303 -
[1] Cui C X, Hu B M, Zhao L, et al. Ti−based alloy production technology, market prospects and industry development[J]. Materials & Design, 2011,32(3):1684−1691. [2] Hou Z Q, Li B H, Feng G W, et al. Development and application of Ti−based alloy casting technologies in the field of aerospace[J]. Aerospace Shanghai (Chinese & English), 2022,39(1):1−14. [3] Shao H, Li Y, Zhao P, et al. Numerical simulation of centrifugal casting process of large thin−wall Ti alloy casting[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2016,850:469−481. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.850.469 [4] Suzuki K, Yao M. Simulation of mold filling and solidification during centrifugal precision casting of Ti−6Al−4V alloy[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2004,10(1):33−38. doi: 10.1007/BF03027361 [5] Jia Y, Xiao S L, Tian J, et al. Modeling of TiAl alloy grating by investment casting[J]. Metals, 2015,5:2328−2339. doi: 10.3390/met5042328 [6] Xiong C, Ma Y C, Chen B, et al. Modeling of filling and solidification process for TiAl exhaust valves during suction casting[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2013,26:33−48. doi: 10.1007/s40195-011-0503-0 [7] Shao Heng. Numerical simulation of centrifugal investment casting of large thin−wall complex Ti−6Al−4V castings[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2017. (邵珩. 大型复杂薄壁Ti−6Al−4V合金铸件离心熔模铸造过程数值模拟[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2017.Shao Heng. Numerical simulation of centrifugal investment casting of large thin−wall complex Ti−6Al−4V castings[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2017. [8] Yang Liang. Composition optimization and investment casting of cast high Nb−TiAl alloy[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2015. (杨亮. 铸造高Nb−TiAl合金成分优化及其精密铸造工艺研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2015.Yang Liang. Composition optimization and investment casting of cast high Nb−TiAl alloy[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2015. [9] He T, Chen Y Y. Influence of mold design on shrinkage porosity of Ti−6Al−4V alloy ingots[J]. Metals, 2022,12:2122. doi: 10.3390/met12122122 [10] Wang J Q, Fu P X, Liu H W, et al. Shrinkage porosity criteria and optimized design of a 100−ton 30Cr2Ni4MoV forging ingot[J]. Materials & Design, 2012,35:446−456. [11] Jia Yi. The effects of B and Y on microstructure and properties of TiAl alloy and investment casting of TiAl alloy[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016. (贾燚. 硼及钇对钛铝合金组织性能的影响及精密铸造工艺研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.Jia Yi. The effects of B and Y on microstructure and properties of TiAl alloy and investment casting of TiAl alloy[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016. [12] Yang L, Chai L H, Zhang L Q, et al. Numerical simulation and process optimization of investment casting of the blades for high Nb containing TiAl alloy[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2013,747:105−110. [13] Liu X J, Hao Z J, Huang M. Optimization of vacuum counter−pressure casting process for an aluminum alloy casing using numerical simulation and defect recognition techniques[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020,107:2783−2795. doi: 10.1007/s00170-020-05018-1 [14] Yang J R, Wang H, Wu Y L, et al. Numerical calculation and experimental evaluation of counter−gravity investment casting of Ti−48Al−2Cr−2Nb alloy[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018,96:3295−3309. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-1784-5 [15] Brotzu A, Felli F, Mondal A, et al. Production issues in the manufacturing of TiAl turbine blades by investment casting[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2020,25:79−87. doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2020.04.012 [16] Wu J X, Chen Y Y, Du Z M, et al. Modeling of investment casting of Ti48Al48Cr2Nb2 (at%) alloy air rudder skeleton[J]. International Journal of Metalcasting, 2023,17:2022−2016. [17] Tian J, Chen Y F, Xiao S L, et al. Influence of pouring temperature and mold preheating temperature on investment casting of TiAl[C]// Proceedings of 69th World Foundry Congress. Hangzhou: World Foundry Organization, 2010. [18] Jia L M, Xu D M, Li M, et al. Casting defects of Ti−6Al−4V alloy in vertical centrifugal casting processes with graphite molds[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2012,18(1):55−61. doi: 10.1007/s12540-012-0007-0 [19] Liu J G, Yang Lei, Fang X G, et al. Numerical simulation and optimization of shell mould casting process for leaf spring bracket[J]. China Foundry, 2020,17:35−41. doi: 10.1007/s41230-020-9089-3 [20] Dahle A K, Karlsen S, Arnberg L. Effect of grain refinement on the fluidity of some binary Al−Cu and Al−Mg alloys[J]. International Journal of Cast Metals Research, 1996,9:103−112. doi: 10.1080/13640461.1996.11819649 [21] Wang J H, Guo X L, Wang L Q, et al. The influence of B4C on the fluidity of Ti−6Al−4V−xB4C composites[J]. Materials Transactions, 2014,55(9):1367−1371. doi: 10.2320/matertrans.M2014142 [22] Yang L, Chai L H, Liang Y F, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental verification of gravity and centrifugal investment casting low pressure turbine blades for high Nb−TiAl alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 2015,66:149−155. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2015.07.006 [23] Cabibbo M, Zherebtsov S, Mironov S, et al. Loss of coherency and interphase α/β angular deviation from the Burgers orientation relationship in a Ti−6Al−4V alloy compressed at 800 ℃[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012,48(3):1100−1110. [24] Yang J H, Xiao S L, Chen Y Y, et al. Effects of nano−Y2O3 addition on the microstructure evolution and tensile properties of a near−α titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2019,761:137977. [25] Zhang Shouyin. Investigation of solidification behavior and microstructure evolution in ZTC4 alloys[D]. Xi,an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2016. (张守银. ZTC4钛合金凝固行为及组织演化研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2016.Zhang Shouyin. Investigation of solidification behavior and microstructure evolution in ZTC4 alloys[D]. Xi,an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2016. [26] Yang Jianhui. Research on deformation behavior and microstructure and mechanical properties of (TiB+TiC+Y2O3)/α−Ti composites[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. (杨建辉. (TiB+TiC+Y2O3)/α−Ti 复合材料变形行为及组织性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.Yang Jianhui. Research on deformation behavior and microstructure and mechanical properties of (TiB+TiC+Y2O3)/α−Ti composites[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. -




 下载:
下载: