Effect of post heat treatment on the microstructure and properties of as-annealed TC4 ELI alloy
-
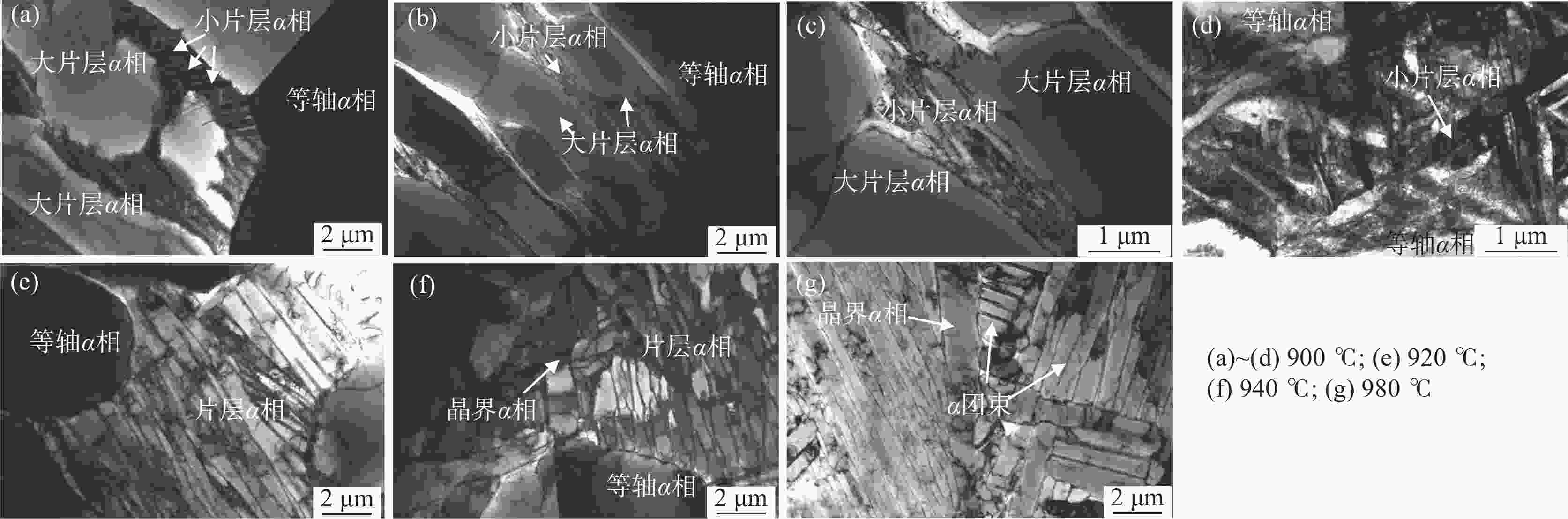
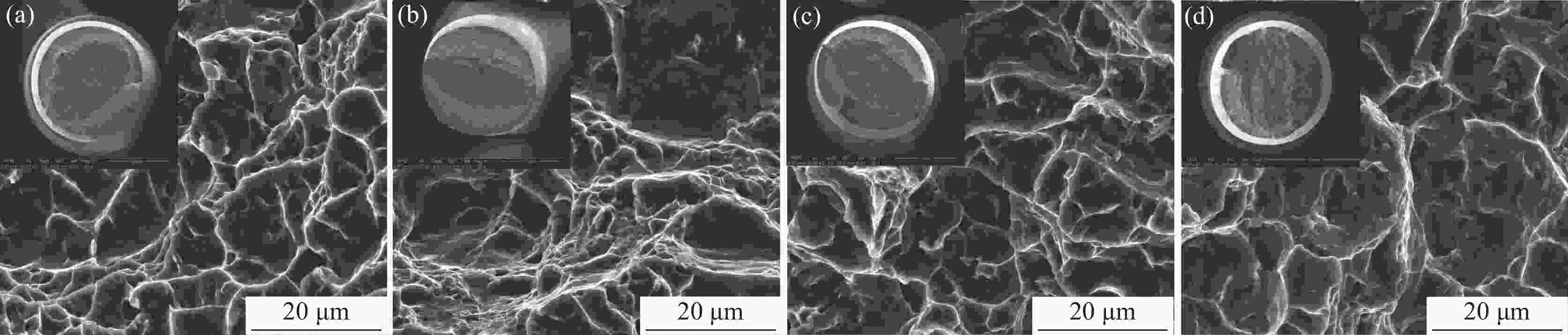
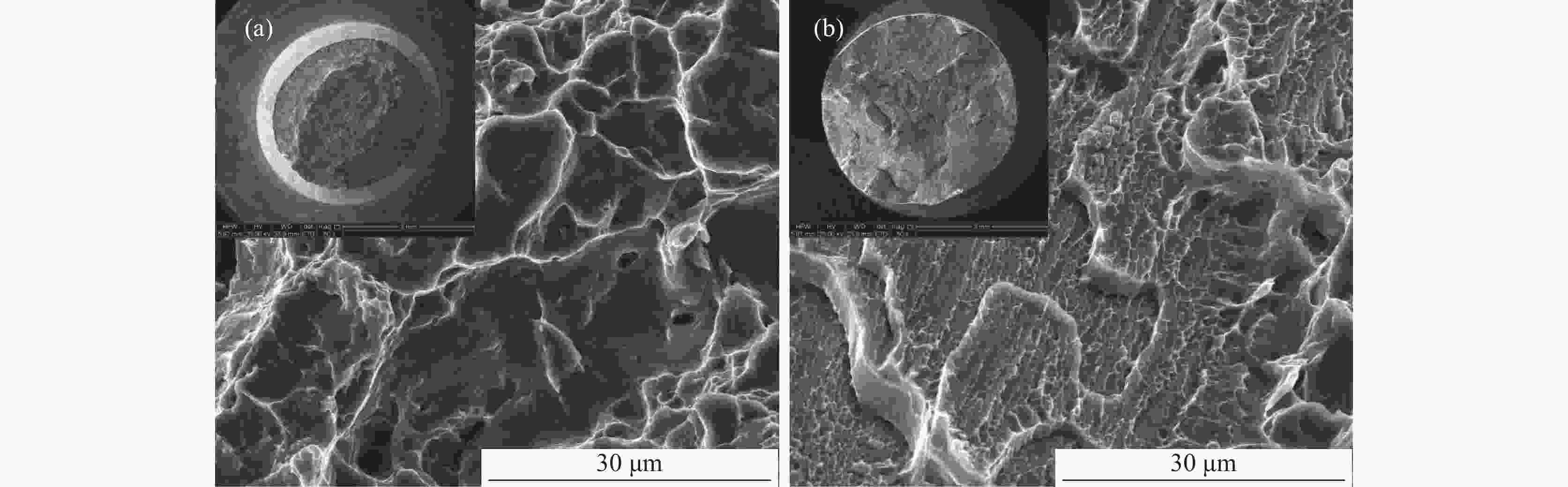
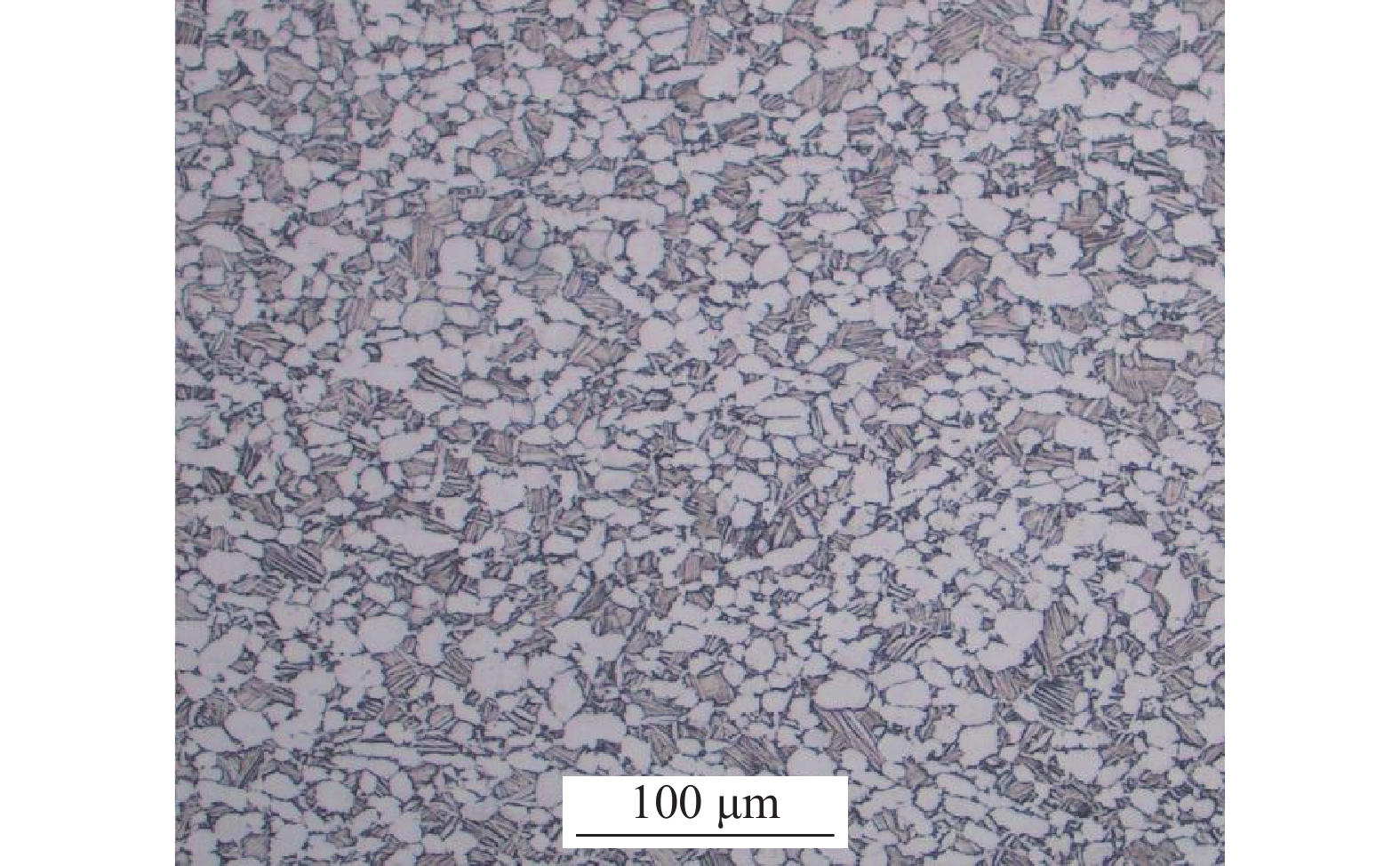
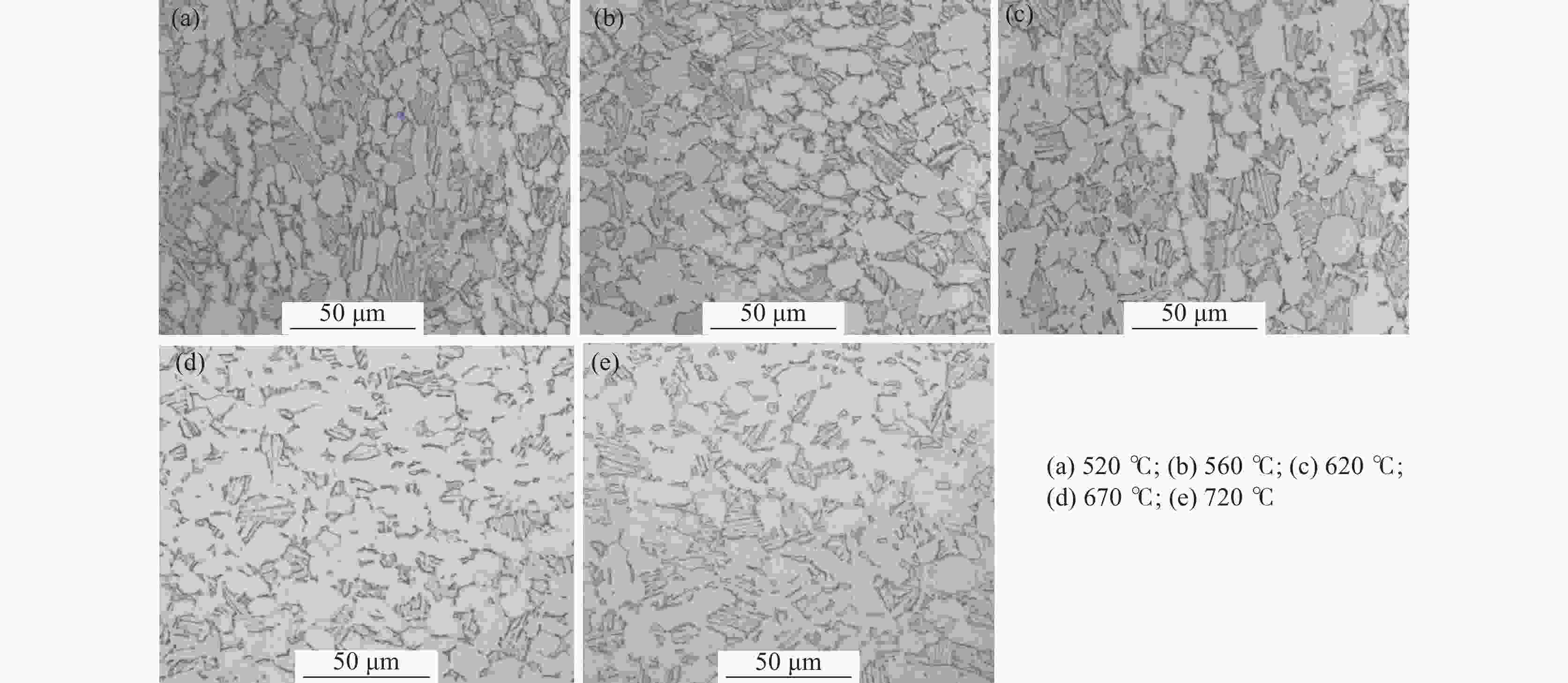
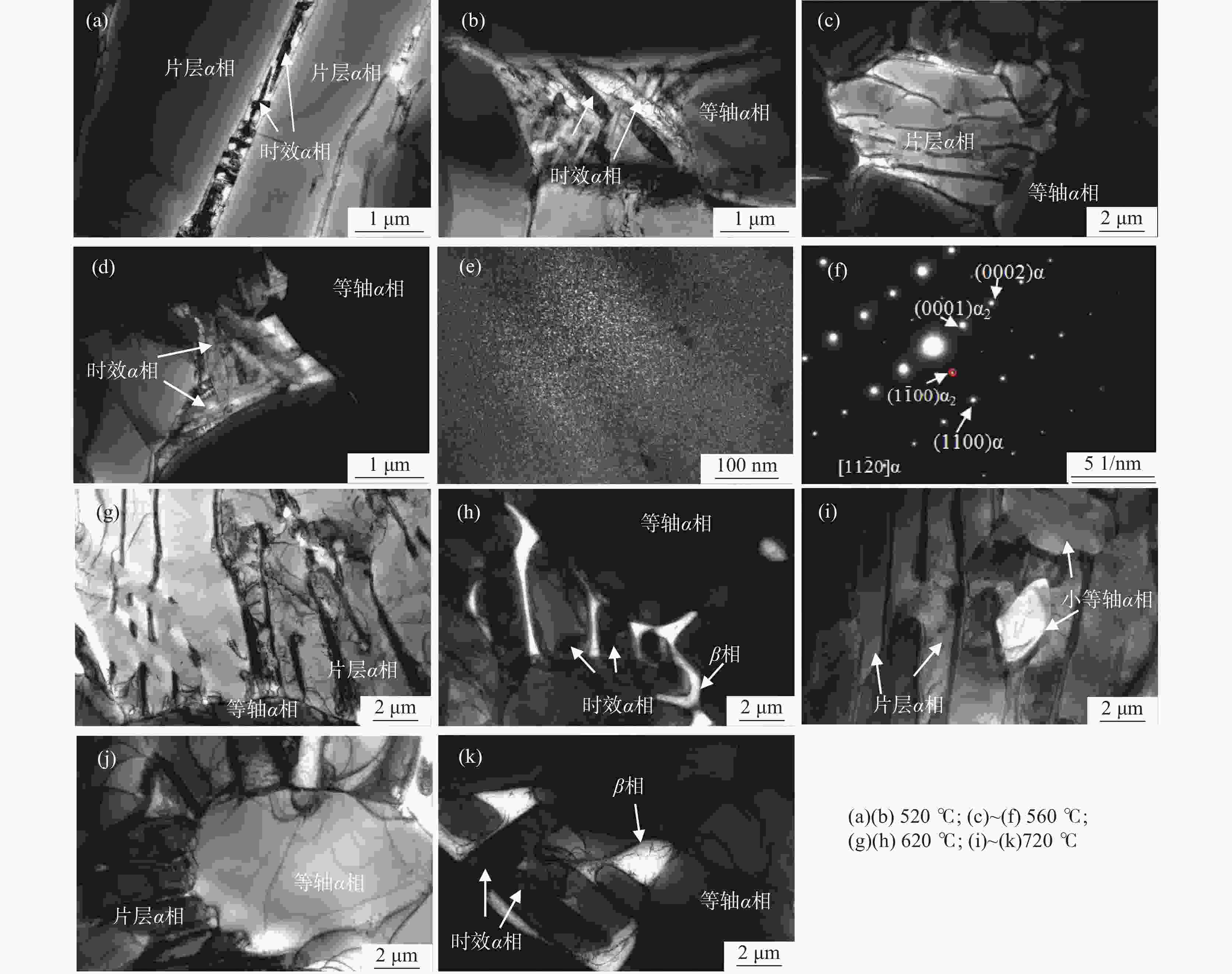
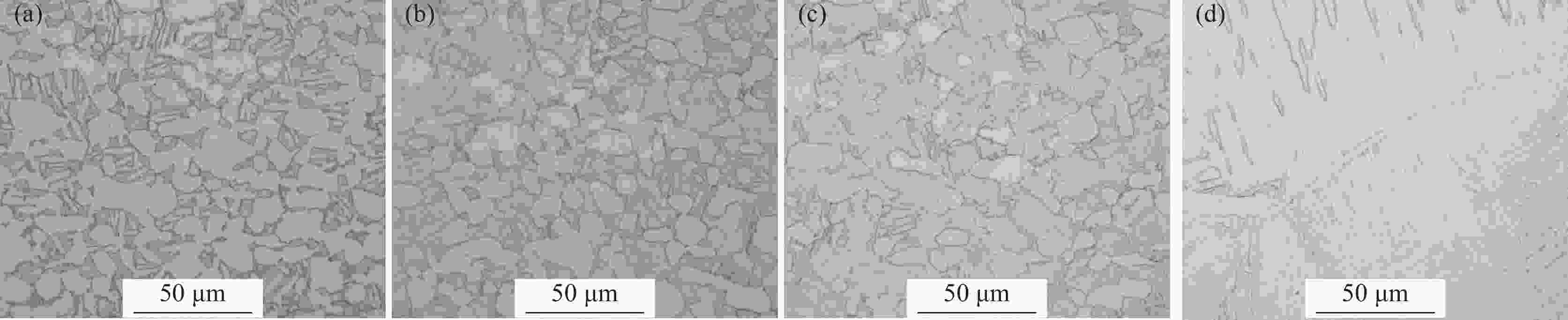
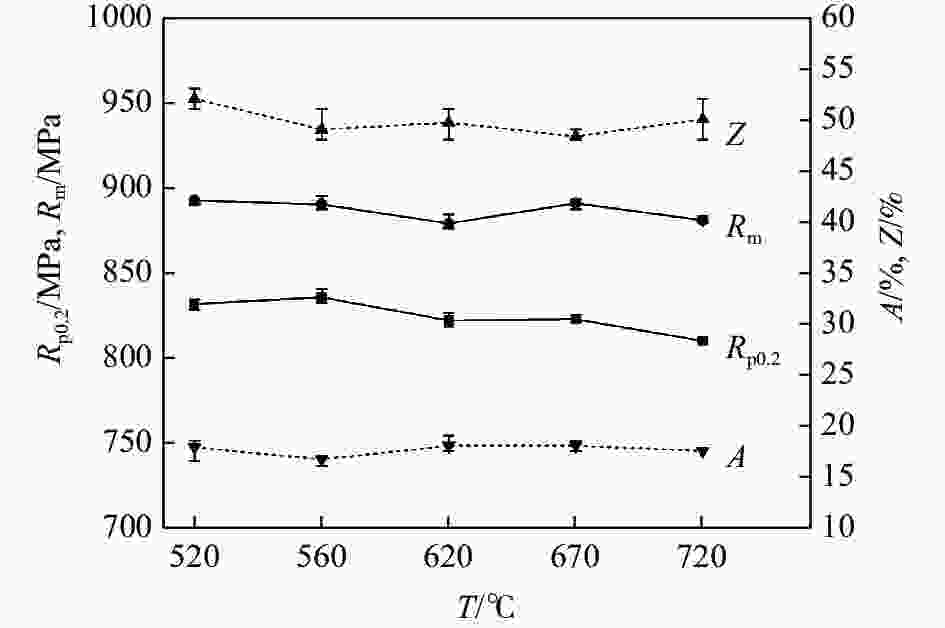
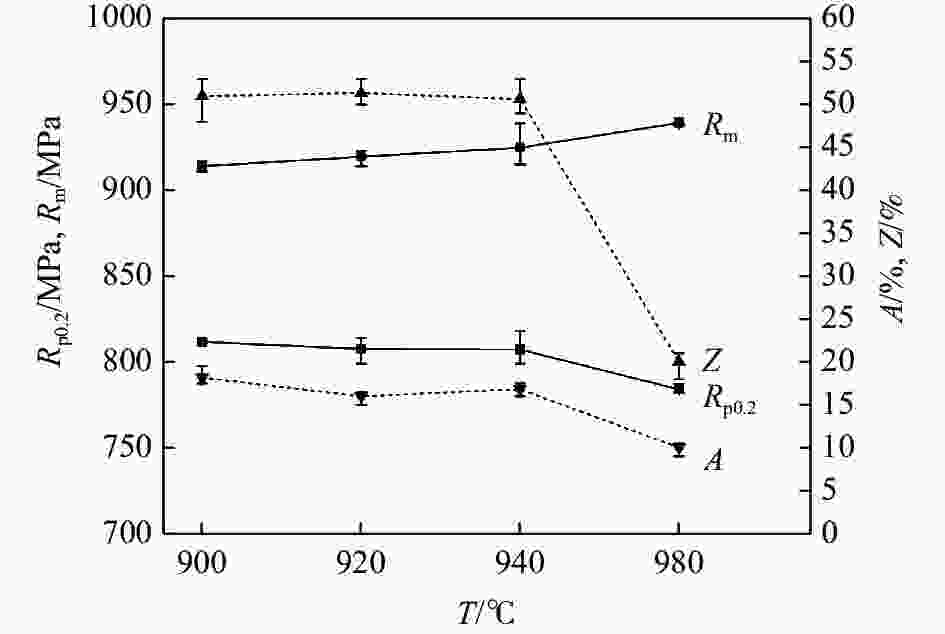
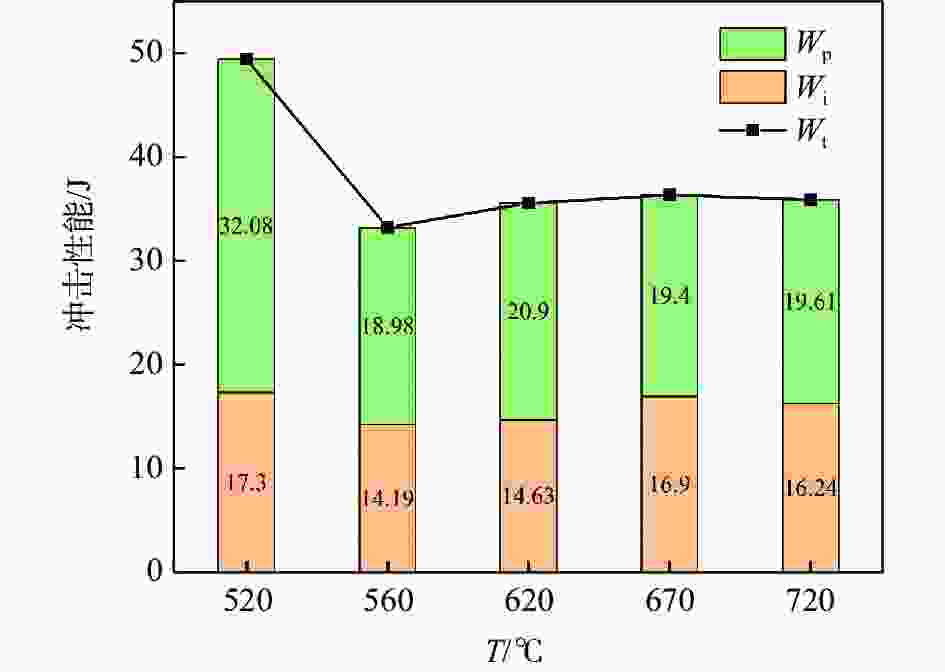
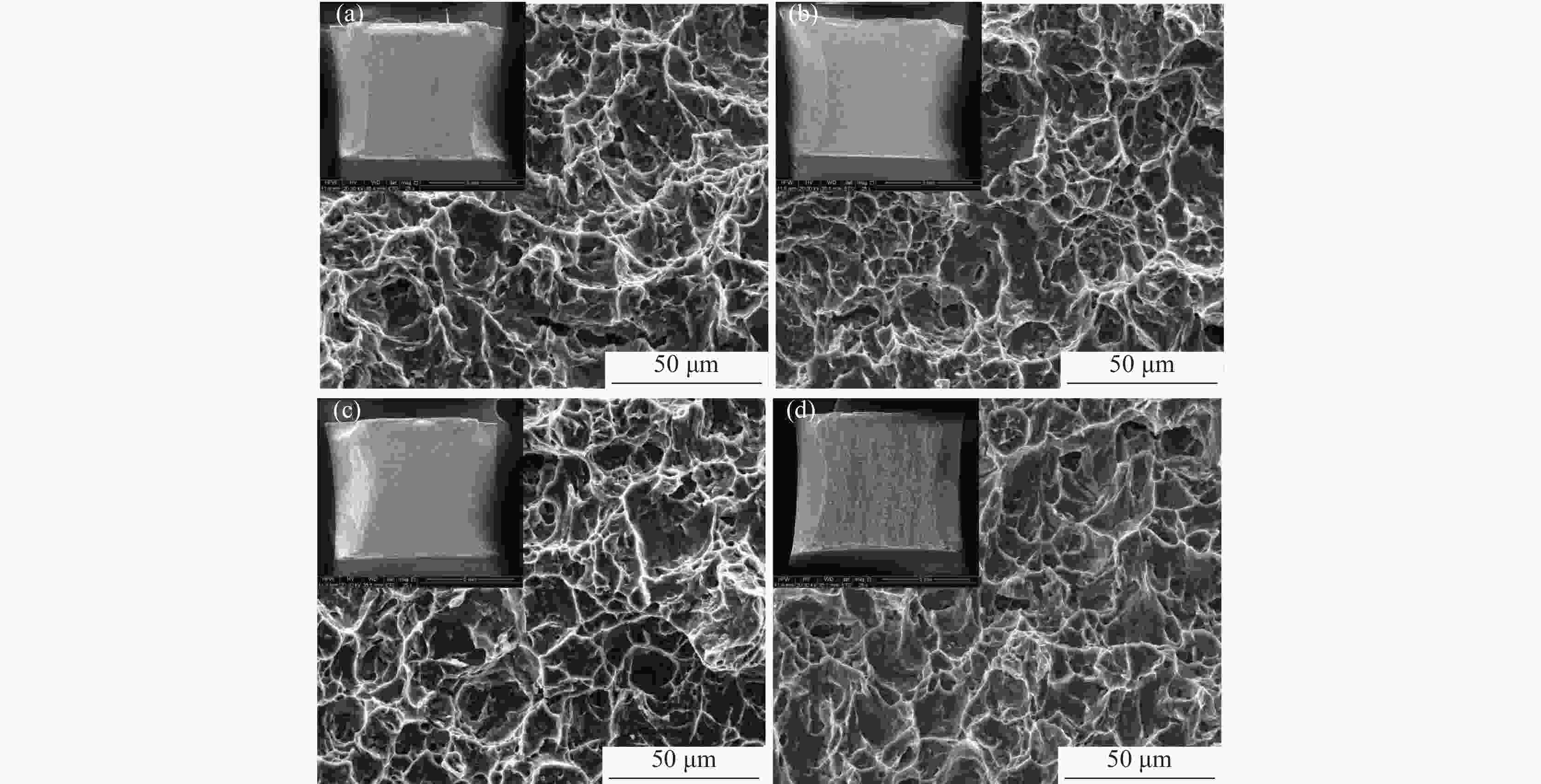
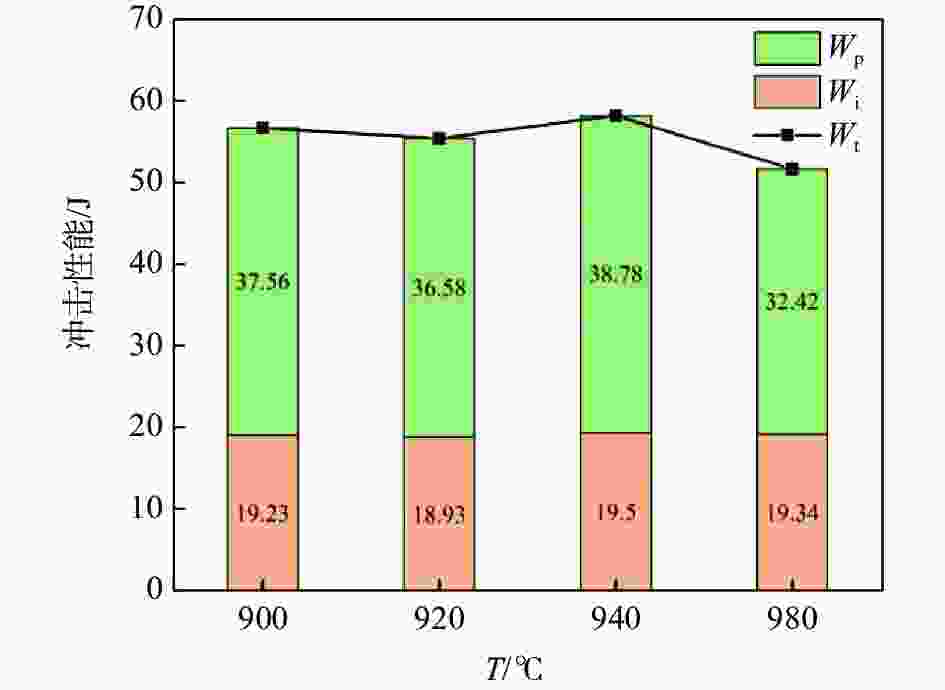
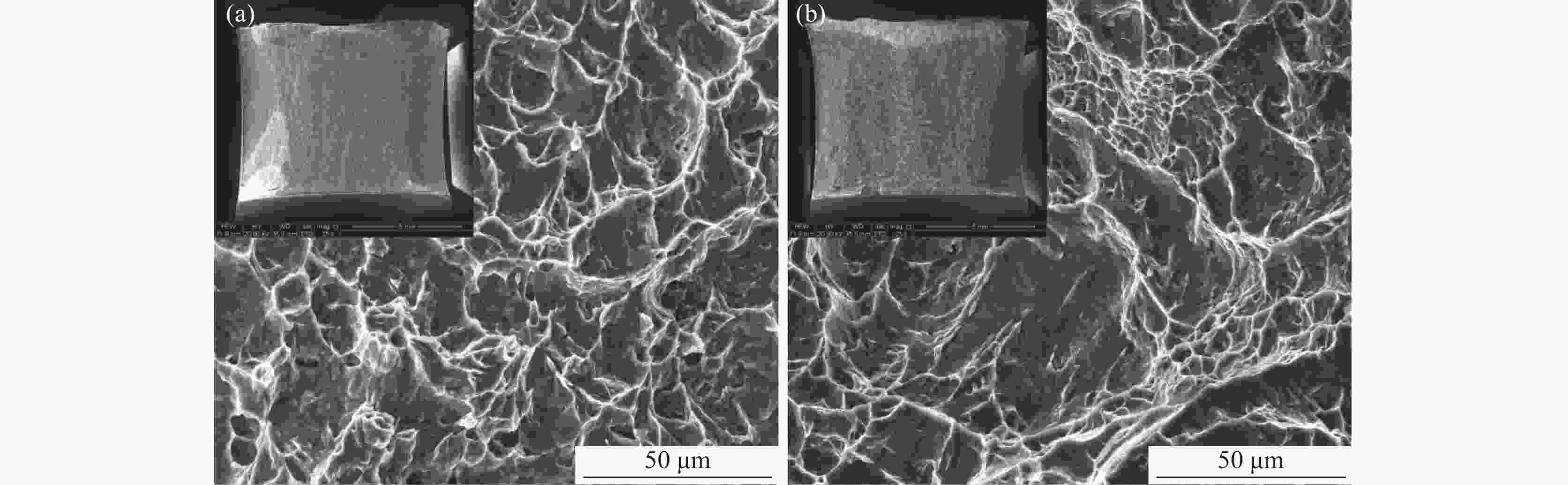
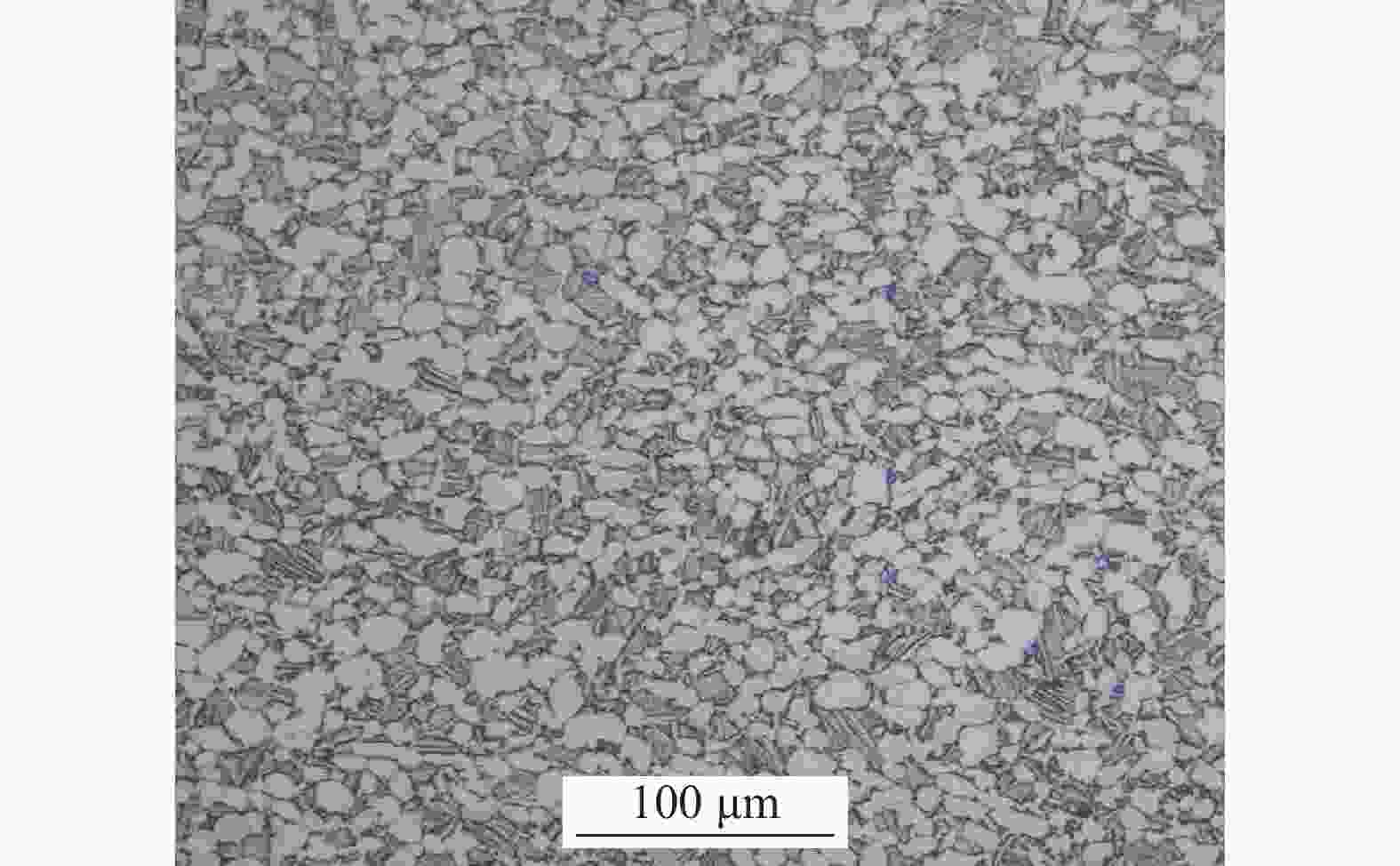
摘要: 采用光学金相显微镜(OM)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、室温拉伸、夏比冲击试验研究了后处理工艺对退火态TC4 ELI合金显微组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明,退火态TC4 ELI合金经520~720 ℃时效处理后发生“双态→等轴”的逆转变现象,强度呈现先升高后降低的趋势;冲击功在560 ℃降至最低后随温度升高稍有提高;时效α相的出现是冲击韧性劣化的主要原因,α2相析出的影响则较小。620 ℃时效态TC4 ELI合金经高温处理后,强度略微升高;温度升至β相区时,组织粗化造成屈服强度突降,晶界α相的出现引起塑性突降;高温处理后,时效α相消失,冲击功得到较大程度的恢复。
-
关键词:
- 退火态TC4 ELI合金 /
- 后处理 /
- 显微组织 /
- 强度 /
- 冲击韧性
Abstract: The effects of post heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of annealed TC4 ELI alloy investigated by optical microscopy (OM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), tensile and Charpy impact test at room temperature. The results show that the "bimodal → equiaxed" reverse transformation occurs in the annealed TC4 ELI alloy after aging at 520-720 ℃, and the strength increases first and then decreases. The impact toughness of the annealed TC4 ELI alloy decreases to the lowest value at 560 ℃, then increases slightly with the increase of temperature. The appearance of aging α phase is the main reason for the deterioration of impact toughness, while the precipitation of α2 phase has little effect. The strength of TC4 ELI alloy aged at 620 ℃ increases slightly after high temperature treatment. When the temperature rises to the β phase region, the coarsening of the microstructure causes a sudden drop in yield strength, and the appearance of the α phase at the grain boundary causes a sudden drop in plasticity. After high temperature treatment, the aging α phase disappears, and the impact toughness is recovered to a greater extent.-
Key words:
- annealed TC4 ELI titanium alloy /
- post heat treatment /
- microstructure /
- strength /
- impact toughness
-
表 1 TC4 ELI合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of TC4 ELI alloy plate %
Ti Al V N H C O Bal. 6.29 4.17 <0.0076 <0.001 <0.008 0.094 表 2 退火态TC4 ELI合金板材的力学性能
Table 2. 2 Mechanical properties of as annealed TC4 ELI alloy plate
Rp0.2/MPa Rm/MPa A/% Z/% aKV2/J 805 879 15.0 50 61 -
[1] Ma Yunyi, Wu Yousheng, Fang Zhigang. Ship equipment and materials[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2016. (马运义, 吴有生, 方志刚. 船舶装备与材料[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2016.Ma Yunyi, Wu Yousheng, Fang Zhigang. Ship equipment and materials[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2016. [2] Hai Minna, Huang Fan, Wang Yongmei. Brief analysis of the application of titanium and titanium alloy in marineequipment[J]. Metal World, 2021(5):16−21. (海敏娜, 黄帆, 王永梅. 浅析钛及钛合金在海洋装备上的应用[J]. 金属世界, 2021(5):16−21.Hai Minna, Huang Fan, Wang Yongmei. Brief analysis of the application of titanium and titanium alloy in marineequipment[J]. Metal World, 2021(5): 16−21. [3] Kriedt F A. Application of titanium for shipboard seawater piping systems[R]. Norfolk: Computer Sciences Corporation, 2009. [4] Mountford J A, Scaturro M R. Titanium – attributes, benefits, use, and applications in the marine market[J]. Journal of Ship Production, 2009,26(1):13−19. [5] Boyer R R, Williams J C. Developments in research and applications in the titanium industry in the USA[C]//Ti-2011 Proceedings of 12th World Conference on Titanium. Beijing: Science Press, 2011. [6] Schutz R W, Scaturro M R. An overview of current and candidate titanium alloy applications on US navy surface ships[J]. Naval Engineers Journal, 1991,103(3):175−191. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-3584.1991.tb00948.x [7] Yin Yanchao, Zhang Shuaifeng, Xu Yali, et al. Influence of pre-strain on deformation behavior of TC4 ELI titanium alloy[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2023,38(1):66−72. (尹艳超, 张帅锋, 许亚利, 等. 预应变对TC4ELI钛合金变形行为的影响[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2023,38(1):66−72.Yin Yanchao, Zhang Shuaifeng, Xu Yali, et al. Influence of pre-strain on deformation behavior of TC4 ELI titanium alloy[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2023, 38(1): 66−72. [8] Rae W, Rahimi S. Effect of stress relaxation on the evolution of residual stress during heat treatment of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2020,321(4):11001. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/202032111001 [9] Huang Zhen, Yuan Wuhua, Zhu Jiajia. Low temperature stress relaxation and morphology evolution of Ti-6.5Al-2Zr-lMo-1V titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2002,51(1):83−91. [10] Yin Yanchao, Fu Chengxue, Sun Zhijie, et al. Effects of cyclic treatment at 600 ℃ on microstructure and mechanical properties of TA31 and TC4 ELI titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2024(15):77−82. (尹艳超, 符成学, 孙志杰, 等. 600 ℃循环热处理对TA31和TC4 ELI钛合金显微结构及力学性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2024(15):77−82.Yin Yanchao, Fu Chengxue, Sun Zhijie, et al. Effects of cyclic treatment at 600 ℃ on microstructure and mechanical properties of TA31 and TC4 ELI titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2024(15): 77−82. [11] Yin Yanchao, Li Longteng, Lü Yifang, et al. Effect of post treatment on the microstructure and properties of as-annealed Ti75 alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(5):68−75. (尹艳超, 李龙腾, 吕逸帆, 等. 后处理对退火态Ti75合金显微组织与性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(5):68−75.Yin Yanchao, Li Longteng, Lü Yifang, et al. Effect of post treatment on the microstructure and properties of as-annealed Ti75 alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(5): 68−75. [12] Yin Yanchao, Liu Jia, Zhang Shuaifeng, et al. Influence of aging treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti75 alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2023,40(22):21−26. (尹艳超, 刘甲, 张帅锋, 等. 时效工艺对Ti75合金显微组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 钛工业进展, 2023,40(22):21−26.Yin Yanchao, Liu Jia, Zhang Shuaifeng, et al. Influence of aging treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti75 alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2023, 40(22): 21−26. [13] Lütjering G. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α+β) titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1998,A243:32−45. [14] Gerd L, James C Williams. Titanium[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2007. [15] Cao S, Lim C, Hinton B, et al. Effects of microtexture and Ti3Al (α2) precipitates on stress-corrosion cracking properties of a Ti-8Al-1Mo-1V alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2017,116:22−33. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.12.012 [16] Liu Z, Welsch G. Effects of oxygen and heat treatment on the mechanical properties of alpha and beta titanium alloys[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1988,19(3):527−542. doi: 10.1007/BF02649267 [17] Conrad H. On the strengthening of titanium by aluminum[J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1973,7(5):509−512. doi: 10.1016/0036-9748(73)90104-X [18] Lütjering G. Property optimization through microstructural control in titanium and aluminum alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1999,A263:117−126. [19] Welsch G, Bunk W. Deformation modes of the α-phase of Ti-6Al-4V as a function of oxygen concentration and aging temperature[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1982,13(5):889−899. doi: 10.1007/BF02642403 [20] Huang Shixing, Zhao Qingyang, Zhao Yongqing, et al. Toughness effects of Mo and Nb addition on impact toughness and crack resistance of titanium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science Technology, 2021,79:147−164. [21] Yu Hui, Cao Shuo, Sabry S Youssef, et al. Generalized stacking fault energies and critical resolved shear stresses of random α-Ti-Al alloys from first - principles calculations[J]. Journal Alloys and Compounds, 2021,850:156314. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156314 [22] Wang Hai, Wei Fenrong, Deng Jiabin, et al. Effect factors for yield ratio of titanium alloy and discussion of function mechanism[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2016,45(22):109−111,115. (王海, 魏芬绒, 邓家彬, 等. 影响钛合金屈强比的因素及作用机理探讨[J]. 热加工工艺, 2016,45(22):109−111,115.Wang Hai, Wei Fenrong, Deng Jiabin, et al. Effect factors for yield ratio of titanium alloy and discussion of function mechanism[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2016, 45(22): 109−111,115. [23] AmbardA, Gue´tazL, Louchet F, et al. Role of interphases in the deformation mechanisms of an α/β titanium alloy at 20 K[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001,319:404−408. [24] Niinomi M, Kobayashi T. Toughness and microstructural factors of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1988,100:45−55. doi: 10.1016/0025-5416(88)90238-8 [25] Niinomi M, Kobayashi T. Fracture characteristics analysis related to the microstructures in titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1996,A212:16−24. [26] Freed C N, Goode R J. Relationship between fracture toughness and estimated plastic zone size in steel, titanium, and aluminum alloys[R]. Washingtou: Naval Research Laboratory, 1969. [27] Lunt D, Busolo T, Xu X, et al. Effect of nanoscale α2 precipitation on strain localization in a two-phase Ti-alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017,129:72−82. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2017.02.068 [28] Sabry S Youssef, Zheng Xiaodong, Qi Min, et al. Effects of Al content and α2 precipitation on the fatigue crack growth behaviors of binary Ti-Al alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2021,A819:141513. [29] Sabry S Youssef, Zheng Xiaodong, Huang Sensen, et al. Precipitation behavior of α2 phase and its influence on mechanical properties of binary Ti-8Al alloy[J]. Journal Alloys and Compounds, 2021,871:159577. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159577 [30] Christophe Buirettea, Julitte Hueza, Nathalie Geyb, et al. Study of crack propagation mechanisms during charpy impact toughness tests on both equiaxed and lamellar microstructures of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2014,A618:546−557. [31] Xu Jianwei, Zeng Weidong, Zhao Yawei, et al. Effect of microstructure evolution of the lamellar alpha on impact toughness in a two-phase titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2016,A676:434−440. [32] Lei Lei, Zhao Yongqing, Zhao Qinyang, et al. Impact toughness and deformation modes of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with different microstructures[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2021,A801:140411. -




 下载:
下载: