Distribution behavior of chromium and sulfur elements during co-treatment of vanadium extraction tailings and red mud
-
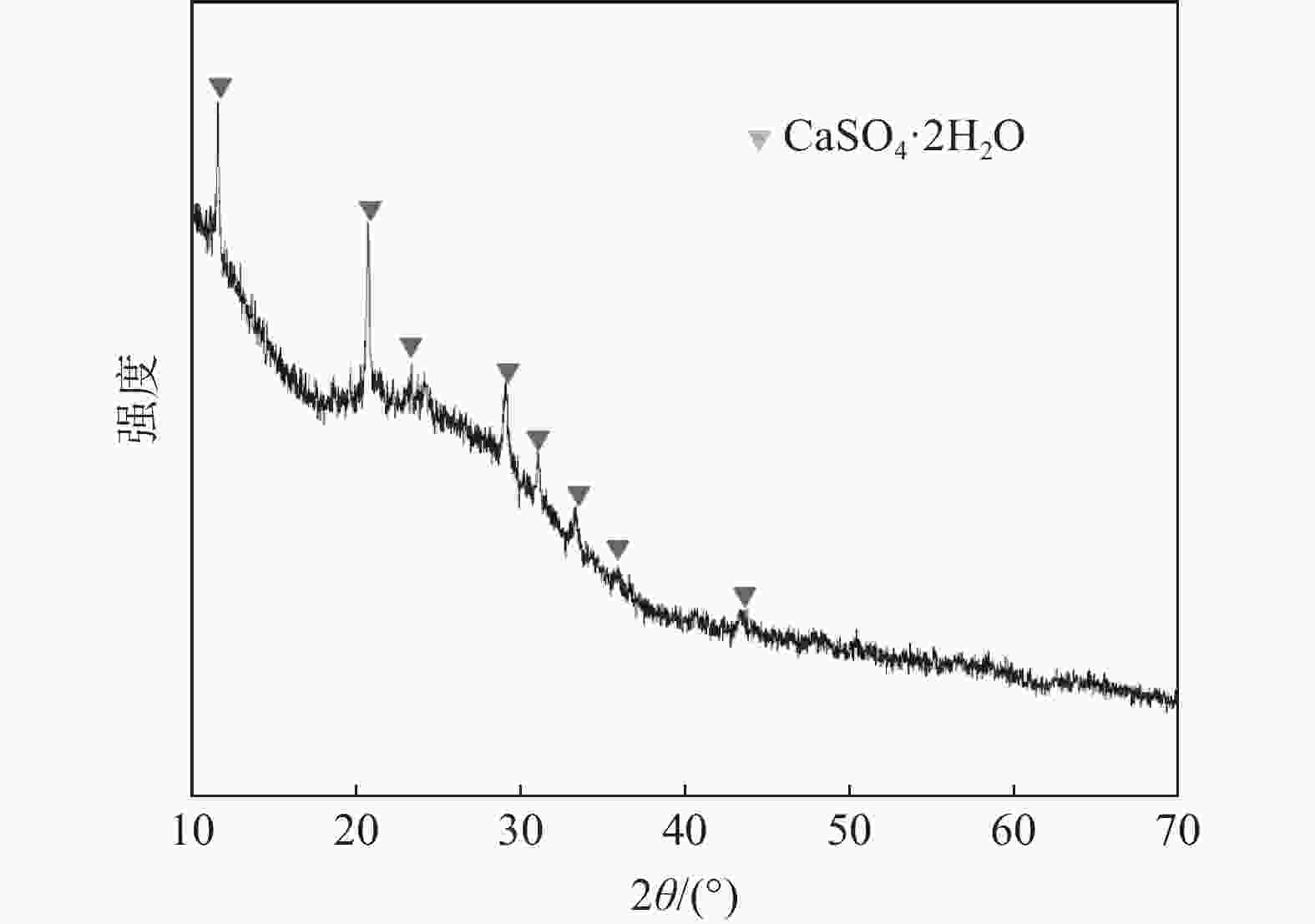
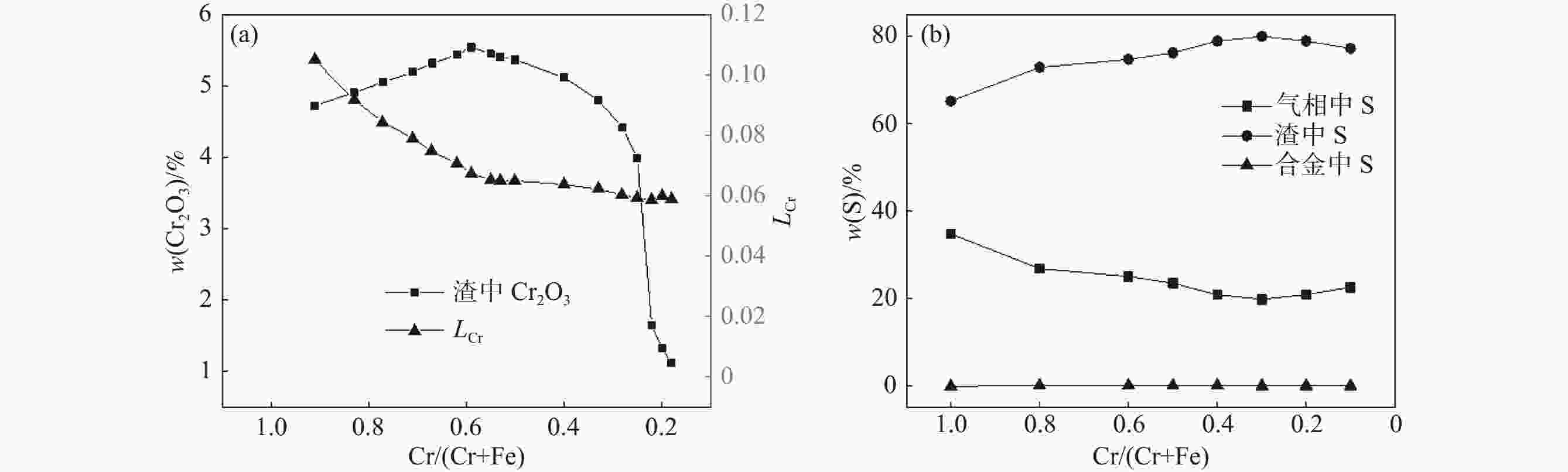
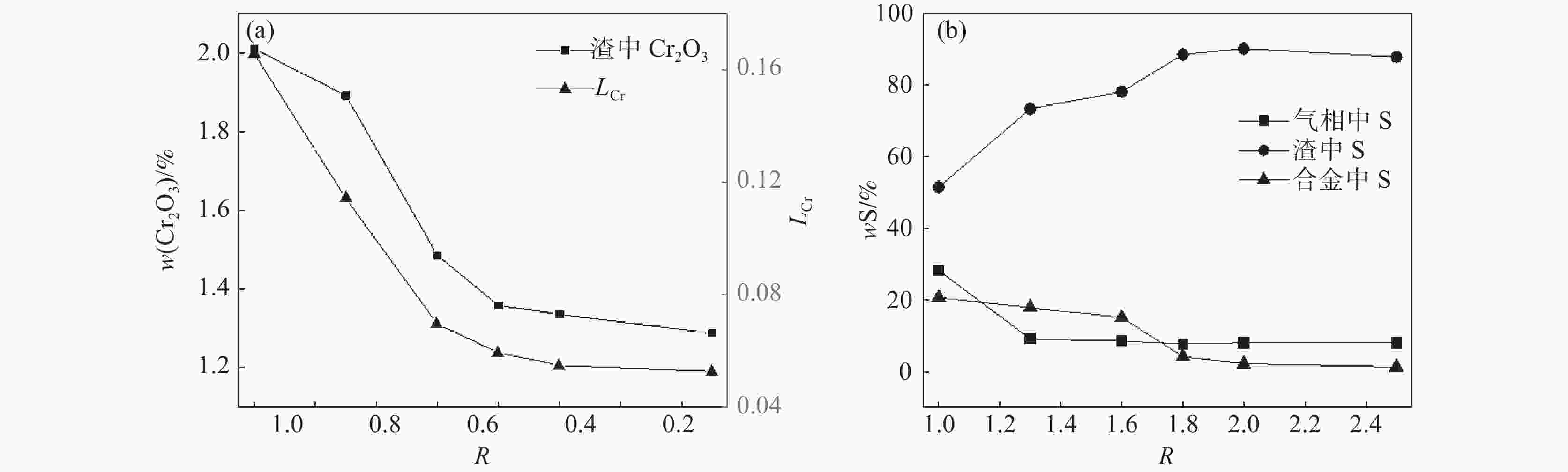
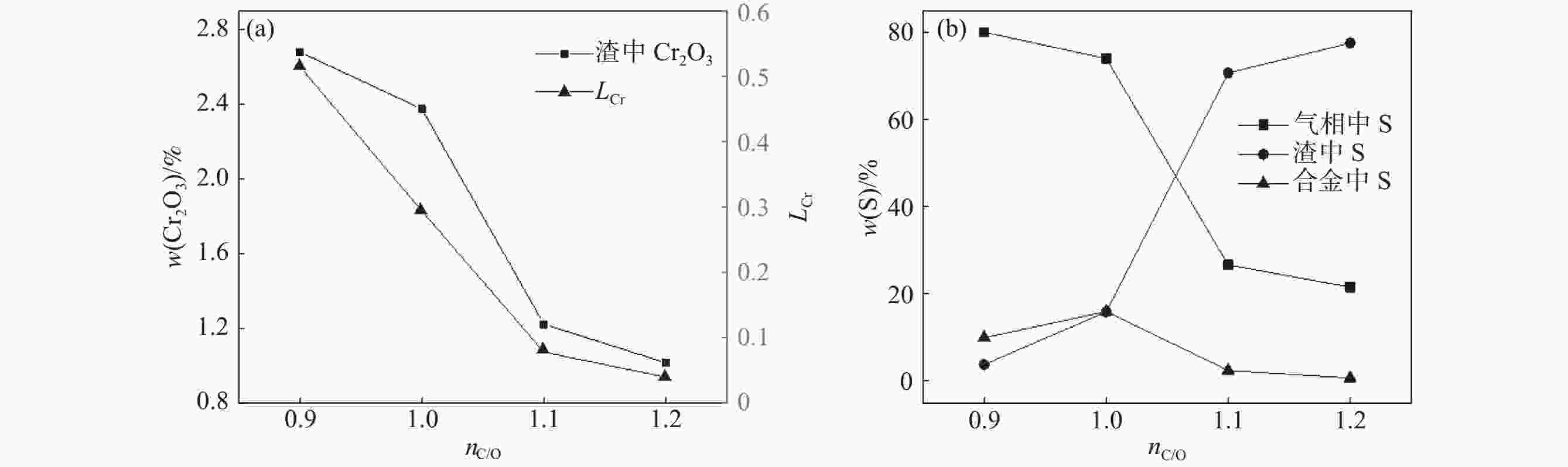
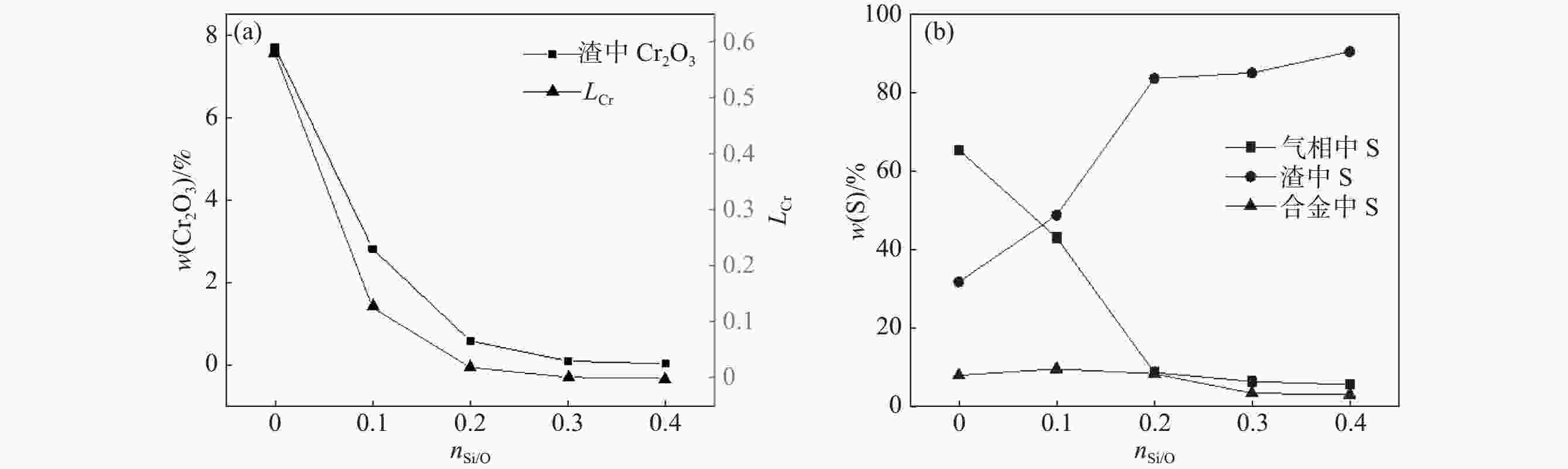
摘要: 钒渣钠化焙烧-水浸提钒过程会产生含有30%~40%Cr2O3的提钒尾渣,形成年堆积百万吨固废。通过加入高铁赤泥协同还原提钒尾渣,赤泥中的Fe2O3在低于铬氧化物初始还原温度下已经被C还原,促使铬还原反应快速进行,从而提升Cr的回收效率。使用FactSage热力学软件对整个反应体系进行模拟,计算了原料铬铁比、炉渣碱度和配C/Si量对铬、硫元素分配行为的影响,得到原料适宜的铬铁比是0.18,炉渣碱度是1.8,配C量nC/O=1.1,配Si量nSi/O=0.2。该研究为含铬提钒尾渣和高铁赤泥的资源化处理和增值化应用提供了一种新的可行性方案。Abstract: The process of blast furnace iron-oxygen top blowing converter blowing vanadium extraction-vanadium slag followed by sodium roasting-water leaching and vanadium extraction will form vanadium tailings containing 30%~40% Cr2O3, forming an annual accumulation of millions of tons of solid waste. In this study, the vanadium tailings were extracted by synergistic reduction of high-iron red mud, and the Fe2O3 in the red mud was reduced by carbon at a temperature lower than the initial reduction temperature of chromium oxide, which promoted the rapid progress of chromium reduction and improved the recovery efficiency of Cr. The whole reaction system was simulated by FactSage thermodynamic software, and the effects of the chromium iron ratio, slag alkalinity and C/Si content on the partition behavior of chromium and sulfur were calculated. The suitable Cr/Fe ratio of the raw materials was 0.18, the alkalinity of the slag was 1.8, the amount of carbon was nC/O = 1.1, and the amount of Si was nSi/O = 0.2. This study provides a new feasible scheme for the resource treatment and value-added application of Cr-containing vanadium tailings and high-iron red mud.
-
表 1 含铬提钒尾渣的主要化学成分
Table 1. The main chemical composition of vanadium tailings containing chromium
% Na2O SiO2 CaO V2O5 Cr2O3 SO3 其他 6.27 21.92 1.27 4.35 30.5 13.85 21.84 表 2 高铁赤泥的主要化学成分
Table 2. The main chemical composition of high-iron red mud %
Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 TiO2 CaO MgO Na2O 其他 7.23 3.46 76.05 2.90 2.53 0.44 0.83 6.56 -
[1] Xie Zhicheng, Hu Bing, Hu Peiwei. Research on new process of efficient and comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(5):14−21. (谢志诚, 胡兵, 胡佩伟. 钒钛磁铁矿高效综合利用新工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(5):14−21.Xie Zhicheng, Hu Bing, Hu Peiwei. Research on new process of efficient and comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(5): 14−21. [2] Wang Shuai, Guo Yufeng, Jiang Tao, et al. Status quo and industrial development direction of comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016,26(10):40−44. (王帅, 郭宇峰, 姜涛, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿综合利用现状及工业化发展方向[J]. 中国冶金, 2016,26(10):40−44.Wang Shuai, Guo Yufeng, Jiang Tao, et al. Status quo and industrial development direction of comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016, 26(10): 40−44. [3] Xiang J Y, Huang Q Y, Lv X W, et al. Multistage utilization process for the gradient-recovery of V, Fe, and Ti from vanadium-bearing converter slag[J]. J. Hazard Mater., 2017,336:1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.04.060 [4] Yue H R, Xue X X. Generated compounds at the V-slag/CaO diffusion surface and diffusion characteristics of V and Ca in calcium vanadate[J]. J. Hazard Mater., 2020,393:122368. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122368 [5] Wu K H, Wang Y R, Wang X R, et al. Co-extraction of vanadium and chromium from high chromium containing vana-dium slag by low-pressure liquid phase oxidation method[J]. J. Clean. Prod., 2018,203:873−884. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.288 [6] Wang G, Lin M M, Diao J, et al. Novel strategy for green comprehensive utilization of vanadium slag with high-content chromium[J]. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2019,7:18133−18141. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05226 [7] Li X S, Xie B, Wang G E, et al. Oxidation process of low-grade vanadium slag in presence of Na2CO3[J]. T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2011,121:1860−1867. [8] Li H Y, Fang H X, Wang K, et al. Asynchronous extraction of vanadium and chromium from vanadium slag by stepwise sodium roasting-water leaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015,156:124−135. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2015.06.003 [9] Jiang T, Wen J, Zhou M, et al. Phase evolutions, microstructure and reaction mechanism during calcification roasting of high chromium vanadium slag[J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2018,742:402−412. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.201 [10] Teng A J, Xue X X. A novel roasting process to extract vanadium and chromium from high chromium vanadium slag using a NaOH-NaNO3 binary system[J]. J. Hazard Mater., 2019,379:120805. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120805 [11] Li Fangfang, Wen Jing, Yu Tangxia, et al. Extraction of vanadium tailings by sodium and synergistic acid leaching of vanadium[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, 2023(11):1−21. (李芳芳, 温婧, 余唐霞, 等. 钠化提钒尾渣协同酸浸提钒[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2023(11):1−21.Li Fangfang, Wen Jing, Yu Tangxia, et al. Extraction of vanadium tailings by sodium and synergistic acid leaching of vanadium[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, 2023(11): 1−21. [12] Hou Jing, Xu Zhong, Wu Enhui, et al. Preparation of thermal collector coatings from vanadium waste slag extraction under the background of double carbon and its properties[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, 2022(2):40−44. (侯静, 徐众, 吴恩辉,等. 双碳背景下提钒弃渣制备集热涂层及其性能[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(2):40−44.Hou Jing, Xu Zhong, Wu Enhui, et al. Preparation of thermal collector coatings from vanadium waste slag extraction under the background of double carbon and its properties[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, 2022(2): 40−44. [13] Hou Jing, Wu Enhui, Li Jun. Research status and progress of comprehensive utilization of vanadium extraction tailings[J]. Mineral Protection and Utilization, 2017(6):103−108. (侯静, 吴恩辉, 李军. 提钒尾渣的综合利用研究现状及进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2017(6):103−108.Hou Jing, Wu Enhui, Li Jun. Research status and progress of comprehensive utilization of vanadium extraction tailings[J]. Mineral Protection and Utilization, 2017(6): 103−108. [14] Liu Jinsheng, Ding Xueyong, Xue Xiangxin, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of vanadium tailings[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021,56(7):152−160. (刘金生, 丁学勇, 薛向欣, 等. 提钒尾渣资源化综合利用的研究进展[J]. 钢铁, 2021,56(7):152−160.Liu Jinsheng, Ding Xueyong, Xue Xiangxin, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of vanadium tailings[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 56(7): 152−160. [15] Wang G, Diao J, Liu L, et al. Highly efficient utilization of hazardous vanadium extraction tailings containing high chromium concentrations by carbothermic reduction[J]. J. Clean. Prod., 2019,237:117832. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117832 [16] Xiang J Y, Huang Q Y, Lv W, et al. Recovery of tailings from the vanadium extraction process by carbothermic reduction method: Thermodynamic, experimental and hazardous potential assessment[J]. J. Hazard Mater., 2018,357:128−137. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.05.064 [17] Xu Zhengzhen, Liang Jinglong, Li Hui, et al. Research status and prospect of vanadium recovery in vanadium-containing wastes[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, 2020(3):8−13. (徐正震, 梁精龙, 李慧, 等. 含钒废弃物中钒的回收研究现状及展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(3):8−13.Xu Zhengzhen, Liang Jinglong, Li Hui, et al. Research status and prospect of vanadium recovery in vanadium-containing wastes[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, 2020(3): 8−13. [18] Yu Xiong, Sun Lifeng, Wang Hesong, et al. Experiments on the carbon-thermal reduction process of vanadium tailings[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2015,38(2):123−129. (喻雄, 孙丽枫, 王鹤松, 等. 提钒尾渣碳热还原过程实验[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2015,38(2):123−129.Yu Xiong, Sun Lifeng, Wang Hesong, et al. Experiments on the carbon-thermal reduction process of vanadium tailings[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2015, 38(2): 123−129. [19] Wang Weibin, Zhang Ziyang, Liu Haitao, et al. Thermodynamic analysis and properties of iron-vanadium alloys prepared by direct reduction of vanadium slag[J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2023,23(5):763−770. (王伟彬, 张子阳, 刘海涛, 等. 直接还原钒渣制备铁钒合金热力学分析及性能[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023,23(5):763−770.Wang Weibin, Zhang Ziyang, Liu Haitao, et al. Thermodynamic analysis and properties of iron-vanadium alloys prepared by direct reduction of vanadium slag[J]. Journal of Process Engineering, 2023, 23(5): 763−770. [20] Wu Tuo. Separation, recovery and reduction reaction endpoint control of chromium in typical solid waste in stainless steel industry[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2019. (吴拓. 不锈钢工业典型固废中铬的分离回收与还原反应终点控制[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2019.Wu Tuo. Separation, recovery and reduction reaction endpoint control of chromium in typical solid waste in stainless steel industry[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2019. [21] Weng Qingqiang, Zhang Wei. Feasibility analysis of secondary vanadium tailings extracted by blast furnace digestion[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, 2012(3):59−61. (翁庆强, 张炜. 高炉消化提钒二次尾渣可行性分析[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2012(3):59−61.Weng Qingqiang, Zhang Wei. Feasibility analysis of secondary vanadium tailings extracted by blast furnace digestion[J]. Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, 2012(3): 59−61. [22] Keskinkilic E, Geveci A, Topkaya Y A. Improving the ladle desulphurization characteristics of ladle furnace slags of a low sulphur steel[J]. Can Metall Quarte., 2013,46:391−396. [23] Hu X F, Teng L D, Wang H J, et al. Carbothermic reduction of synthetic chromite with/without the addition of iron powder[J]. ISIJ Int., 2016,56:2147−2155. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2016-337 [24] Morita K, Sano N. Thermodynamic properties of the CaO-SiO[subscript 2]-CrOx slags for the decarburization of stainless steels[C]//58th Electric Furnace Conference and 17th Process Technology Conference Proceedings. Orlando, Florida. Iron and Steel Society, 2000: 1097−1108. -




 下载:
下载: