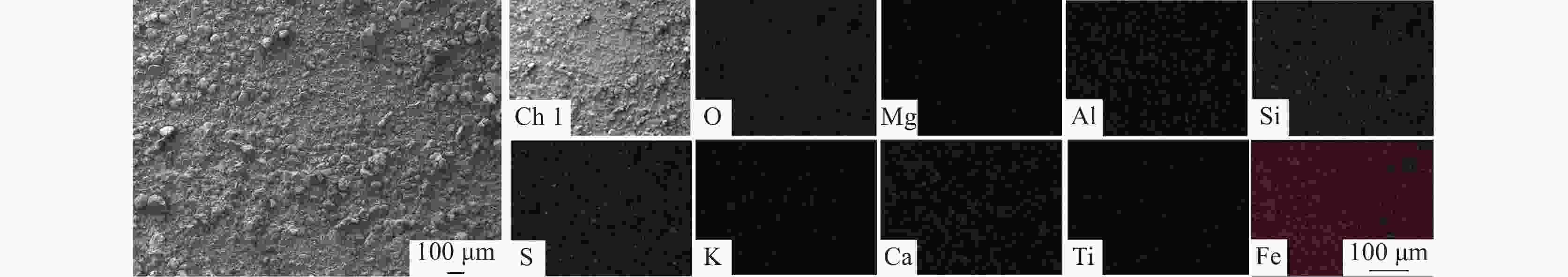
Optimization of reduction leaching conditions for pyrite cinder using titanium dioxide waste acid by response surface methodology
-
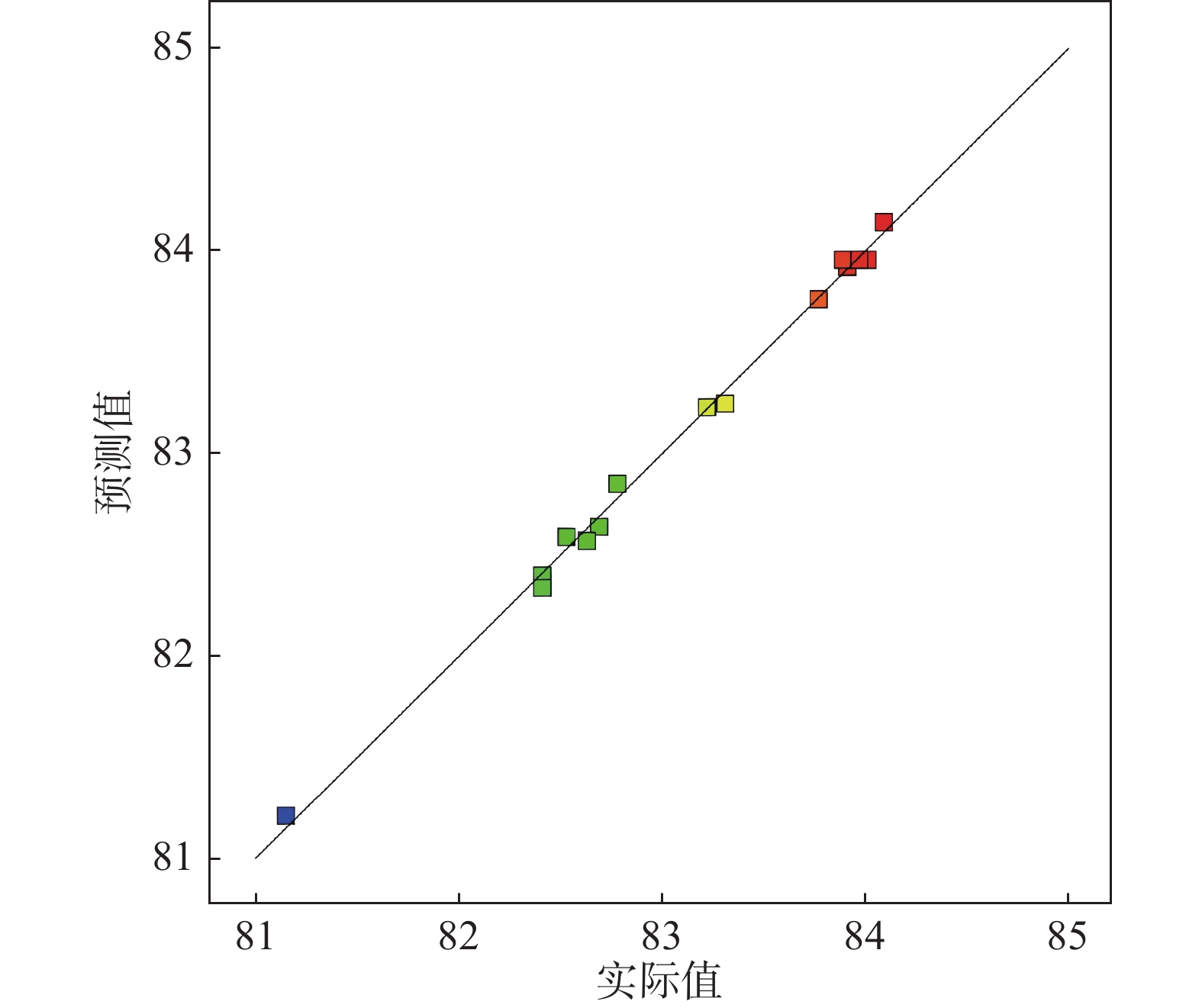
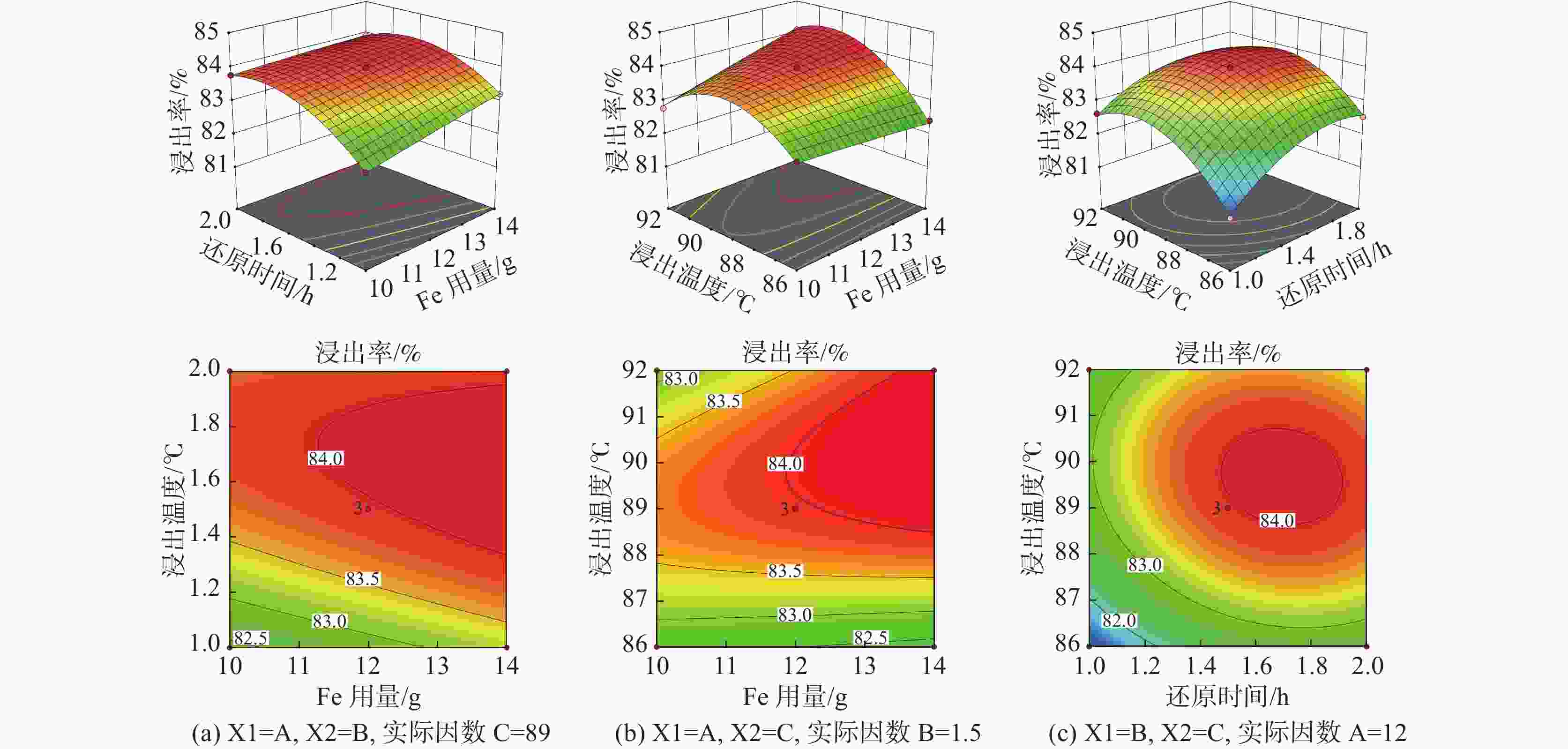
摘要: 采用Box-Behnken设计的响应面法,选取铁粉用量、还原时间和浸出温度三个变量,研究并优化了钛白废酸还原浸出硫酸烧渣的浸出条件。建立了拟合效果较好的浸出条件的预测模型,以预测浸出率或优化浸出变量值。回归方程模型显著可靠,相关系数R2为0.9961。浸出条件对反应平衡、浸出物溶解度及反应体系性质等有重要影响,其中铁粉用量与浸出温度的协同交互作用影响最大。验证试验表明,在铁粉用量10.347 g、还原时间2 h、浸出温度88 ℃的最佳条件下,浸出率可达83.63%以上。Abstract: The reduction leaching conditions for pyrite cinder leaching by titanium dioxide waste acid were investigated and optimized, using the response surface methodology designed by Box-Behnken method, and the iron powder dosage, reduction time, and leaching temperature were selected as the three variables. The established predictive model for leaching conditions was with good fitting results to predict leaching yields or optimize leaching variable values. The regression equation model was significantly reliable, with a correlation coefficient R2 of 0.9961. The leaching conditions had important effects on the leaching reaction equilibrium, solubility of leached materials, and properties of reaction systems, among which the synergistic interaction between iron powder dosage and leaching temperature had the greatest impact. The verification experiments confirmed that the leaching yield values could be achieved over 83.63% under the optimal conditions, with the iron powder dosage of 10.347 g, reduction time of 2 h and leaching temperature of 88 ℃.
-
表 1 优化浸出条件的BBD试验因素和水平
Table 1. Factors and levels of BBD method for the optimized leaching conditions
水平 因素 还原铁粉用量/g
(X1)还原时间 /h
(X2)浸出温度/ ℃
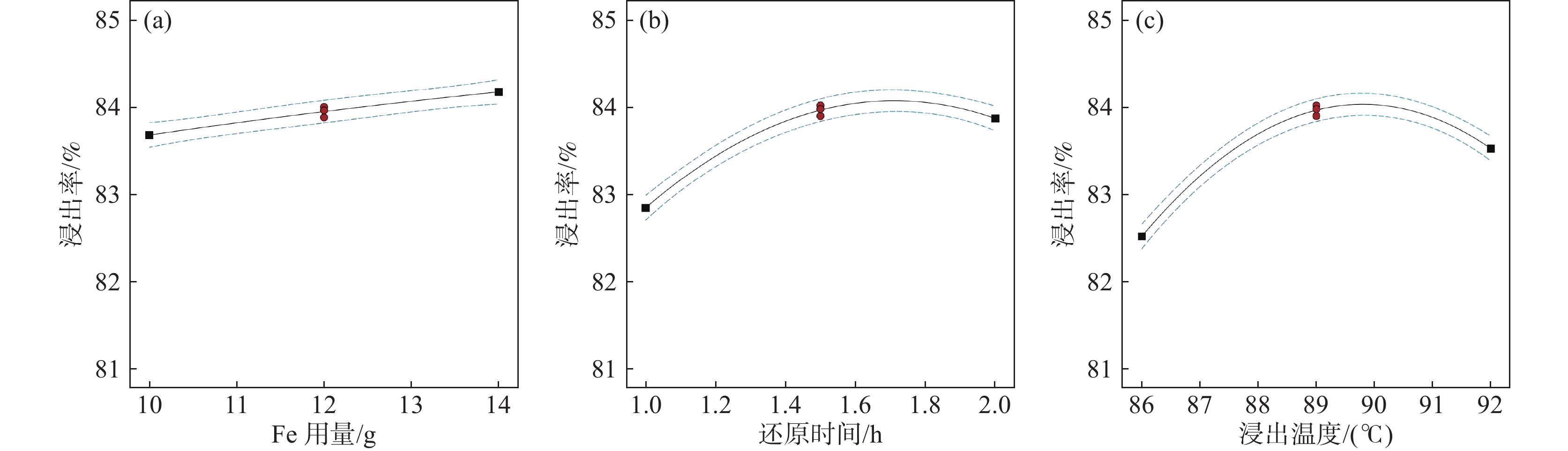
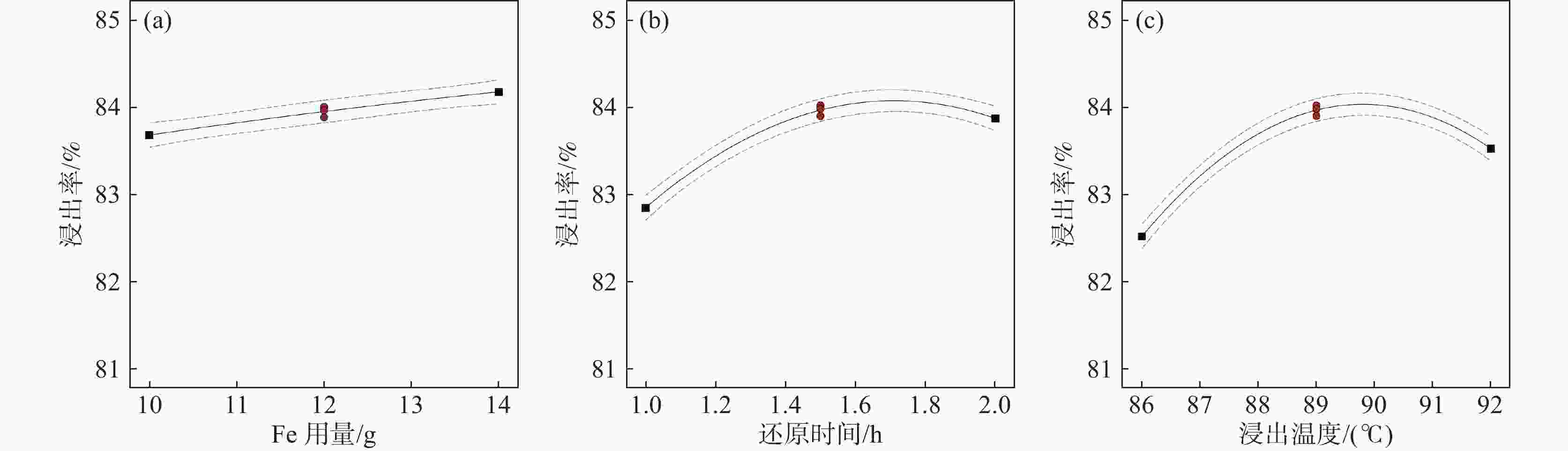
(X3)-1 10 1 86 0 12 1.5 89 1 14 2 92 表 2 烧渣浸出率的试验设计矩阵、试验结果及预测值
Table 2. Experimental design matrix, experimental leaching results and predicted values for pyrite cinder
序号 X1/g X2/ h X3/ ℃ Y 试验值/% Y 预测值/% 1 14 1.0 89 83.22 83.23 2 12 1.5 89 84.01 83.96 3 12 1.0 92 82.63 82.57 4 10 1.5 86 82.69 82.64 5 10 1.0 89 82.41 82.40 6 14 1.5 86 82.41 82.34 7 12 2.0 86 82.53 82.59 8 12 1.5 89 83.89 83.96 9 10 2.0 89 83.77 83.76 10 12 1.0 86 81.15 81.21 11 14 1.5 92 84.09 84.14 12 14 2.0 89 83.91 83.92 13 10 1.5 92 82.78 82.85 14 12 1.5 89 83.97 83.96 15 12 2.0 92 83.31 83.25 表 3 硫铁矿烧渣浸出率的响应面试验结果方差分析
Table 3. Variance analysis of response surface experimental results of the leaching yield
平方和 自由度(df ) 均方 F值 P值 显著 模型 9.88 9 1.1 143.35 < 0.0001 ** X1 0.49 1 0.49 63.99 0.0005 ** X2 2.11 1 2.11 275.71 < 0.0001 ** X3 2.03 1 2.03 265.09 < 0.0001 ** X1 X2 0.1122 1 0.1122 14.65 0.0123 * X1 X3 0.632 1 0.632 82.53 0.0003 ** X2 X3 0.1225 1 0.1225 16 0.0103 * X1 ² 0.0016 1 0.0016 0.2093 0.6665 X2² 1.37 1 1.37 178.42 < 0.0001 ** X3 ² 3.29 1 3.29 429.04 < 0.0001 ** 残差 0.0383 5 0.0077 失拟合 0.0308 3 0.0103 2.75 0.2777 纯误差 0.0075 2 0.0037 总计 9.92 14 注:R²=0.9961, R 2 Adj =0.9892, R 2 Predj =0.9486。C.V= 0.1053%。
*表示对结果有显著的影响(P < 0.05);**表示对结果有非常显著的影响(P < 0.01)。表 4 验证测试结果
Table 4. Verification test results
编号 铁粉加量/g 还原时间/h 浸出温度/ ℃ 浸出率/% 预测优化值 10.347 2 87.98 83.673 16 10.347 2 88 83.64 17 10.347 2 88 83.66 18 10.347 2 88 83.63 -
[1] Wang Quanyong, Xu Xiudong, Wu Yongji, et al. Preparation of battery-grade iron phosphate from iron sulfide slag[J]. Renewable Resources and Circular Economy, 2023,16(02):44−47. (王权永, 徐修冬, 吴勇基, 等. 利用硫铁矿烧渣制备电池级磷酸铁工艺研究[J]. 再生资源与循环经济, 2023,16(2):44−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0912.2023.02.012Wang Quanyong, Xu Xiudong, Wu Yongji, et al. Preparation of battery-grade iron phosphate from iron sulfide slag[J]. Renewable Resources and Circular Economy, 2023, 16(02): 44−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0912.2023.02.012 [2] Liao Kangcheng, Yang Man. Production and operation situation and outlook of sulfuric acid industry in China in 2022[J]. Phosphorus Fertilizer and Compound Fertilizer, 2023,38(8):1−6. (廖康程, 杨曼. 2022年我国硫酸行业生产运行情况及展望[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2023,38(8):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2023.08.002Liao Kangcheng, Yang Man. Production and operation situation and outlook of sulfuric acid industry in China in 2022[J]. Phosphorus Fertilizer and Compound Fertilizer, 2023, 38(8): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2023.08.002 [3] 中新化网. 增长6.3%!2023年我国钛白粉总产量达416万吨 [EB/OL]. [2024-01-08] http://www.ccin.com.cn/detail/e7acc0755a109e3ce32a6cfbddf21102Sinochem New Network. An increase of 6.3%! China's total titanium dioxide output will reach 4.16 million tons in 2023 [EB/OL]. [2024-01-08] http://www.ccin.com.cn/detail/e7acc0755a109e3ce32a6cfbddf21102 ( [4] Zhou Jianfeng. New technology of reusing titanium dioxide waste acid for energy saving and concentration[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2023,50(19):26−28. (周建锋. 钛白废酸回用节能提浓新技术[J]. 广东化工, 2023,50(19):26−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2023.19.010Zhou Jianfeng. New technology of reusing titanium dioxide waste acid for energy saving and concentration[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2023, 50(19): 26−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2023.19.010 [5] Zhang W G, Zhang T A, Cai L L, et al. Preparation of doped iron phosphate by selective precipitation of iron from titanium dioxide waste acid[J]. Metals, 2020,10:789. doi: 10.3390/met10060789 [6] Ju J R, Feng Y L, Li H R, et al. Extraction of valuable metals from acidic wastewater and blast furnace slag by a collaborative utilization process[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022,17:e2777. doi: 10.1002/apj.2777 [7] Ju J R, Feng Y L, Li H R, et al. Resource utilization of strongly acidic wastewater and red gypsum by a harmless self-treatment process[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023,172:594−603. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2023.02.067 [8] Song Y W, Wang H R, Wang R, et al. Novel approach for high-efficiency recovery of titanium dioxide, hydrochloric acid, and organic solvents from titanium white waste acid[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021,315:128105. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128105 [9] Ma G Q, Cheng M. Experimental study on preparation of titanium-rich material by pressure leaching of titanium concentrate from titanium dioxide waste acid[J]. Ferroelectrics, 2021,581:281−286. doi: 10.1080/00150193.2021.1903258 [10] Fang Xiaoyu. Study on the process conditions for the preparation of iron oxide red/ferric chloride from sulfuric acid slag [D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2020. (方晓宇. 硫酸烧渣制备氧化铁红/三氯化铁的工艺条件研究 [D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2020.Fang Xiaoyu. Study on the process conditions for the preparation of iron oxide red/ferric chloride from sulfuric acid slag [D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2020. [11] Jiang T, Tu Y K, Su Z J, et al. A novel value-added utilization process for pyrite cinder: Selective recovery of Cu/Co and synthesis of iron phosphate[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020,193:105314. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2020.105314 [12] Yang Baojun, Fang Xiaoyu, Wang Bainian, et al. Extraction of iron from sulfuric acid slag by oxalic acid additive-enhanced acid leaching[J]. Chemical Progress, 2019,38(3):1552−1560. (杨保俊, 方晓宇, 王百年, 等. 草酸助剂强化酸浸法提取硫酸烧渣中的铁[J]. 化工进展, 2019,38(3):1552−1560.Yang Baojun, Fang Xiaoyu, Wang Bainian, et al. Extraction of iron from sulfuric acid slag by oxalic acid additive-enhanced acid leaching[J]. Chemical Progress, 2019, 38(3): 1552−1560. [13] Fu Kaibin, Jiao Yu, Xu Xin, et al. Study on the process of preparing iron red from sulfuric acid leachate of a sulfuric iron ore slag burned in Shandong[J]. Applied Chemical Engineering, 2018,47(2):293−295. (傅开彬, 焦宇, 徐信, 等. 山东某硫铁矿烧渣硫酸浸出液制备铁红工艺研究[J]. 应用化工, 2018,47(2):293−295. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.02.021Fu Kaibin, Jiao Yu, Xu Xin, et al. Study on the process of preparing iron red from sulfuric acid leachate of a sulfuric iron ore slag burned in Shandong[J]. Applied Chemical Engineering, 2018, 47(2): 293−295. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.02.021 [14] Kerkez D, Becelic-Tomin M, Gvoic V, et al. Pyrite cinder as an effective fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of reactive azo dye: Effects of process parameters and complete effluent characterization[J]. Catalysts, 2023,13(2):424. doi: 10.3390/catal13020424 [15] Liu L B , Yi L S, Song Y F. Comprehensive utilization of pyrite concentrate pyrolysis slag by oxygen pressure leaching [J] . Minerals, 2023, 13(6): 726. [16] Li Y, Xue H T, Taskinen P, et al. Sustainable phase-conversion method for antimony extraction and sulfur conservation and waste treatment at low temperature[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020,268:121950. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121950 [17] Kenzhaliyev B, Surkova T, Yessimova D, et al. On the question of the complex processing of pyrite cinders[J]. Inorganics, 2023,11(4):171. doi: 10.3390/inorganics11040171 [18] Sun J W, Han P W, Liu Q, et al. Pilot plant test on the recovery of valuable metals from pyrite cinder by a combined process based on chlorinating roasting[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2019,72(4):1053−1061. doi: 10.1007/s12666-019-01580-9 [19] Zhang H Q, Chen G H, Cai X, et al. The leaching behavior of copper and iron recovery from reduction roasting pyrite cinder[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021,420:126561. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126561 [20] Ferreira S C, Bruns R E, Ferreira H S, et al. Box-Behnken design: an alternative for the optimization of analytical methods[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2007,597:179−186. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2007.07.011 -




 下载:
下载: