Simulation of operation inner profile of blast furnace with smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite
-
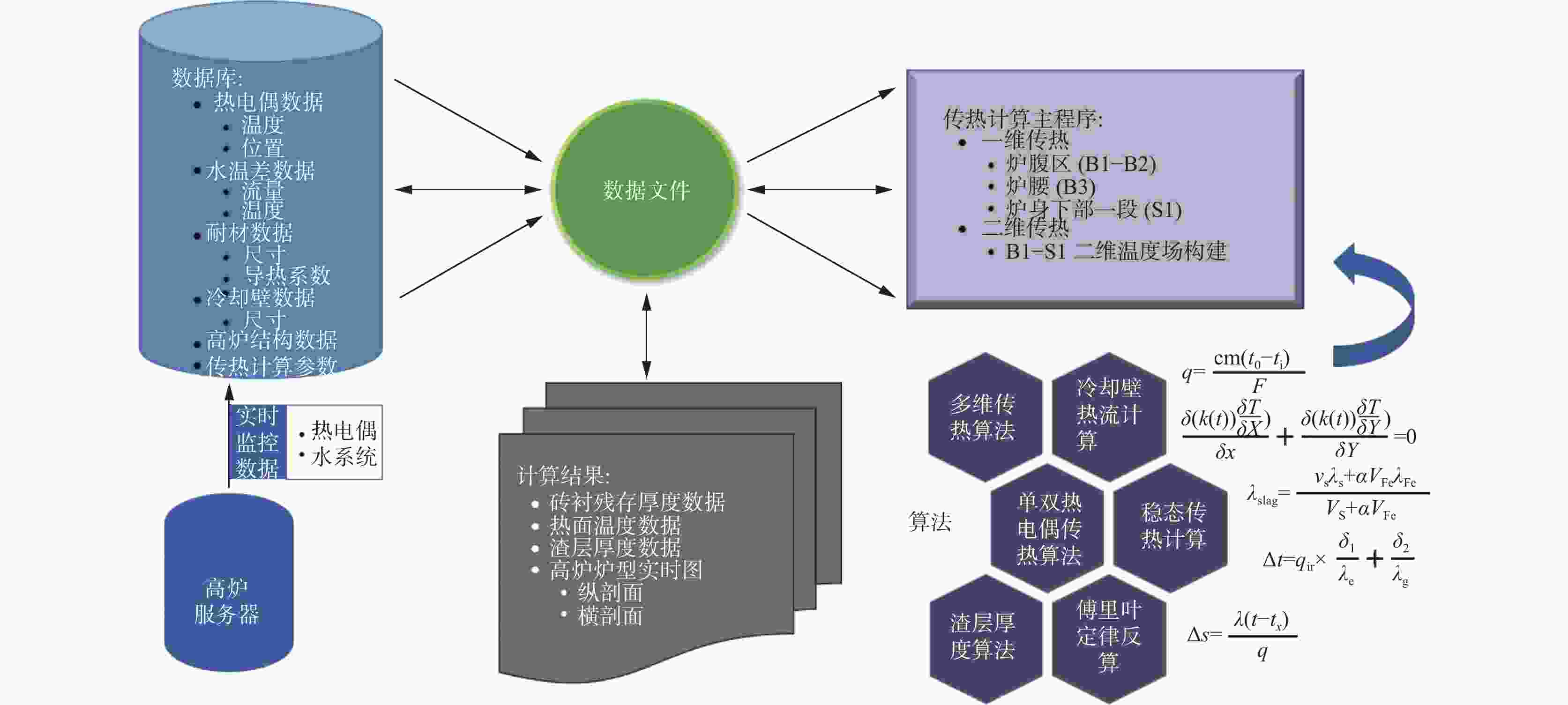
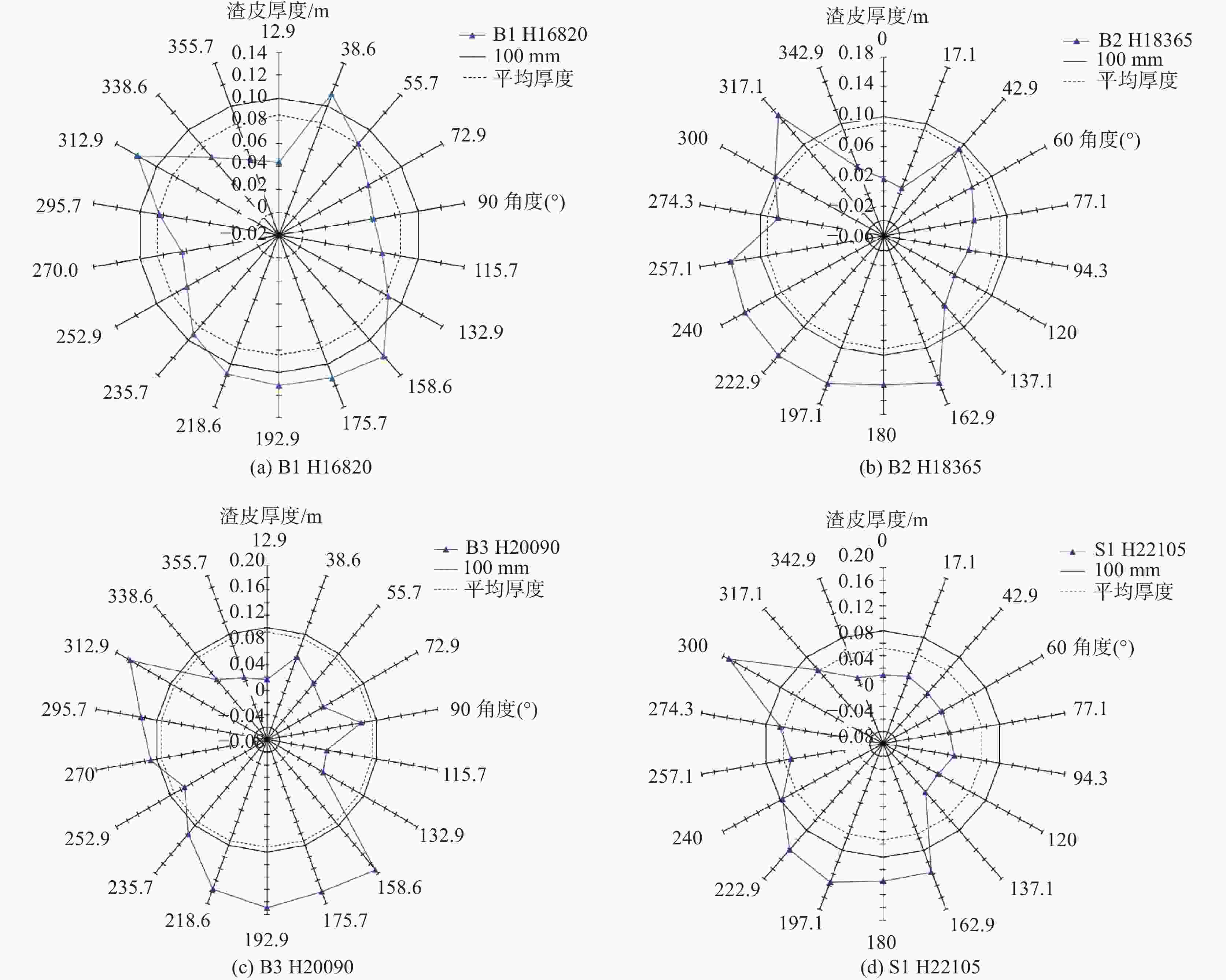
摘要: 根据某钒钛磁铁矿冶炼高炉炉型设计参数和生产工况数据,通过MATLAB计算软件建立该高炉操作炉型计算模型,研究高炉运行中高温区域炉墙挂渣情况。计算结果表明:受高炉边缘气流控制较弱影响,高温区域炉墙的热负荷大多在12 kW/(m2·s)以下,冷却壁壁体温度接近炉壳温度,冷却壁热面的渣皮厚度普遍高于100 mm,且渣皮厚度分布不均匀,个别方向达到200 mm以上;对比普通高炉,冶炼钒钛磁铁矿高炉在同等热负荷下,高温区域挂渣能力更强,从安全性与渣皮稳定性考虑,高炉冷却壁热负荷应控制在10.50~34.50 kW/(m2·s)。Abstract: Based on the design parameters and production conditions of a vanadium-titanium magnetite smelting blast furnace, a numerical model of the vanadium-titanium blast furnace operation inner model was established through a MATLAB calculation software in order to study the slag adhering situation of the furnace wall within high temperature zone of the blast furnace operation. The predicated results show that the heat load of the furnace wall within high temperature zone is mostly below than 12 kW/(m2·s) due to the weaker airflow control at the edge of the blast furnace. The temperature on cooling staves is close to that on shell. Besides, It is higher than 100 mm, and the slag skull thickness at the hot surface on staves is generally higher than 100 mm while unevenly distributed, even reaching up to more than 200 mm at specific directions. Compared with ordinary blast furnaces, vanadium-titanium magnetite smelting blast furnaces show stronger slag adhering capacity within high-temperature zones given the same thermal load. Considering safety and slag skull stability, the heat load of vanadium-titanium blast furnace cooling staves should be controlled within 10.50~34.50 kW/ (m2·s).
-
Key words:
- blast furnace /
- vanadium-titanium magnetite /
- operation inner profile /
- MATLAB software /
- slag skull
-
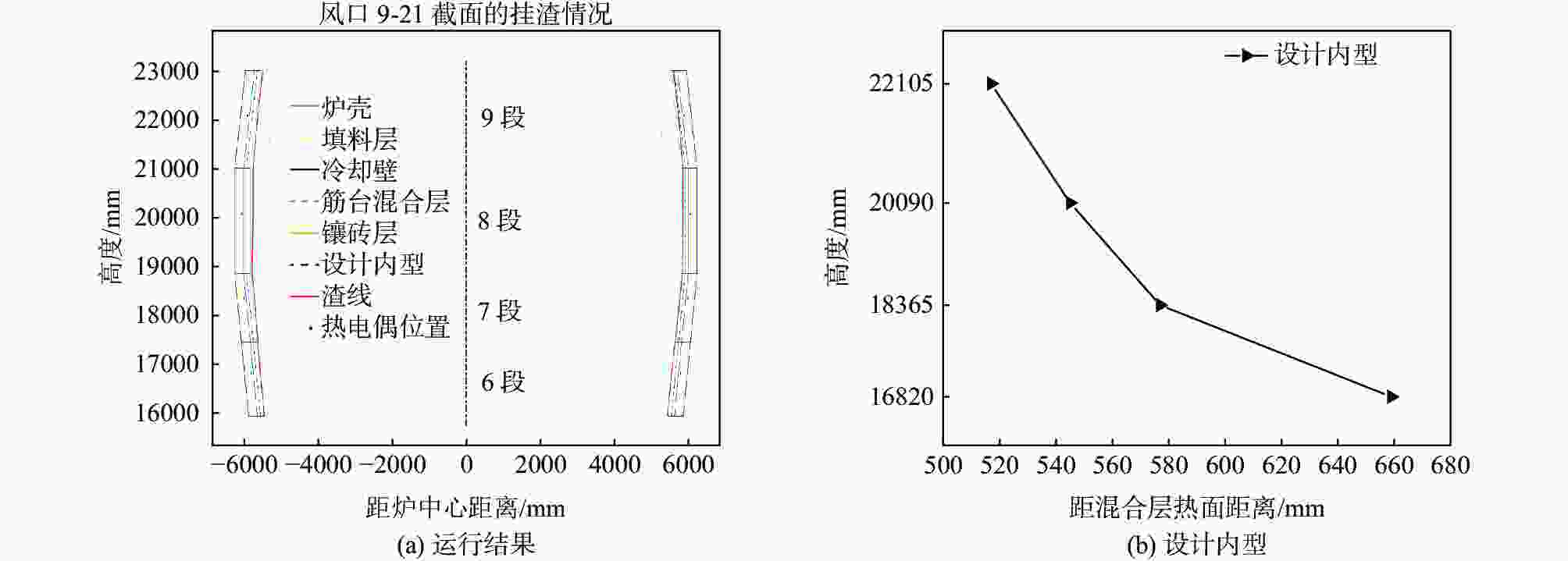
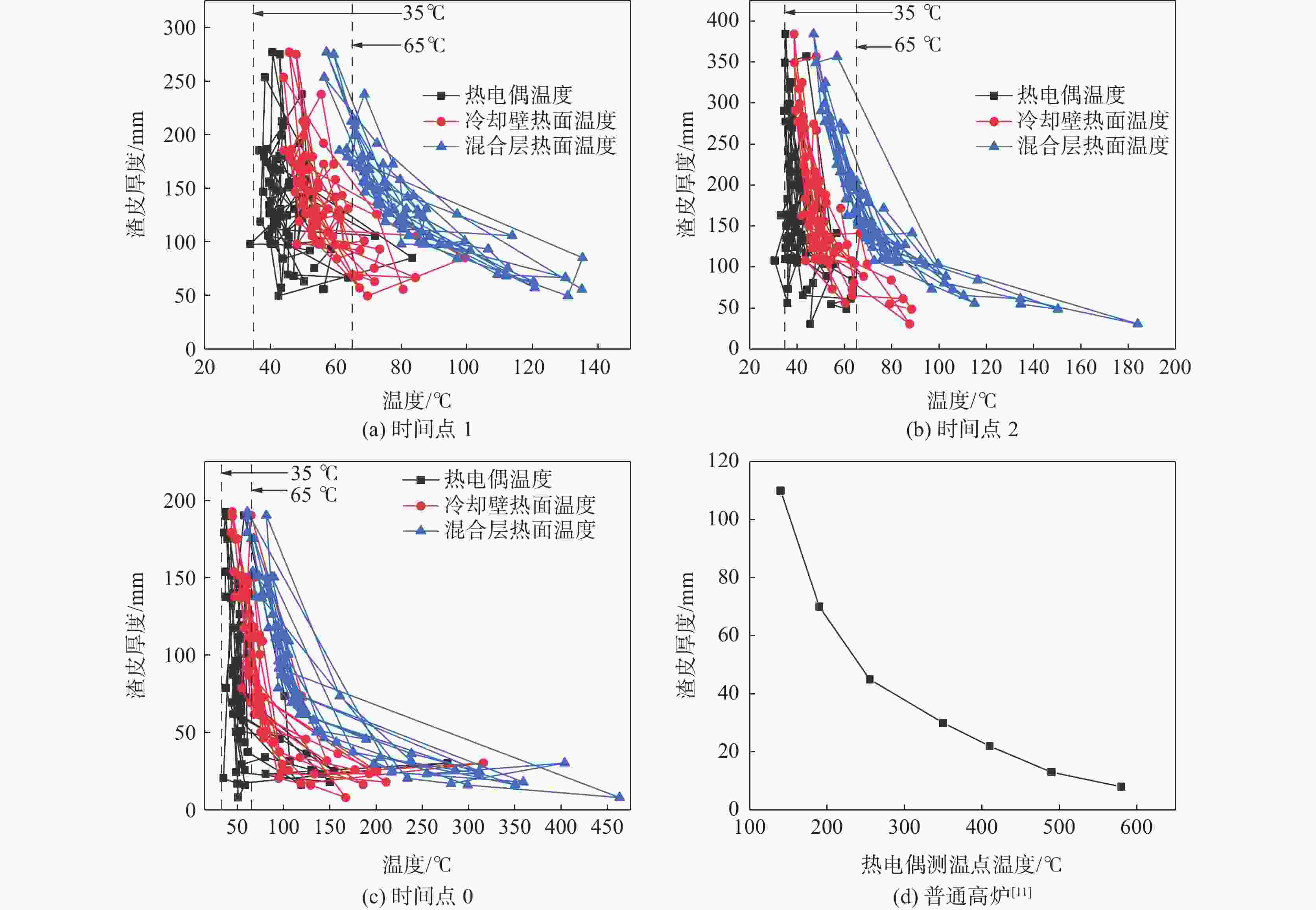
图 4 渣皮厚度与炉墙热流强度(热负荷)对应关系
Figure 4. Correspondence between thickness of slag skull and heat flow intensity (heat load) of furnace wall
(a) 钒钛高炉; (b) 普通高妒[9]
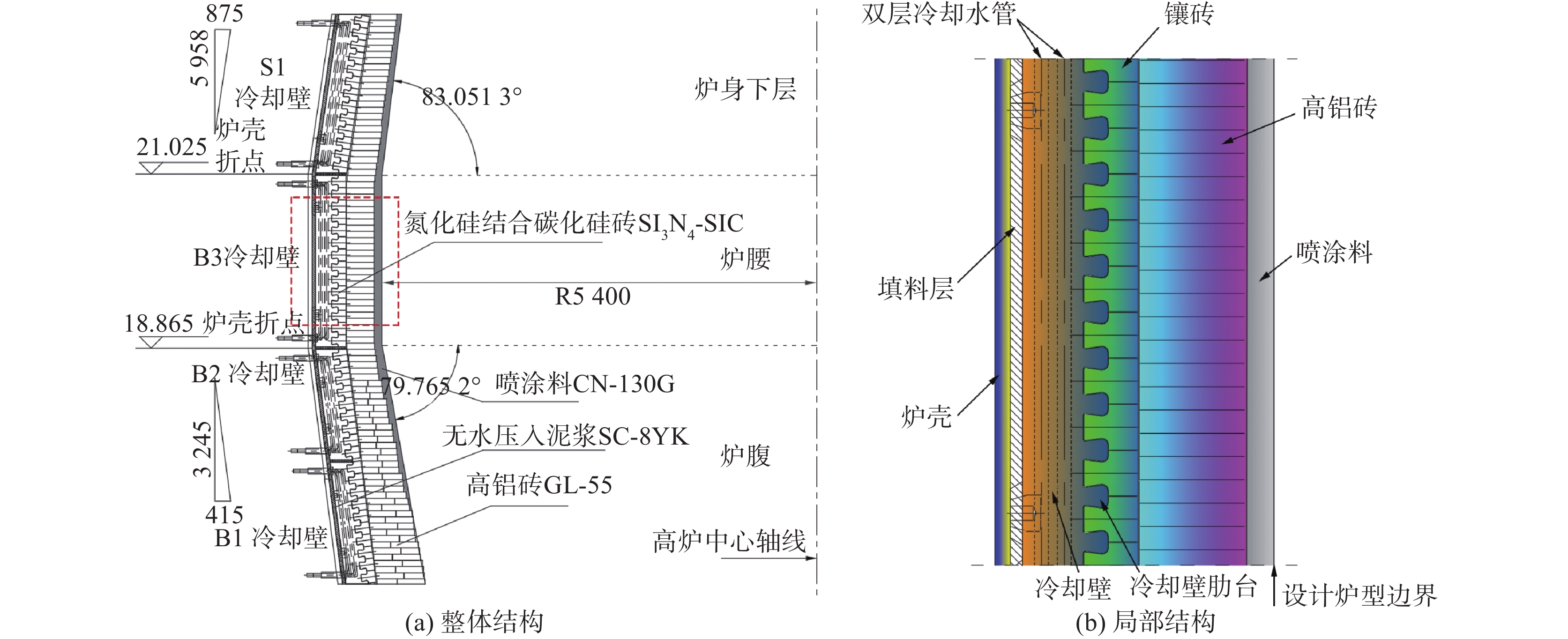
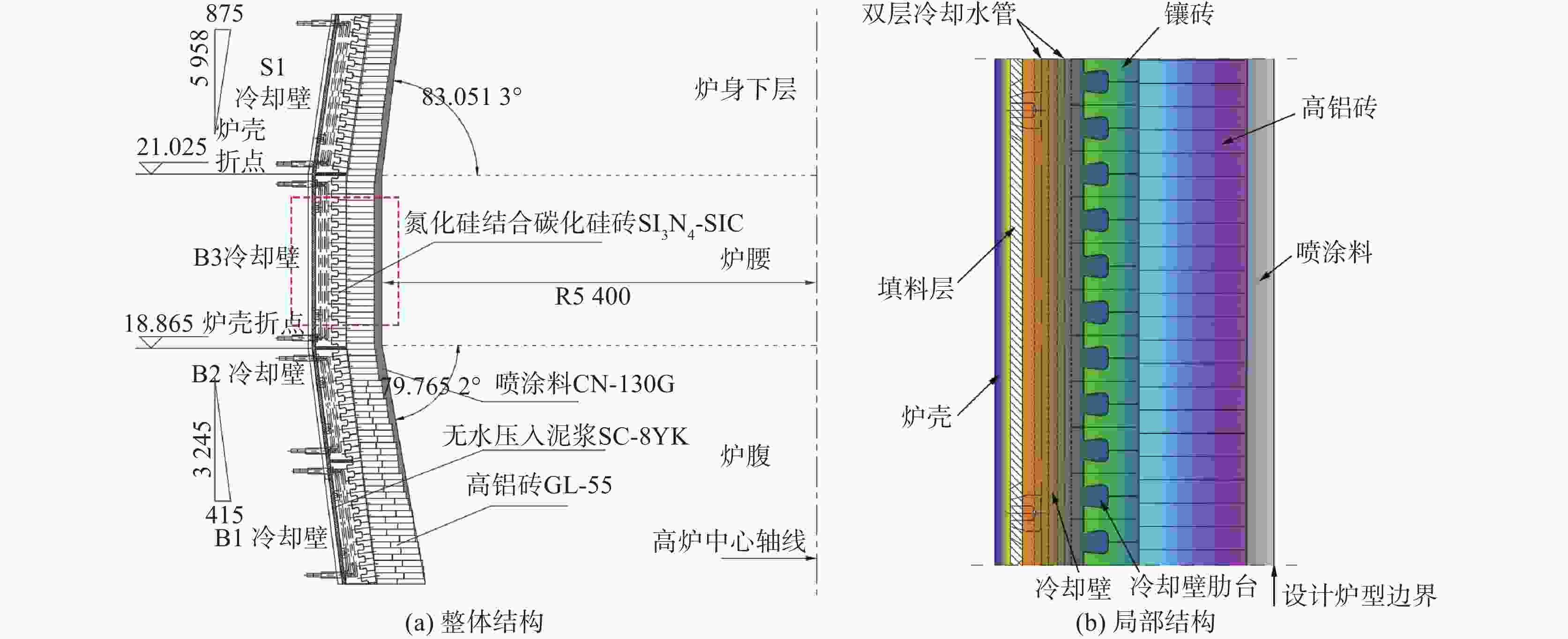
表 1 炉墙设计参数
Table 1. The design parameters of furnace wall
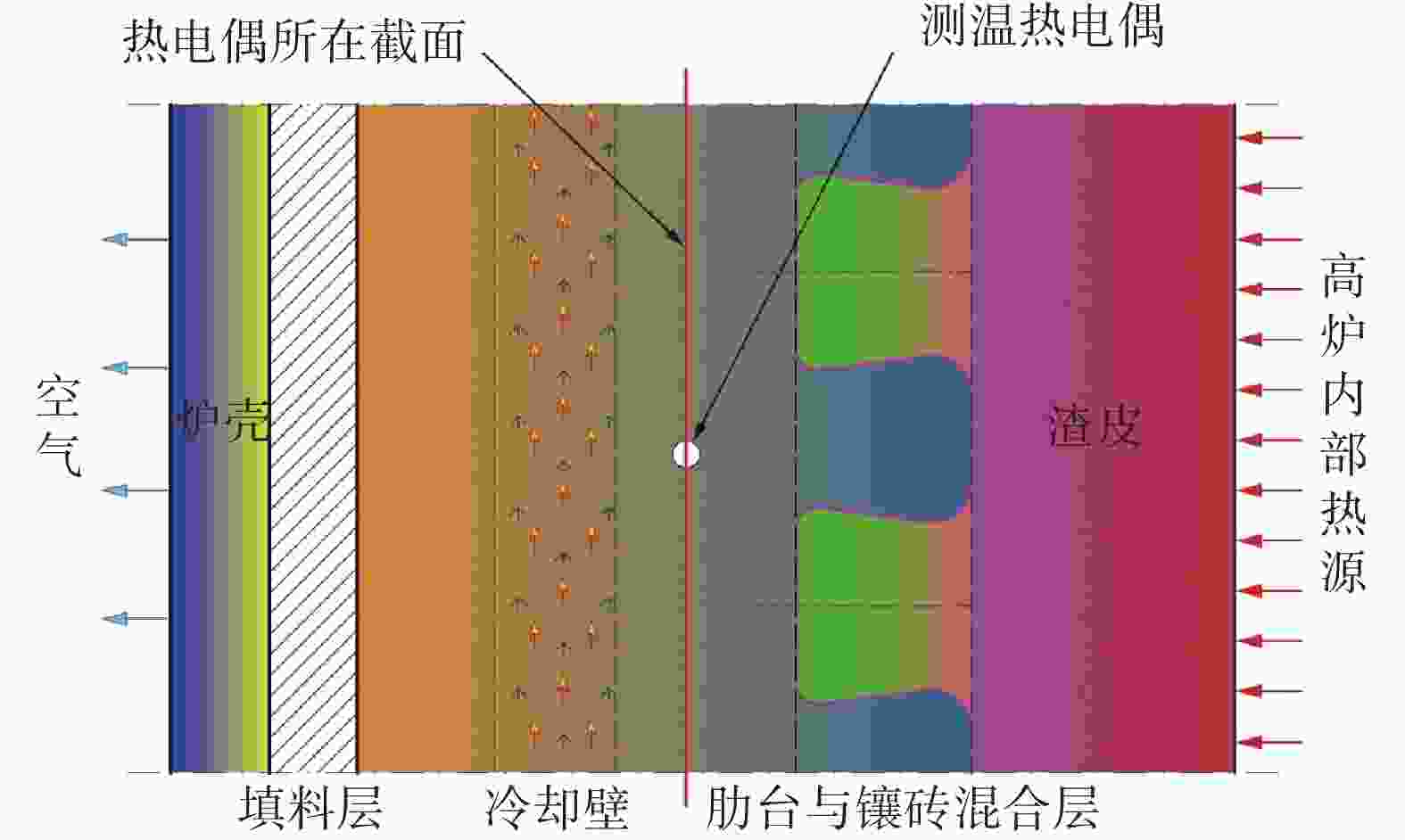
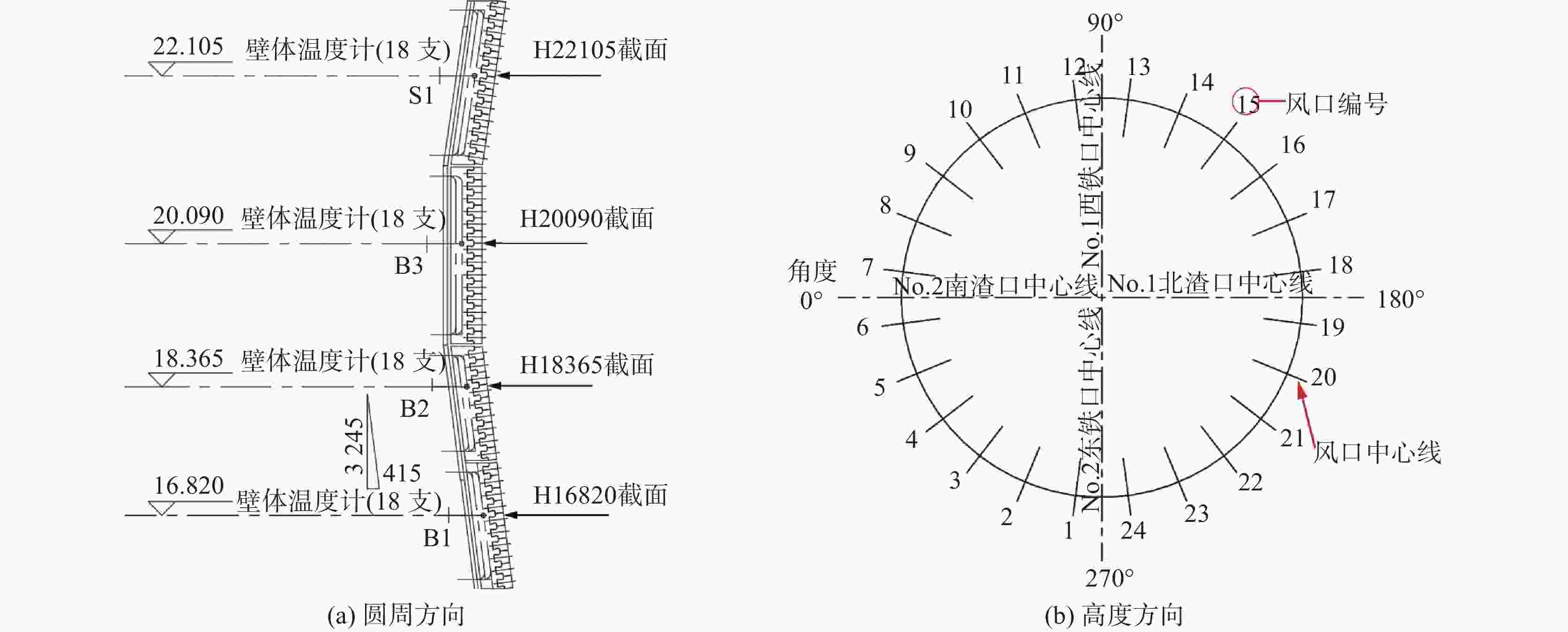
炉壳厚度/mm 填料层厚度/mm 冷却壁厚度/mm 冷却壁高度/mm 冷却壁总数量/块 水管尺寸/mm B1 B2 B3 S1 45 40 280 1540 1400 2160 1 995 42×4 Φ45×6 肋台厚度
/mm镶砖厚度
/mm炉腰设计內型半径
/mm冷却壁热面总面积/m2 炉身角/(°) 炉腹角/(°) B1 B2 B3 S1 80 180 5400 54.6 51.2 80.2 73 83.0513 79.765 2 表 2 高炉B1~S1段冷却系统和炉壳实测数据
Table 2. Measured data of cooling system and furnace shell of B1~S1 section of blast furnace
水流量均值/
(t·h−1)水温差
均值/ ℃炉壳温度
均值/ ℃环境温度
均值/ ℃2.57 2.06 43.42 21.00 表 3 模型部分计算参数
Table 3. Some calculation parameters of the model
铸铁冷却壁导热
系数/[W·(m·℃)−1]镶砖导热
系数/[W·(m·℃)−1]渣皮导热
系数/[W·(m·℃)−1]热电偶插入
深度/mm不同温度下铁的导热系数/[W·(m·℃)−1] 400 ℃ 600 ℃ 800 ℃ 1000 ℃ 1200 ℃ 42.05-0.026 89t 17-0.009t 1.2 405 49.9 38.6 29.3 29.3 31.1 注:t为材料温度值, ℃。 -
[1] Lin Chengcheng, Xiang Zhongyong. Characteristics of baosteel blast furnace profiles and their effects on operation[J]. Baosteel Technology, 2009,(2):49-53. (林成城, 项钟庸. 宝钢高炉炉型特点及其对操作的影响[J]. 宝钢技术, 2009,(2):49-53.Lin Chengcheng, Xiang Zhongyong. Characteristics of baosteel blast furnace profiles and their effects on operation[J]. Baosteel Technology, 2009(2): 49. [2] Chen Lingkun, Wang Yong, Fu Lianchun. Application of the balst furnace expert system to profile management on No. 4 BF at WISGCO[J]. Iron & Steel, 2000,35(9):5-9. (陈令坤, 汪勇, 付连春. 高炉冶炼专家系统在炉型管理中的应用[J]. 钢铁, 2000,35(9):5-9.Chen Lingkun, Wang Yong, Fu Lianchun. Application of the balst furnace expert system to profile management on No. 4 BF at WISGCO[J]. Iron & Steel, 2000, 35(9): 5. [3] Chen Peidun, Shao Shudong, Xue Yuqing. On furnace shape management and smooth work of furnace status of BF operation[J]. China Metallurgy, 2006,16(3):48-49. (陈培敦, 邵书东, 薛玉卿. 浅谈高炉操作炉型管理与炉况顺行[J]. 中国冶金, 2006,16(3):48-49.Chen Peidun, Shao Shudong, Xue Yuqing. On furnace shape management and smooth work of furnace status of BF operation[J]. China Metallurgy, 2006, 16(3): 48. [4] Shi Lin, Cheng Susen, Zuo Haibin. Numerical simulation of erosion boundary identification of blast furnace lining[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2006,18(4):1-5. (石琳, 程素森, 左海滨. 高炉炉衬侵蚀边界识别的数值模拟[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2006,18(4):1-5.Shi Lin, Cheng Susen, Zuo Haibin. Numerical simulation of erosion boundary identification of blast furnace lining [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2006, 18(4): 1. [5] Li Junfeng, He Chuanyun, Ding Yuehua. Study on heat transfer and slag skull thickness in bosh and belly of blast furnace[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 2014,42(6):12−15. (李骏峰, 何川云, 丁跃华. 高炉炉腹炉腰传热及渣皮厚度的研究[J]. 钢铁研究, 2014,42(6):12−15.Li Junfeng, He Chuanyun, Ding Yuehua. Study on heat transfer and slag skull thickness in bosh and belly of blast furnace[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 2014, 42(6): 12-15. [6] Chen Zeshao, Qian Jun, Ye Yihuo. Predicting theory of effective thermal conductivity of complex material[J]. Journal of China University of Science and Technology, 1992,22(4):416−424. (陈则韶, 钱军, 叶一火. 复合材料等效导热系数的理论推算[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报, 1992,22(4):416−424.Chen Zeshao, Qian Jun, Ye Yihuo. Predicting theory of effective thermal conductivity of complex material[J]. Journal of China University of Science and Technology, 1992, 22(4): 416-424. [7] Zhang Feng, Xiao Jianzhuang, Song Zhiwen. The prediction models of thermal conductivity of concrete and their application[J]. Ready-Mixed Concrete, 2009,(2):23-25,51. (张枫, 肖建庄, 宋志文. 混凝土导热系数的理论模型及其应用[J]. 商品混凝土, 2009,(2):23-25,51.Zhang Feng, Xiao Jianzhuang, Song Zhiwen. The prediction models of thermal conductivity of concrete and their application[J]. Ready-Mixed Concrete, 2009(2): 23. [8] Ji Xiulan, Liu Zengxun, Lü Qing. Analysis on slag skull on bf copper cooling stave for vanadium-bearing titaniferous magnetite smelting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012,33(1):65−69. (计秀兰, 刘增勋, 吕庆. 冶炼钒钛磁铁矿高炉的铜冷却壁挂渣分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2012,33(1):65−69.Ji Xiulan, Liu Zengxun, Lv Qing. Analysis on slag skull on bf copper cooling stave for vanadium-bearing titaniferous magnetite smelting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012, 33(1): 65-69. [9] Liu Zengxun, Lü Qing. Heat transfer analysis for slag skull thickness of blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2008,29(3):55−58. (刘增勋, 吕庆. 高炉渣皮厚度的传热分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2008,29(3):55−58.Liu Zengxun, Lv Qing. Heat transfer analysis for slag skull thickness of blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2008, 29(3): 55-58. [10] Cao Yingjie, Zhang Jianliang, Guo Hongwei. Calculation of blast furnace inner wall thickness[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2015,(1):7−11. (曹英杰, 张建良, 国宏伟. 高炉炉墙内型厚度的计算[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2015,(1):7−11.Cao Yingjie, Zhang Jianliang, Guo Hongwei. Calculation of blast furnace inner wall thickness[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2015(1): 7-11. [11] 刘增勋. 高炉冷却壁热力耦合分析[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2009.Liu Zengxun. Coupled thermos-mechanical analysis about blast furnace staves[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2009. [12] Cheng Susen, Qian Liang, Zhao Hongbo. Monitoring method for blast furnace wall with copper staves[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2007,14(4):1−5. -




 下载:
下载: