Research on the influence of various process parameters on the properties of 304 stainless steel prototypes by electron beam free form fabrication
-
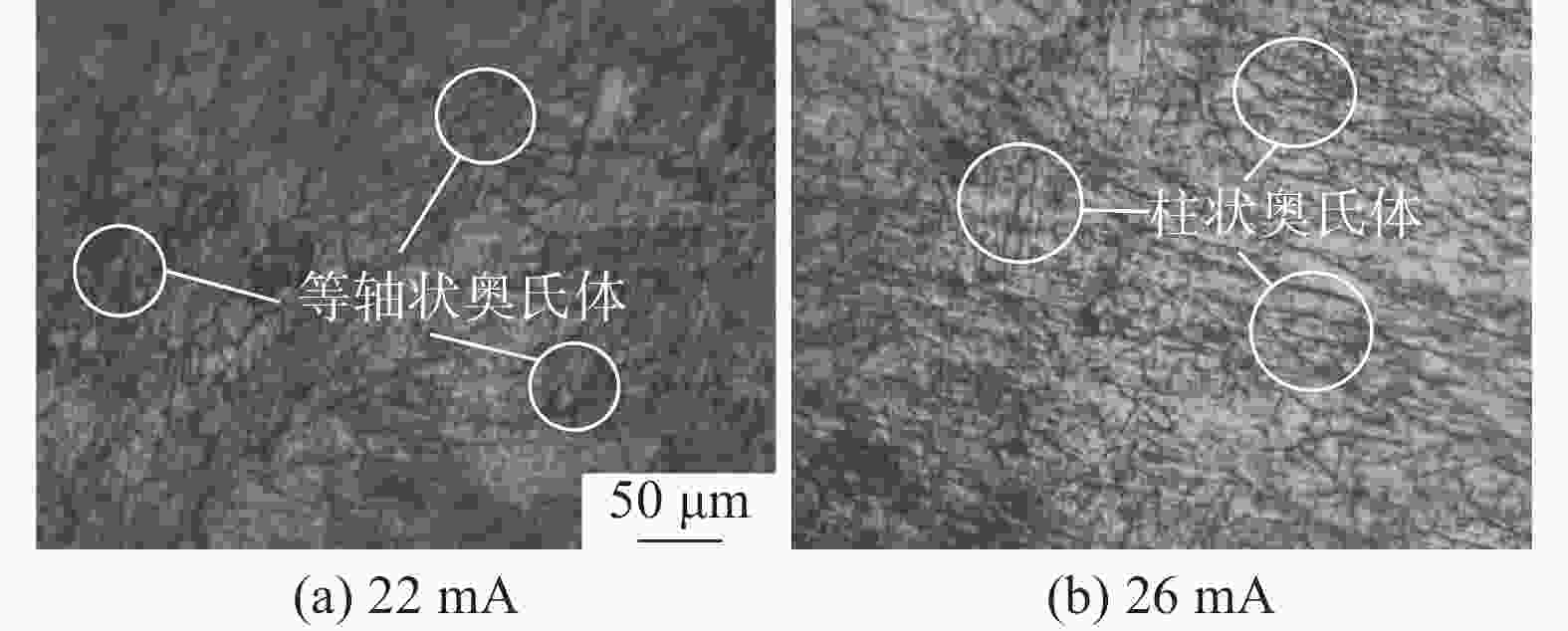
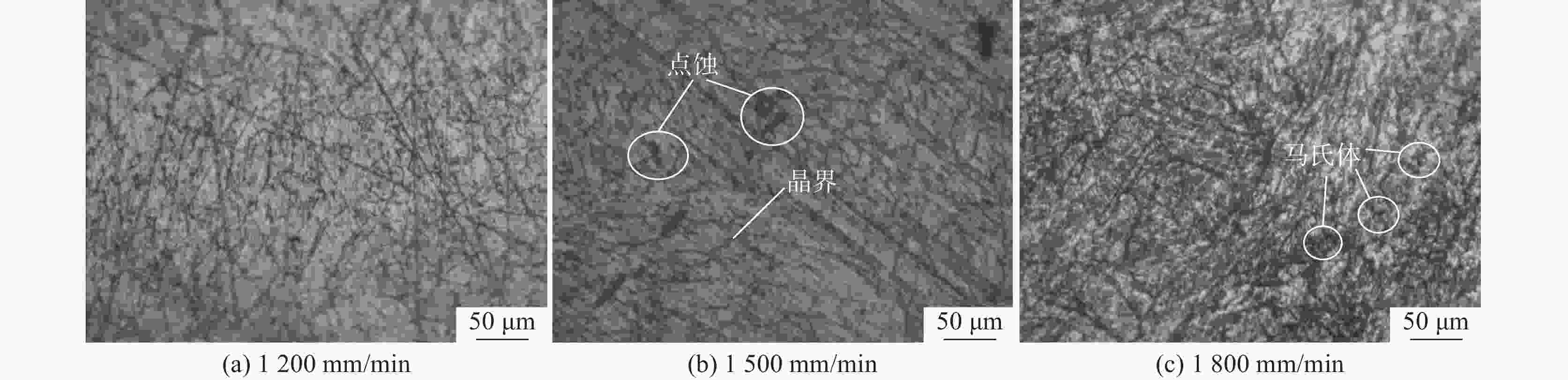
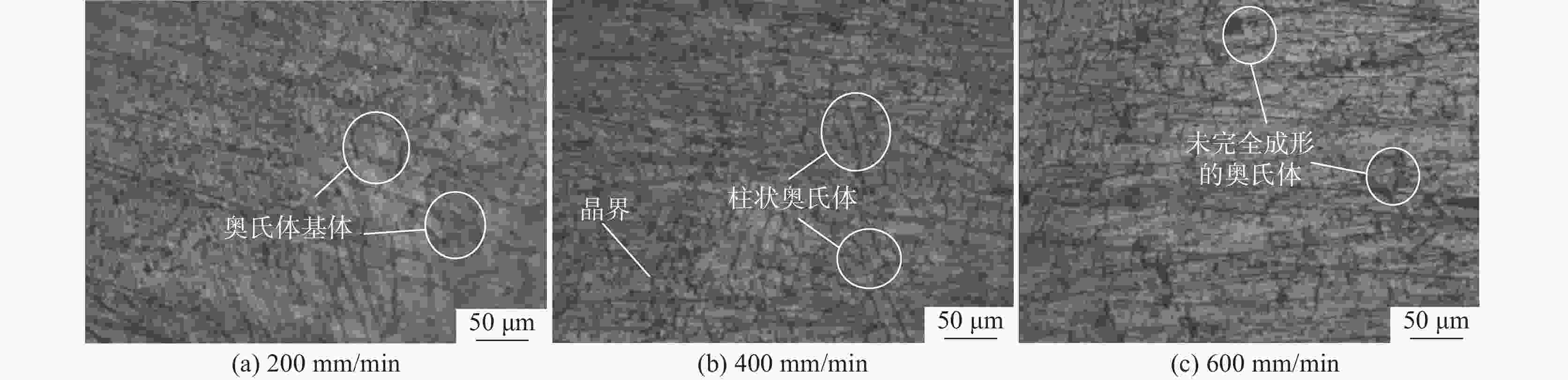
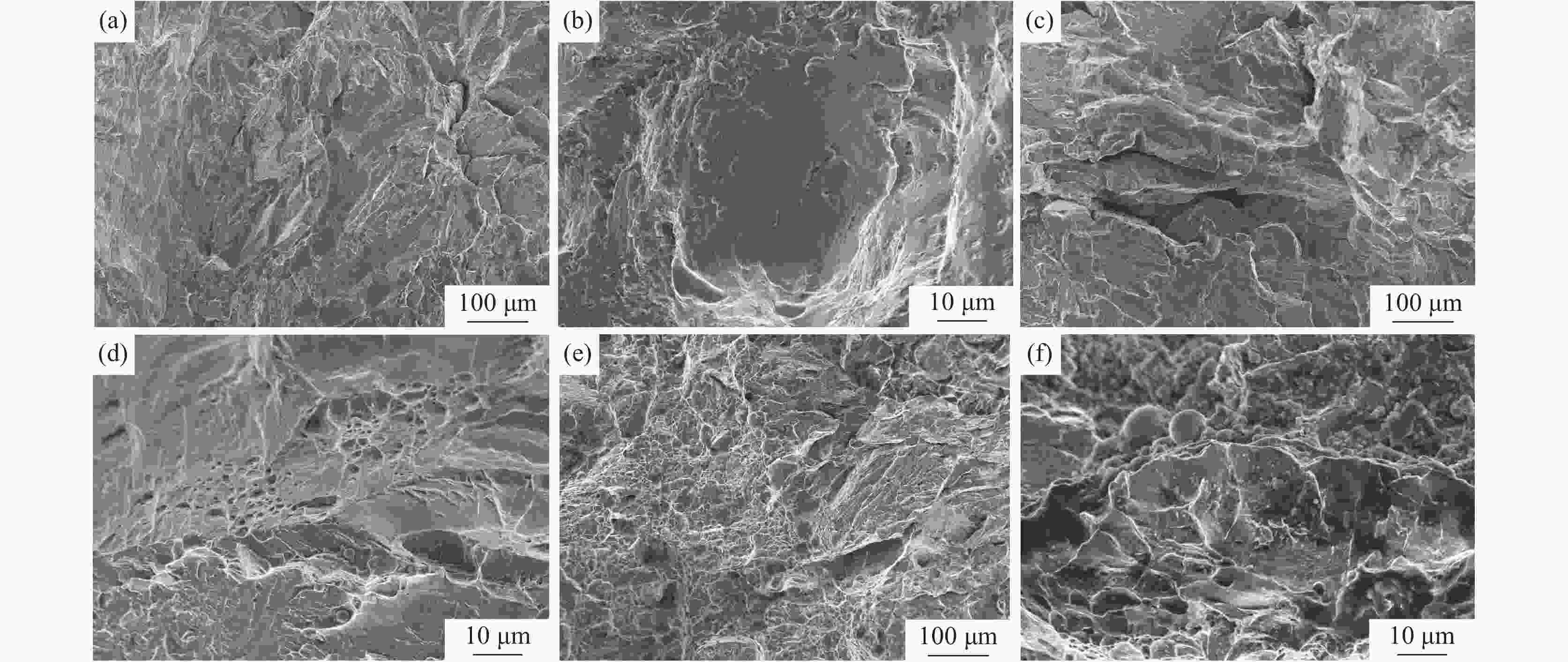
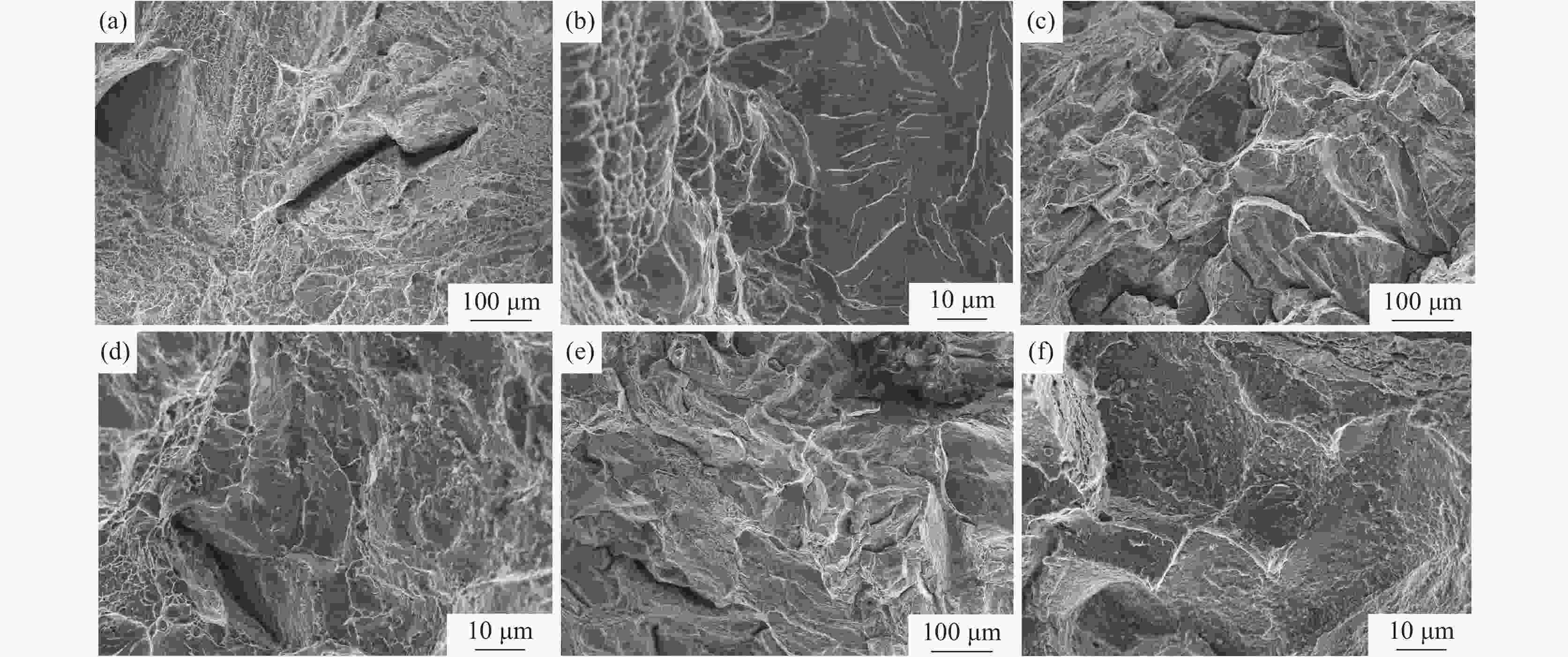
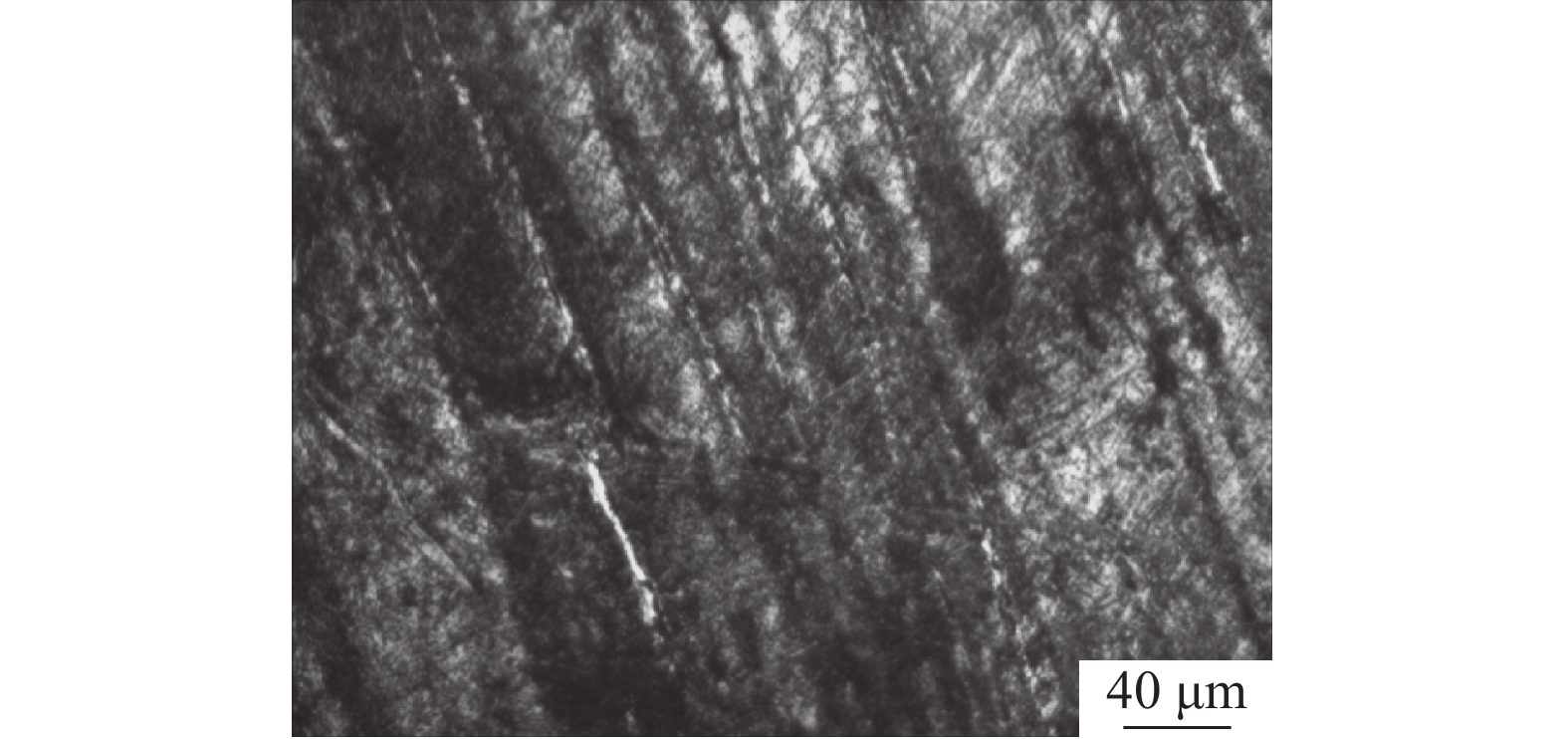
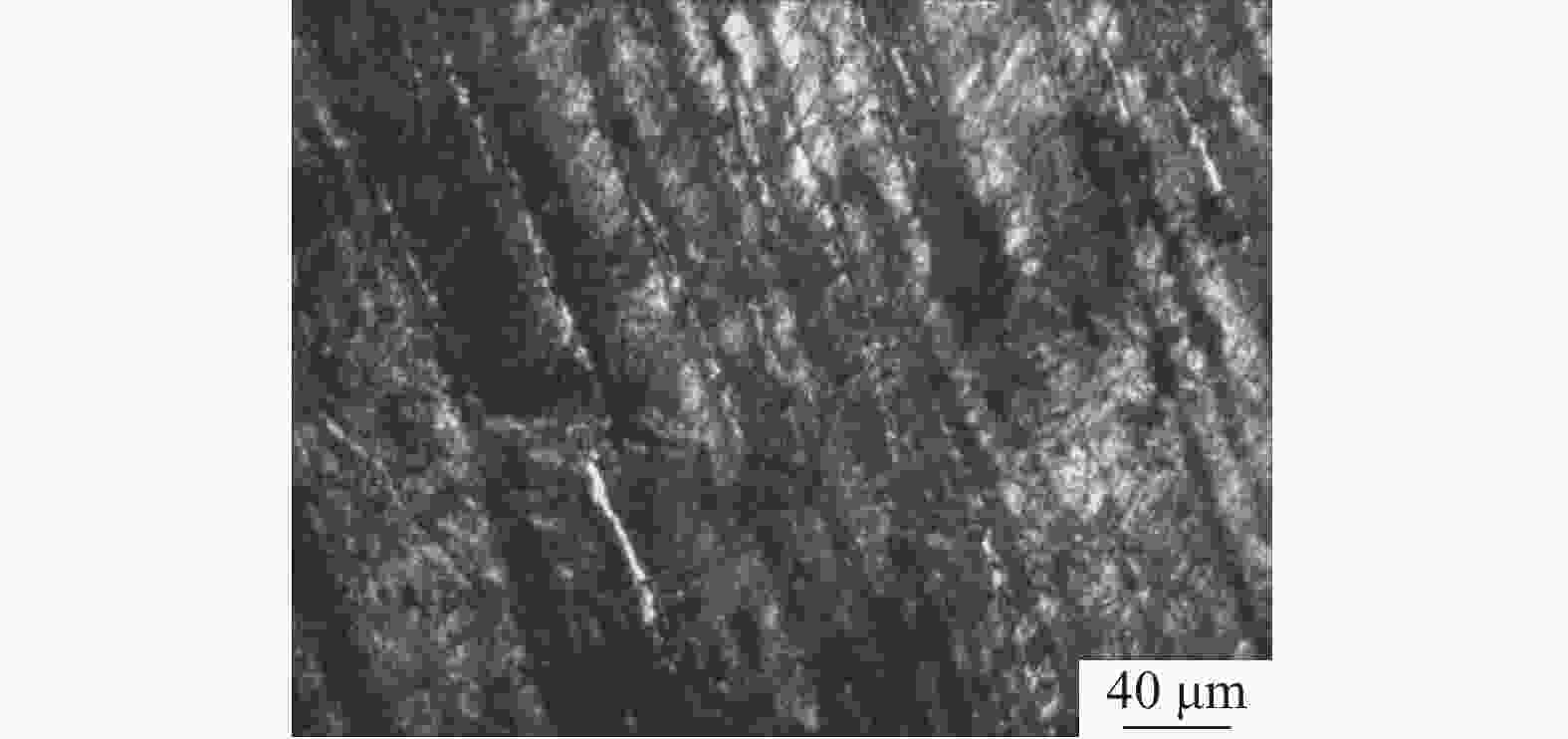
摘要: 采用直径为1 mm的304不锈钢丝材为材料,以电子束熔丝沉积技术(EBF3)制备304不锈钢试样,并进行力学性能及显微组织分析。设计了9组试验方案进行单因素试验,分别改变束流强度、送丝速度以及基板进给速度三个参数进行打印。结果表明,9组试件的抗拉强度和屈服强度均表现优异,但断后伸长率表现一般,其中当束流为26 mA、送丝速度为1400 mm/min、进给速度为400 mm/min时,试件各项特征表现最好,拉伸强度为1328.92 MPa,屈服强度为711.60 MPa,断后伸长率为34.45%。通过综合分析可知,改变送丝速度对试件的塑性影响最大,改变进给速度对试件的强度影响最大。此外,改变束流与进给速度的试件内部金相组织基体由奥氏体组成,改变送丝速度的试件显微组织则多为奥氏体转变和过程析出的组织为组成部分;改变束流和送丝速度的试件中以组织的构成变化为主,改变进给速度的试件中组织则以晶粒度的变化为主,最终形成了不同拉伸件性能间的差异。在进行扫描电镜断口分析中可以发现,试件在拉伸试验中均发生脆性断裂。Abstract: 304 stainless steel wire with a diameter of 1 mm was used as the material to prepare 304 stainless steel samples using electron beam fusion deposition technology (EBF3) for mechanical properties and microstructure analysis. Nine sets of experimental were designed for single factor experiments, where the beam intensity, wire feeding speed, and substrate feeding speed were changed for printing. The results showed that the tensile strength and yield strength of 9 groups of specimens were excellent, but their elongations were average. Among them, when the beam current was 26 mA, the wire feeding speed was 1400 mm/min, and the feed speed was 400 mm/min, the characteristics of the specimens were the best, with a maximum tensile strength of 1328.92 MPa, a maximum yield strength of 711.60 MPa, and a fracture elongation of 34.45%. Through the comprehensive analysis, it can be concluded that changing the wire feeding speed has the greatest impact on the plasticity of 304 stainless steel tensile parts, and changing the moving speed has the greatest impact on the strength of 304 stainless steel specimens. In addition, the microstructure of 304 stainless steel specimens with varying beam and feeding rates was composed of austenite. While, the microstructure of specimens with varying wire feeding rates was mostly composed of austenitic transformation phases precipitates; The changes in beam flow and wire feeding speed were mainly due to changes in the composition of the microstructure, while the changes in feed speed were mainly due to changes in grain size, ultimately resulting in the properties variation of different tensile parts. During the fracture analysis by scanning electron microscopy, it was found that brittle fracture occurred in all specimens during the tensile tests.
-
Key words:
- EBF3 /
- 304 stainless steel /
- wire feed speed /
- beam intensity /
- wire feeding speed /
- microstructure /
- tensile property
-
表 1 304不锈钢丝材及基板的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of 304 stainless steel wire and substrate
% 材料 C Si Mn S P Cr Ni Mo Fe 丝材 0.06 0.7 1.2 0.014 0.03 18 8 0.18 Bal. 基板 0.12 0.17 0.5 0.027 0.028 Bal. 表 2 电子束熔丝沉积成形304不锈钢工艺参数
Table 2. Process parameters of 304 stainless steel formed by EBF3
试样
编号束流强
度/mA送丝速度/
(mm·min−1)进给速度/
(mm·min−1)抗拉强度/
MPa屈服强度/
MPa断后伸
长率/%A1 18 1400 500 A2 22 1400 500 1347.91 593.77 34.90 A3 26 1400 500 1142.94 938.06 31.54 B1 26 1200 500 1137.74 511.67 24.63 B2 26 1500 500 893.27 453.41 20.61 B3 26 1800 500 1240.80 880.00 35.67 C1 26 1400 200 1228.25 600.43 29.13 C2 26 1400 400 1328.92 711.60 34.45 C3 26 1400 600 1213.10 546.42 28.07 -
[1] Huang Xingguang, Sun Baofu, Sun Guohui, et al. Study on the heat treatment performance of TC4 titanium alloy formed parts based on electron beam additive manufacturing[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(6):102−108. (黄星光, 孙宝福, 孙国辉, 等. 基于电子束增材制造的TC4钛合金成形件热处理性能研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(6):102−108.Huang Xingguang, Sun Baofu, Sun Guohui, et al. Study on the heat treatment performance of TC4 titanium alloy formed parts based on electron beam additive manufacturing[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(6): 102−108. [2] Tang Huiping, Wang Jian, Lu Shenglu, et al. Research progress in selective electron beam melting[J]. Materials China, 2015,34(3):225−235. (汤慧萍, 王建, 逯圣路, 等. 电子束选区熔化成形技术研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2015,34(3):225−235.Tang Huiping, Wang Jian, Lu Shenglu, et al. Research progress in selective electron beam melting[J]. Materials China, 2015, 34(3): 225−235. [3] Sun Baofu, Xu Bohan, Zhang Liping, et al. Research and optimization of the forming path for electron beam fusion additive manufacturing: Taking 304 stainless steel as an example[J]. Mechanical Strength, 2021,43(3):570−576. (孙宝福, 徐博翰, 张莉萍, 等. 电子束熔丝增材制造成形路径的研究与优化——以304不锈钢为例[J]. 机械强度, 2021,43(3):570−576.Sun Baofu, Xu Bohan, Zhang Liping, et al. Research and optimization of the forming path for electron beam fusion additive manufacturing: Taking 304 stainless steel as an example[J]. Mechanical Strength, 2021, 43(3): 570−576. [4] Taminger K M B, Hafley R A, Domack M S. Evolution and control of 2219 aluminium microstructural features through electron beam freeform fabrication[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2006,519:1297−1302. [5] Matz J E, Eagar T W. Carbide formation in alloy 718 during electron-beam solid freeform fabrication[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002,33(8):2559−2567. doi: 10.1007/s11661-002-0376-y [6] Wanjara P, Brochu M, Jahazi M. Electron beam freeforming of stainless steel using solid wire feed[J]. Materials & Design, 2007,28(8):2278−2286. [7] Węglowski M S, Błacha S, Pilarczyk J, et al. Electron beam additive manufacturing with wire–analysis of the process [C]//AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing LLC, 2018, 1960(1): 140015. [8] Polonsky A T, Lenthe W C, Echlin M L P, et al. Solidification-driven orientation gradients in additively manufactured stainless steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2020,183:249−260. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2019.10.047 [9] Bush R W, Brice C A. Elevated temperature characterization of electron beam freeform fabricated Ti–6Al –4V and dispersion strengthened Ti–8Al–1Er[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2012,554:12−21. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.05.083 [10] Dai Xiaoqin, Chen Hanning, Lei Jianbo, et al. Study on microstructure characteristics and properties of 304 stainless steel fabricated by laser additive[J]. Hot Working Process, 2017,46(16):83−86. (戴晓琴, 陈瀚宁, 雷剑波, 等. 激光增材制造304不锈钢显微结构特征与性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017,46(16):83−86.Dai Xiaoqin, Chen Hanning, Lei Jianbo, et al. Study on microstructure characteristics and properties of 304 stainless steel fabricated by laser additive[J]. Hot Working Process, 2017, 46(16): 83−86. [11] He Yuanling. Microstructure characterization and properties invertigation of welded joints of SUS304 stainless steel with welding [D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2019. (何远灵. SUS304不锈钢TIG焊接接头的组织表征与性能研究 [D]. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2019.He Yuanling. Microstructure characterization and properties invertigation of welded joints of SUS304 stainless steel with welding [D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2019. [12] Lippold J C, Kotecki J. Welding metallurgy and weldability of stainless steels [M]. John Wiley &Sons Inc. , 2005. [13] Shuxi. Study on the deposition process and stability of 304 stainless steel electron beam fusion wire[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. (树西. 304不锈钢电子束熔丝沉积工艺及稳定性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.Shuxi. Study on the deposition process and stability of 304 stainless steel electron beam fusion wire[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. [14] Zhong Qunpeng, Zhao Zihua, Zhang Zheng. Development of “fractography"and research of fracture micromechanism[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2005,27(3):358−370. (钟群鹏, 赵子华, 张峥. 断口学的发展及微观断裂机理研究[J]. 机械强度, 2005,27(3):358−370.Zhong Qunpeng, Zhao Zihua, Zhang Zheng. Development of “fractography"and research of fracture micromechanism[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2005, 27(3): 358−370. [15] Li Hongying. Fracture analysis of metal tensile specimens[J]. Journal of Shanxi Datong University (Natural Science Edition), 2011,27(1):76−79. (李红英. 金属拉伸试样的断口分析[J]. 山西大同大学学报(自然科学版), 2011,27(1):76−79.Li Hongying. Fracture analysis of metal tensile specimens[J]. Journal of Shanxi Datong University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 27(1): 76−79. -




 下载:
下载: