Effect of vanadium microalloying on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of medium Mn based hot stamping steel
-
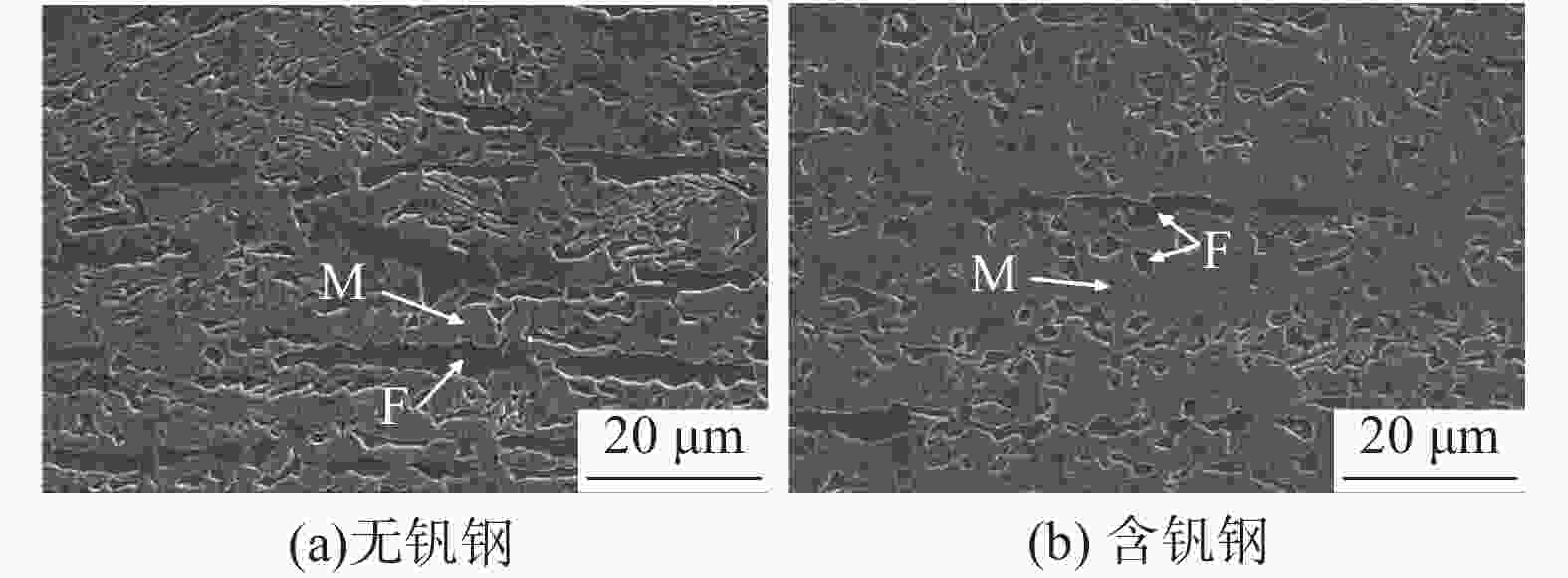
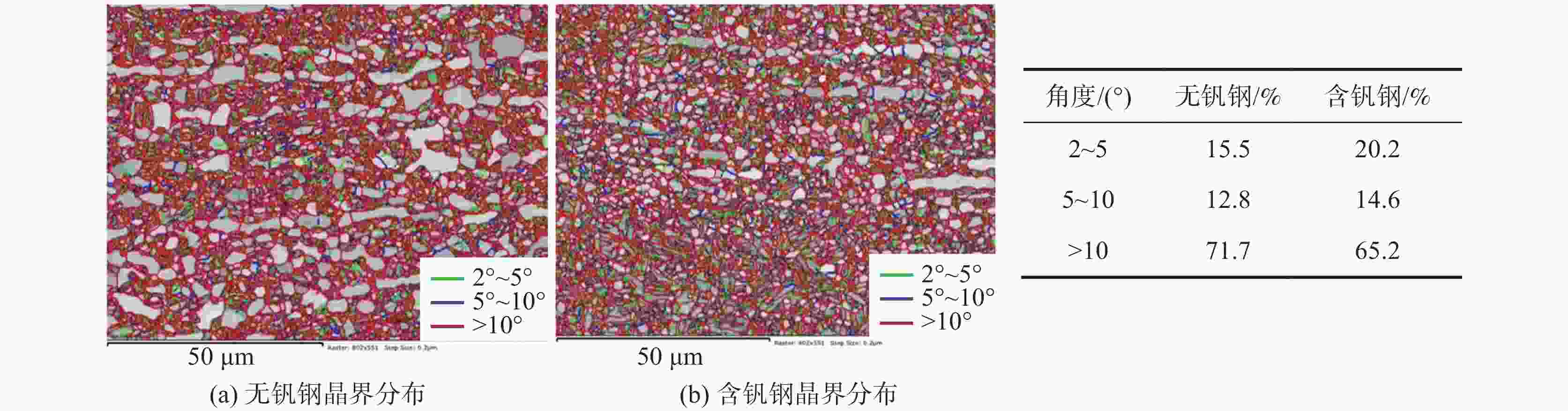
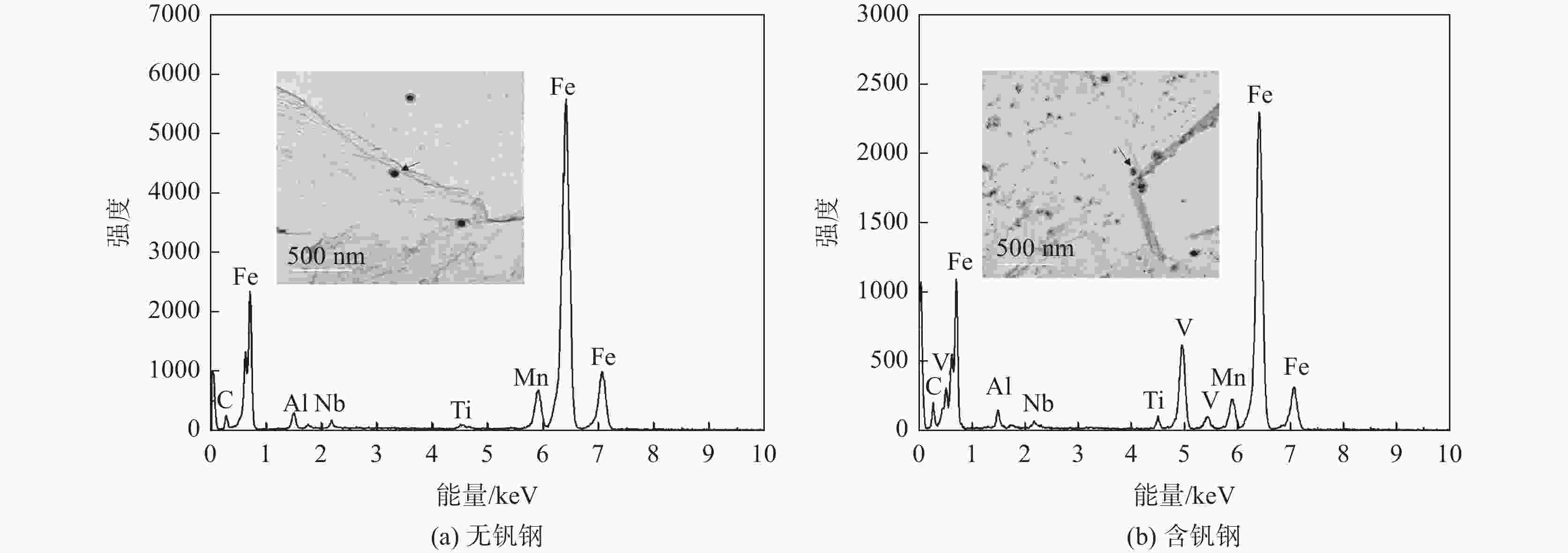
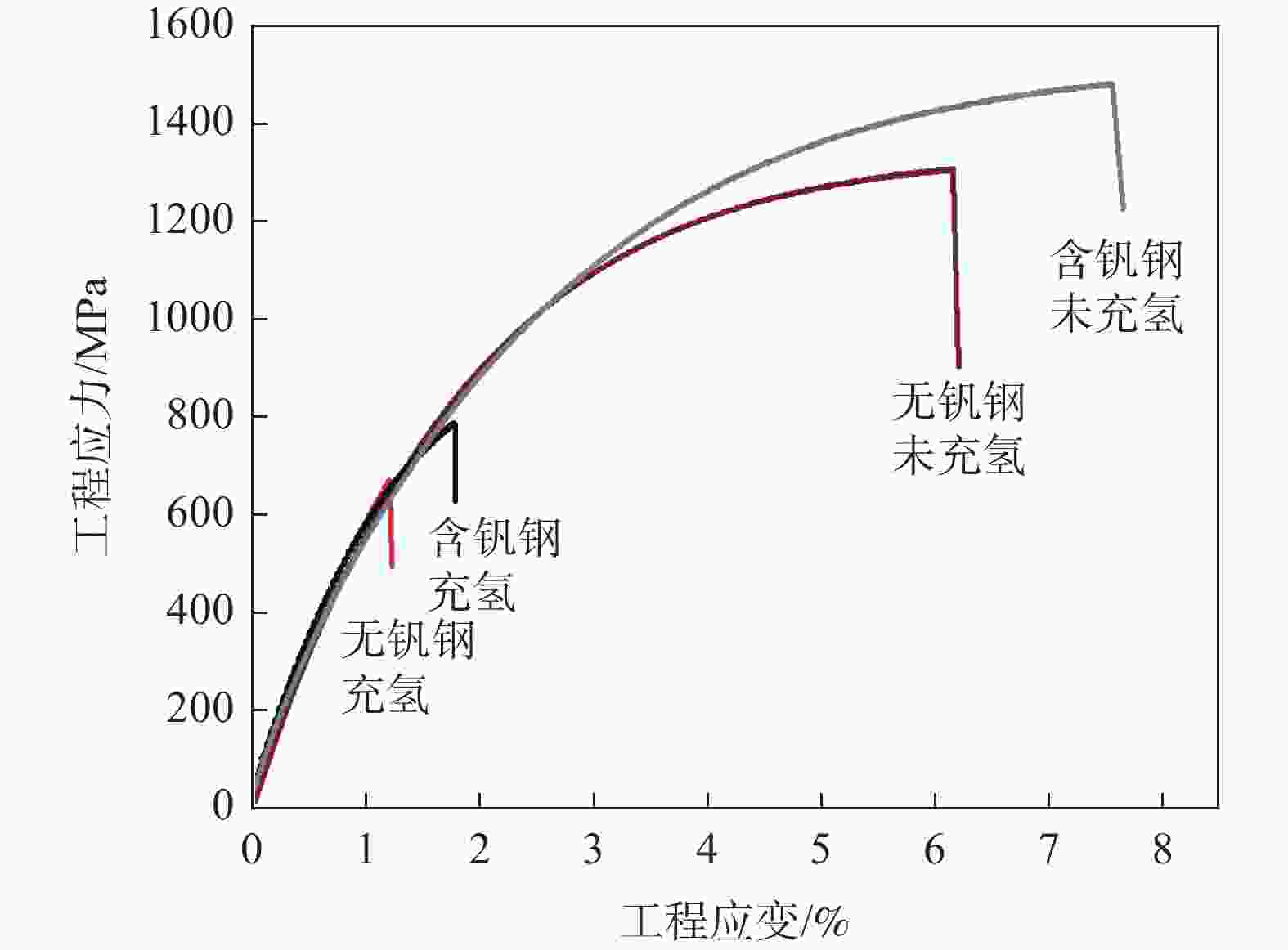
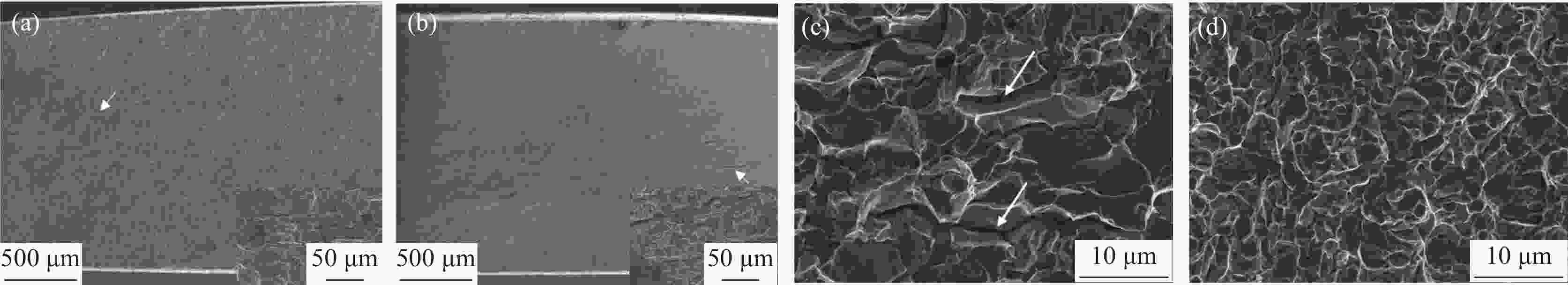
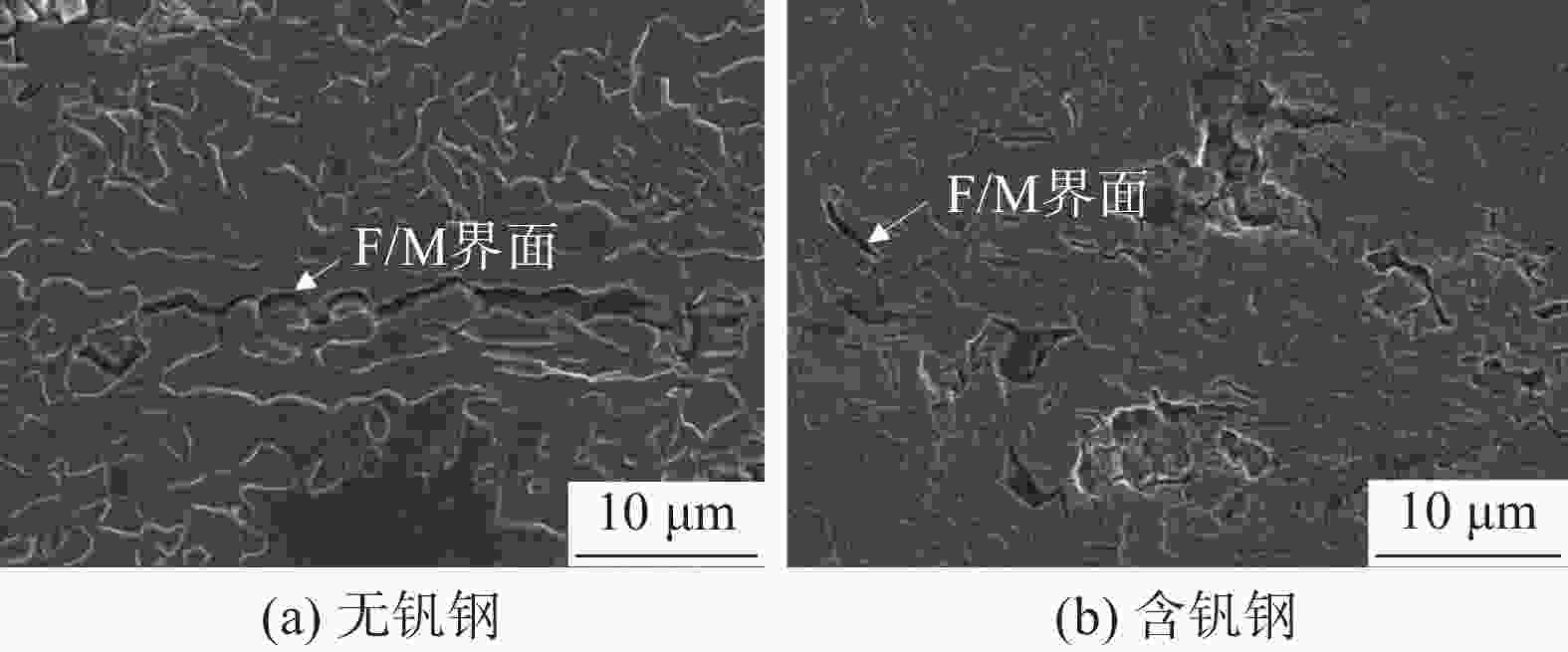
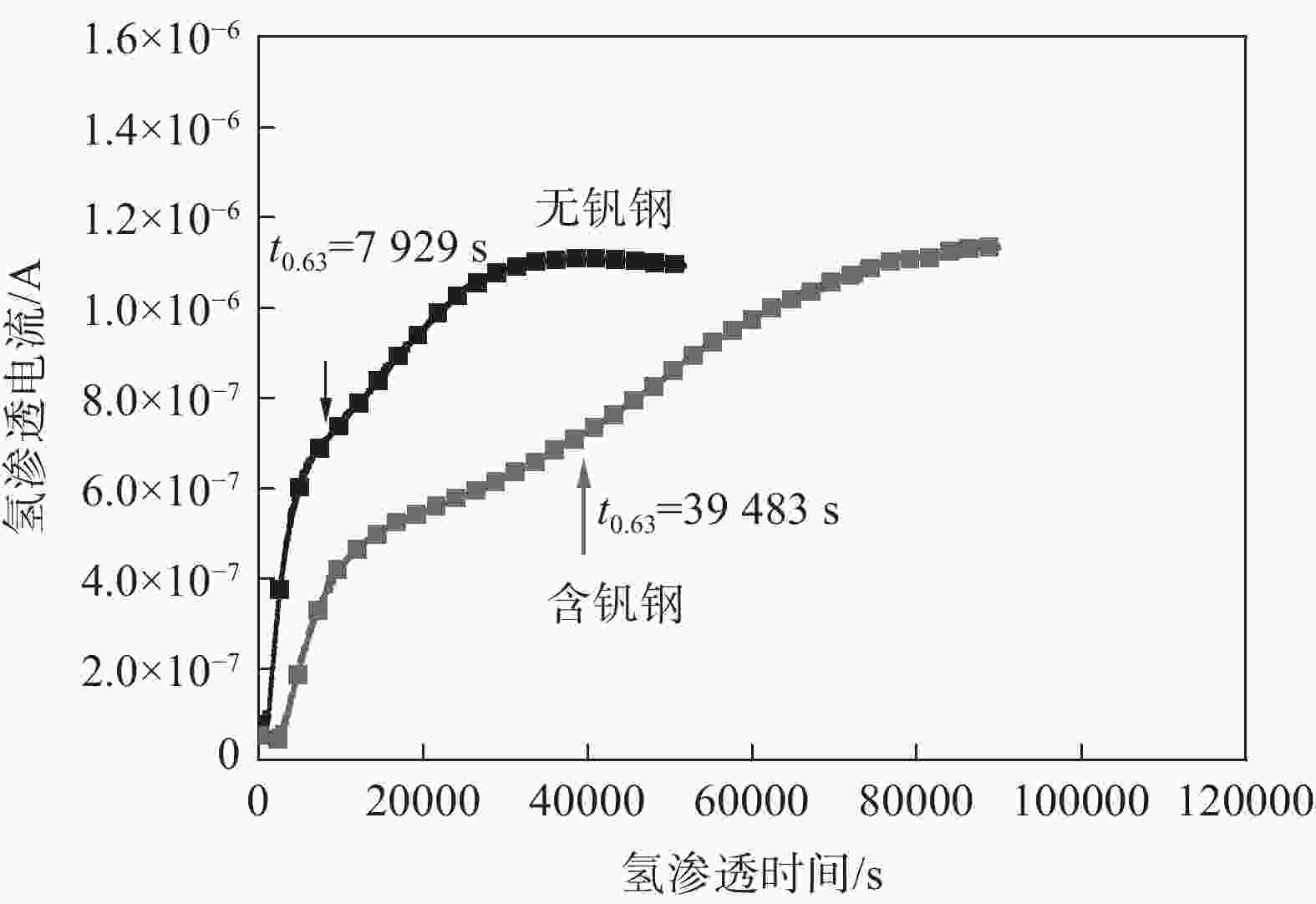
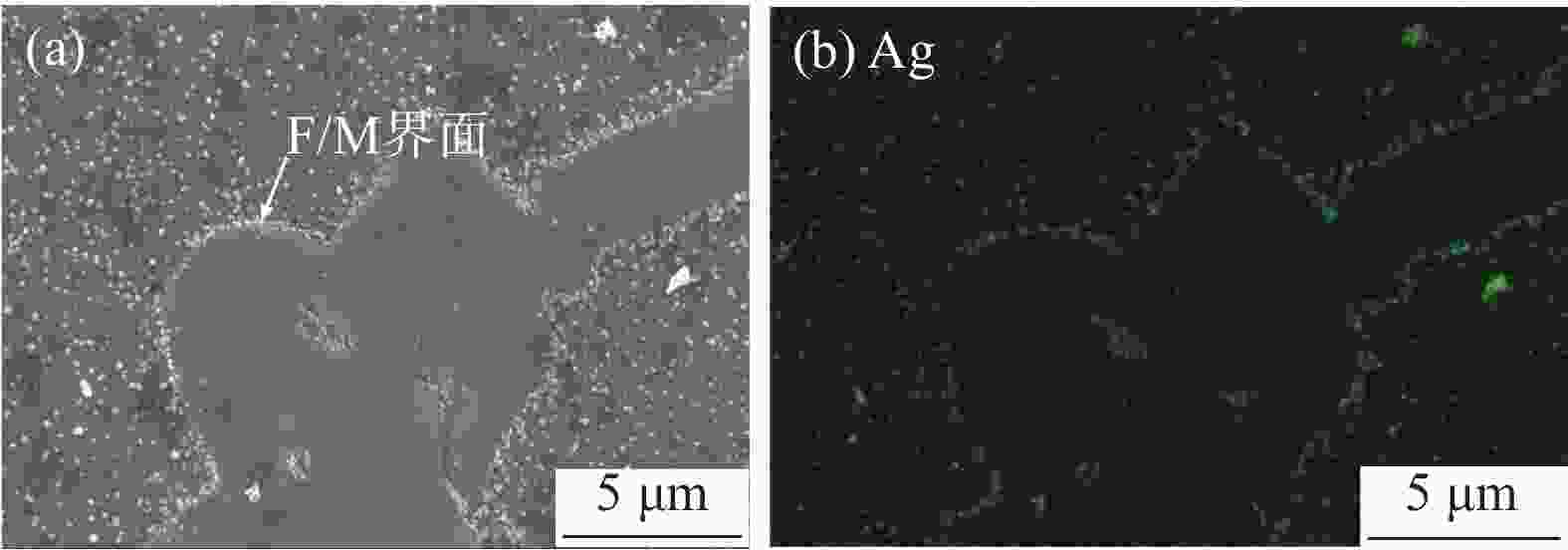
摘要: 利用慢应变速率拉伸、氢渗透以及氢显试验,结合SEM、TEM、EBSD分析,研究了0.12%钒对中锰热成形钢氢脆敏感性的影响。结果表明,钒微合金化对中锰热成形钢氢脆敏感性具有双重影响:一方面,钒不仅显著细化晶粒、析出了大量的纳米级含钒碳化物,使钢中的氢陷阱密度大幅增加,有效抑制了氢向铁素体/马氏体界面的富集,而且添加钒后长条状铁素体明显减少、小角度晶界占比增加,可进一步抑制裂纹的连续扩展,从而降低试验钢的氢脆敏感性;但另一方面,钒使钢中马氏体含量增加,会在一定程度上增加氢脆发生的风险。在常规的热成型工艺下,钒微合金化产生的有益作用更为显著,使含钒试验钢具备更优异的氢脆抗力。Abstract: The effect of adding 0.12% vanadium on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of medium Mn based hot stamping steel was studied by using slow strain rate tensile, hydrogen permeability and hydrogen microprinting experiments, combined with SEM, TEM, and EBSD analysis. The results show that vanadium microalloying on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility has double effects. On the one hand, vanadium not only significantly refines grains and precipitates a large number of nano-scale vanadium-containing carbides in steel, which greatly increases the hydrogen trap density and effectively inhibites hydrogen enrichment to the ferrite/martensite interface. Moreover, the addition of vanadium reducing the long strip-shaped ferrite and increasing the proportion of small angle grain boundaries can further restrain the continuous crack propagation and decrease the hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility. But on the other hand, vanadium increases the martensite content, which increases the risk of hydrogen embrittlement to a certain extent. Under conventional hot forming process, the beneficial effect of vanadium microalloying is more significant, which makes the test steel containing vanadium has better hydrogen embrittlement resistance.
-
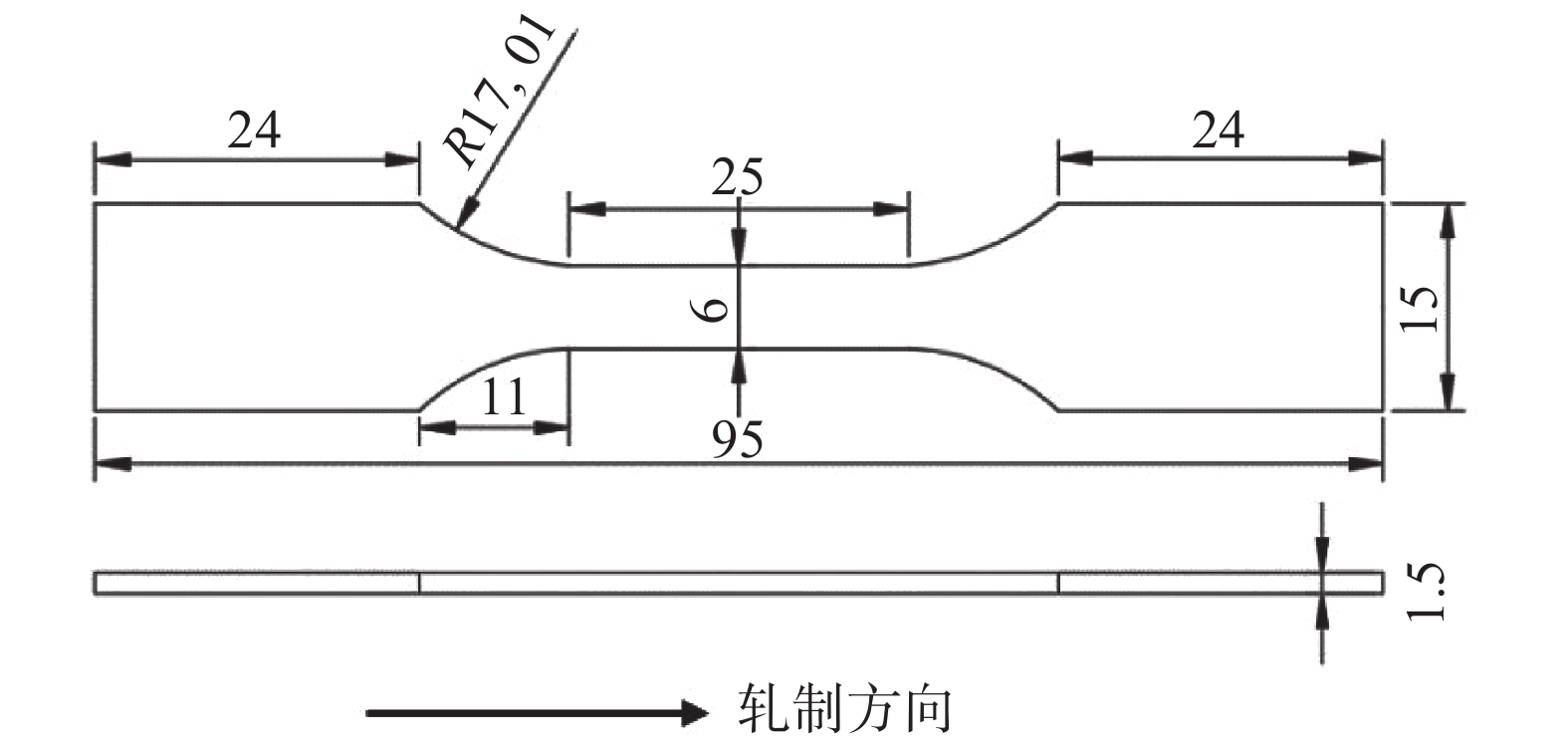
表 1 试验钢的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of test steels
% 材料 C Si Mn Al Nb Ti V Fe 无钒钢 0.22 0.22 5.12 2.94 0.02 0.01 Bal 含钒钢 0.23 0.20 5.37 2.88 0.02 0.03 0.12 Bal -
[1] Jin Xuejun, Gong Yu, Han Xianhong, et al. A review of current state and prospect of the manufacturing and application of advanced hot stamping automobile steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020,56(4):411. (金学军, 龚煜, 韩先洪, 等. 先进热成形汽车钢制造与使用的研究现状与展望[J]. 金属学报, 2020,56(4):411.Jin Xue Jun, Gong Yu, Han Xian Hong, et al. A Review of Current State and Prospect of the Manufacturing and Application of Advanced Hot Stamping Automobile Steels [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020, 56 (4): 411. [2] Liu Hanhua. Study on hydrogen embrittlement resistance of Ti-microalloying hot forming steel for automobile[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(4):178−183. (刘汉华. 不同钛含量汽车用热成型钢的抗氢脆敏感性研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(4):178−183.Liu Han Hua. Study on hydrogen embrittlement resistance of Ti-microalloying hot forming steel for automobile [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(4): 178-183. [3] Ge Rui, Yang Rui, Liu Ziqi, et al. Effect of vanadium microalloying on mechanical properties of medium Mn based hot stamping steel and corresponding strengthening mechanism[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2022,3:1−10. (葛锐, 杨睿, 刘子奇, 等. 钒对中锰热成形钢性能的影响及其强化机制[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2022,3:1−10.Ge Rui, Yang Rui, Liu Zi Qi, et al. Effect of vanadium microalloying on mechanical properties of medium Mn based hot stamping steel and corresponding strengthening mechanism [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2022, 3: 1-10. [4] Li Longfei, Song Bo, Cai Zeyun, et al. Effect of vanadium content on hydrogen diffusion behaviors and hydrogen induced ductility loss of X80 pipeline steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2019,742:712−721. [5] Zhao Haoyang, Wang Pei, Li Jinxu, et al. Effect of vanadium content on hydrogen embrittlement of 1400 MPa grade high strength bolt[J]. Hydrogen Energy, 2021,46:34983−34997. [6] Park Tak Min, Kim Hye Jin, Um Ho Yong, et al. The possibility of enhanced hydrogen embrittlement resistance of medium-Mn steels by addition of micro-alloying elements [J].Materials Characterization, 2020, 165: 110386. [7] Wang Zhen, Liu Jing, Zhang Shiqi, et al. Effect of strain rate on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of DP780 steel with hydrogen pre-charging[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2022,42(1):106−111. (王贞, 刘静, 张施琦, 等. 应变速率对预充氢DP780钢氢脆敏感性的影响[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2022,42(1):106−111.Wang Zhen, Liu Jing, Zhang Shi Qi, et al. Effect of strain rate on hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of DP780 steel with hydrogen pre-charging [J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2022, 42(1): 106-111. [8] Ichitani Koji, Kanno Motohiro, Kuramoto Shigeru. Recent development in hydrogen microprint technique and its application to hydrogen embrittlement[J]. ISIJ International, 2007,43(4):496−504. [9] Zhang Dazheng, Li Weijuan, Gao Xiuhua, et al. Effect of cold deformation before heat treatment on the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of high-strength steel for marine risers[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2022,845:143220. [10] Chen Yong, Liu Jing, Huang Feng, et al. Influence of inclusions on hydrogen induced delayed cracking in hot stamping steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2019,26(11):10. [11] Huang Shan, Wu Riming, Chen Meng, et al. Effect of vanadium content on microstructure and mechanical properties of 4Cr5Mo2V steel[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2022,46(7):70−75. (黄山, 吴日铭, 陈蒙, 等. 钒含量对4Cr5Mo2V钢显微组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2022,46(7):70−75.Huang Shan, Wu Ri Ming, Chen Meng, et al. Effect of vanadium content on microstructure and mechanical properties of 4 Cr5 Mo2 V steel [J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 46(7): 70-75. [12] Wang Zhen, Liu Jing, Huang Feng, et al. Hydrogen diffusion and its effect on hydrogen embrittlement in DP steels with different martensite content[J]. Frontiers in Materials, 2020,7:1−12. [13] Hadžipašić Anita Begić, Malina Jadranka, Nižnik Štefan. The influence of microstructure on hydrogen diffusion in dual phase steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Slovaca, 2011,17(2):129−132. [14] Takahashi Jun, Kawakami Kazuto, Kobayashi Yukiko. Origin of hydrogen trapping site in vanadium carbide precipitation strengthening steel [J]. Acta Mater., 2018, 153: 193−204. [15] Koyama Motomichi, Lee Taekyung, Lee Chong Soo, et al. Grain refinement effect on cryogenic tensile ductility in a Fe-Mn-C twinning-induced plasticity steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2013,49:234−241. -




 下载:
下载: