Study on preparation of VOSO4 by chemical synthesis of sodium metavanadate
-
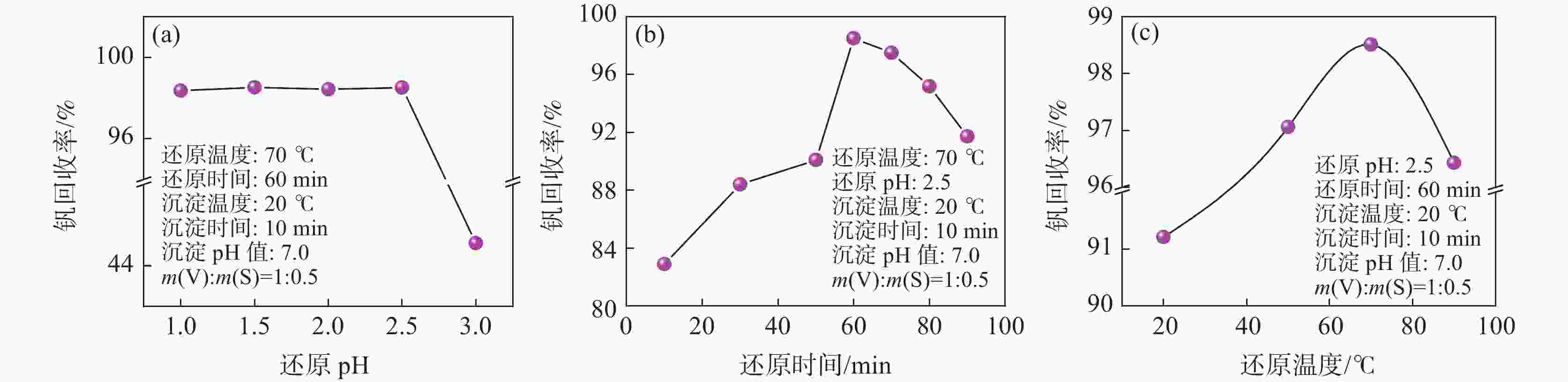
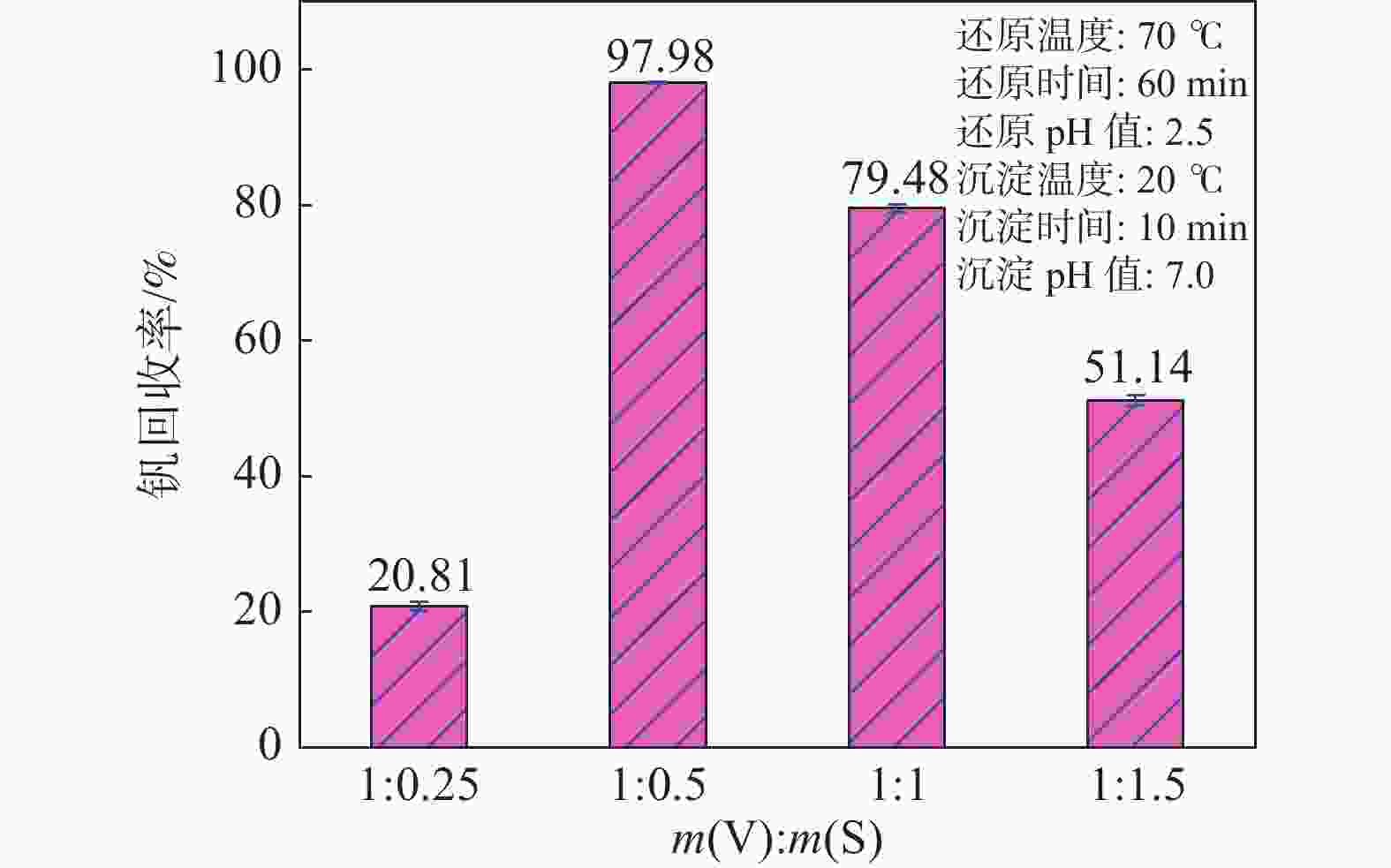
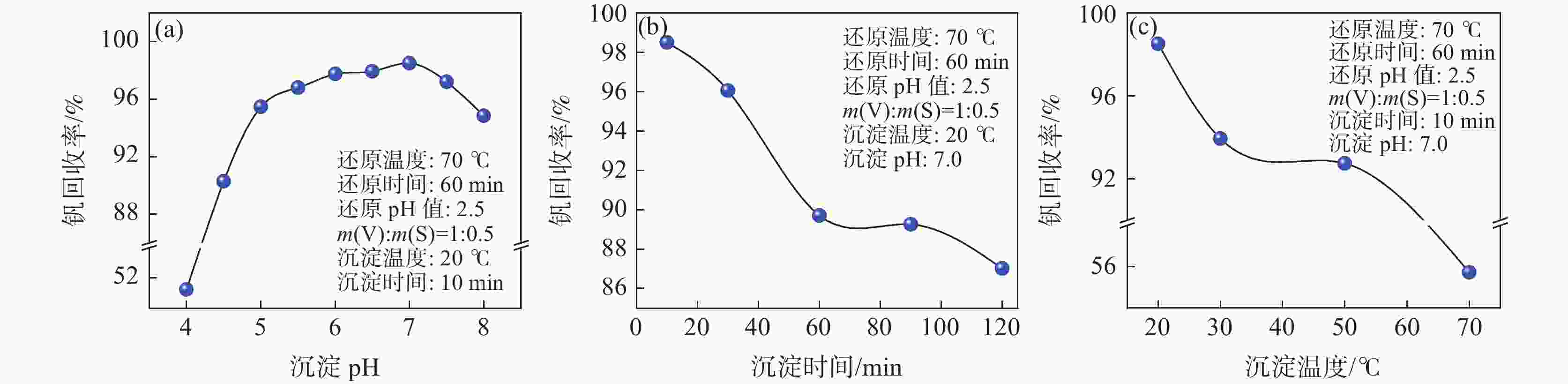
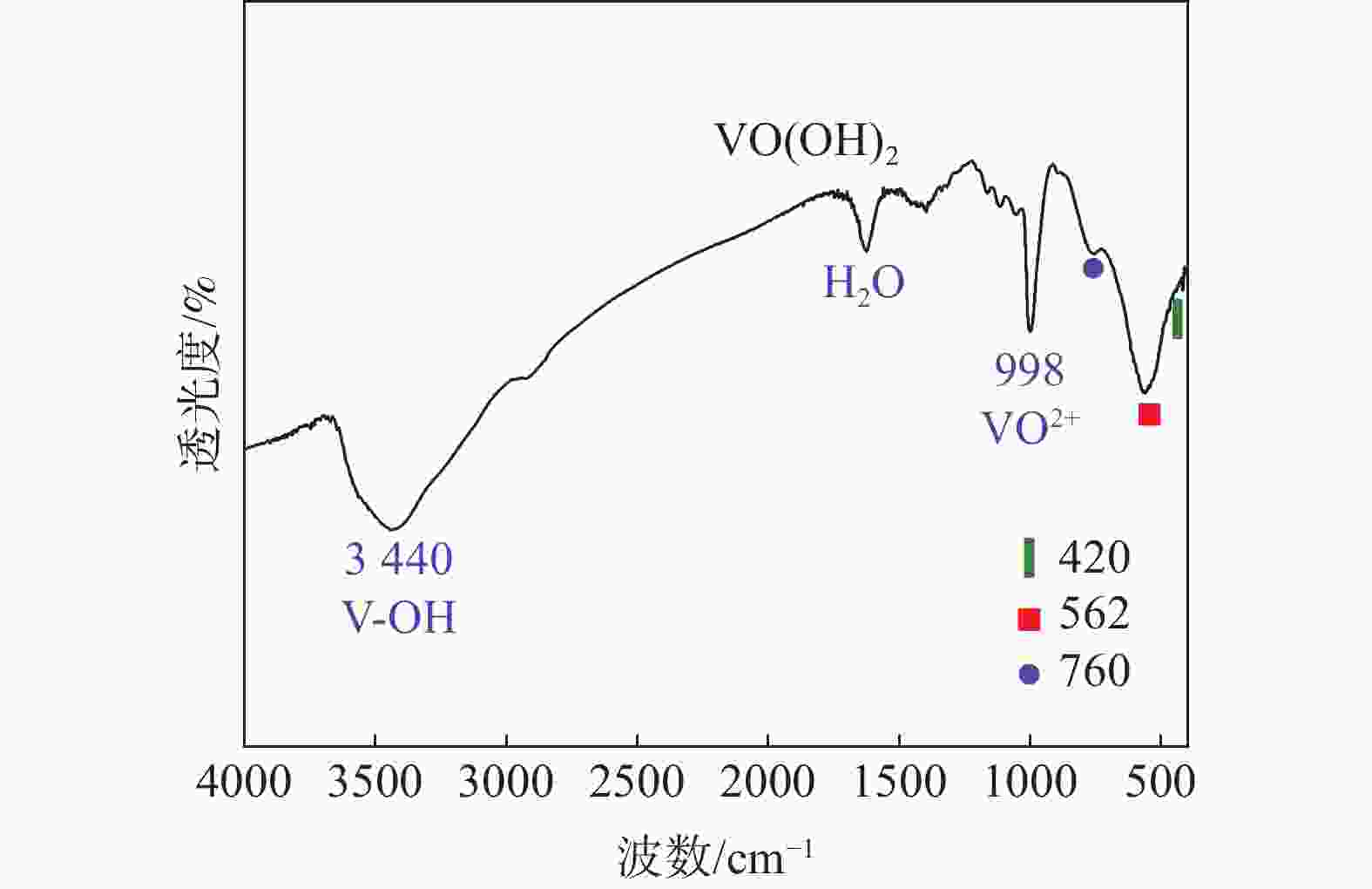
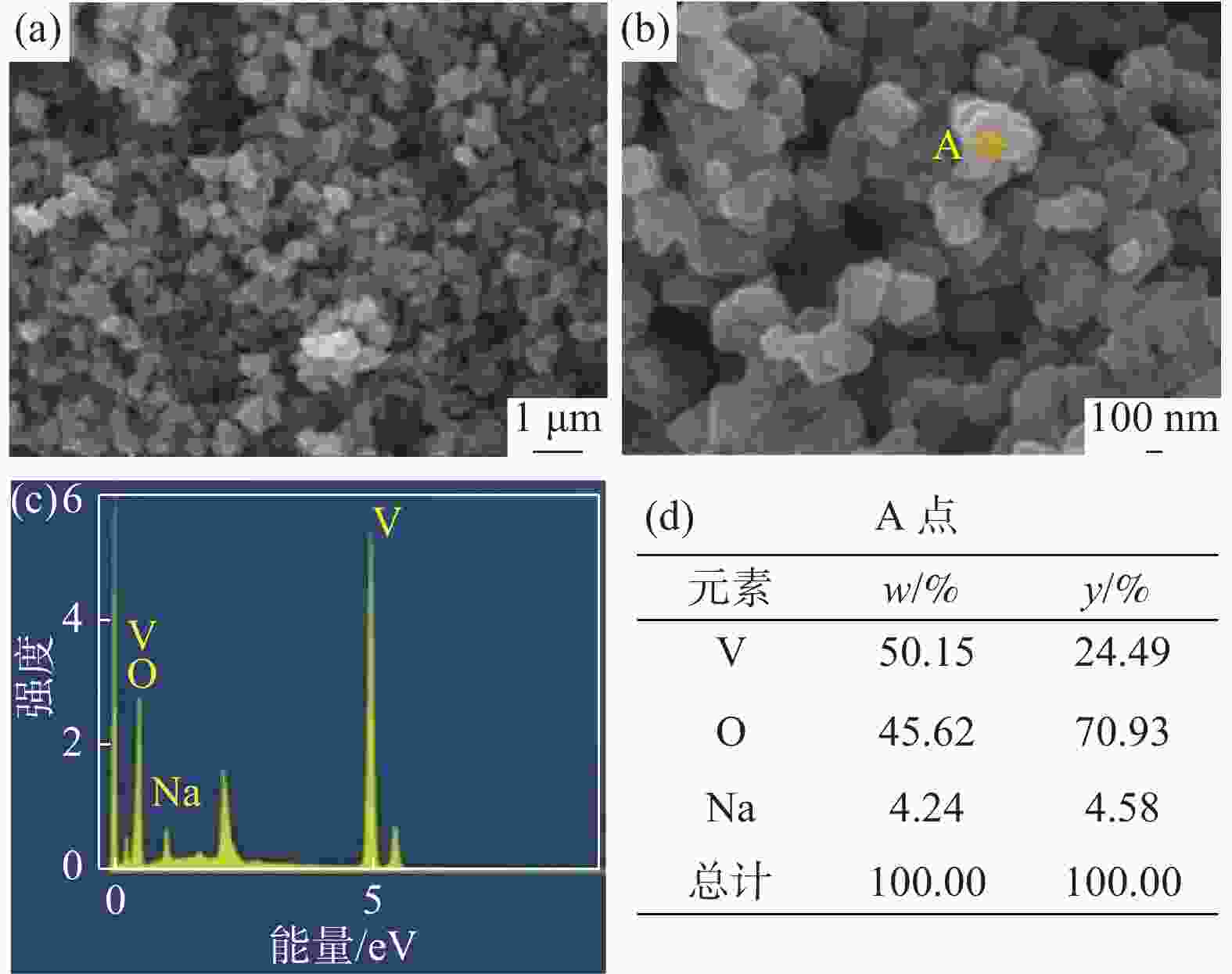
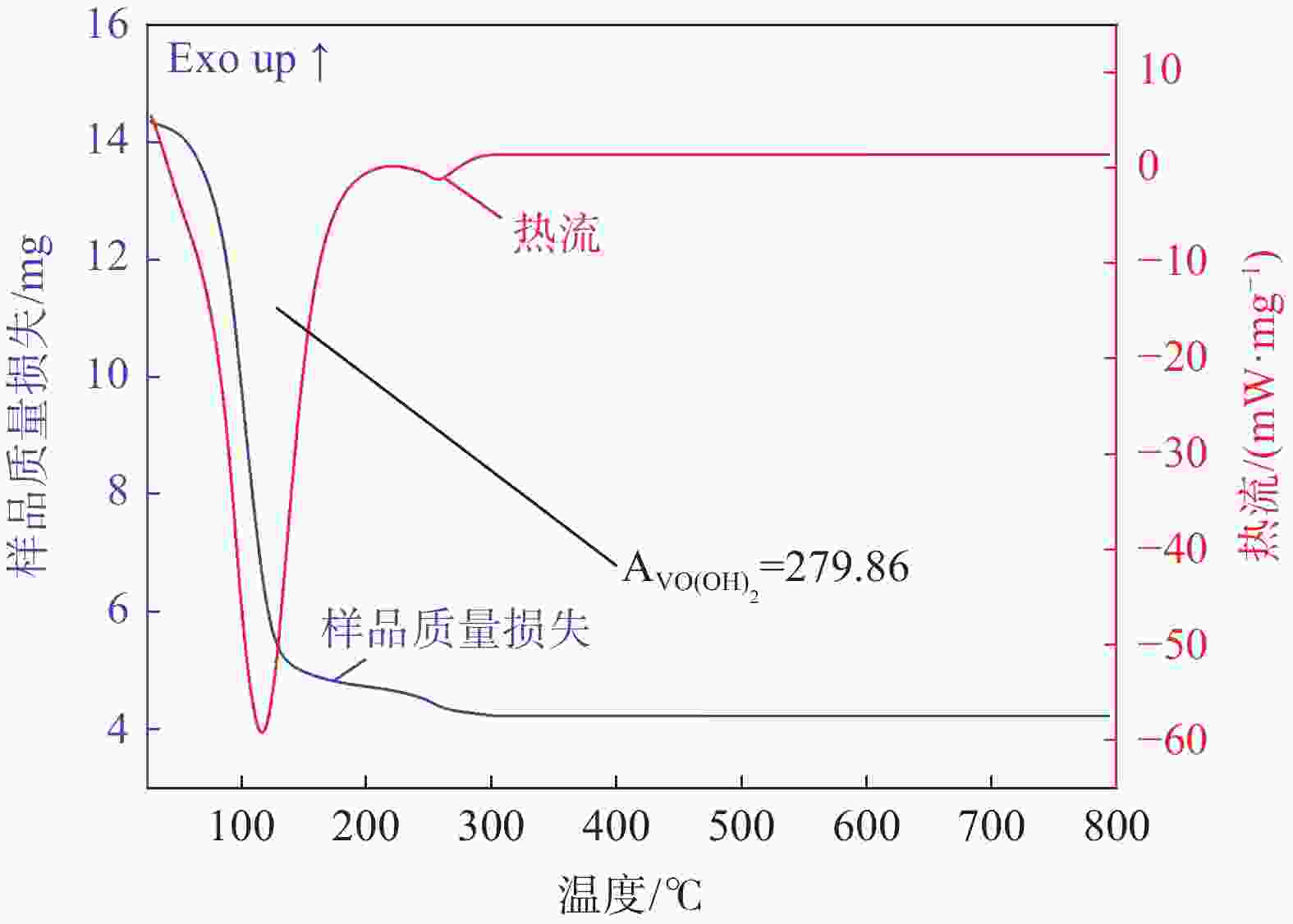
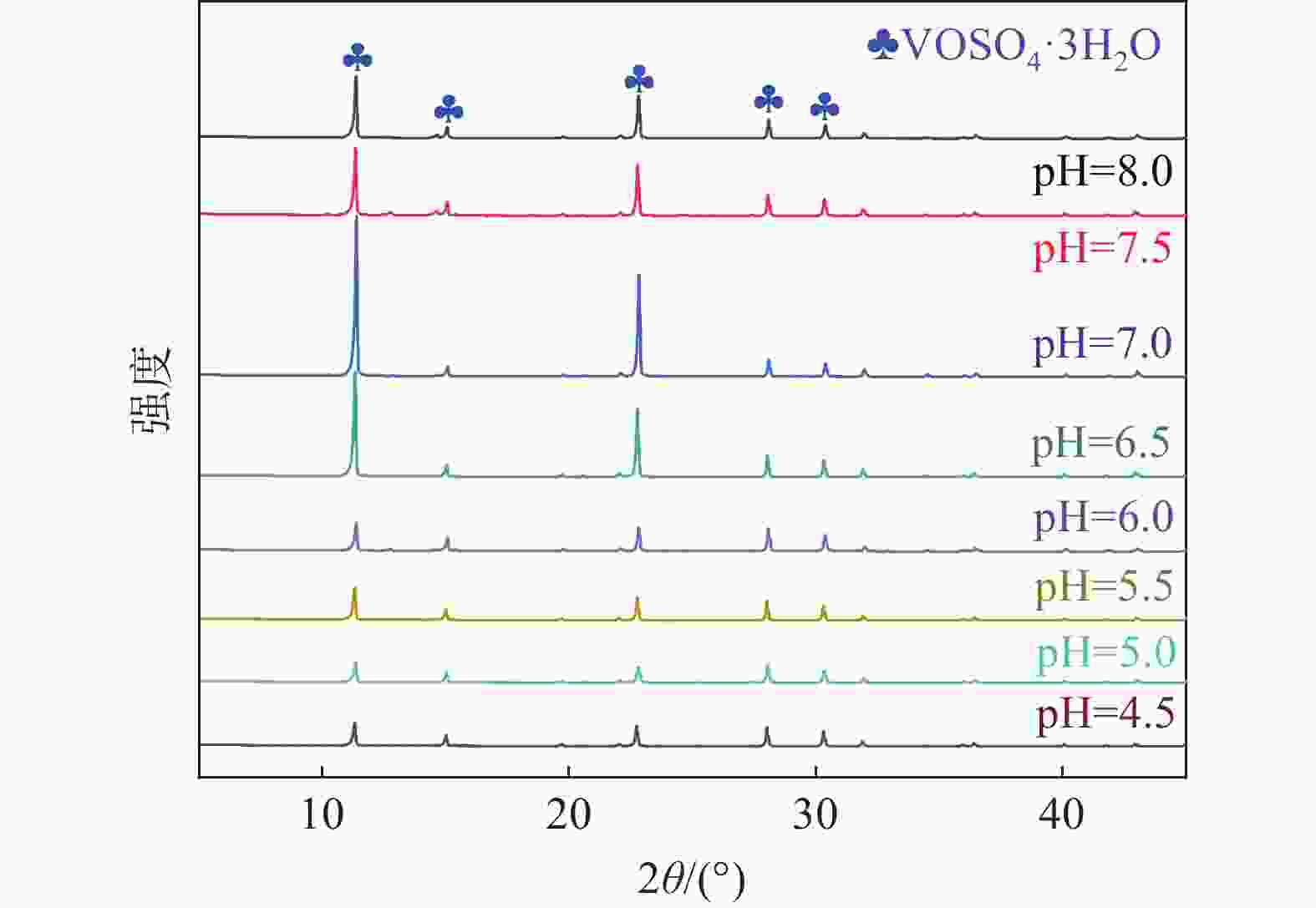
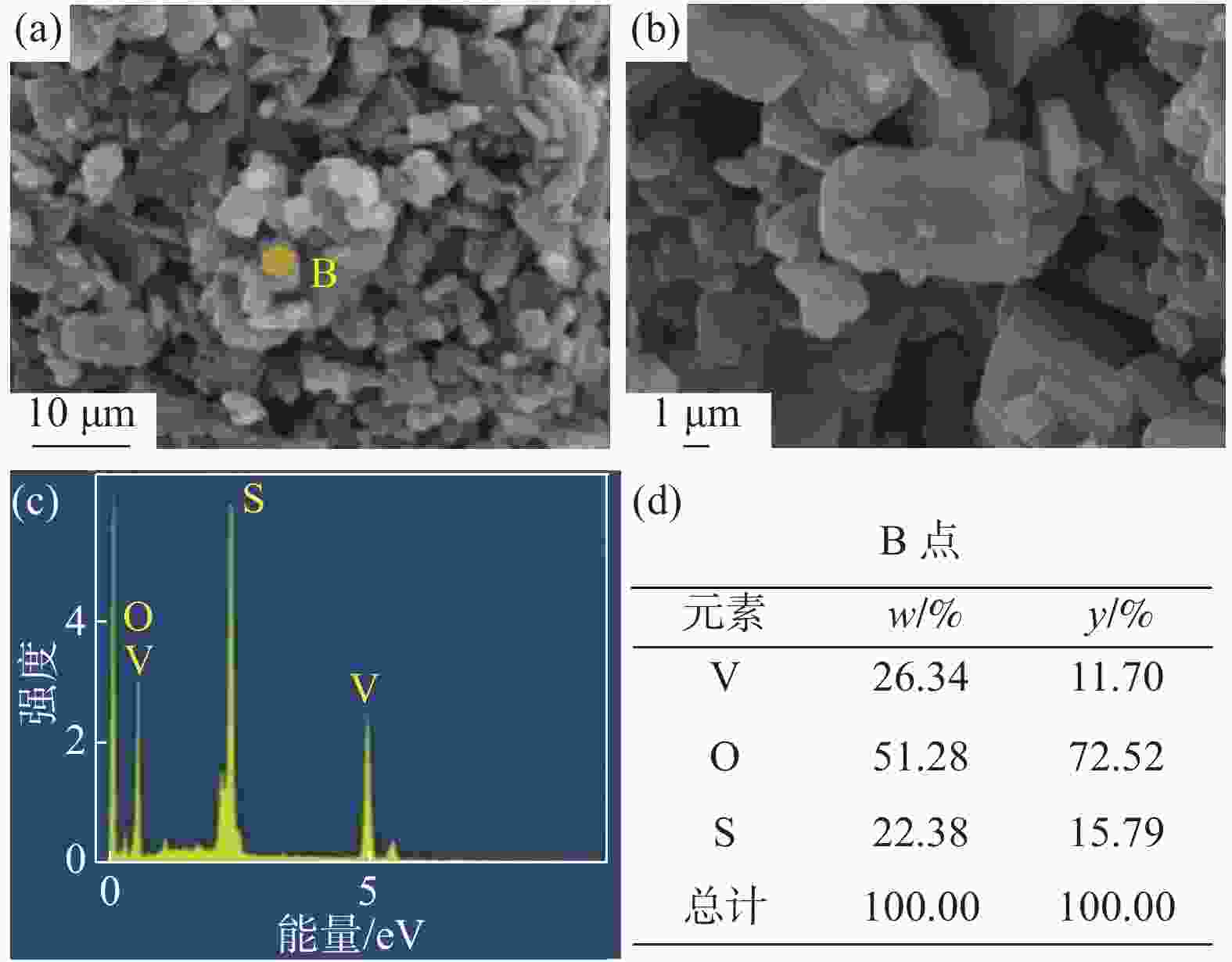
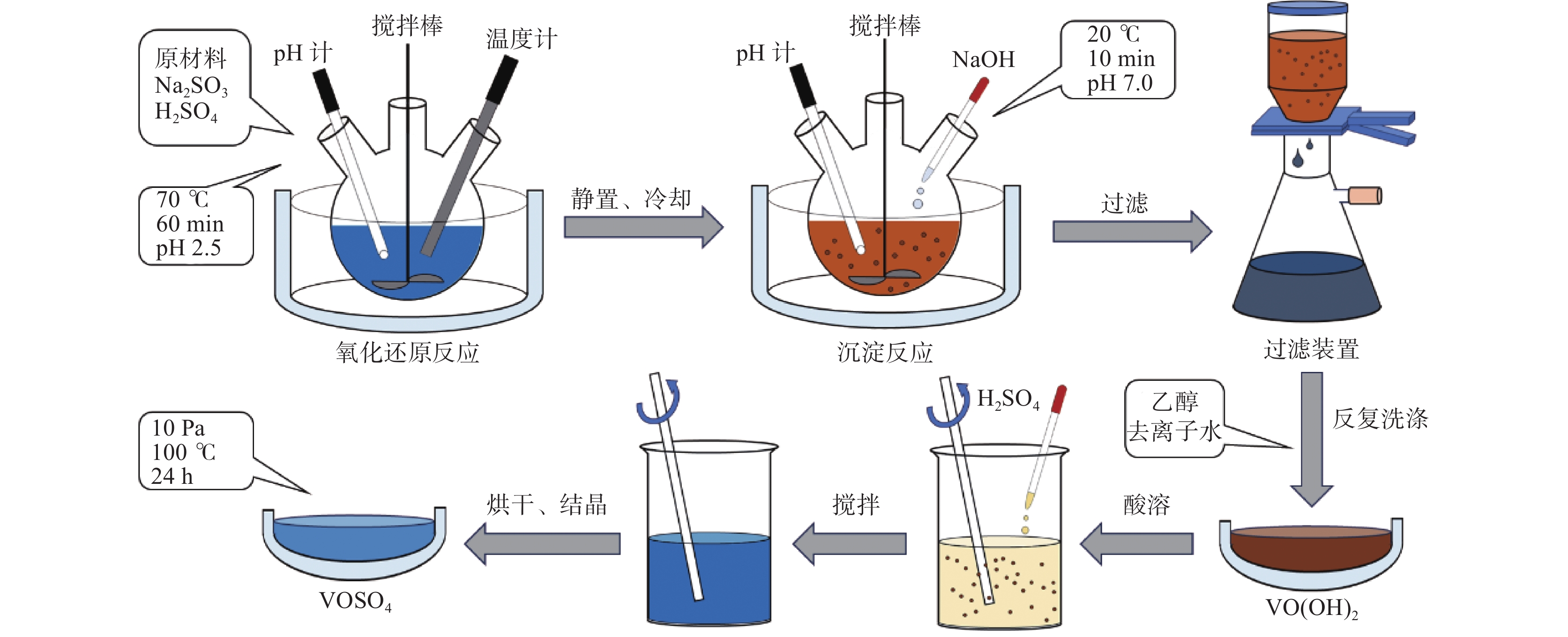
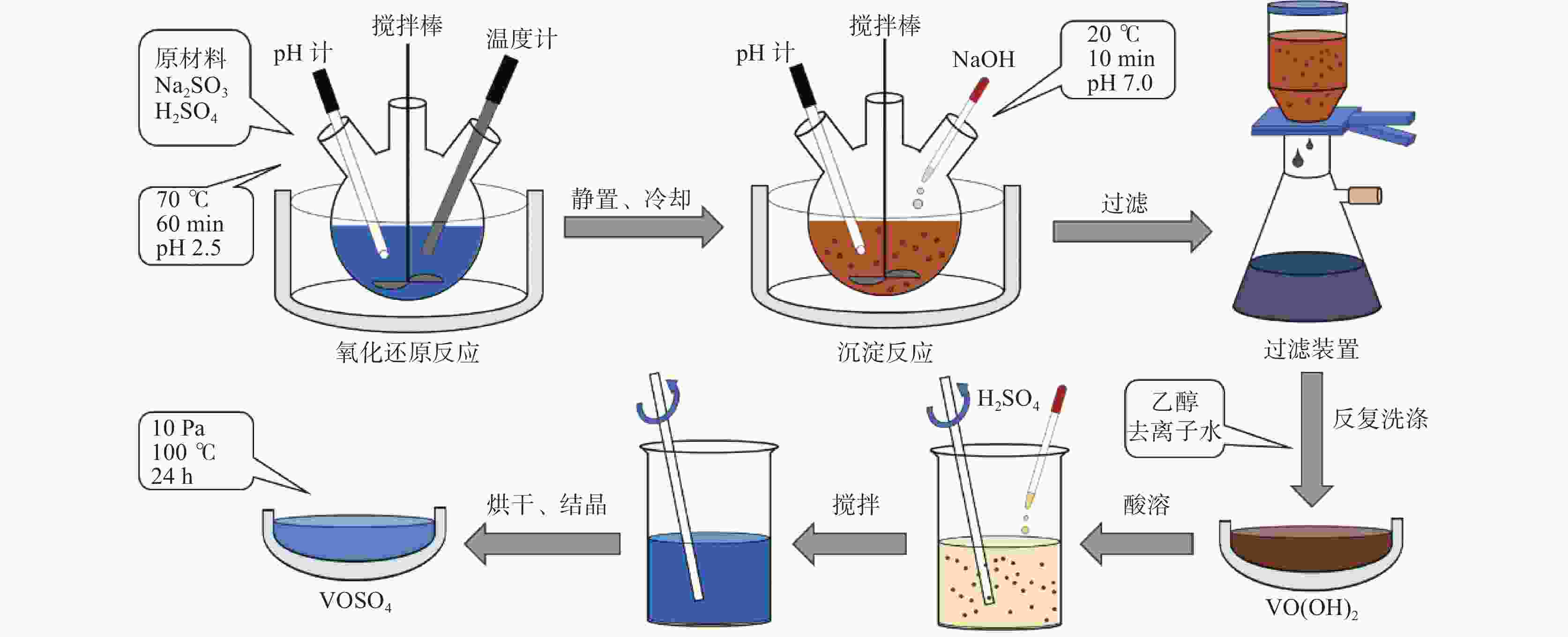
摘要: 硫酸氧钒(VOSO4)电解液是钒电池中电化学反应的活性物质和能量载体,其品质直接影响钒电池的能量效率、能量密度和使用寿命等性能。以偏钒酸钠(NaVO3)为原料,亚硫酸钠(Na2SO3)为还原剂,通过还原、沉淀、酸溶、结晶工艺制得了VOSO4产物,探索了各因素对钒回收率的影响,并对中间产物VO(OH)2和VOSO4产物进行表征。结果表明:偏钒酸钠浸出液以m(V):m(S)为1:0.5加入亚硫酸钠,在pH为2.5的溶液中于70 ℃恒温下还原60 min后,实现了钒(V)还原为钒(IV)。将pH调至7.0,并在20 ℃下反应10 min,蓝色溶液可转化成VO(OH)2中间产物,此时钒回收率最高,为98.51%。VO(OH)2由直径为50~200 nm球状结构组成,将其用硫酸溶解可得蓝色VOSO4溶液,烘干结晶后得到平均直径为5 μm的固体VOSO4晶体,产物品质符合国标二级标准。该研究为利用钒渣钠化焙烧浸出液原位制备VOSO4提供了前期试验基础。Abstract: Vanadium sulfate (VOSO4) electrolyte is the active material and energy carrier of electrochemical reaction in vanadium battery, and its quality directly affects the performance of vanadium battery such as energy efficiency, energy density and service life. In this paper, VOSO4 was synthesized from sodium metavanadate (NaVO3) and sodium sulfite (Na2SO3) by reduction, precipitation, acid dissolution and crystallization. The effects of various factors on vanadium recovery were investigated, and the intermediate products VO(OH)2 and VOSO4 were characterized. The results show that vanadium (V) can be reduced to vanadium (IV) by adding sodium sulfite into the leaching solution of sodium metavanadate with a mass ratio of m(V):m(S) of 1:0.5 and keeping it at 70 ℃ for 60 min in a solution with pH 2.5. When pH value was adjusted to 7.0 and the reaction temperature was 20 ℃ for 10 min, the blue solution could be converted into VO(OH)2 intermediate product, achieving a highest vanadium recovery of 98.51%. The diameter of VO(OH)2 spherical structure was 50~200 nm. Blue VOSO4 solution can be obtained by dissolving VO(OH)2 with sulfuric acid. After drying and crystallizing, VOSO4 crystal with an average diameter of 5 μm was obtained, and the quality of the product met the second grade standard of national standard. This study provides a preliminary experimental basis for in-situ preparation of VOSO4 from sodium leaching solution of vanadium slag.
-
Key words:
- VOSO4 /
- sodium metavanadate /
- vanadium battery electrolyte /
- VO(OH)2 /
- vanadium recovery rate
-
表 1 中间产物V离子和Na离子含量
Table 1. Content of V4+ and Na+ in intermediate products
g/L V4+ Na+ 洗涤前 30.6 0.69 洗涤后 30.2 0.02 表 2 VOSO4产物主要离子含量
Table 2. Main ions content in VOSO4 product
mg/L 成分 V2O5 SO42− Na+ 国标二级 ≥ 136500 ≥ 220800 ≤200 产物 136500 343400 166 -
[1] Yang Baoxiang. Vanadium based material manufacture[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2014. (杨保祥. 钒基材料制造[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2014.Yang Baoxiang. Vanadium based material manufacture[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2014. [2] Chen Housheng. Vanadium compounds. encyclopedia of chemical engineering vol. 4[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1993. (陈厚生. 钒化合物. 化工百科全书·第4卷[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 1993.Chen Housheng. Vanadium compounds. encyclopedia of chemical engineering vol. 4[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1993. [3] Zhou Zheng. Preparation of electrolyte for vanadium battery with energy storage[J]. Journal of Chengdu Electronic Mechanical College, 2009, 12(2):29-32. (周筝. 储能钒电池电解液制备[J]. 成都电子机械高等专科学校学报, 2009, 6.Zhou Zheng. Preparation of electrolyte for vanadium battery with energy storage[J]. Journal of Chengdu Electronic Mechanical College, 2009, 12(2): 29-32. [4] Cui Yanhua, Meng Fanming. Research on the vanadium ion redox flow battery[J]. Power Technology, 2000,24(6):356-358. [5] Rychcik M, Skyllas-Kazacos M. Characteristics of new all-vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Power Sources, 1988,22(1):59-67. doi: 10.1016/0378-7753(88)80005-3 [6] Liu Dafan, Li Xiaolei, Guo Xifeng, et al. Current development status of all vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Inorganic Chemical Industry, 2010,42(8):4-6. [7] Li L, Kim S, Wang W, et al. A stable vanadium redox-flow battery with high energy density for large-scale energy storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2011,1(3):394-400. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201100008 [8] Li Linde, Zhang Bo, Huang Kelong, et al. Preparation of electrolyte for vanadium ion flow battery by electrolysis: China, CN1598063[P]. 2005-03-23. (李林德, 张波, 黄可龙, 等. 全钒离子液流电池电解液的电解制备方法: 中国,CN1598063[P]. 2005-03-23.Li Linde, Zhang Bo, Huang Kelong, et al. Preparation of electrolyte for vanadium ion flow battery by electrolysis: China, CN1598063[P]. 2005-03-23. [9] Skyllas Kazacos M, Kazacos G, Poon G, et al. Recent advanced with UNSW vanadium-based redox flow batteries[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2010,34(2):182-189. doi: 10.1002/er.1658 [10] Chang Fang, Meng Fanming, Lu Ruisheng. Development and prospect of the vanadium electrolyte for the vanadium battery[J]. Power Technology, 2006,10:860-862. [11] Luo Dongmei. Study on vanadium redox flow battery[D]. Shenyang: Northeast University, 2005. [12] Yan Jun, Zhao Lifei. Application of energy storage technology to distributed generation[J]. North China Electric Power Technology, 2006,10:55-57. [13] Zhao Ping, Zhang Huamin, Zhou Hantao, et al. Research outline of redox flow cells for energy storage in China[J]. Power Technology, 2005,10(2):96-99. [14] Yang Lihua. Preparation and mechanism of high purity vanadium sulfate for vanadium battery by solvent extraction[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2021. (杨莉花.基于溶剂萃取法制备钒电池用高纯硫酸氧钒与机理研究[D]. 广州:广东工业大学, 2021.Yang Lihua. Preparation and mechanism of high purity vanadium sulfate for vanadium battery by solvent extraction[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology, 2021. [15] Li Xiaoshan. Study on stable high concentration electrolyte for all vanadium redox flow battery[D]. Beijing:Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2012. (李小山. 全钒液流电池用稳定的高浓度电解液研究[D]. 北京:北京化工大学, 2012.Li Xiaoshan. Study on stable high concentration electrolyte for all vanadium redox flow battery[D]. Beijing:Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2012. [16] Liu Cong. Preparation of vanadium battery electrolyte by short process extraction from vanadium precipitation wastewater[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2020. (刘聪. 从沉钒废水中萃取法短流程制备钒电池电解液的研究[D]. 武汉:武汉科技大学, 2020.Liu Cong. Preparation of vanadium battery electrolyte by short process extraction from vanadium precipitation wastewater[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2020. [17] Li Dan. Preparation of high purity vanadium oxysulfate from vanadium-containing chloride solution by short process[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Process Engineering), 2017. (李丹. 含钒氯化物溶液短流程制备高纯硫酸氧钒研究[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学 (过程工程研究所), 2017.Li Dan. Preparation of high purity vanadium oxysulfate from vanadium-containing chloride solution by short process[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Process Engineering), 2017. [18] Skyllas kazacos M, Rychcik M, Robins R G, et al. New all-vanadium redox flow cell[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1986,133(5):1057. doi: 10.1149/1.2108706 [19] Kazacos M S, Kazacos M, Samad M S, et al. Stabilized electrolyte solution methods of preparation thereof and redox cells and batteries containing stabilized electrolyte solution: AU, EP0729648B1[P]. 2003-04-02. [20] Johnson D A, Reid M A. Chemical and electrochemical behavior of the Cr(Ⅲ)/Cr(Ⅱ) half-cell in the ion-chemigum redox energy store system[J]. Electro Chem Soc, 1985(132):1058-1064. [21] Guo Qiusong, Liu Zhiqiang, Zhu Wei, et al. Preparation of ultra-pure vanadium oxysulfate by D2EHPA/TBP synergistic extraction from iron, chromium and manganese[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2013,7(2):77-81. (郭秋松, 刘志强, 朱薇, 等. D2EHPA/TBP协同萃取除铁铬锰制备超纯硫酸氧钒[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2013,7(2):77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2013.02.003Guo Qiusong, Liu Zhiqiang, Zhu Wei, et al. Preparation of ultra-pure vanadium oxysulfate by D2EHPA/TBP synergistic extraction from iron, chromium and manganese[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2013, 7(2): 77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2013.02.003 [22] Chen Meng, Zhang Yifu, Liu Yanyan, et al. A novel intercalation pseudocapacitive electrode material: VO(OH)2/CNT composite with cross-linked structure for high performance flexible symmetric supercapacitors[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 492: 746-755. -




 下载:
下载: