Research on wet gringding dispersion properties of different rutile TiO2 initial products
-
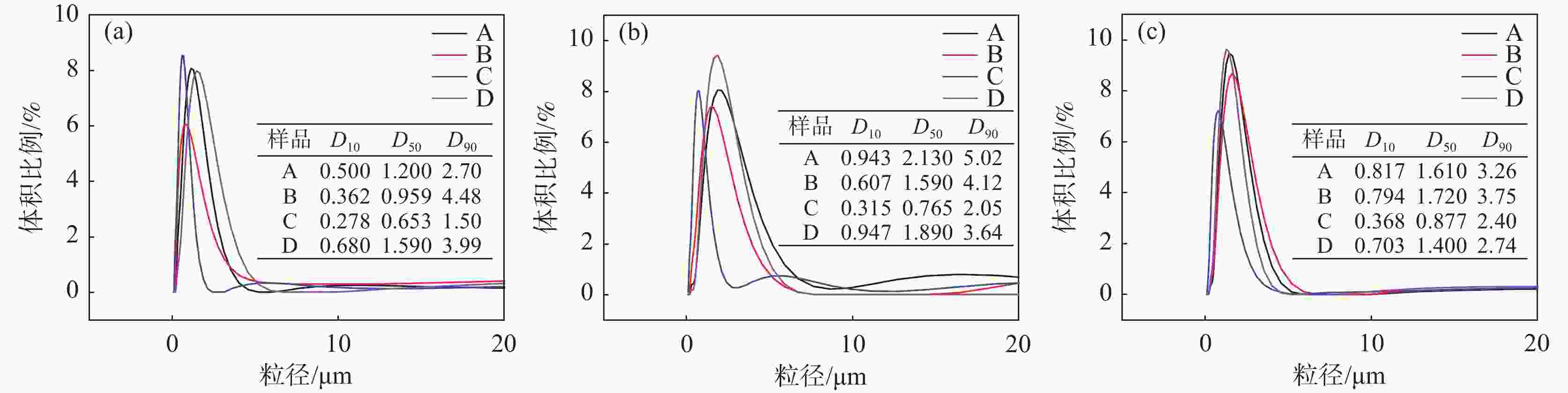
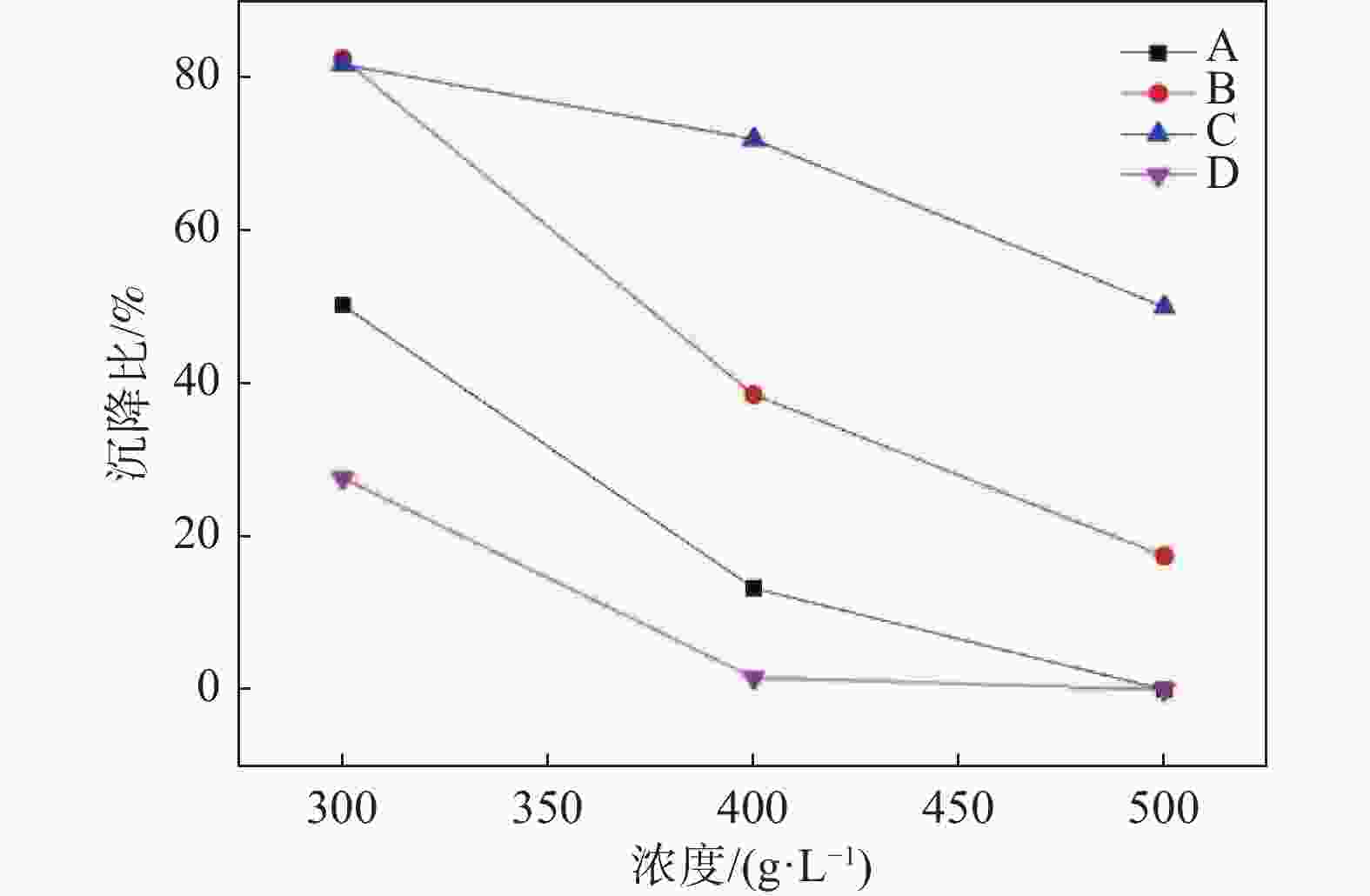
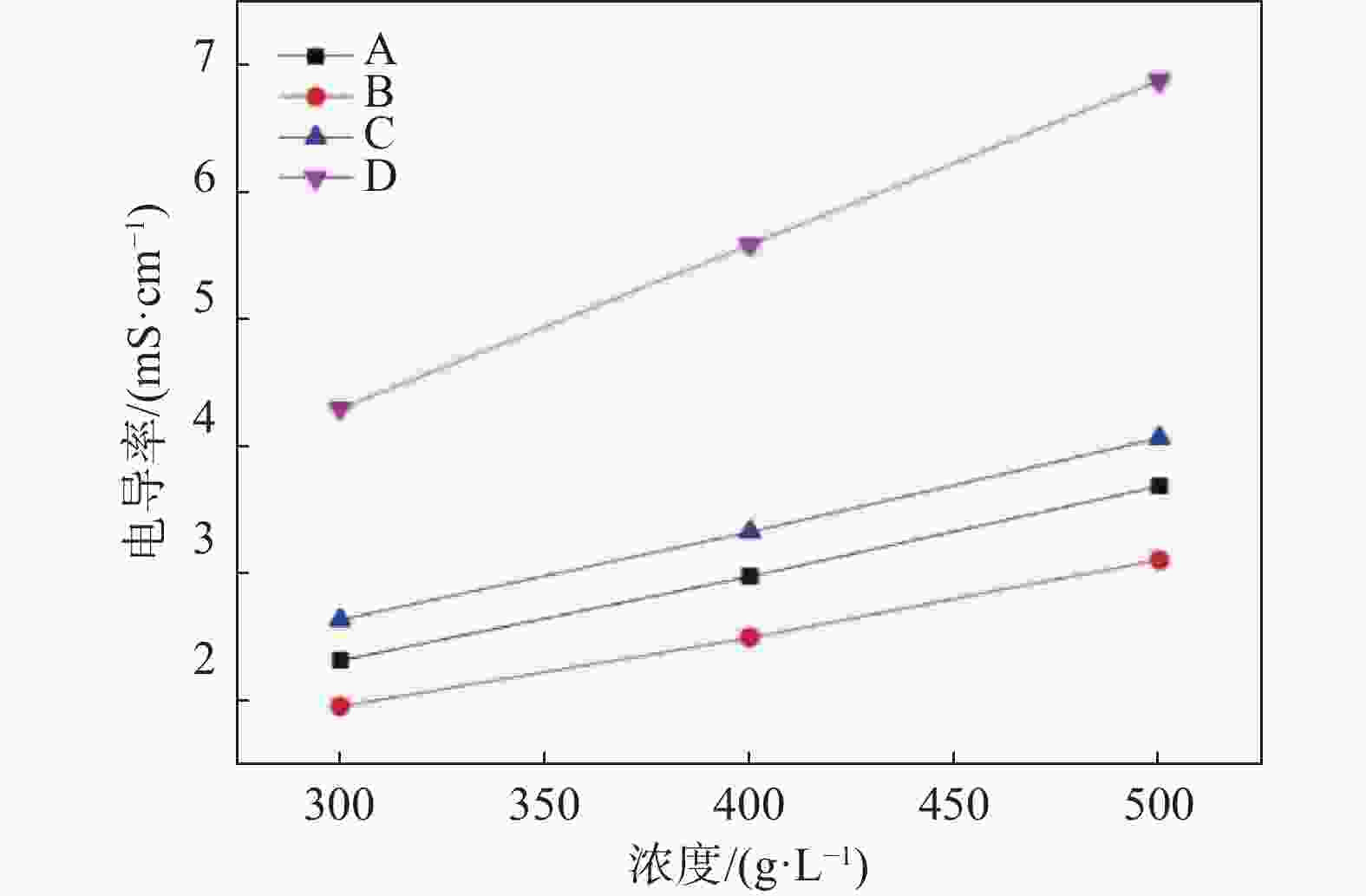
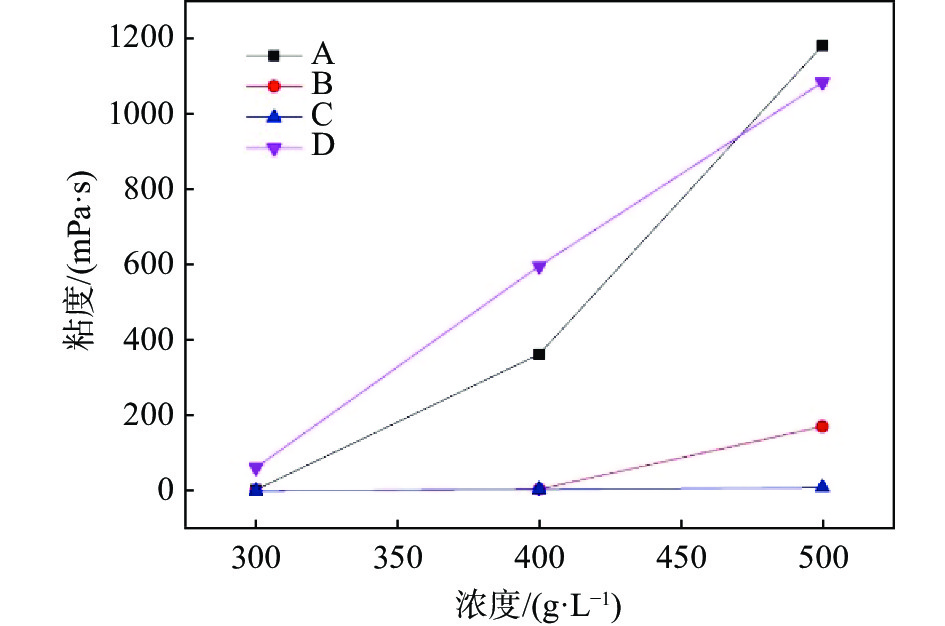
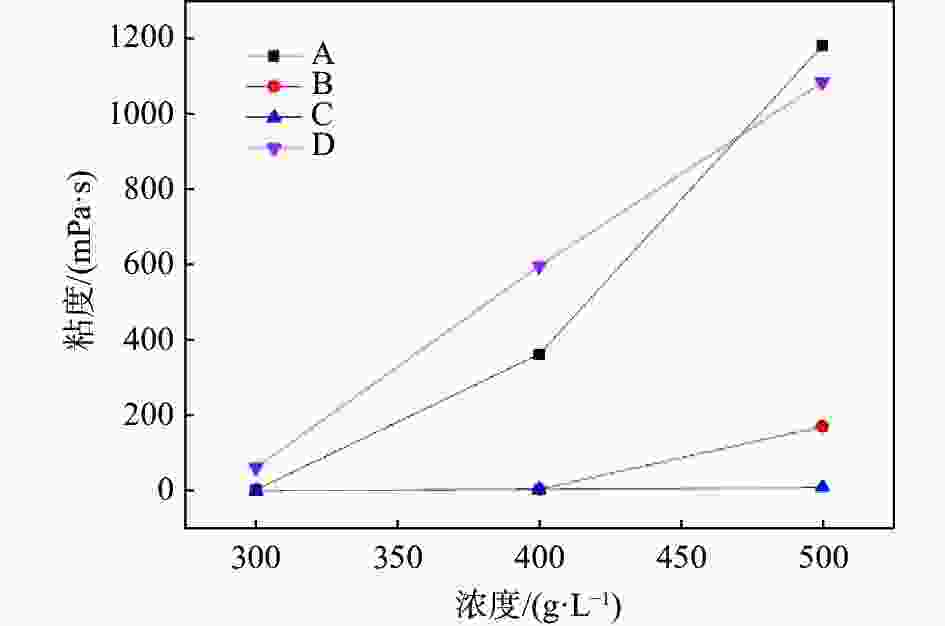
摘要: 以四种工业钛白粉辊压磨初品为原料,研究锌铝两系金红石钛白初品在不同打浆浓度条件下的湿磨分散性能,通过浆料粘度、分散稳定性、分散粒度及上清液电导率表征分散性能的差异。结果表明:同等硅酸钠分散工艺下,锌系初品分散性能均弱于铝系初品,且浆料粘度随打浆浓度升高而增大;各锌系初品的极限打浆浓度差异较大,硅酸钠加量为SiO2/TiO2质量比0.30%时,锌系初品B极限分散浓度可达500 g/L,但仍未达到铝系初品水平。低浓度状态下,各初品浆料中存在更多的小粒子,分散更加稳定,随着打浆浓度升高,浆料分散稳定性随之降低;粘度更低的浆料沉降比更高,即分散稳定性越差。各类初品表面电荷量各不相同,表面电荷更多的初品其粘度更低。Abstract: In this work, four kinds of industrial TiO2 initial products were used as raw materials to study the wet gringding dispersion of Zn series TiO2 and Al series TiO2 at different concentrations. Then, the difference of dispersion properties was analyzed by the characterization of slurry viscosity, dispersion stability, particle size and supernatant conductivity. The results show that the dispersibility of Zn series products is weaker than that of Al series products under the same sodium silicate dispersion process, and the slurry viscosity increases with the increase of beating concentration. The limit beating concentration of each Zn series products is different. When Na2SiO3 addition is 0.30% of the mass ratio of SiO2/TiO2, the highest dispersion concentration of Zn series B can reach 500 g/L, but it still can not reach the level of Al series products. At low concentrations below 300 g/L, there are more small particle size particles in each product, so the dispersion is more stable. With the increase of concentration, the dispersion stability of slurry decreases. The lower the viscosity of the slurry, the worse the dispersion stability. The amount of surface charge of all kinds of raw materials varies, and TiO2 with more surface charge has lower viscosity.
-
Key words:
- TiO2 powder /
- Zn series /
- Al series /
- dispersion property /
- sodium silicate
-
表 1 钛白粉初品元素含量、比表面积及粒径
Table 1. The element content, specific surface area and particle size of initial TiO2 products
编号 w/% 比表面积/
(m2·g−1)粒径/nm P S Fe Zn K2O Al2O3 P2O5 ZnO A 0.078 0.05 <0.01 0.083 0.234 <0.01 0.1787 0.1033 6.505± 0.0128 2.2178 B 0.074 0.033 <0.01 0.083 0.199 <0.01 0.1695 0.1033 5.983± 0.0325 2.2048 C 0.127 0.037 <0.01 <0.01 0.282 0.318 0.2910 5.9501 ±0.0422.1933 D 0.057 0.135 <0.01 0.076 0.272 <0.01 0.1306 0.0945 5.647± 0.0288 2.2093 表 2 主要试验设备
Table 2. The main experimental devices
设备名称 生产厂家 型号 电导率仪 上海仪电科学仪器有限公司 DDSJ-318T 流变仪 标格达精密仪器(广州)有限公司 BGD 157/TS 离心机 北京时代北利离心机有限公司 GT10-2 立式砂磨机 Shenzhen INVT Electric Co., Ltd CHE1000R7G-S2 搅拌器 上海梅颖浦仪器仪表制造有限公司 H2010G 比表面仪 Micromeritics Instrument Crop Gemini VII 激光粒度仪 Malvern Instruments Ltd Mastersizer 3000 表 3 砂磨浆料静置沉降上清液浑浊度
Table 3. The turbidity of supernatant of slurry after settling
打浆浓度/(g·L−1) A B C D 300 ▲▲▲▲▲ ▲▲▲▲▲ ▲▲▲▲▲ ▲ 400 ▲▲▲▲ ▲▲▲▲ ▲▲▲▲ 500 ▲▲▲ ▲▲▲ 注:▲表示上层清液浑浊度,个数越多越浑浊。 表 4 上清液电导率-打浆浓度线性拟合结果
Table 4. The fitting results of supernatant conductivity and concentration
编号 线性拟合公式 R2 A 电导率 = 0.2567 +0.006850× 浓度1 B 电导率 = 0.2210 +0.005755 ×浓度0.999 C 电导率 = 0.4867 +0.007150 ×浓度1 D 电导率 = 0.4300 +0.012900× 浓度1 -
[1] Liu Yong, Wang Zhenying, Guo Rufeng. Selection and optimization of crushing equipment for solid particles during titanium dioxide production[J]. Paint & Coatings Industry, 2015,45(12):28-33. (刘勇, 王振英, 郭如峰. 钛白粉生产中固体颗粒粉碎设备的选型及技术优化[J]. 涂料工业, 2015,45(12):28-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4312.2015.12.005Liu Yong, Wang Zhenying, Guo Rufeng. Selection and optimization of crushing equipment for solid particles during titanium dioxide production[J]. Paint & Coatings Industry, 2015, 45(12): 28-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4312.2015.12.005 [2] Wang Haibo, Wang Bin, Du Jianqiao, et al. Research on sand milling process of rutile titanium white[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(4):35-39. (王海波, 王斌, 杜剑桥, 等. 金红石型钛白砂磨工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(4):35-39. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.04.007Wang Haibo, Wang Bin, Du Jianqiao, et al. Research on sand milling process of rutile titanium white[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016, 37(4): 35-39. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.04.007 [3] Zhou Hua. Analysis of factors affecting wet grinding particle size in titanium dioxide production[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2021(19):25-26. (周华. 影响钛白粉生产湿磨粒径的因素分析[J]. 当代化工研究, 2021(19):25-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2021.19.011Zhou Hua. Analysis of factors affecting wet grinding particle size in titanium dioxide production[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2021(19): 25-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2021.19.011 [4] Cai Hong, Wang Zhenyao, Zhang Gancheng, et al. Effect of the surface structure of quartz powder on the morphology of empty secondary particles in calcineite[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1999,14(3):431-436. (蔡红, 王贞尧, 张干诚, 等. 石英微粉表面结构对硬硅钙石中空二次粒子形貌的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 1999,14(3):431-436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-324X.1999.03.018Cai Hong, Wang Zhenyao, Zhang Gancheng, et al. Effect of the surface structure of quartz powder on the morphology of empty secondary particles in calcineite[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1999, 14(3): 431-436. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-324X.1999.03.018 [5] Jiang Guimin, Yan Jikang, Yang Gang, et al. Influencing factors of crystal phase transformation (A→R) of TiO2[J]. Material Guide, 2016,30(19):95-99. (姜贵民, 严继康, 杨钢, 等. Ti02晶型转变(A→R)的影响因素[J]. 材料导报, 2016,30(19):95-99.Jiang Guimin, Yan Jikang, Yang Gang, et al. Influencing factors of crystal phase transformation (A→R) of TiO2[J]. Material Guide, 2016, 30(19): 95-99. [6] Cho J, Lee J G, Kim B, et al. Effect of P2O5 and AlPO4 coating on LiCoO2 cathode material[J]. Chem. Inform, 2003,34(45):3190-3193. [7] Takahashi K, Yamasaki N, Mishima K, et al. Coating of pulp fiber with xonotlite under hydrothermal conditions[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2002,21(19):1521-1523. doi: 10.1023/A:1020048531741 [8] Katsumata H, Kaneco S, Matsuno R, et al. Removal of organic polyelectrolytes and their metal complexes by adsorption onto xonotlite[J]. Chemosphere, 2003,52(5):909-915. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00285-6 [9] Ko Y M, Kwon W T, Kim Y W. Development of Al2O3–SiC composite tool for machining application[J]. Ceramics International, 2004,30(8):2081-2086. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2003.11.011 [10] Sun Chuanyao. Principle of silicate mineral flotation [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. (孙传尧. 硅酸盐矿物浮选原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.Sun Chuanyao. Principle of silicate mineral flotation [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. [11] Tang Liming, Lü Shaohua, Chen Jiujun, et al. Adsorption and zeta potential analysis of titania pigment and polyacrylic dispersant water system[J]. Chemical World, 2005,46(6):325-327. (唐黎明, 吕少华, 陈久军, 等. 钛白粉与分散剂水性体系的吸附和Zeta电位研究[J]. 化学世界, 2005,46(6):325-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0367-6358.2005.06.002Tang Liming, Lü Shaohua, Chen Jiujun, et al. Adsorption and zeta potential analysis of titania pigment and polyacrylic dispersant water system[J]. Chemical World, 2005, 46(6): 325-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0367-6358.2005.06.002 -




 下载:
下载: