Prediction of high temperature rheological behavior of TC4 titanium alloy based on Z-A constitutive model
-
摘要: 在描述材料承受不同变形条件下的响应行为及其热成形工艺过程优化方面,本构模型具有重要意义。因此,为了获得准确描述TC4钛合金高温流变行为的物理本构模型,利用Gleeble-
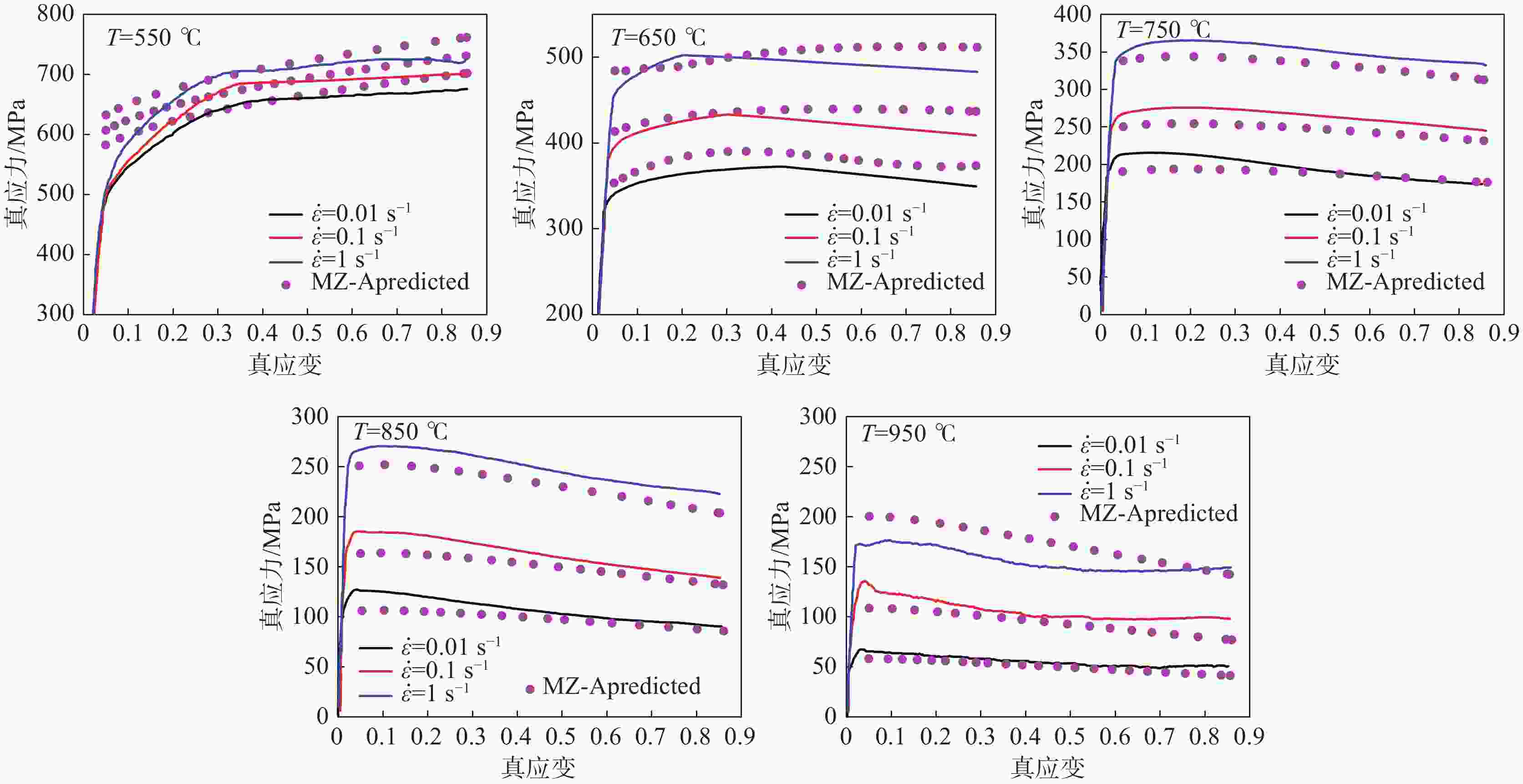
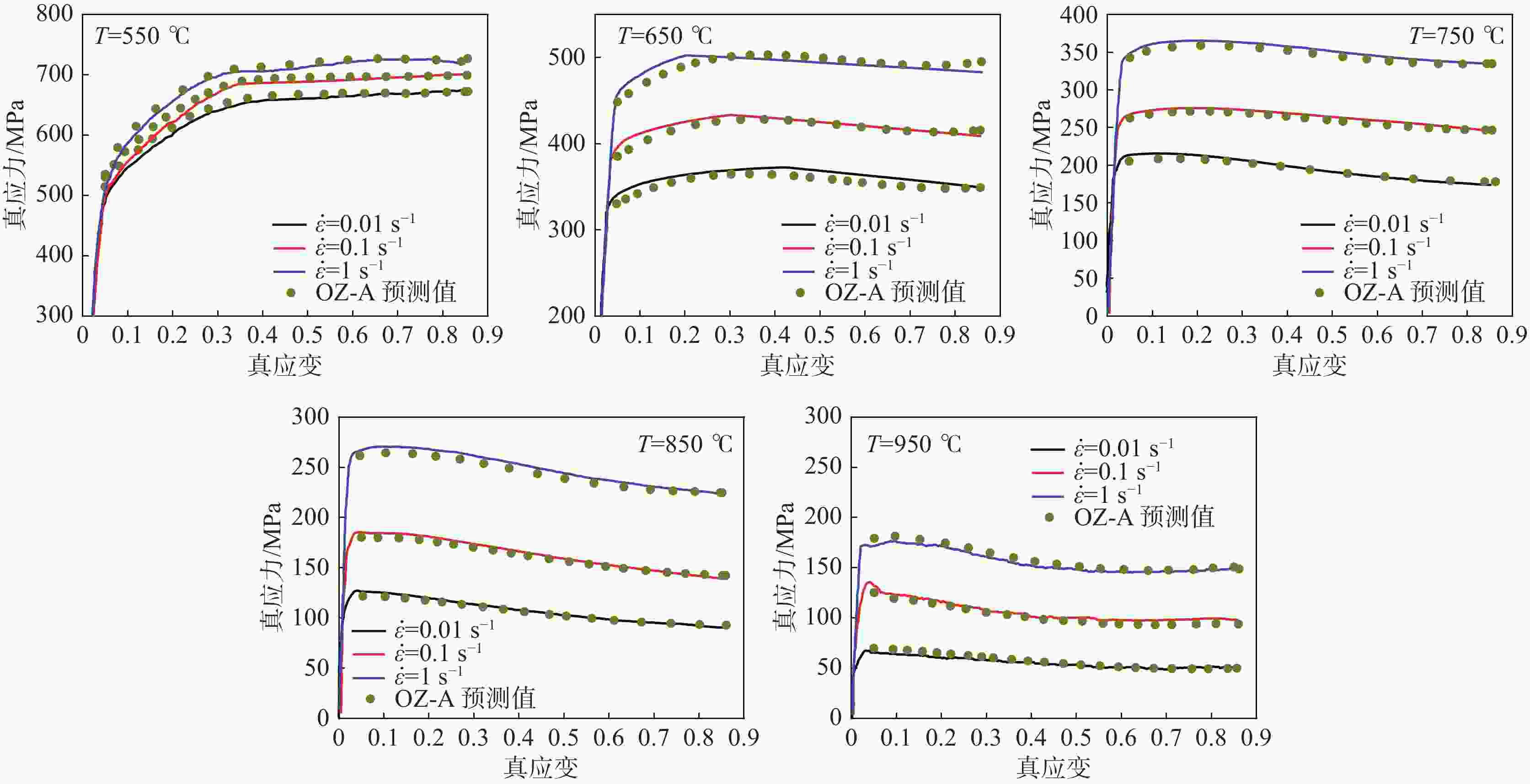
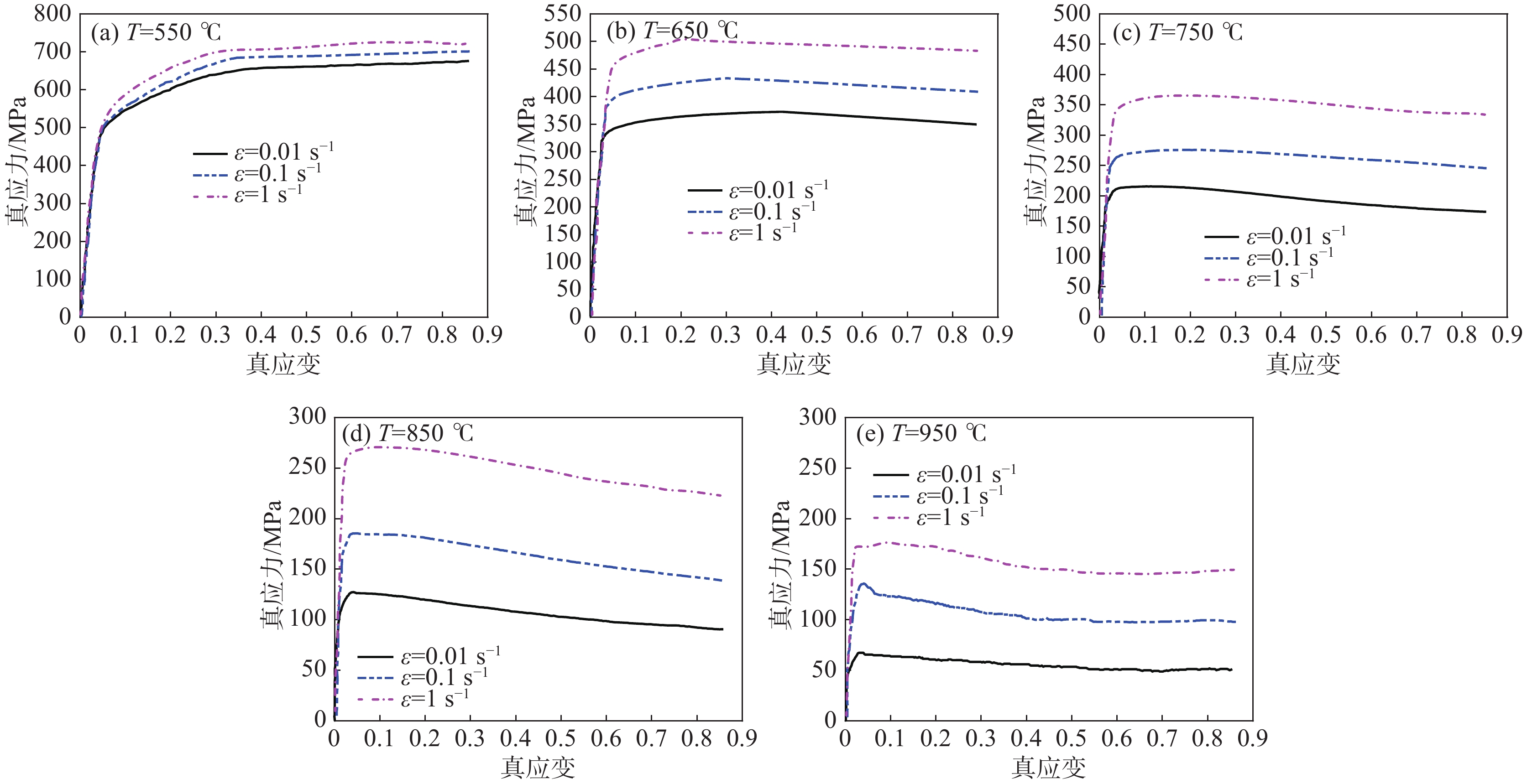
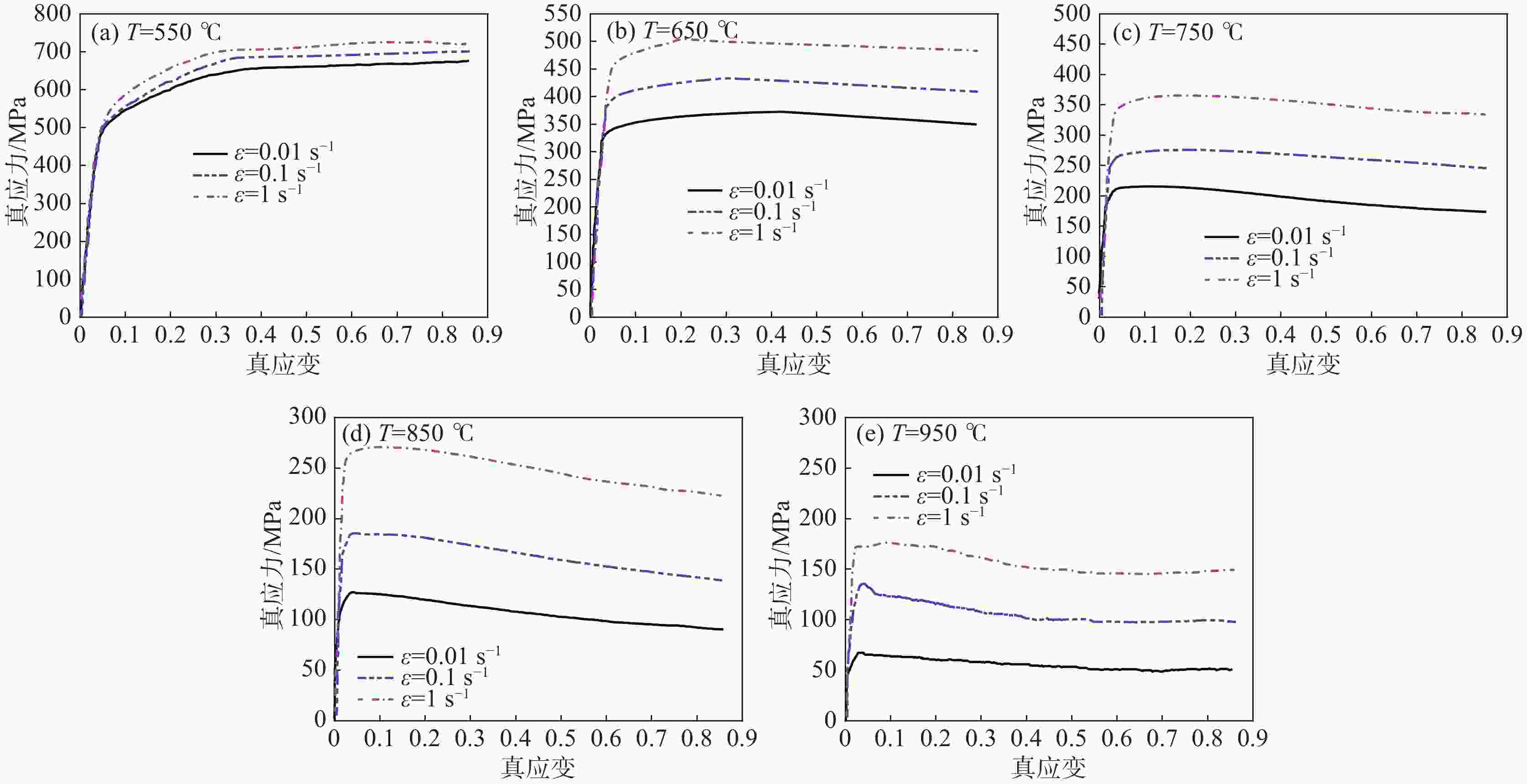
3800 热模拟试验机,在不同温度(550 ~950 ℃)下、不同应变速率(0.01、0.1、1 s−1)下完成了等温压缩试验。依据试验数据,对改进的Z-A本构模型参数进行了标定,并对其有效性进行了分析。基于分析结果,建立了一种优化的Z-A本构模型,借助相关性系数R,平均相对误差值AARE和均方根误差RSME三种统计参数,探讨了该模型的可预测性。结果表明优化的Z-A本构模型能够准确地预测该材料的高温流变行为,其模型的R、AARE和RSME分别为0.9994 ,1.62%和1.3248 。Abstract: The constitutive model plays an important role in describing the response behavior of materials under different deformation conditions and in optimizing the hot forming process. Therefore, in order to obtain the physical constitutive model for accurately describing the high temperature rheological behavior of TC4 titanium alloy, the isothermal compression experiments were performed under different temperatures (500~900 ℃) and different strain rates (0.01, 0.1, 1 s−1) by using the Gleeble-3800 thermal simulator. According to the experimental data, the parameters of modified Z-A constitutive model are calibrated, and its effectivity is analyzed. Based on the analysis results, an optimized Z-A constitutive model was established, and the predictability of the model was discussed with the help of correlation coefficient R, mean absolute relative error value AARE and root mean square error RSME. The results indicate that the optimized Z-A constitutive model can accurately predict the high-temperature rheological behavior of the material. The R, AARE and RSME of the model are0.9992 , 1.63% and1.3252 , respectively. -
表 1 TC4钛合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of TC4 titanium alloy
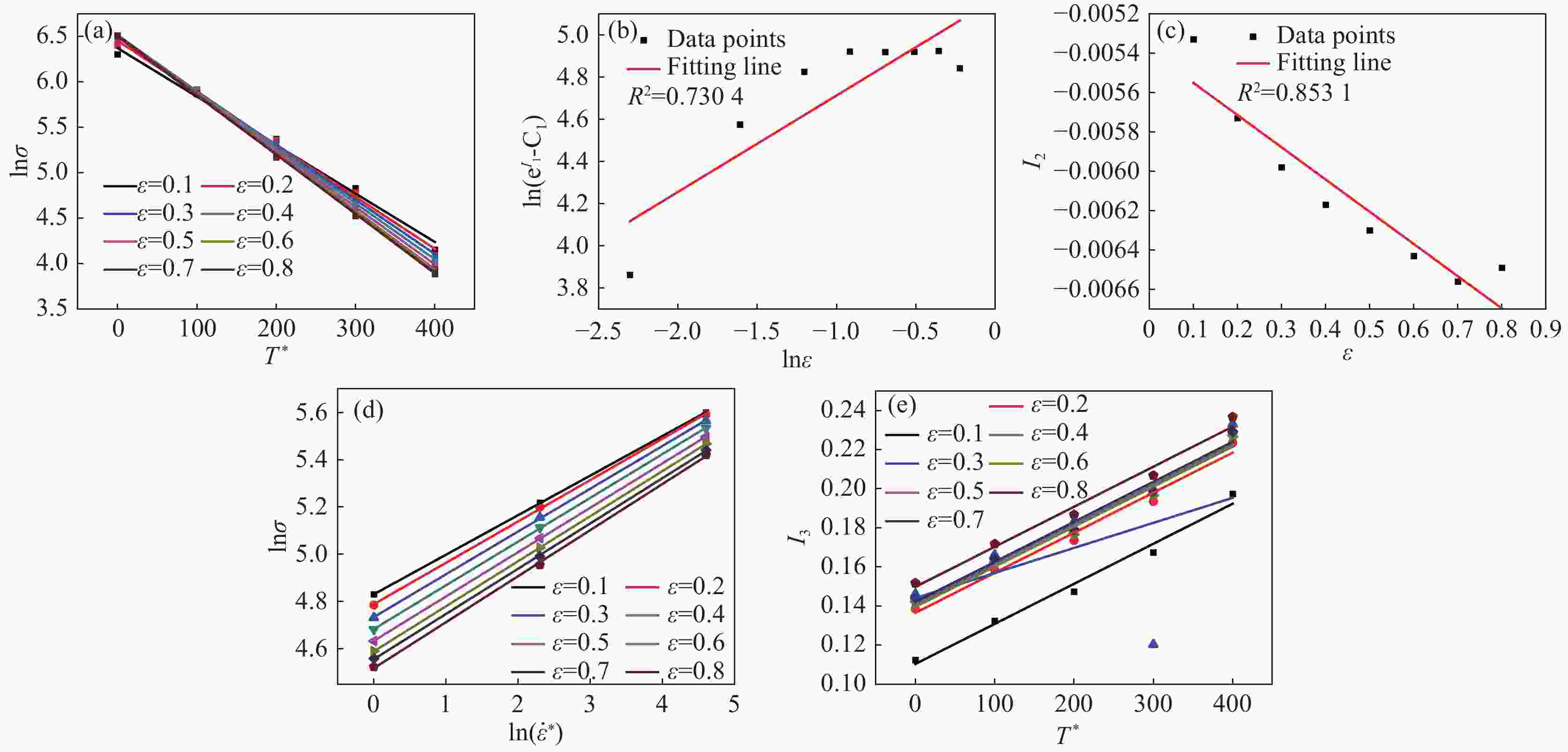
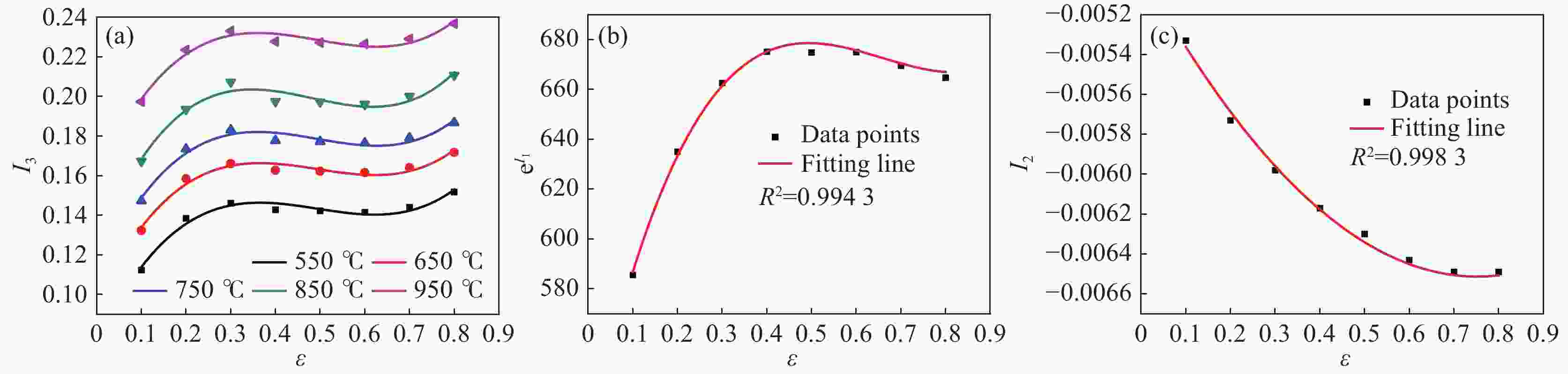
% Al V Fe C N H O Ti 6.5 4.2 0.28 0.08 0.04 0.012 0.18 Bal. 表 2 不同应变处C5、 C6的值
Table 2. Values of C5 and C6 at different strains
ε C5 C6 0.1 0.01507 0.000497 0.2 0.01701 0.000524 0.3 0.01765 0.000530 0.4 0.01642 0.000556 0.5 0.01763 0.000583 0.6 0.01843 0.000545 0.7 0.01781 0.000564 0.8 0.01896 0.000596 表 3 改进的Z-A本构模型参数
Table 3. Parameters of the modified Z-A constitutive model
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 n 538 175.98169 − 0.00539 − 0.00164 0.01781 0.000564 0.45742 表 4 参数d0~d5的数值
Table 4. Values of d0~d5 parameters
d0 d1 d2 d3 d4 d5 0.015377 0.006469 − 0.008046 0.007020 0.000501 0.000075 表 5 优化的Z-A模型相关性系数(R)平均相对误差(AARE)及均方根误差(RMSE)
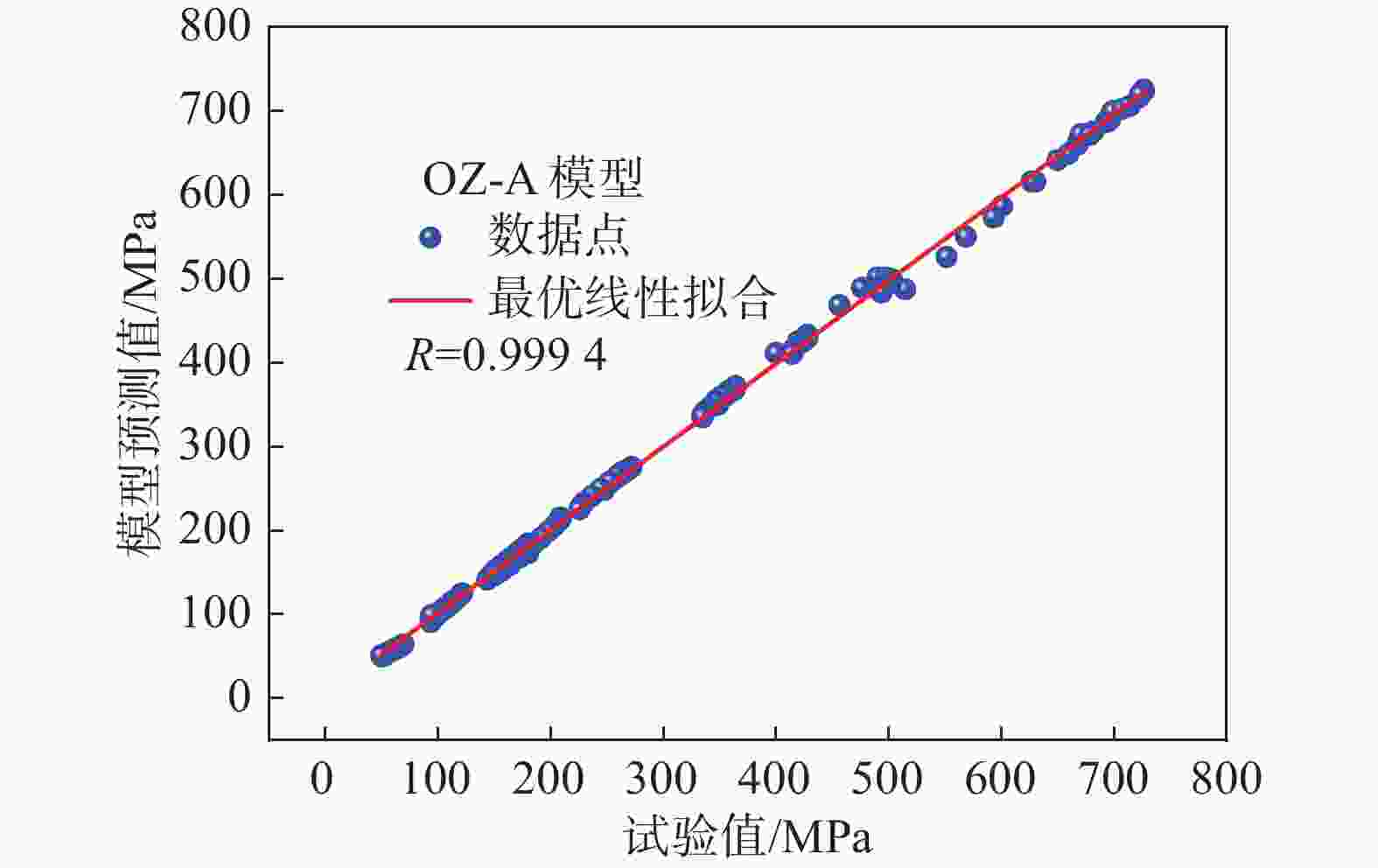
Table 5. Correlation coefficient and average relative error of the optimized Z-A model
本构模型 相关性系数(R) 平均相对误差(AARE)/% 均方根误差(RMSE) OZ-A 0.9994 1.62 1.3248 -
[1] Williams J C, Boyer R R. Opportunities and issues in the application of titanium alloys for aerospace components[J]. Metals, 2020,10(6):705. doi: 10.3390/met10060705 [2] Ji Ce, Huang Huagui, Wang Tao, et al. Recent advances and future trends in processing methods and characterization technologies of aluminum foam composite structures: A review[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 93: 116-152. [3] Jin Hexi, Wei Kexiang, Li Jianming, et al. Research progress of titanium alloys for aviation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015,25(2):280-292. (金和喜, 魏克湘, 李建明, 等. 航空用钛合金研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015,25(2):280-292.Jin Hexi, Wei Kexiang, Li Jianming, et al. Research progress of titanium alloys for aviation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(2): 280-292. [4] Zhu Zhishou. Research status and development of titanium alloy technology for aviation in China[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2014,34(4):44-50. (朱知寿. 我国航空用钛合金技术研究现状及发展[J]. 航空材料学报, 2014,34(4):44-50. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2014.4.004Zhu Zhishou. Research status and development of titanium alloy technology for aviation in China[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2014, 34(4): 44-50. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2014.4.004 [5] Zhang Bi, Yang Fulun, Wang Jiexin. Fundamental aspects in vibration-assisted tapping[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003,132(1-3):345-352. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00950-0 [6] Hor A, Morel F, Lebrun J, et al. An experimental investigation of the behaviour of steels over large temperature and strain rate ranges[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2013,67:108-122. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.01.003 [7] Muszka K, Dziedzic D, Madej L, et al. The development of ultrafine-grained hot rolling products using advanced thermomechanical processing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014,610:290-296. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.05.051 [8] Ma Xiong, Zeng Weidong, Sun Yu, et al. Modeling constitutive relationship of Ti17 titanium alloy with lamellar starting microstructure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012,538:182-189. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.01.027 [9] Wu Shuaihuai, Zhu Baohong, Jiang Wei, et al. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of a novel Al-Zn-Mg-Li-Cu alloy[J]. Materials, 2022,15(19):6769. doi: 10.3390/ma15196769 [10] Zhang Ming, Liu Xianli, Yue Caixu. Study on constitutive model for titanium alloy by coupling strain-temperature and dynamic crystallization mechanical[J]. Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2021,40(11):1641-1648. (张铭, 刘献礼, 岳彩旭, 等. 考虑应变-温度耦合与高温动态结晶的钛合金本构模型研究[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2021,40(11):1641-1648.Zhang Ming, Liu Xianli, Yue Caixu. Study on constitutive model for titanium alloy by coupling strain-temperature and dynamic crystallization mechanical[J]. Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2021, 40(11): 1641-1648. [11] Shin H, Ju Y, Choi M K, et al. Flow stress description characteristics of some constitutive models at wide strain rates and temperatures[J]. Technologies, 2022,10(2):52. doi: 10.3390/technologies10020052 [12] Jiang Ziwei, Yang Dong, Chen Jianbin. Dynamic constitutive model of titanium alloy Ti-6A1-4V for high speed cutting: A review[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2023,43(4):55-67. (姜紫薇, 杨东, 陈建彬. 面向高速切削的钛合金Ti-6Al-4V动态本构模型: 综述[J]. 航空材料学报, 2023,43(4):55-67. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2022.000169Jiang Ziwei, Yang Dong, Chen Jianbin. Dynamic constitutive model of titanium alloy Ti-6A1-4V for high speed cutting: A review[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2023, 43(4): 55-67. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2022.000169 [13] Feng Qiuyuan, Guo Jialin, Yang Jun, et al. Hot deformation behavior of Ti60 high temperature titanium alloy I: Constitutive equations[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2021,28(11):158-166. (冯秋元, 郭佳林, 杨军, 等. Ti60高温钛合金的热变形行为 Ⅰ: 本构方程[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2021,28(11):158-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2021.11.022Feng Qiuyuan, Guo Jialin, Yang Jun, et al. Hot deformation behavior of Ti60 high temperature titanium alloy I: Constitutive equations[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2021, 28(11): 158-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2021.11.022 [14] Chen Xuewen, Zhang Bo, Du Yuqing, et al. Constitutive model parameter identification based on optimization method and formability analysis for Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Materials, 2022,15(5):1748. doi: 10.3390/ma15051748 [15] Wen Feijuan, Wen Qifei, Long Zhang, et al. Hot deformation behavior and constitutive model of TC17 titanium[J]. Alloy Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2023,47(8):86-92, 99. (温飞娟, 温奇飞, 龙樟, 等. TC17钛合金热变形行为及本构模型[J]. 机械工程材料, 2023,47(8):86-92, 99. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202308014Wen Feijuan, Wen Qifei, Long Zhang, et al. Hot deformation behavior and constitutive model of TC17 titanium[J]. Alloy Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 47(8): 86-92, 99. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202308014 [16] Song Gao, Sang Ye, Li Qihan, et al. Constitutive modeling and microstructure research on the deformation mechanism of Ti-6Al-4V alloy under hot forming condition[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 892: 162128. [17] Chen Can, Chen Minghe, Xie Lansheng, et al. Flow behavior of TA32 titanium alloy at high temperature and its constitutive model[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019,48(3):827-834. (陈灿, 陈明和, 谢兰生, 等. TA32新型钛合金高温流变行为及本构模型研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2019,48(3):827-834.Chen Can, Chen Minghe, Xie Lansheng, et al. Flow behavior of TA32 titanium alloy at high temperature and its constitutive model[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019, 48(3): 827-834. [18] Zhan H Y, Wang G, Kent D, et al. Constitutive modelling of the flow behaviour of a β titanium alloy at high strain rates and elevated temperatures using the Johnson–Cook and modified Zerilli–Armstrong models[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2014,612:71-79. [19] Samantaray D, Mandal S, Borah U, et al. A thermo-viscop-lastic constitutive model to predict elevated-temperature flow behaviour in a titanium-modified austenitic stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009,526(1-2):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.08.009 [20] Mirzaie T, Mirzadeh H, Cabrera J M. A simple Zerilli–Armstrong constitutive equation for modeling and prediction of hot deformation flow stress of steels[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2016,94:38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2015.11.013 [21] Jia Haishen, Xia Shiyu, Zhang Jilin, et al. Study on rheological behavior and constitutive model of TA 17 titanium alloy at high strain rate[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2022,44(4):837-844. (贾海深, 夏世玉, 张继林, 等. 高应变率下TA17钛合金的流变行为及其本构模型研究[J]. 机械强度, 2022,44(4):837-844.Jia Haishen, Xia Shiyu, Zhang Jilin, et al. Study on rheological behavior and constitutive model of TA 17 titanium alloy at high strain rate[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2022, 44(4): 837-844. [22] Shayanpoor A A, Rezaei Ashtiani H R. The phenomeno-logical and physical constitutive analysis of hot fow behavior of Al/Cu bimetal composite[J]. Applied Physics A, 2022,128:636. doi: 10.1007/s00339-022-05769-6 -




 下载:
下载: