Change of phase composition and valuable elements in V-Ti pellet during softening-melting and dripping process
-
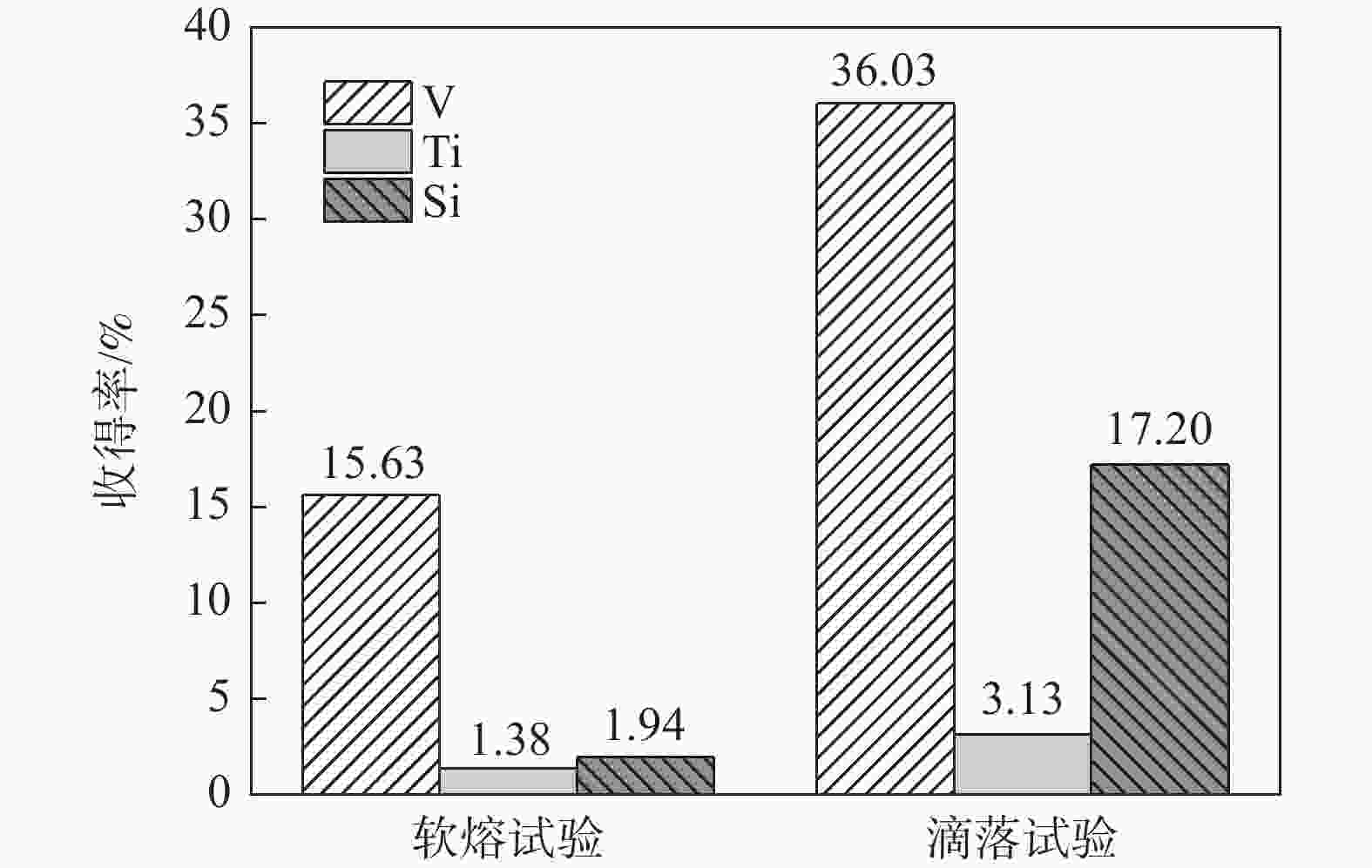
摘要: 模拟高炉冶炼气氛,对攀钢酸性钒钛球团矿在软熔和滴落过程中的物相组成和有价元素的变化进行了定量化的研究。结果表明,在钒钛球团矿的软熔滴落过程中,Ti和V逐渐从钛赤铁矿和钛铁矿迁移至渣相中。TiO2既可生成Ti进入金属铁,也可大量生成碳氮化钛。滴落试验中V在金属铁中的收得率为36.03%,远高于Ti和Si的3.13%和17.20%。炉渣和金属铁吸收焦炭中的S与渣铁间的脱硫反应同时进行,金属铁中S所占的比例由软熔时的72.84%降低至滴落时的50%。软熔液泛渣中辉石和黑钛石超过80%,渣中超过70%的V和Ti分布于黑钛石中。软熔未滴落渣中辉石明显减少,橄榄石和尖晶石明显增加,尖晶石中的V和Ti明显增加。滴落试验过程中TiO2逐渐被还原,TiC和TiN的质量分数之和超过20%,炉渣逐渐由TiO2质量分数超过30%的高钛渣转变为TiO2质量分数低于10%的低钛渣,未滴落渣中黑钛石以及分布于其中的V和Ti明显减少,橄榄石以及分布于其中的V和Ti增加。Abstract: The change of phase composition and valuable elements in the process of softening-melting and dripping of acidic V-Ti pellet of Pangang were quantitatively studied by simulating the smelting atmosphere in blast furnace. The results show that Ti and V gradually migrated from titanohematite and ilmenite to slag phase during the softening-melting and dripping process of V-Ti pellet. TiO2 could not only be reduced to Ti into metal iron, but also generate a large amount of titanium carbonitride. In the dripping test, the yield of V in metallic iron was 36.03%, which was much higher than 3.13% of Ti and 17.20% of Si. The absorbing S from coke by slag and metallic iron and the desulfurization reaction between them were carried out simultaneously, and the ratio of S in metallic iron decreased from 72.84% after softening-melting test to 50% after dripping test. Pyroxene and anosovite were more than 80% in the flooding slag of softening-melting test, and more than 70% of V and Ti in this slag were distributed in anosovite. While in residual slag of softening-melting test, pyroxene decreased obviously, olivine and spinel increased obviously, and V and Ti increased obviously in spinel. During the dripping test, TiO2 was gradually reduced until the sum of TiC and TiN mass fraction exceeded 20%, so the slag was gradually transformed from high titanium-type slag with TiO2 mass fraction over 30% to low titanium-type slag with TiO2 mass fraction less than 10%, and anosovie and its V and Ti in the residual slag were significantly reduced, while olivine and its distribution of V and Ti were increased.
-
表 1 钒钛球团矿的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of V-Ti pellet
% TFe FeO CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 S 53.38 3.63 0.64 5.65 3.59 3.96 9.76 0.683 0.008 表 2 焦炭的化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of coke
% Fcad Mt St Vdaf Ad K2O Na2O CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Fe2O3 合计 85.88 0.23 0.63 1.09 0.08 0.10 0.49 7.24 0.13 3.73 1.03 12.80 表 3 球团矿软熔和滴落试验的渣铁质量
Table 3. Mass of slag and metallic iron of pellet after softening-melting test and dripping test
g 类别 液泛渣 未滴落炉渣 滴落渣 滴落金属铁 未滴金属铁 合计 软熔试验 92.9 40.3 166.3 103.5 403.1 滴落试验 46.1 6.0 75.9 22.8 150.8 表 4 软熔和滴落试验炉渣的化学成分
Table 4. Chemical compositions of slags after softening-melting and dripping test
% 样品名称 TFe MFe FeO CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 S TiC TiN 软熔试验液泛渣 8.90 4.00 6.30 2.34 21.2 9.54 12.07 30.50 2.26 0.063 <0.1 0.155 软熔试验未滴渣 16.30 12.40 5.02 1.18 19.84 9.67 10.94 25.89 1.92 0.073 0.178 <0.1 软熔试验合计 11.14 6.54 5.91 1.99 20.79 9.58 11.73 29.11 2.16 0.07 滴落试验未滴落渣 45.75 45.00 0.96 1.53 15.80 7.32 8.31 2.30 1.32 0.120 11.24 0.73 滴落试验滴落渣 12.56 11.50 1.36 2.79 32.14 11.27 15.30 19.55 0.68 0.090 0.26 <0.1 滴落试验合计 41.93 41.14 1.01 1.68 17.68 7.77 9.11 4.29 1.25 0.12 9.98 表 5 不计MFe时造渣组份的相对质量分数
Table 5. Relative mass fraction of slagging components of different slags without MFe
% 样品名称 FeO CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 S TiC TiN 软熔试验液泛渣 6.56 2.44 22.08 9.94 12.57 31.77 2.35 0.07 <0.1 0.16 软熔试验未滴渣 5.73 1.35 22.65 11.04 12.49 29.56 2.19 0.08 0.203 <0.1 滴落试验未滴渣 1.75 2.78 28.73 13.31 15.11 4.18 2.40 0.22 20.44 1.33 滴落试验滴落渣 1.54 3.15 36.32 12.73 17.29 22.10 0.77 0.10 0.29 <0.1 表 6 不计算MFe和FeO时造渣组分相对质量分数
Table 6. Relative mass fraction of slagging components of different slags without MFe and FeO
% 样品名称 CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 S TiC TiN 软熔试验液泛渣 2.61 23.63 10.64 13.46 34.00 2.52 0.07 0.11 0.17 软熔试验未滴渣 1.43 24.03 11.71 13.25 31.67 2.33 0.09 0.22 0.12 软熔试验炉渣合计 2.27 23.75 10.94 13.40 33.65 2.46 0.08 0.14 0.16 滴落试验未滴渣 2.83 29.24 13.55 15.38 7.74 2.44 0.22 20.80 1.35 滴落试验滴落渣 3.20 36.88 12.93 17.56 22.74 0.78 0.10 0.30 0.11 滴落试验炉渣合计 2.90 30.56 13.44 15.76 10.35 2.15 0.20 17.24 1.14 表 7 软熔和滴落试验金属铁的化学成分
Table 7. Chemical compositions of metallic iron after softening-melting and dripping test
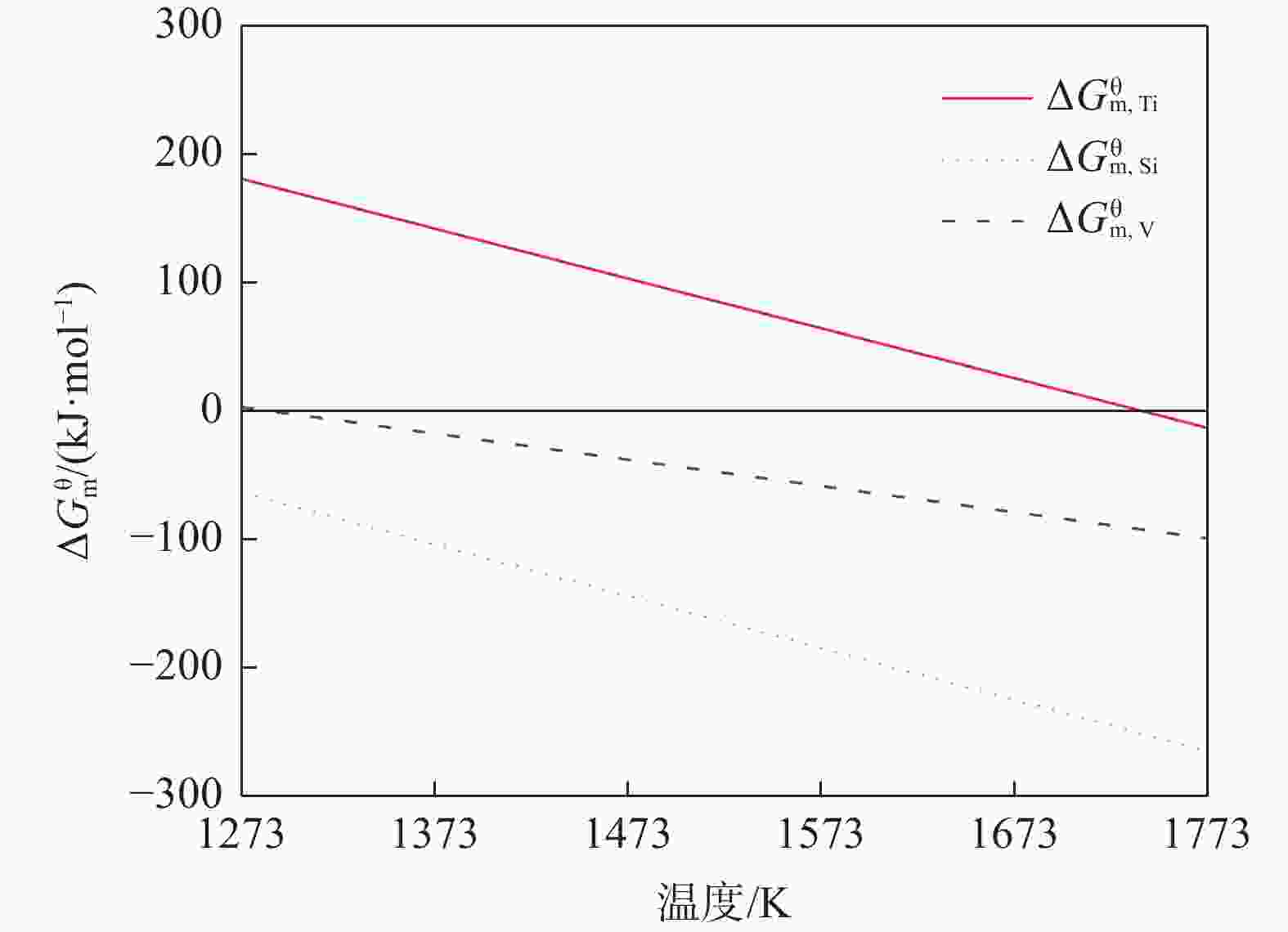
% 样品名称 C S V Ti Si 软熔试验未滴铁 5.29 0.088 0.112 0.170 0.133 软熔试验滴落铁 5.31 0.087 0.104 0.087 0.066 滴落试验未滴铁 4.72 0.100 0.242 0.528 1.77 重熔试验滴落铁 5.13 0.050 0.130 0.130 0.240 生产铁样 4.42 0.087 0.333 表 8 Ti的相互作用系数、活度及反应(1)的吉布斯自由能
Table 8. Interaction coefficient and activity of Ti and $ \Delta G $ of reaction (1)
温度/K $ e_{{\text{Ti}}}^{\text{C}} $ $ e_{{\text{Ti}}}^{\text{S}} $ $ e_{{\text{Ti}}}^{{\text{Si}}} $ $ e_{{\text{Ti}}}^{{\text{Ti}}} $ ${ {{a} }_{\left[ { {\text{Ti} } } \right]} }$ $ \Delta G $/(kJ·mol−1) 1273 −0.44 −0.12 0.074 0.071 0.0035 −85.05 1373 −0.41 −0.11 0.068 0.066 0.0038 −90.92 1473 −0.38 −0.10 0.064 0.061 0.0041 −96.79 1573 −0.36 −0.10 0.060 0.058 0.0043 −102.66 1673 −0.34 −0.09 0.056 0.054 0.0045 −108.53 1773 −0.32 −0.08 0.053 0.051 0.0047 −114.40 1873 −0.3 −0.08 0.05 0.0483 0.0049 −120.27 表 9 软熔和滴落试验中S的质量
Table 9. Mass of S during softening-melting and dripping test
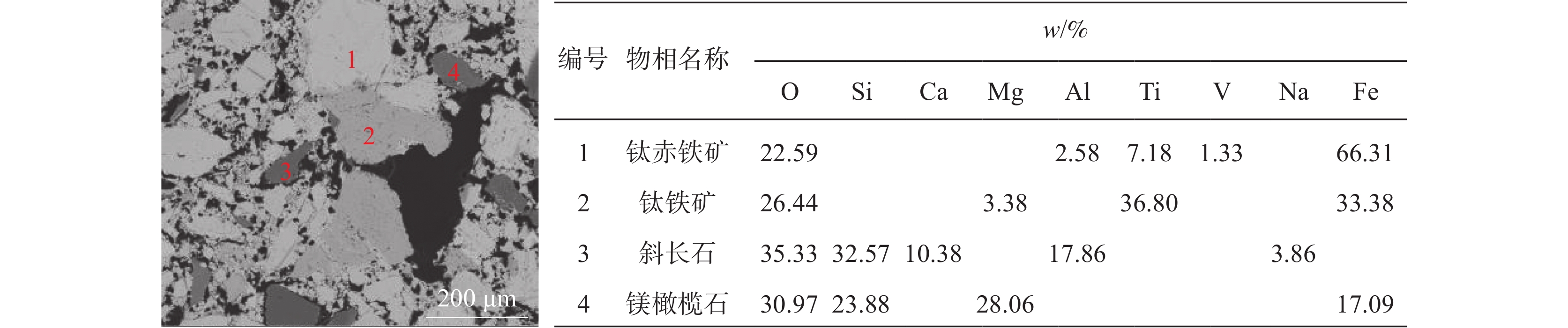
g 阶段 原料质量 S质量 合计 炉渣 金属铁 炉渣S 金属铁S 软熔 133.2 269.8 0.088 0.236 0.324 重熔 52.1 98.7 0.061 0.061 0.122 球团矿 500 0.040 表 10 不同炉渣的物相组成和元素分布
Table 10. Phase and element distribution of different slag
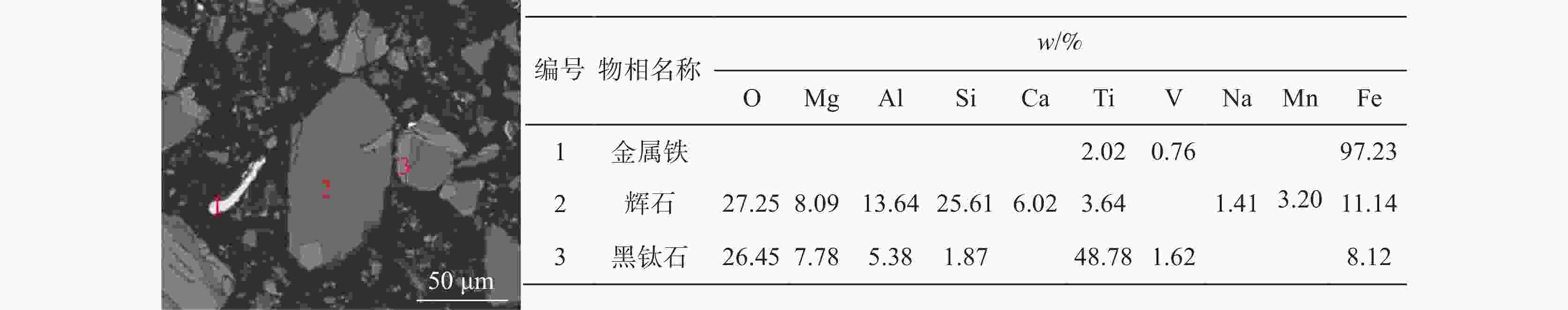
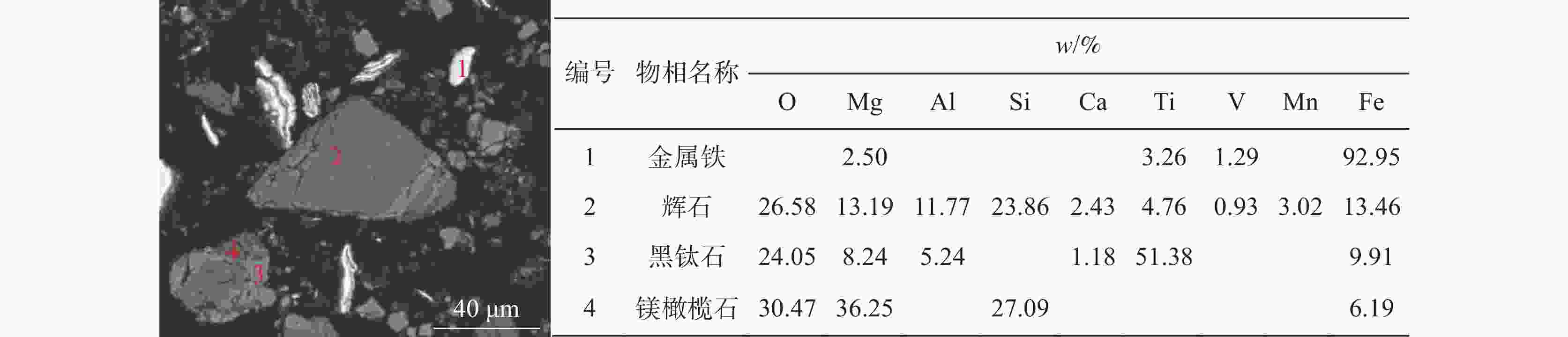
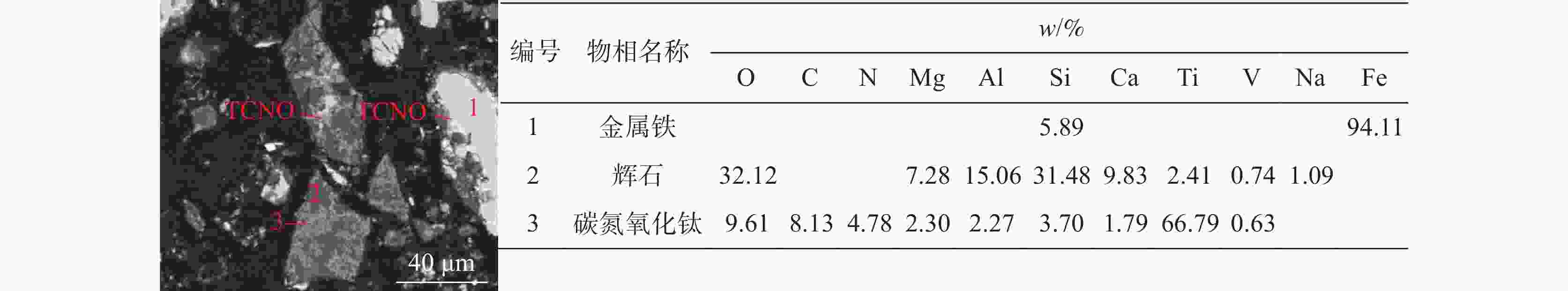
% 物相名称 软熔试验液泛渣 软熔试验未滴落渣 滴落试验未滴落渣 w Fe V Ti w Fe V Ti w Fe V Ti 金属铁 9.63 52.9 2.67 1.07 30.18 80.91 10.08 5.84 56.58 90.14 31.18 6 黑钛石 30.51 6.3 71.11 75.39 22.13 2.15 41.29 63.22 1.92 0.28 10.19 9.19 辉石 47.44 33.59 19.53 19.15 15.07 5.27 10.54 12.5 17.11 3.54 24.44 37.81 橄榄石 0.65 0.87 0.73 0.17 5.48 1.5 3.23 1.29 6.64 0.9 5.94 9.2 玻璃质 9.21 2.03 0.06 2.06 9.06 0.96 0.26 2.54 1.57 0.08 0.47 0.91 尖晶石 1.18 0.84 3.36 0.98 13.71 4.57 28.27 10.92 6.69 0.37 7.86 7.02 碳氮氧化钛 0.1 0.01 0.19 0.25 0.41 0.02 0.41 1.07 3.75 0.12 6.88 18.56 氮化钛 0.03 0 0.14 0.09 0.02 0 0.07 0.06 0.52 0.02 3.48 4.06 氧化铁 0.11 0.4 0.06 0.06 0.28 0.55 0.13 0.17 1.22 1.23 1.68 0.79 铁板钛矿 1.1 3.02 2.13 0.79 2.78 3.96 4.56 2.29 3.42 2.92 7.42 5.53 绿泥石 0.01 0 0.03 0 0.56 0.08 1.15 0.08 0.08 0.01 0.26 0.02 其它 0.04 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.33 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.51 0.41 0.21 0.9 -
[1] Yang Gangqing, Yang Wenkang, Li Xiaosong, et al. Comparative study of microstructure changes in vanadium titanium sinter and ordinary sinter during reduction process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(2):102-109. (杨广庆, 杨文康, 李小松, 等. 钒钛烧结矿与普通烧结矿还原过程中微观结构变化对比研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(2):102-109.Yang Gangqin, Yang Wenkang, Li Xiaosong, et al. Comparative study of microstructure changes in vanadium titanium sinter and ordinary sinter during Reduction Process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39(2): 102-109 [2] Gan Qin, He Qun, Wen Yongcai. Study on influence of MgO on mineral composition and metallurgical properties of V-bearing titaniferous magnetite sinter[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008,43(8):7-11. (甘勤, 何群, 文永才. MgO对钒钛烧结矿矿物组成及冶金性能影响的研究[J]. 钢铁, 2008,43(8):7-11.Gan Qin, He Qun, Wen Yongcai. Study on influence of MgO on mineral composition and metallurgical properties of V-bearing titaniferous magnetite sinter[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008, 43(8): 7-11 [3] Bai Dongdong, Han Xiuli, Li Changcun, et al. Influence of mineral structure of vanadium-titanium sinter on its metallurgical properties[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(5):111-115. (白冬冬, 韩秀丽, 李昌存, 等. 钒钛烧结矿矿相结构对其冶金性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(5):111-115.Bai Dongdong, Han Xiuli, Li Changcun, et al. Influence of mineral structure of vanadium-titanium sinter on its metallurgical properties[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39(5): 111-115 [4] 王强. 钒钛磁铁精矿烧结物性及其强化技术的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.Wang Qiang. Research on sintering characteristics of vavadium-tianium magnetite concentrate and strengthening technologies[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012. [5] Zhang Jianliang, Yang Guangqing, Guo Hongwei, et al. Microstructure change of V-Ti magnetite concentrate pellets during reduction[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2013,35(1):42-48. (张建良, 杨广庆, 国宏伟, 等. 含钒钛铁矿球团还原过程中微观结构变化[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2013,35(1):42-48.Zhang Jianliang, Yang Guangqin, Guo Hongwei, et al. Microstructure change of V-Ti magnetite concentrate pellets during reduction[J]. Journal of University of Science and technology Beijing, 2013, 35(1): 42-48 [6] Zhan Xing. Anatomical study on smelting vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite in small blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1984,5(2):3-15. (詹星. 小高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿解剖研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1984,5(2):3-15.Zhan Xin. Anatomical study on smelting vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite in small blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1984, 5(2): 3-15 [7] Song Guocai, Yuan Tianyu, Chen Xiaowu. Study on phase composition of the cohesive dripping zone in BF during smelting V-bearing titaniferrous maganetite sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1996,17(2):25-27. (宋国才, 苑天宇, 陈小武. 高炉冶炼钒钛烧结矿软熔滴落带物相组成研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1996,17(2):25-27.Song Guocai, Yuan Tianyu, Chen Xiaowu. Study on phase composition of the cohesive dripping zone in BF during smelting V-bearing titaniferrous maganetite sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1996, 17(2): 25-27 [8] Diao Risheng. Difference in behaviors of V-Ti bearing and common iron ores within blast furnace[J]. Iron and Steel, 1996,31(2):12-16, 38. (刁日陞. 钒钛矿与普通矿在高炉各带行为差异的研究[J]. 钢铁, 1996,31(2):12-16, 38.Diao Risheng. Difference in behaviors of V-Ti bearing and common iron ores within blast furnace[J]. Iron and Steel, 1996, 31(2): 12-16, 38 [9] Bao Yicheng, Jia Xueqing, Song Guocai. Simulation study on reduction process of softening-melting and dripping zone in blast furnace smelting for vanadium-titanium sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993,14(2):1-11. (包毅成, 贾学庆, 宋国才. 钒钛烧结矿高炉冶炼软熔滴落带还原过程模拟研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1993,14(2):1-11.Bao Yicheng. Jia Xueqin, Song Guocai. Simulation study on reduction process of softening-melting and dripping zone in blast furnace smelting for vanadium-titanium sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993, 14(2): 1−11 [10] 程功金. 块状带高铬型钒钛磁铁矿还原动力学及有价组元迁移行为的研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013.Cheng Gongjin. Study on kinetics of high chromia vanadium-titanium magnetite reduction and migration behavior of valuable elements in lumpy zone[D]. Shenyang: Northeatern University, 2013. [11] 刘建兴. 软熔滴落带高铬型钒钛磁铁矿有价组元迁移机理[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013.Liu Jianxing. The migration mechanism of valuable components for high chromia vanadium-titanium magnetite in cohesive zone[D]. Shenyang: Northeatern University, 2013. [12] Wang Hongtao, Zhao Wei, Chu Mansheng, et al. Effect and function mechanism of sinter basicity on softening-melting behaviors of mixed burden made from chromium-bearing vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017,24:39. [13] Liu Songli, Bai Chenguang, Hu Tu, et al. Quick and direct reduction process of vanadium and titanium ore concentrate with carbon-containing pellets at high temperature[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2011,34(1):60-65. (刘松利, 白晨光, 胡途, 等. 钒钛铁精矿内配碳球团高温快速直接还原历程[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2011,34(1):60-65.Liu Songli, Bai Chenguang, Hu Tu, et al. Quick and direct reduction process of vanadium and titanium ore concentrate with carbon-containing pellets at high temperature[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 34(1): 60-65. [14] Chen Shuangyin, Tang Yu, Chu Mansheng, et al. Reduction process of vanadium titano-magnetite with coal powder[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2013,13(2):236-240. (陈双印, 唐钰, 储满生, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿的煤粉还原过程[J]. 过程工程学报, 2013,13(2):236-240.Chen Shuangyin, Tang Jue, Chu Mansheng, et al. Reduction process of vanadium titano-magnetite with coal powder[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2013, 13(2): 236-240 [15] Xie Hongen, Hu Peng, Zheng Kui, et al. Study on phase and chemical composition of V-Ti sinter during softening, melting and dripping process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(2):107-117. (谢洪恩, 胡鹏, 郑魁, 等. 钒钛烧结矿软熔滴落过程中的物相组成及化学成分变化规律研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(2):107-117.Xie Hongen, Hu Peng, Zheng Kui, et al. Study on phase and chemical composition of V-Ti sinter during softening, melting and dripping process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(2): 107-117 [16] Wang Dongsheng. Experimental study of Fe removal from TiC-containing slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(4):87-91. (王东生. 含TiC炉渣除铁试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(4):87-91.Wang Dongsheng. Experimental study of Fe removal from TiC-containing slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(4): 87-91 [17] Wang Cui, Jiao Kexin, Zhang Jianliang, et al. Characterization of Ti(C, N) superstructure derived from hot metal[J]. ISIJ International, 2021,61(1):138. [18] Jiang Tinfang, Zhao Lang, Luo Xiangyu, et al. Study on separation of titanium and slag during carbonization of titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(6):51-58. (简廷芳, 赵朗, 罗翔宇, 等. 含钛高炉渣碳化过程钛-渣分离研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(6):51-58.Jiang Tinfang, Zhao Lang, Luo Xianyu, et al. Study on separation of titanium and slag during carbonization of titanium-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(6): 51-58 [19] Tian Ye, Chen Shujun, Sun Yanqin, et al. Settlement process of iron in titania bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(3):91-97. (田野, 陈树军, 孙艳芹, 等. 含钛高炉渣中铁沉降行为研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(3):91-97.Tian Ye, Chen Shujun, Sun Yanqin, et al. Settlement process of iron in titania bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016, 37(3): 91-97 [20] 马世伟. 高钛型高炉渣泡沫化机理的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2013.Ma Shiwei. Research on the mechanism of foaming for the blast furnace slag bearing high titania[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2013. [21] 黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013.Huang Xihu. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013. [22] 王筱留. 钢铁冶金学(炼铁部分)[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2018.Wang Xiaoliu. Iron and steel metallurgy (ironmaking)[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2018. [23] Donald R Askeland, Pradeep P Phulé. 材料科学与工程基础(影印本)[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015.Donald R Askeland, Pradeep P Phulé. Essentials of materials science and engineering[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015. [24] 杜鹤桂. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.Du Hegui. Principle of smelting vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite in blast furnace[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. [25] Hu Qingqing, Ma Donglai, Zhou Kai, et al. Phase transformation and slag evolution of vanadium-titanium magnetite pellets during softening-melting process[J]. Powder Technology, 2022,(396):710-717. [26] Tang Wendong, Yang Songtao, Xue Xiangxin. Effect of titanium on the smelting process of chromium-bearing vanadium titanomagnetite pellets[J]. JOM, 2021,73(5):1362-1370. -




 下载:
下载: