Effect of precipitates on the creep rupture behavior of GH4141 superalloy
-
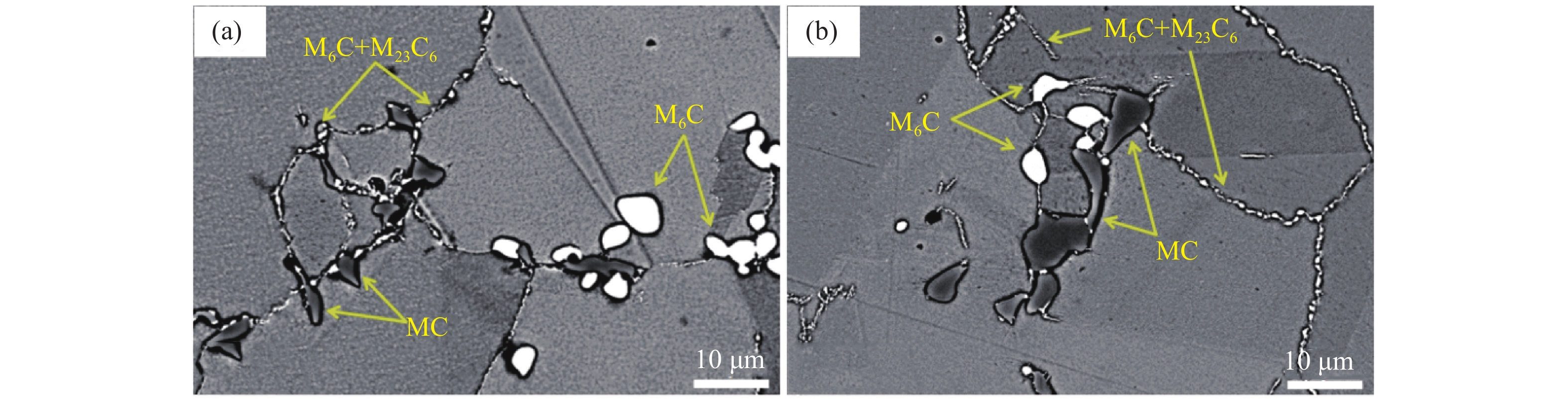
摘要: 研究了析出相与GH4141合金蠕变持久断裂行为的交互作用,涉及蠕变裂纹萌生和扩展。表征手段采用二次电子和电子背散射衍射技术,重点关注了析出相(包括MC、M6C、M23C6型碳化物和γ′弥散强化相)、孔隙和晶界裂纹,同时分析了晶粒塑性变形和强化机制。孔隙主要发生在晶界与M6C和M23C6碳化物的界面处,相邻孔隙聚合形成涟漪形貌,裂纹生长加剧了其前端区域的塑性变形。晶粒内部强化涉及γ′析出相对位错运动的抑制,由于应变激活多个滑移系统,加快了位错塞积和缠结现象,起到强化晶粒的效果。Abstract: This study focused on the effect of precipitates on the creep rupture behavior of GH4141 superalloy, involving creep crack initiation and propagation. Microstructures including carbides, γ′ precipitate hardening phase, void and intergranular crack were characterized by SE and EBSD. Meanwhile, plastic deformation and hardening mechanisms for crystal grains were analyzed. Voids occurred at the interfaces of grain boundary and carbides. Voids coalescence with wavy morphology were observed. The increase in crack length enhanced plastic deformation degree in front of the crack tip. The crystal grain strengthening was caused by the suppression of dislocation motion resulting from γ′ pinning effect. Due to the activation of multiple glide systems, dislocation piled up and tangled to enable crystal grain strengthening.
-
Key words:
- GH4141 superalloy /
- creep rupture /
- precipitate /
- crack propagation /
- precipitates hardening
-
表 1 GH4141合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of GH4141 superalloy
% C Cr Al Ti Co Mo B Mn Si S Fe Ni 0.06~0.12 18~20 1.4~1.8 3~3.5 10~12 9~10.5 0.003~0.01 <0.1 <0.5 <0.015 <5.0 Bal. -
[1] Yu Huichen, Xie Shishu, Zhao Guangpu, et al. High temperature tensile and creep rupture properties in Ni-based superalloy GH141[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2003,(9):3-6. (于慧臣, 谢世殊, 赵光普, 等. GH141合金的高温拉伸及持久性能[J]. 材料工程, 2003,(9):3-6.Yu Hui-chen, Xie Shi-shu, Zhao Guang-pu, et al. High Temperature Tensile and Creep Rupture Properties in Ni-based Superalloy GH141[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2003 (9): 3-6. [2] Radavich J F, Korth G E. High temperature degradation of alloy 718[C]// Proceedings of Seventh International Symposium on Superalloys, Seven. Springs, MD. 1992: 497-506. [3] Kuo C M, Yang Y T, Bor H Y, et al. Aging effects on the microstructure and creep behavior of Inconel 718 superalloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2009,510:289-294. [4] Lin Y C, Yin L X, Luo S C, et al. Effects of initial δ phase on creep behaviors and fracture characteristics of a nickel‐based superalloy[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2018,20(4):1700820. doi: 10.1002/adem.201700820 [5] Liu Gang, Xiao Xueshan, Muriel Véron, et al. The nucleation and growth of η phase in nickel-based superalloy during long-term thermal exposure[J]. Acta Materialia, 2020,185:493-506. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2019.12.038 [6] Wang D, Zhang J, Lou L H. Formation and stability of nano-scaled M23C6 carbide in a directionally solidified Ni-base superalloy[J]. Materials Characterization, 2009,60(12):1517-1521. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2009.08.008 [7] He L Z, Zheng Q, Sun X F, et al. Effect of carbides on the creep properties of a Ni-base superalloy M963[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2005,397(1-2):297-304. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2005.02.038 [8] Furillo F T, Davidson J M, Tien J K, et al. The effects of grain boundary carbides on the creep and back stress of a nickel-base superalloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1979,39(2):267-273. doi: 10.1016/0025-5416(79)90065-X [9] Buerstmayr R, Theska F, Webster R, et al. Correlative analysis of grain boundary precipitates in Ni-based superalloy René 41[J]. Materials Characterization, 2021,178:111250. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111250 [10] Li Q, Tian S, Yu H, et al. Effects of carbides and its evolution on creep properties of a directionally solidified nickel-based superalloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2015,633:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.02.056 [11] Zhang K, Liu X, Fan P, et al. Characterization of geometrically necessary dislocation evolution during creep of P91 steel using electron backscatter diffraction[J]. Materials Characterization, 2023,195:112501. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2022.112501 -





 下载:
下载: