Effect of alloying elements V and Cu on microstructure and properties of Cu-bearing steels
-
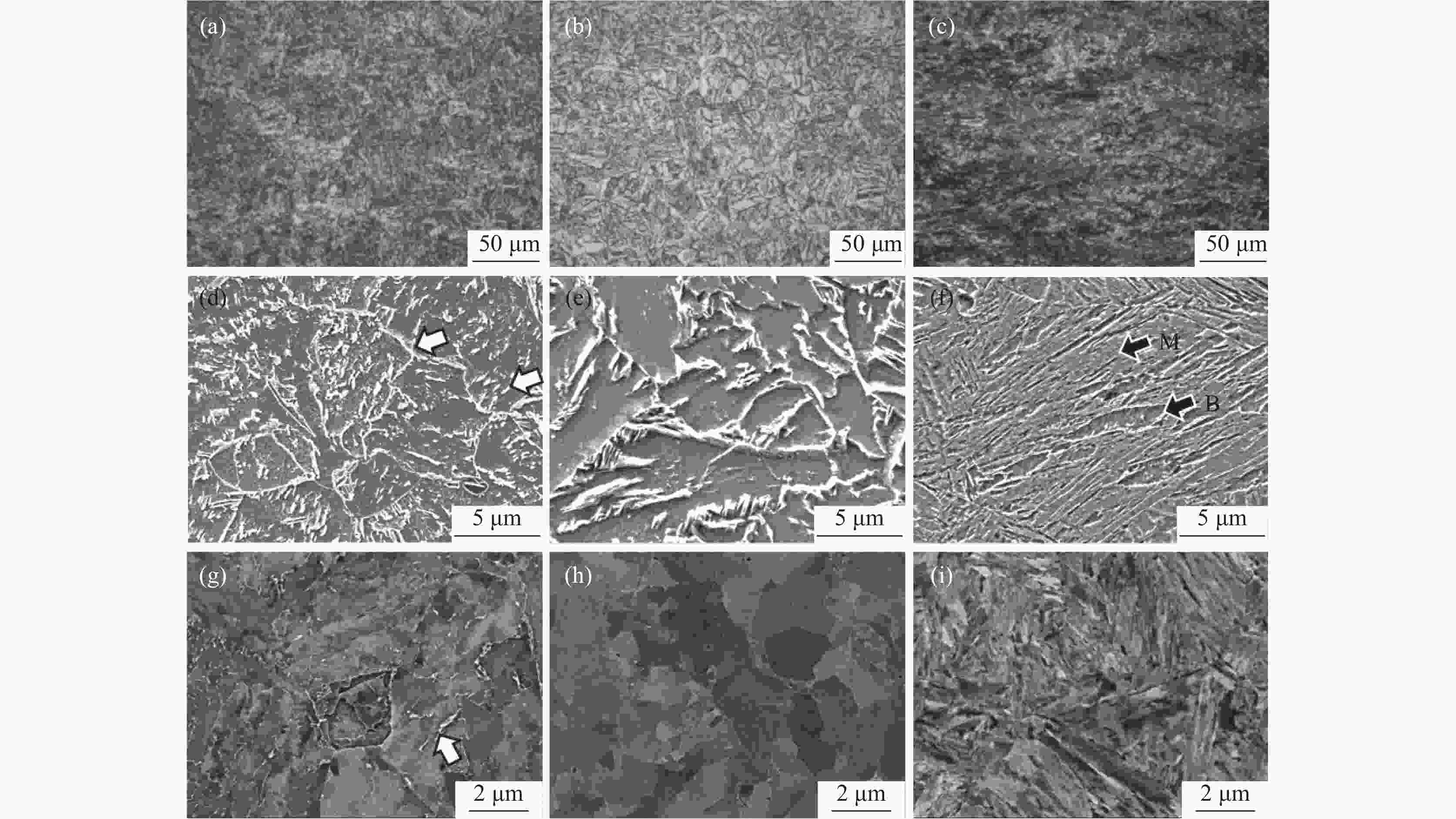
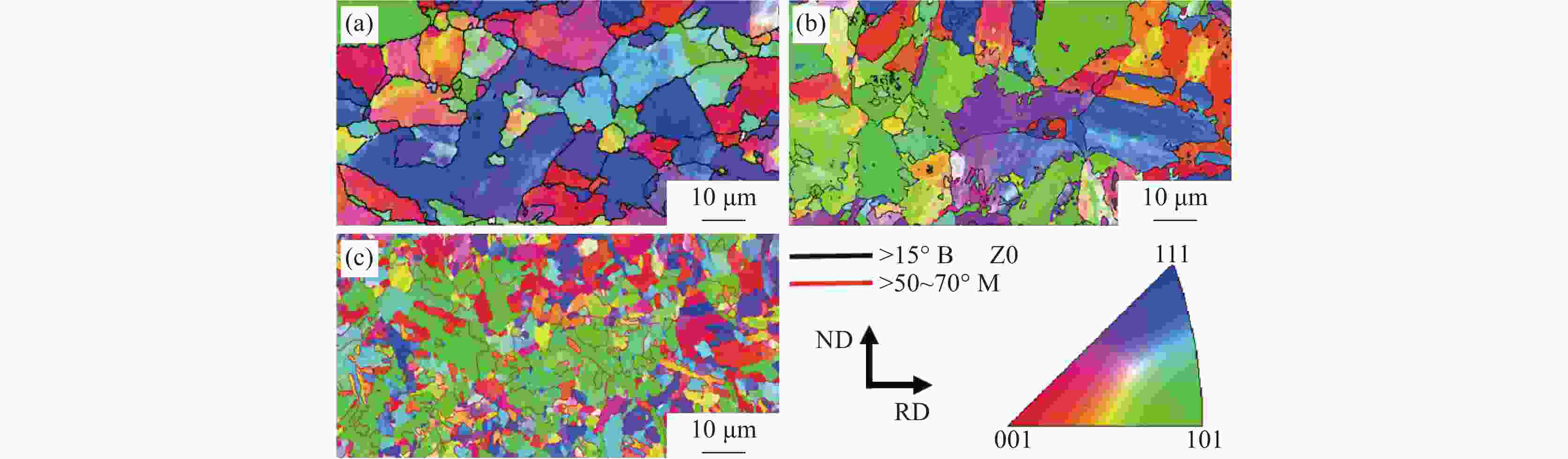
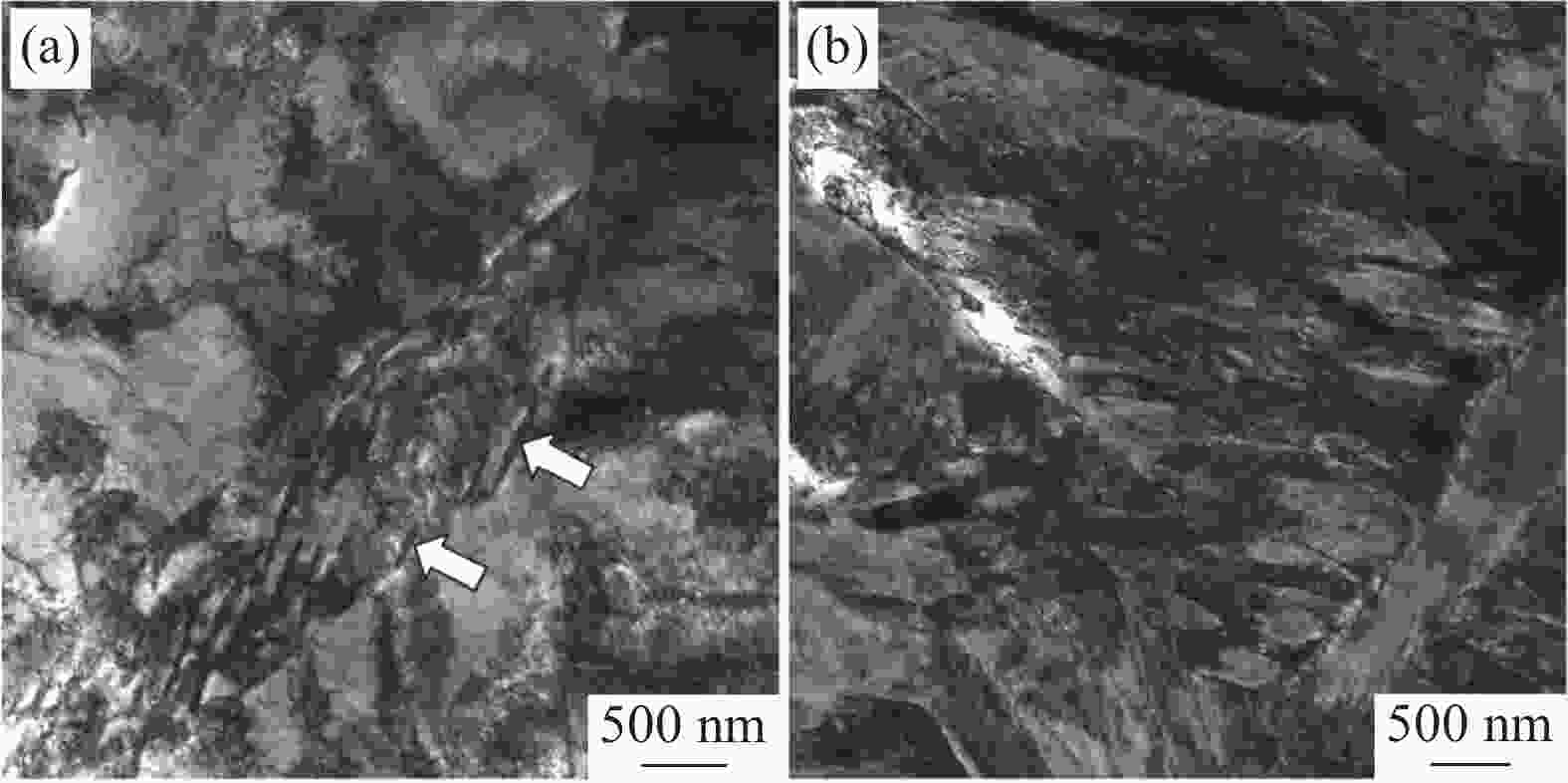
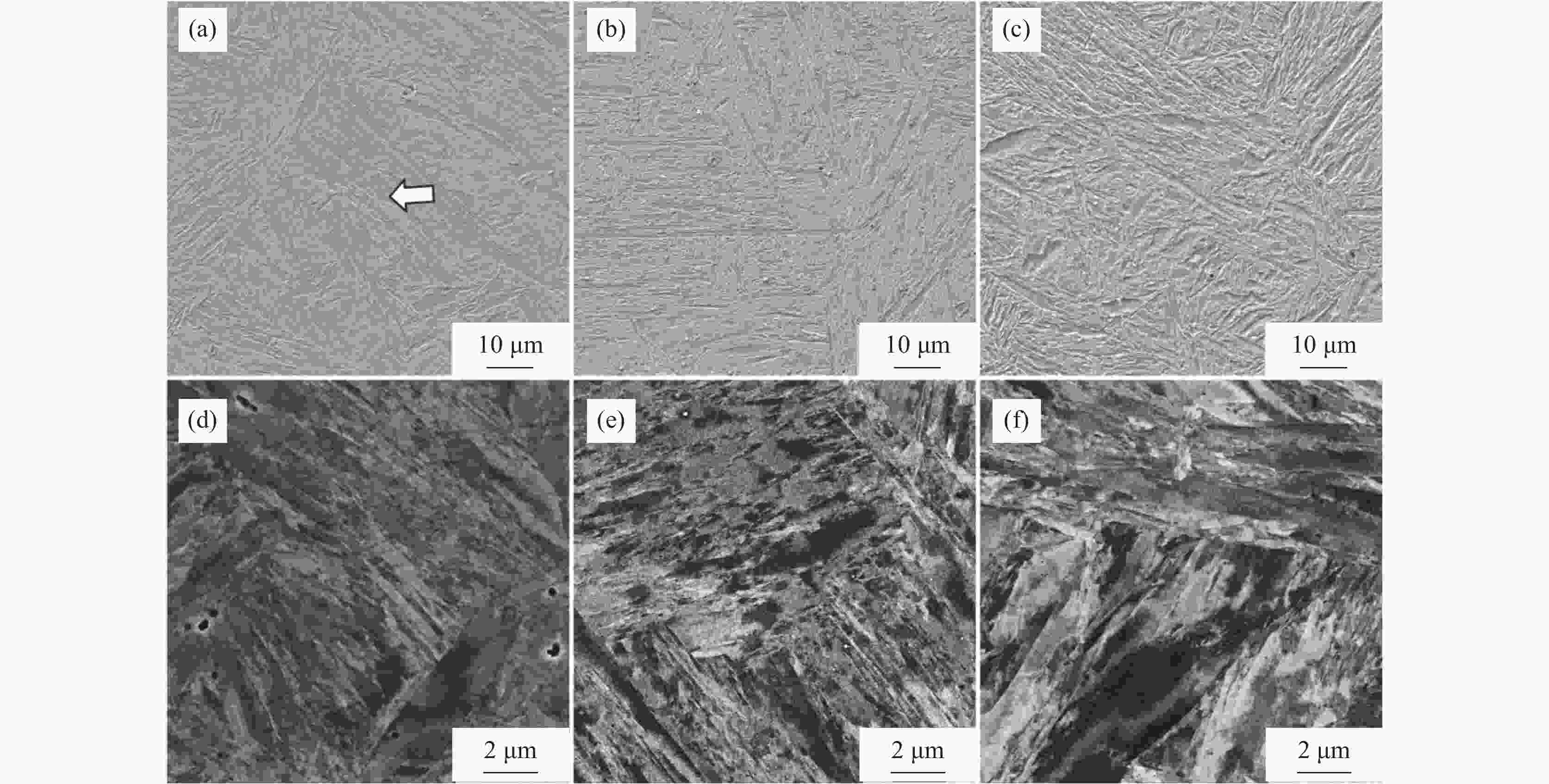
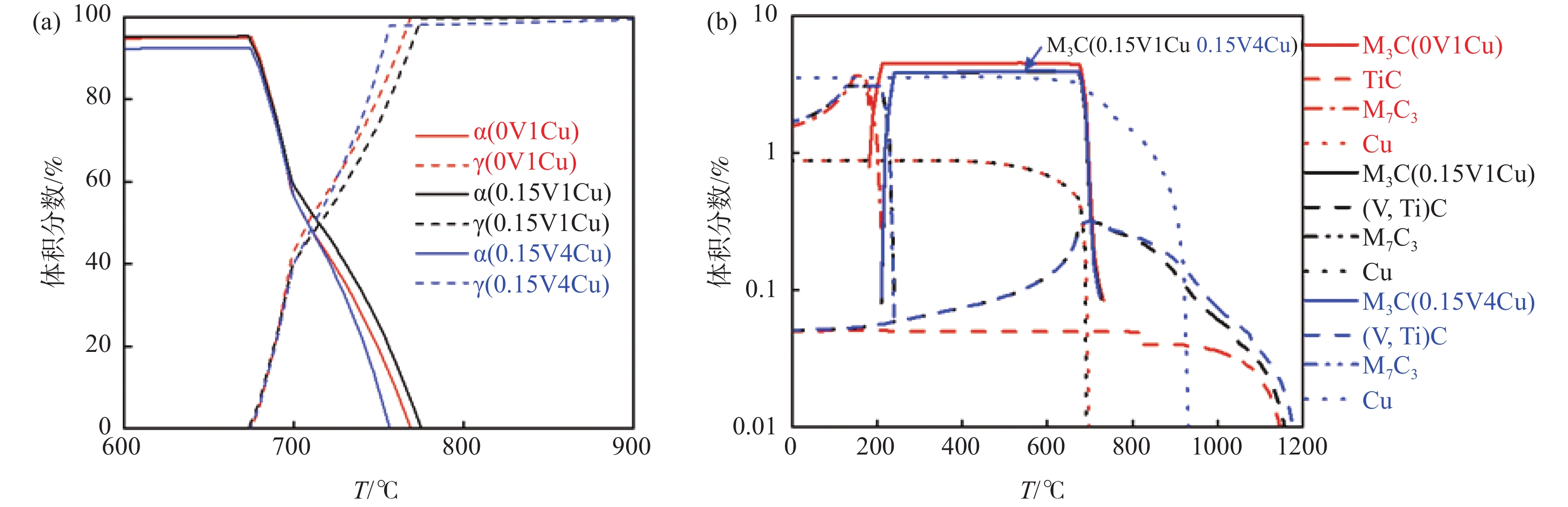
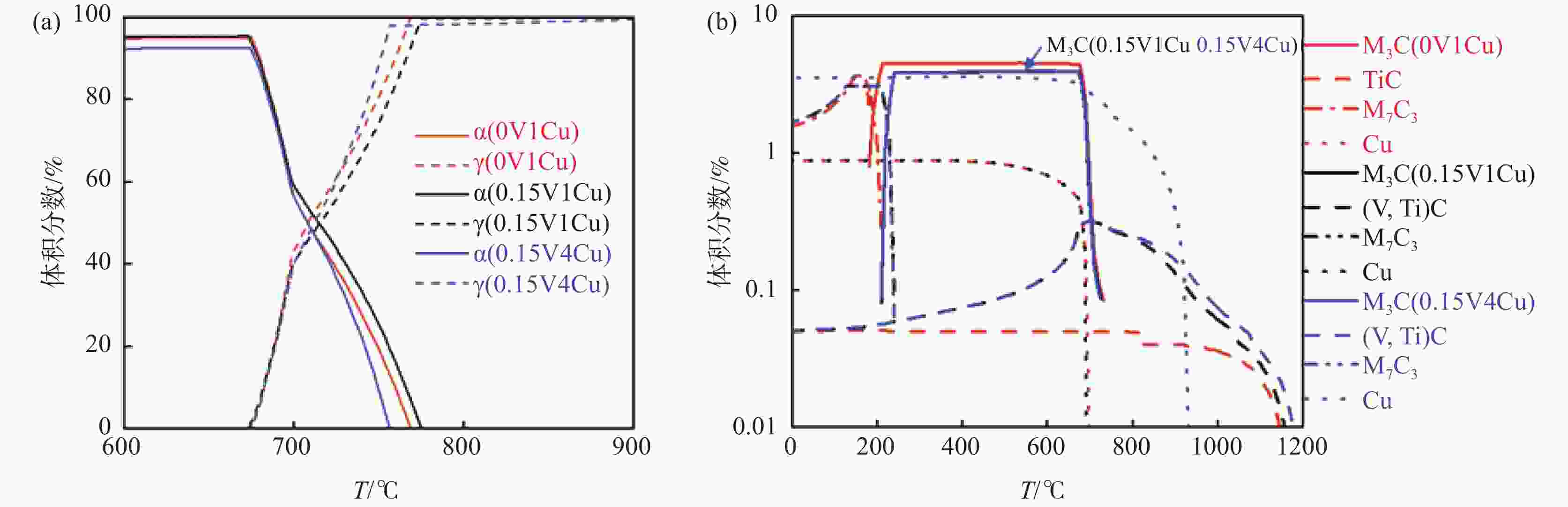
摘要: 设计了0V1Cu钢、0.15V1Cu钢和0.15V4Cu钢3种含Cu高强钢,研究了V、Cu元素对其组织和性能的影响规律。采用相变热力学与动力学计算、LOM、SEM、TEM及显微硬度测试等系统研究了试验钢相变、显微组织和显微硬度的变化规律。结果表明:3种试验钢的Ac1温度在673~675 °C;添加1%Cu且V含量由0提高到0.15%时,Ac3温度由769 °C升高到775 °C;添加0.15%V且Cu含量由1%提高到4%时,Ac3温度由775 °C下降到757 °C。0V1Cu钢和0.15V1Cu钢热轧态组织均为粒状贝氏体,而0.15V4Cu钢的热轧态组织为马氏体和少量贝氏体,经
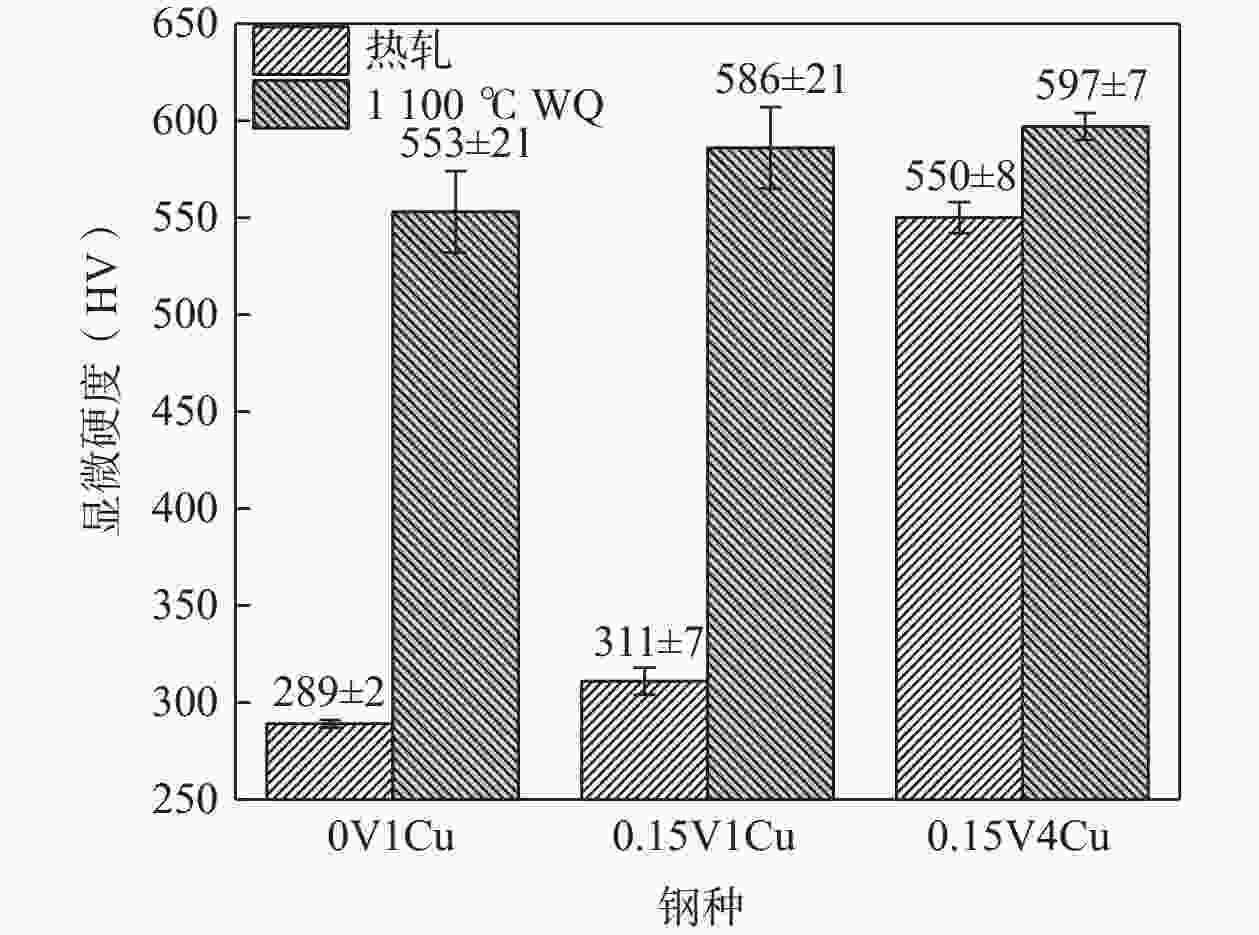
1100 °C奥氏体化后淬火,3种试验钢组织均为板条马氏体。添加0.15%V以及V和Cu复合添加均可提高试验钢的淬火硬度。其中,0.15V4Cu钢淬火硬度(HV)最高,为597±7,与0V1Cu钢和0.15V1Cu钢相比,分别提高了44和11。以上研究表明,通过调控V和Cu的添加可以实现试验钢热轧及淬火态显微组织和显微硬度的大幅度调控,为新型超高强韧含铜钢的研发提供理论指导。Abstract: Three kinds of Cu-bearing high strength steels, namely 0V1Cu steel, 0.15V1Cu steel and 0.15V4Cu steel, respectively, were designed to study the effect of V and Cu elements on microstructure and properties. The phase transformation, microstructure and microhardness of experimental steels were investigated using various microstructure characterization techniques, such as LOM, SEM, TEM, along with thermodynamic and kinetic calculations. The experimental results revealed that the Ac1 temperature of the three steels was within the range of 673~675 °C. When 1%Cu was added and V increased from 0 to 0.15%, the Ac3 temperature increased from 769 °C to 775 °C, and with Cu increased from 1% to 4% in steel including 0.15%V, the Ac3 temperature decreased from 775 °C to 757 °C. After hot rolling, the microstructures of 0V1Cu steel and 0.15V1Cu steel were identified as granular bainite, while 0.15V4Cu steel exhibited a microstructure consisting of martensite and a small fraction of bainite. Lath martensite was obtained in all the three steels after austenitization at 1100 °C for 5 min, followed by quenching in water. The addition of V and Cu lead to an increase in the microhardness of the Cu-bearing steels, with the highest microhardness (HV) of 597±7 observed in 0.15V4Cu steel, which was 44 and 11 higher than 0V1Cu steel and 0.15V1Cu steel, respectively. These findings demonstrated that the microstructure and mechanical properties of the studied steels could be adjusted over a wide range by varying the amounts of V and Cu, providing valuable insights for the design of Cu-bearing steels with excellent overall performance.-
Key words:
- Cu-bearing steel /
- V /
- Cu /
- phase transformation /
- microhardness /
- microstructure /
- quenching
-
表 1 试验钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of experimental steels %
编号 C Cu Si Mn V Ti B Fe 0V1Cu 0.3 1.0 0.8 1.5 0 0.025 0.0025 Bal. 0.15V1Cu 0.3 1.0 0.8 1.5 0.15 0.025 0.0025 Bal. 0.15V4Cu 0.3 4.0 0.8 1.5 0.15 0.025 0.0025 Bal. -
[1] Wang Lei, Zhu Sheng, Evans Steve, et al. Automobile recycling for remanufacturing in China: A systematic review on recycling legislations, models and methods[J]. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 2023,36:369-385. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2023.01.016 [2] Li Yungang, Ren Xiqiang, Qi Yanfei, et al. Progress on yield strength and hydrogen embrittlement of Cu alloyed lightweight steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2024,59(3):19-31. (李运刚, 任喜强, 齐艳飞, 等. 铜合金化轻质钢屈服强度及氢脆性能的研究进展[J]. 钢铁, 2024,59(3):19-31.Li Yungang, Ren Xiqiang, Qi Yanfei, et al. Progress on yield strength and hydrogen embrittlement of Cu alloyed lightweight steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2024, 59(3): 19-31. [3] Li Yunjie, Yuan Guo, Li Linlin, et al. Ductile 2-GPa steels with hierarchical substructure[J]. Science, 2023,379:168-173. doi: 10.1126/science.add7857 [4] Gao Junheng, Jiang Suihe, Zhang Huairuo, et al. Facile route to bulk ultrafine-grain steels for high strength and ductility[J]. Nature, 2021,590(7845):262-267. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03246-3 [5] Jiao Z B, Luan J H, Miller M K, et al. Co-precipitation of nanoscale particles in steels with ultra-high strength for a new era[J]. Materials Today, 2017,20(3):142-154. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2016.07.002 [6] Shen Qing, Huang Daozu, Liu Wenqing, et al. Effect of Cu content on the precipitation behavior of Cu-rich and NiAl phases in steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2022,187:111849. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2022.111849 [7] Misra R D K, Jia Z, O’malley R, et al. Precipitation behavior during thin slab thermomechanical processing and isothermal aging of copper-bearing niobium-microalloyed high strength structural steels: The effect on mechanical properties[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011,528(29):8772-8780. [8] Yamada K, Osuki T, Ogawa K, et al. Effects of Mo and Cu contents on sigma phase precipitation in 25Cr-5Ni-Mo-Cu-1Mn-0.18N duplex stainless steel[J]. ISIJ International, 2023,63(1):143-149. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2022-361 [9] Jiao Z B, Luan J H, Miller M K, et al. Precipitation mechanism and mechanical properties of an ultra-high strength steel hardened by nanoscale NiAl and Cu particles[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015,97:58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.06.063 [10] Kan L, Ye Q, Wang Z, et al. Improvement of strength and toughness of 1 GPa Cu-bearing HSLA steel by direct quenching[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022,855:143875. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.143875 [11] Song H, Jo M, Kim D W. Vanadium or copper alloyed duplex lightweight steelwith enhanced hydrogen embrittlement resistance at room temperature[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021,817:141347. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141347 [12] Lee S, Estrin Y, De Cooman B C. Constitutive modeling of the mechanical properties of V-added medium manganese TRIP Steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013,44(7):3136-3146. doi: 10.1007/s11661-013-1648-4 [13] Zhang Zhengyan, Sun Xinjun, Yong Qilong, et al. Precipitation behavior of nanometer-sized carbides in Nb-Mo microalloyed high strengh steel and its strengthening mechanism[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016,52(4):410-418. (张正延, 孙新军, 雍岐龙, 等. Nb-Mo微合金高强钢强化机理及其纳米级碳化物析出行为[J]. 金属学报, 2016,52(4):410-418.Zhang Zhengyan, Sun Xinjun, Yong Qilong, et al. Precipitation behavior of nanometer-sized carbides in Nb-Mo microalloyed high strengh steel and its strengthening mechanism[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(4): 410-418. [14] Zhang Xianguang, Miyamoto Goro, Toji Yuki, et al. Role of cementite and retained austenite on austenite reversion from martensite and bainite in Fe-2Mn-1.5Si-0.3C alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2021,209:116772. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116772 [15] Pavlina E J, Lee S J, Virtanen E T, et al. Effects of copper on the hardenability of a medium-carbon steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011,42(12):3572-3576. doi: 10.1007/s11661-011-0906-6 [16] Takahashi M, Bhadeshia H K D H. Model for transition from upper to lower bainite[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1990,6:592-603. doi: 10.1179/mst.1990.6.7.592 [17] Caballero F G, Garcia Mateo C, Miller M K. Design of novel bainitic steels: Moving from ultrafine to nanoscale structures[J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2014,66(5):747-755. doi: 10.1007/s11837-014-0908-0 [18] Morsdorf L, Tasan C C, Ponge D, et al. 3D structural and atomic-scale analysis of lath martensite: Effect of the transformation sequence[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015,95:366-377. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.05.023 [19] Hou Z Y, Babu R P, Hedström P, et al. Early stages of cementite precipitation during tempering of 1C-1Cr martensitic steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019,54(12):9222-9234. doi: 10.1007/s10853-019-03530-8 [20] Ali M, Nyo T, Kaijalainen A, et al. Incompatible effects of B and B + Nb additions and inclusions' characteristics on the microstructures and mechanical properties of low-carbon steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021,819:141453. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141453 [21] Luo Haiwen, Wang Xiaohui, Liu Zhenbao, et al. Influence of refined hierarchical martensitic microstructures on yield strength and impact toughness of ultra-high strength stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2020,51:130-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.04.001 [22] Cheng Zhaoyang, Liu Jing, Chen Wensi, et al. Effect of 0.5 mass% Cu addition on ductility and magnetic properties of Fe-6.5Si alloy[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2016,23(7):717-721. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(16)30111-X [23] Couturier L, De Geuser F, Descoins M, et al. Evolution of the microstructure of a 15-5PH martensitic stainless steel during precipitation hardening heat treatment[J]. Materials & Design, 2016,107:416-425. [24] Zeng Bin, Li Zhaodong, Sun Xinjun, et al. A novel low-cost hot rolled high strength steel for an automatic teller machine[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2015,22(3):272-278. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(15)60041-3 [25] Liu Linxi, Zhao Liyuan, Sun Meng, et al. Importance of cold rolling and tempering on the microstructure evolution, precipitation behavior and mechanical responses of 9Cr3Co3W1Cu ferritic/martensitic steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2023,206:113376. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2023.113376 [26] Yang Zhigang, Fang Hongsheng. An overview on bainite formation in steels[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2005, 9(6): 277-286. [27] Hou Ziyong, Hedström Peter, Xu Yunbo, et al. Microstructure of martensite in Fe-C-Cr and its implications for modelling of Carbide precipitation during tempering[J]. ISIJ International, 2014,54:2649-2656. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.54.2649 [28] Maki T, Tsuzaki K, Tamura I. The morphology of microstructure composed of lath martensites in steels[J]. ISIJ International, 1980,20:207-214. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational1966.20.207 [29] Zhang Gongting, Tang Di, Zheng Zhiwang, et al. Effects of heat-treatment processes on microstructures and properties of a 1000 MPa grade vanadium-alloyed high strength steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(4):139-144. (张功庭, 唐荻, 郑之旺, 等. 热处理工艺对1000 MPa级含钒高强钢组织和性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(4):139-144.Zhang Gongting, Tang Di, Zheng Zhiwang, et al. Effects of heat-treatment processes on microstructures and properties of a 1000 MPa grade vanadium-alloyed high strength steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(4): 139-144. [30] Liu S, Challa V S A, Natarajan V V, et al. Significant influence of carbon and niobium on the precipitation behavior and microstructural evolution and their consequent impact on mechanical properties in microalloyed steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017,683:70-82. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.11.102 [31] He S H, He B B, Zhu K Y, et al. Evolution of dislocation density in bainitic steel: Modeling and experiments[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018,149:46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.02.023 [32] Pešička J, Kužel R, Dronhofer A, et al. The evolution of dislocation density during heat treatment and creep of tempered martensite ferritic steels[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003,51(16):4847-4862. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(03)00324-0 [33] Wang X L, Wang Z Q, Huang A R, et al. Contribution of grain boundary misorientation to intragranular globular austenite reversion and resultant in grain refinement in a high-strength low-alloy steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2020,169:110634. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110634 [34] Karmakar A, Ghosh M, Chakrabarti D. Cold-rolling and inter-critical annealing of low-carbon steel: Effect of initial microstructure and heating-rate[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013,564:389-399. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.11.109 [35] Xiong Jie, Tong Yaolin, Peng Jielong, et al. Strength-toughness improvement of 13Cr4NiMo martensitic stainless steel with thermal cyclic heat treatment[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2023,30(8):1499-1510. doi: 10.1007/s42243-023-00960-2 [36] Meng Qingping, Rong Yonghua, Xu Zuyao. Nucleation of martensitic transformation[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004,40(4):337-341. (孟庆平, 戎咏华, 徐祖耀. 马氏体相变的形核问题[J]. 金属学报, 2004,40(4):337-341. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2004.04.001Meng Qingping, Rong Yonghua, Xu Zuyao. Nucleation of martensitic transformation[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004, 40(4): 337-341. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2004.04.001 -




 下载:
下载: