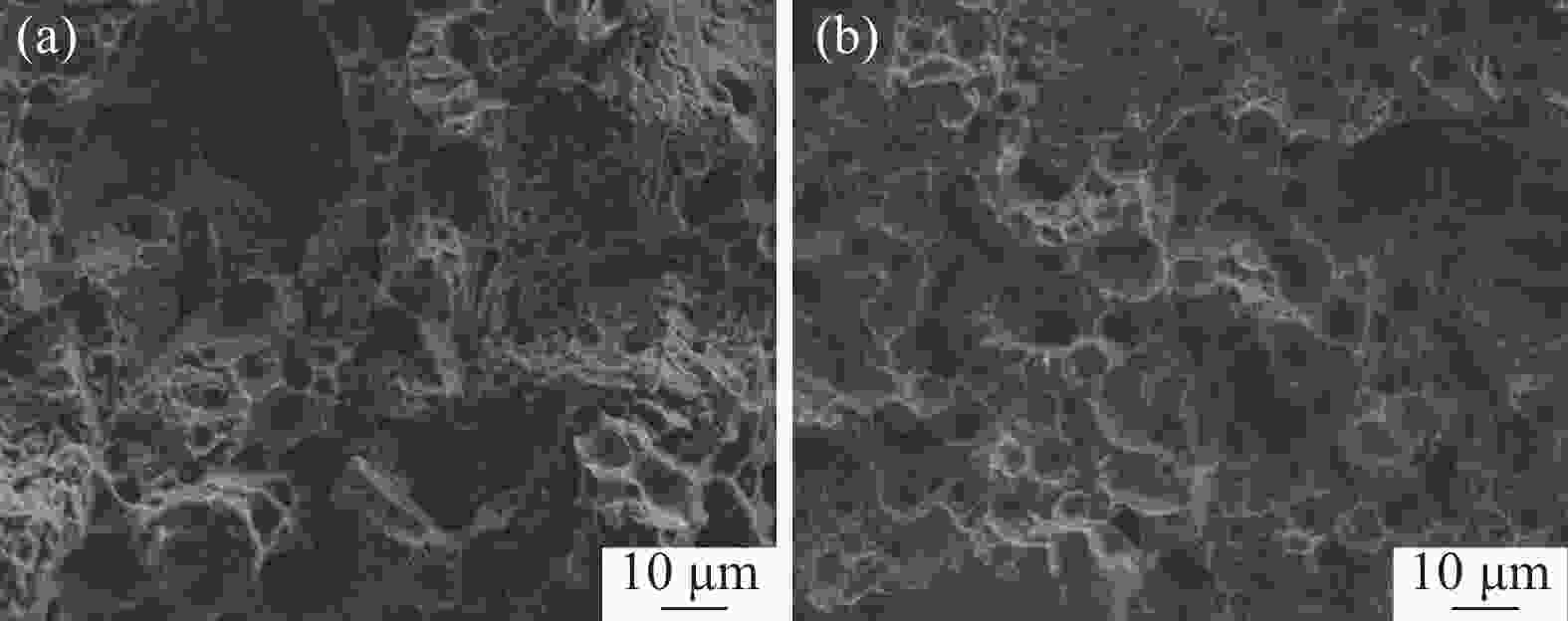
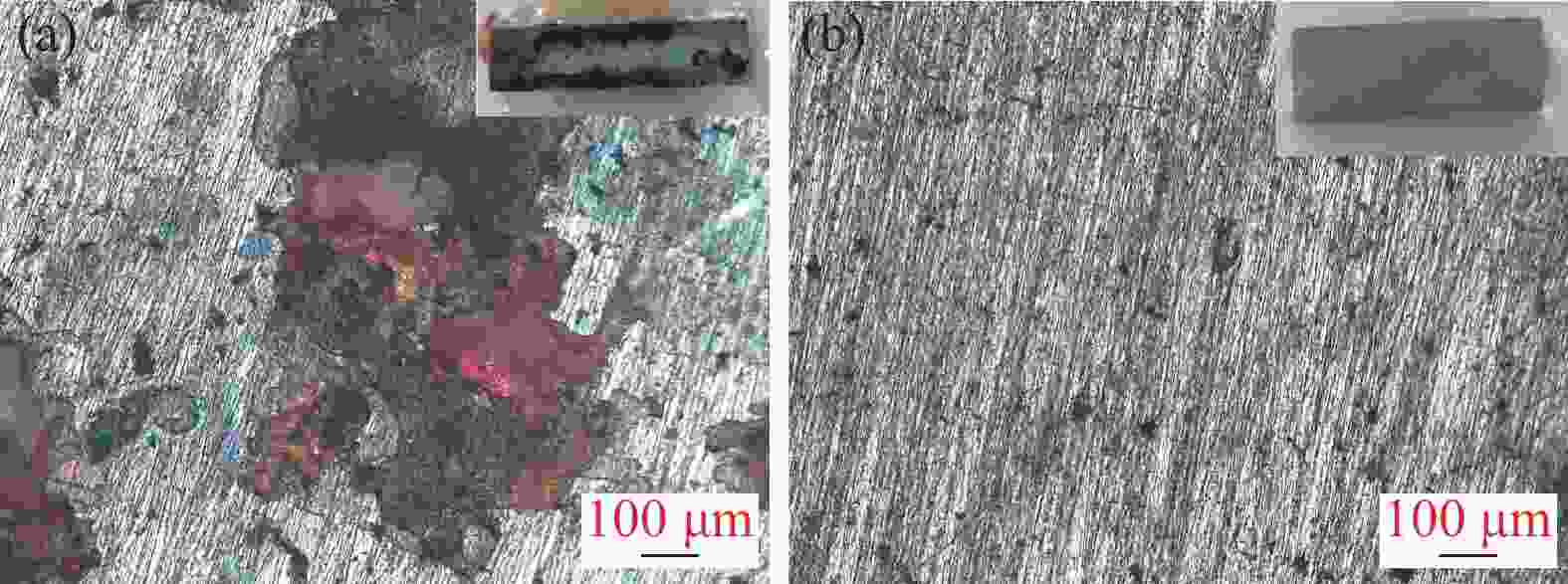
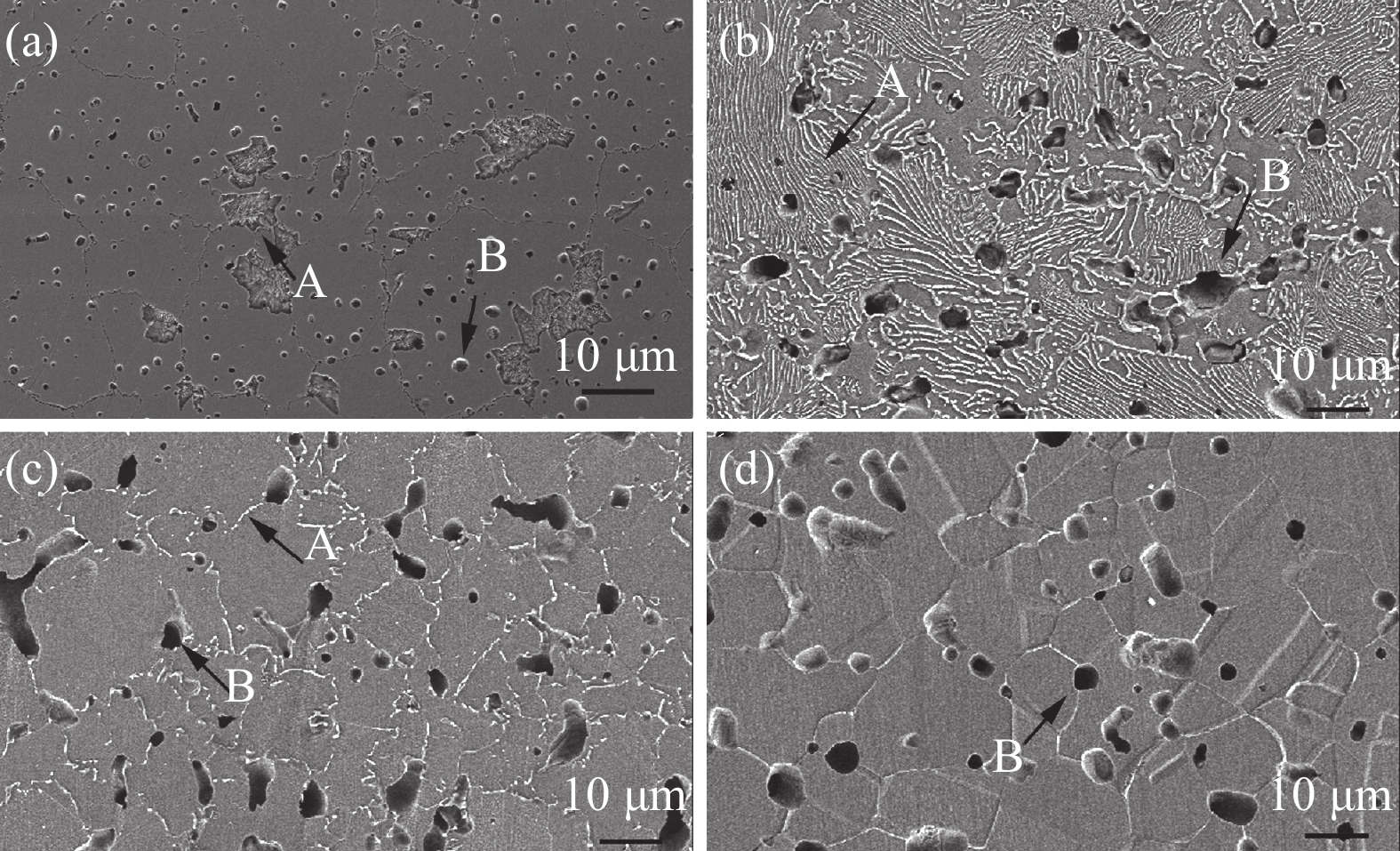
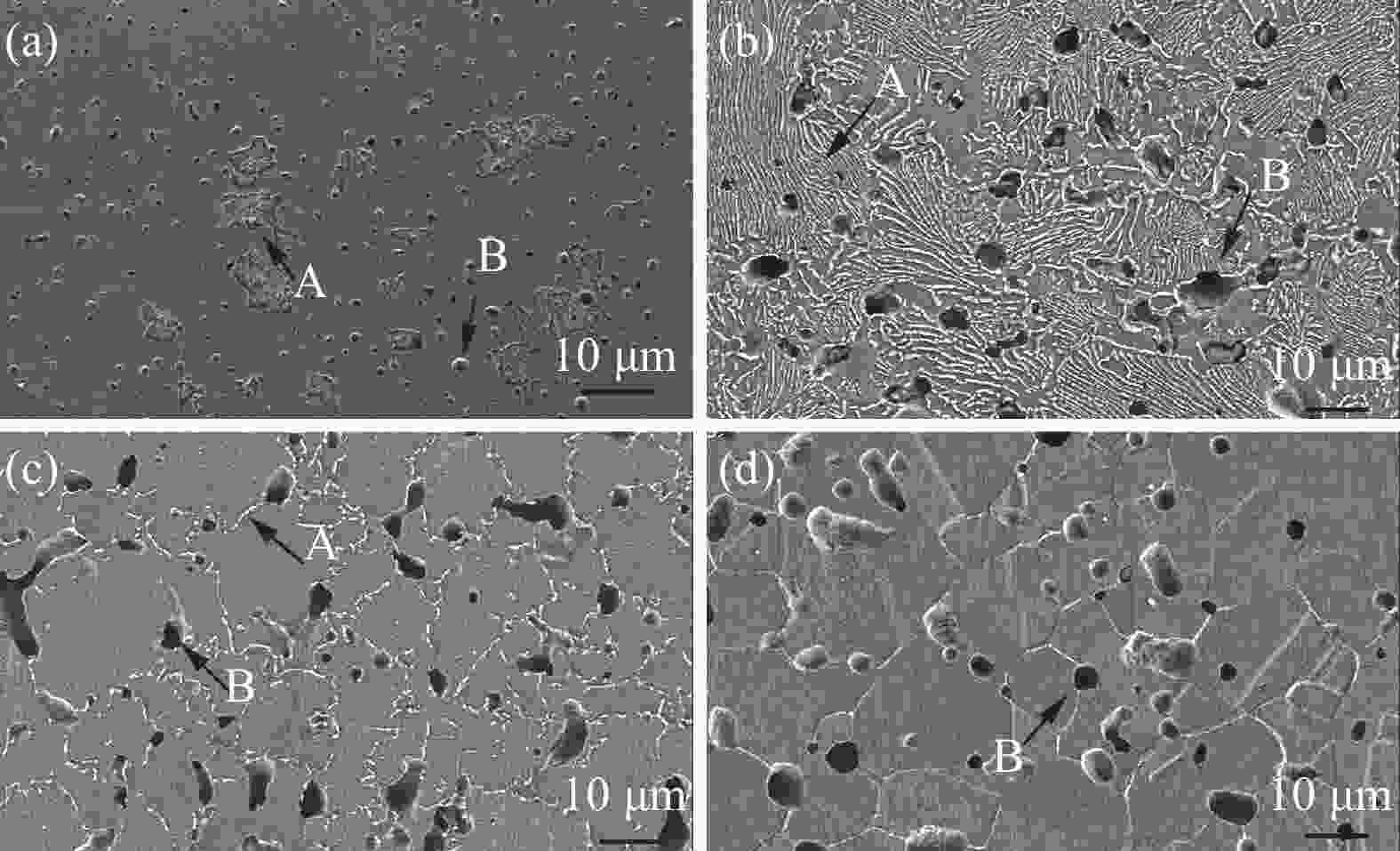
Effects of solution treatment on the microstructures and properties of high nitrogen nickel-free stainless steel prepared by MIM
-
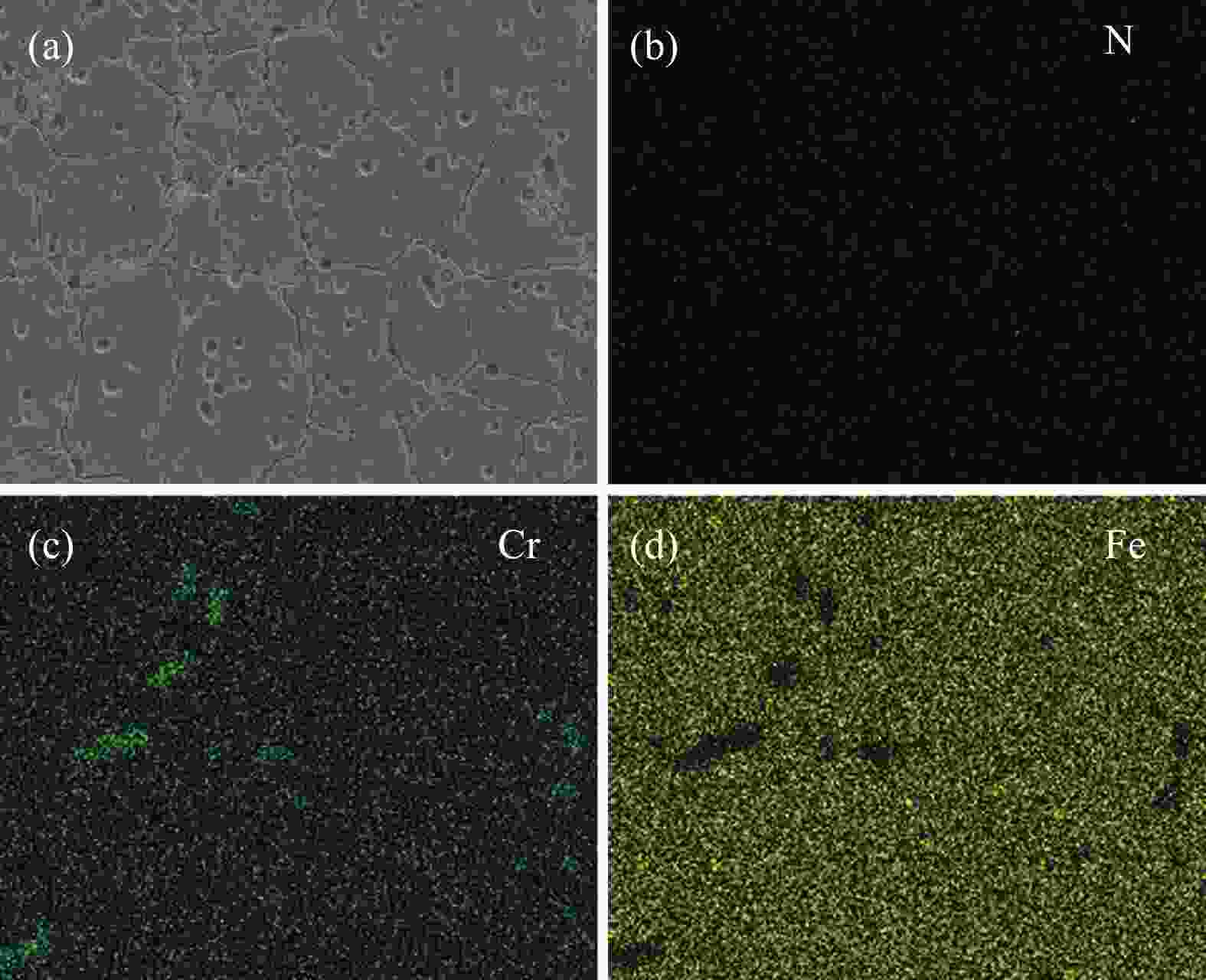
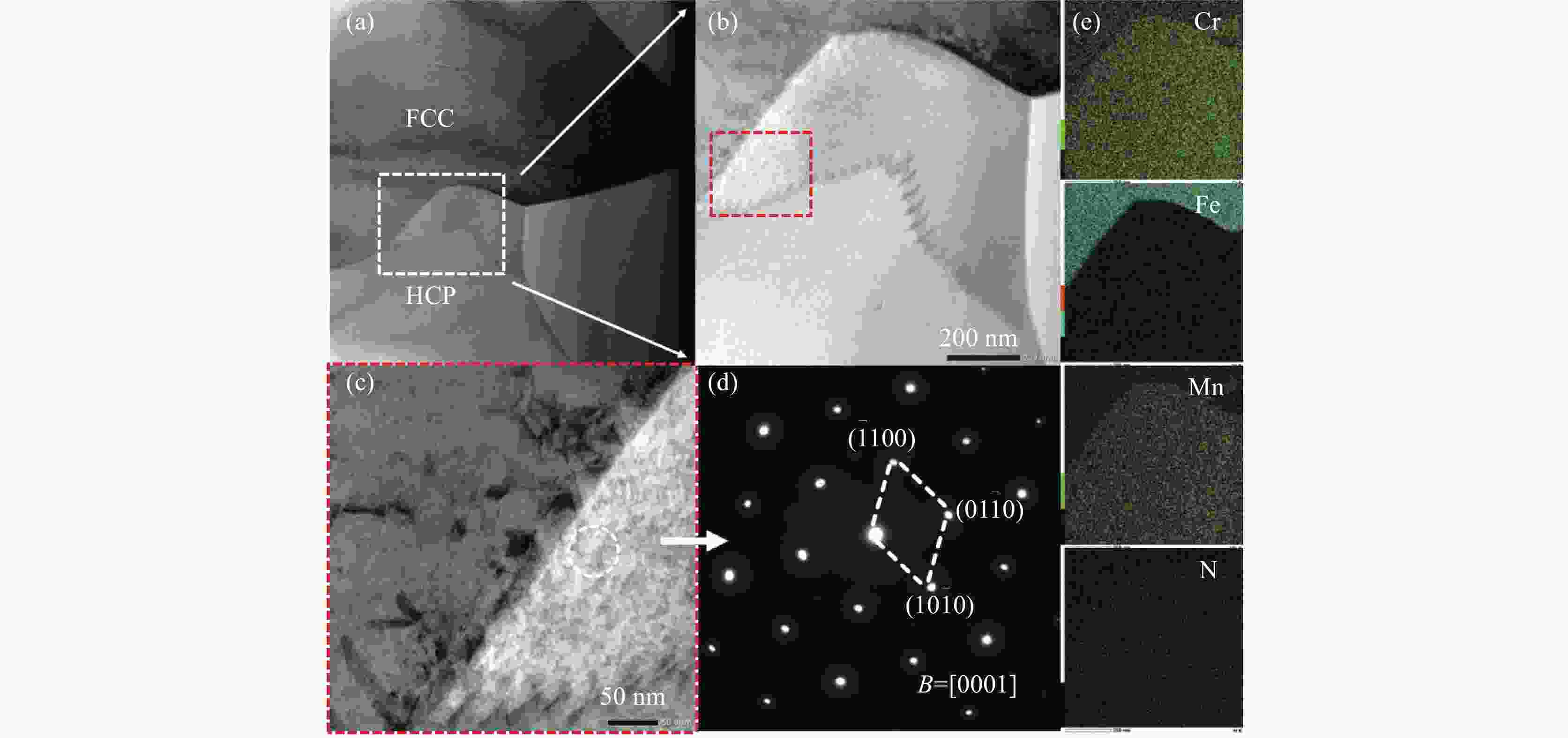
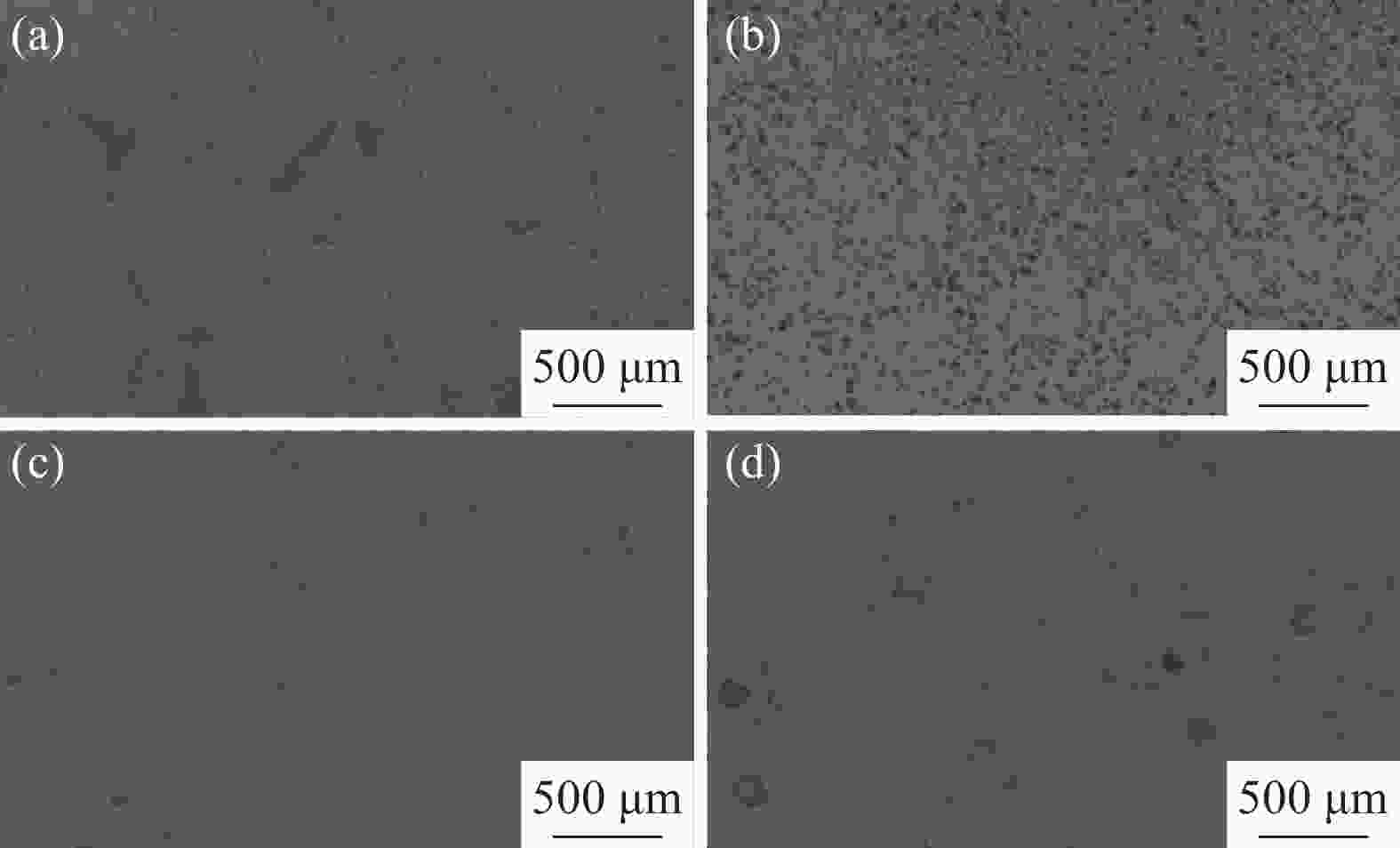
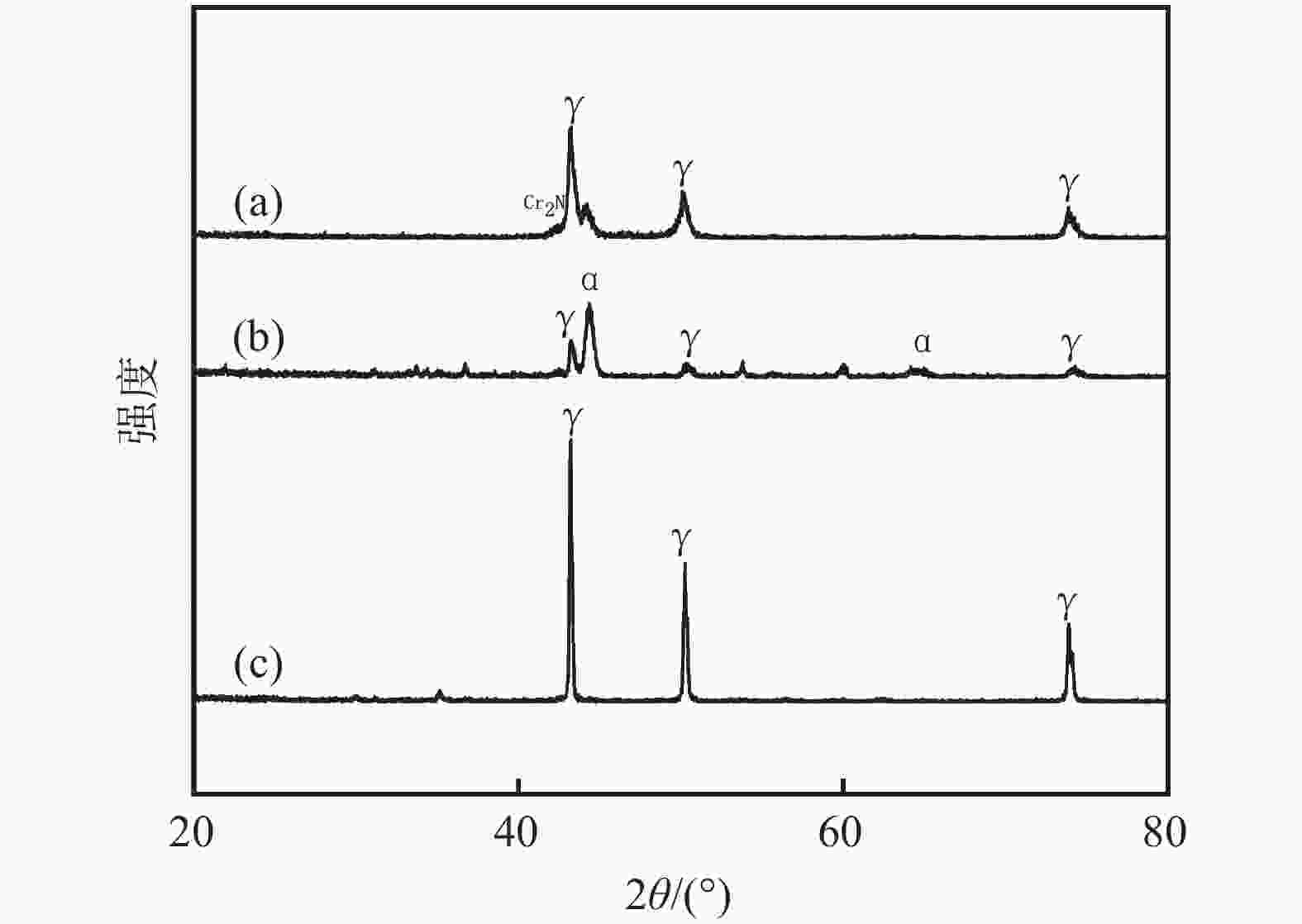
摘要: 为了提高粉末注射成形技术制备的高氮无镍奥氏体不锈钢的性能,开展了后续固溶热处理。系统研究了固溶温度、固溶保温时间对不锈钢微观组织和力学性能的影响,并对固溶前后不锈钢样品的耐腐蚀性能进行了比较。结果显示:渗氮烧结后奥氏体基体中析出的Cr2N第二相影响了不锈钢的力学和耐腐蚀性能。固溶处理后,烧结形成的Cr2N第二相消失,为纯奥氏体组织。当固溶温度为
1150 ℃,固溶保温时间为10 min时,不锈钢抗拉强度达到889 MPa,延伸率达到16.8%,力学性能最优。与固溶处理前相比,固溶处理后不锈钢样品腐蚀评级由0级提高到10级,耐腐蚀性能大幅提高。Abstract: In this study, subsequent solution heat treatment was carried out in order to improve the properties of high nitrogen nickel-free austenitic (HNNFA) stainless steel prepared by MIM. The effects of solution temperature and duration on the microstructures and mechanical properties of HNNFA stainless steel were systematically studied. In addition, the corrosion resistances of stainless steel specimens before and after solution treatment were compared. The results show that Cr2N precipitates in the austenitic matrix after sintering, thus affecting the mechanical and corrosion resistance of the HNNFA stainless steel. The secondary phase of Cr2N disappears after solution heat treatment and the microstructure is composed of pure austenite. When the solution temperature is 1 150 ℃ and the holding time is 10 min, the HNNFA stainless steel has the best mechanical properties. Its tensile strength reaches 889 MPa and elongation reaches 16.8%. Compared with the specimens before solid solution treatment, the corrosion rating of HNNFA stainless steel after solution treatment is increased from 0 to 10, and the corrosion resistance is greatly improved. -
表 1 高氮无镍不锈钢的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of the sintered stainless steel %
C N Cr Mo Mn 其它 Fe 0.02 0.76 17.5 3.5 12 0.1 余量 表 2 不同固溶时间下样品的力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of samples with different annealing times at
1150 ℃固溶时间/min 屈服强度/ MPa 抗拉强度 /MPa 延伸率/% 0 665 819 2.6 10 648 889 16.8 50 614 832 10.5 90 602 682 8.5 -
[1] Ji Wenhua. Classification and selection of stainless steel[J]. Scientific and Technological Information, 2012(4):455. (季文华. 不锈钢的分类与选择[J]. 科技信息, 2012(4):455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9960.2012.04.411Ji Wenhua. Classification and selection of stainless steel[J]. Scientific and Technological Information, 2012(4): 455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9960.2012.04.411 [2] Hull F C. Delta ferrite and martnesite formation in stainless steels[J]. Welding Journal, 1973,52(5):193. [3] Ren Y, Ke Y, Zhang B. In vitro study of platelet ahesion on medical nickel-free stainless steel surface[J]. Materials Letters, 2005,59(14-15):1785−1789. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2005.01.067 [4] Uggowitzer P J, Magdowski R, Speidel M O, et al. Nickel free high nitrogen austenitic steels[J]. ISIJ International, 2007,36:901−908. [5] Rashev T V, Eliseev A V, Zhekova L T, et al. High-nitrogen steel[J]. Steel in Translation, 2019,49(7):433−439. doi: 10.3103/S0967091219070106 [6] Yuan Zhizhong, Dai Qixun, Cheng Xiaonong, et al. The role of nitrogen in austenitic stainless steels[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2002(3):72−75. (袁志钟, 戴起勋, 程晓农, 等. 氮在奥氏体不锈钢中的作用[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版), 2002(3):72−75.Yuan Zhizhong, Dai Qixun, Cheng Xiaonong, et al. The role of nitrogen in austenitic stainless steels[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2002(3): 72−75. [7] Simmons J W. Overview: High-nitrogen alloying of stainless steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996,207(2):159−169. doi: 10.1016/0921-5093(95)09991-3 [8] Hu Ling. Preparation, microstructure and properties of high-nitrogen nickel-free austenitic stainless steel prepared by powder metallurgy[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020. (胡玲. 粉末冶金高氮无镍奥氏体不锈钢的制备、组织和性能[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020.Hu Ling. Preparation, microstructure and properties of high-nitrogen nickel-free austenitic stainless steel prepared by powder metallurgy[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020. [9] Jia Chengchang, Kuang Chunjiang. The development history of powder metallurgy high nitrogen stainless steel[J]. Metal World, 2015(1):23−27. (贾成厂, 况春江. 粉末冶金高氮不锈钢的发展历程[J]. 金属世界, 2015(1):23−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6826.2015.01.08Jia Chengchang, Kuang Chunjiang. The development history of powder metallurgy high nitrogen stainless steel[J]. Metal World, 2015(1): 23−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6826.2015.01.08 [10] Cui Dawei, Jiang Junsheng, Cao Guangming, et al. Preparation of high nitrogen and nickel-free austenitic stainless steel by powder injection molding[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2008(2):151−154. [11] Huang Chengcheng. Fabrication, microstructure and properties of injection molding high-N Ni-free austenitic stainless steel[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021. (黄成成. 金属注射成型高氮无镍奥氏体不锈钢制备与组织性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2021.Huang Chengcheng. Fabrication, microstructure and properties of injection molding high-N Ni-free austenitic stainless steel[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021. [12] Rawers J. Injection moulding of nitrogen enhanced stainless steel[J]. Metal Powder Report, 1997,52(3):37−41. [13] Turan Y N, Koursaris A. Nitrogen-alloyed austenitic stainless steels and their properties[J]. Journal of the South African Institute of Mining & Metallurgy, 1993,93(4):97−104. [14] Liu Ruiyang, Zou Liming, Wang Libiao, et al. Sintering optimization of high-nitrogen nickel-free austenitic stainless steel prepared by metal injection molding[J]. Engineering and Technological Research, 2023,8(4):1−4. (刘瑞洋, 邹黎明, 王力彪, 等. 金属注射成形制备高氮无镍奥氏体不锈钢的烧结优化[J]. 工程技术研究, 2023,8(4):1−4. doi: 10.12417/2705-0998.23.04.001Liu Ruiyang, Zou Liming, Wang Libiao, et al. Sintering optimization of high-nitrogen nickel-free austenitic stainless steel prepared by metal injection molding[J]. Engineering and Technological Research, 2023, 8(4): 1−4. doi: 10.12417/2705-0998.23.04.001 [15] Liu Ruiyang. Dynamic injection molding of high nitrogen nickel free austenitic stainless steel[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2021. (刘瑞洋. 高氮无镍奥氏体不锈钢的动态注射成形技术研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2021.Liu Ruiyang. Dynamic injection molding of high nitrogen nickel free austenitic stainless steel[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2021. [16] Li Jingyuan, Liu Huinan, Huang Peiwu. Effects of pre-precipitation of Cr2N on microstructures and properties of high nitrogen stainless steel[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012,19(5):1189−1195. doi: 10.1007/s11771-012-1127-x [17] Lee T H, Kim S J, Jung Y C, et al. Crystallographic details of precipitates in Fe-22Cr-21Ni-6Mo-(N) superaustenitic stainless steels aged at 900 ℃[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 2000,31A:1713−1723. [18] Wei W, Wei Y, Ke Y, et al. Temperature dependence of tensile behaviors of nitrogen-alloyed austenitic stainless steels[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2010,19(8):1214−1219. doi: 10.1007/s11665-010-9603-7 [19] Bannykh I O, Sevost’yanov M A, Prutskov M E. Effect of heat treatment on the mechanical properties and the structure of a high-nitrogen austenitic 02Kh20AG10N4MFB steel[J]. Russian Metallurgy (Metally), 2016(7):613−618. [20] Kartik B, Veerababu R, Sundararaman M, et al. Effect of high temperature ageing on microstructure and mechanical properties of a nickel-free high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2015,642:288−296. [21] Wu X Q, Xu S, Huang J B, et al. Uniform corrosion and intergranular corrosion behavior of nickel-free and manganese alloyed high nitrogen stainless steels[J]. Materials & Corrosion, 2015,59(8):676−684. [22] Talha M, Behera C K, Sinha O P. A review on nickel-free nitrogen containing austenitic stainless steels for biomedical applications[J]. Materials Science & Angineering, 2013,33(7):3563−3575. -




 下载:
下载: