Effect of trace Mg addition on microstructure and mechanical properties in 2.25Cr1Mo steel
-
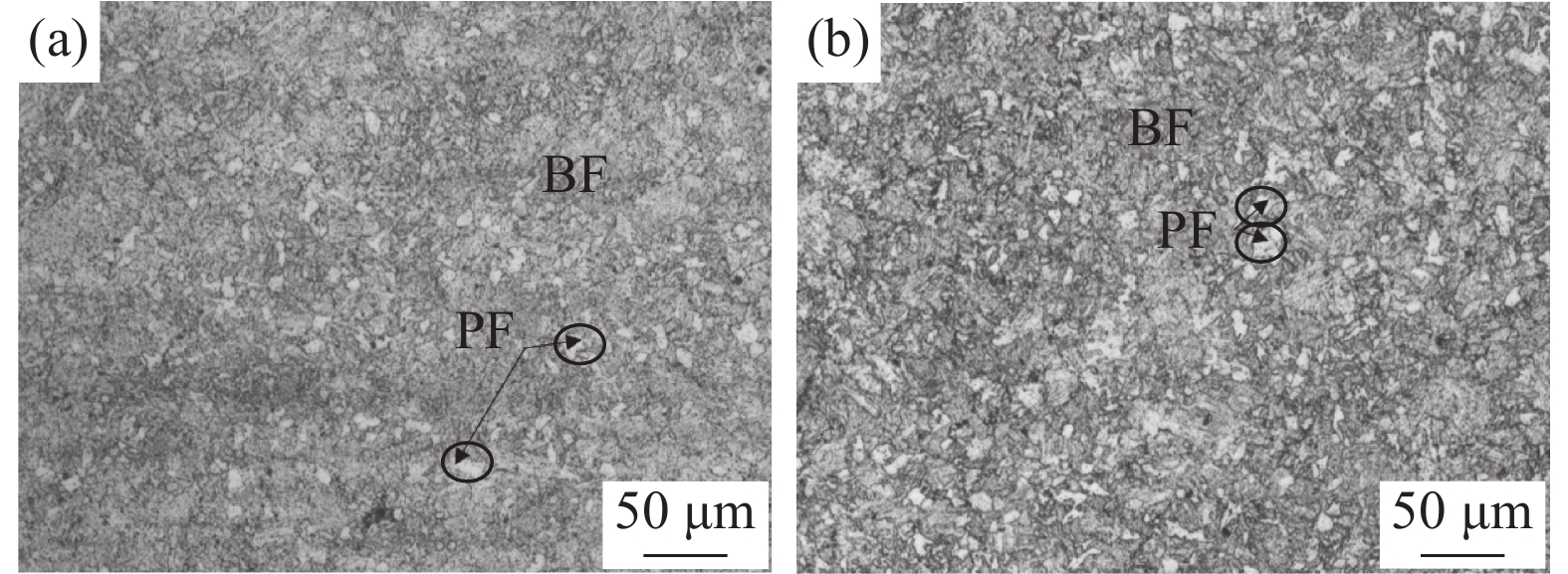
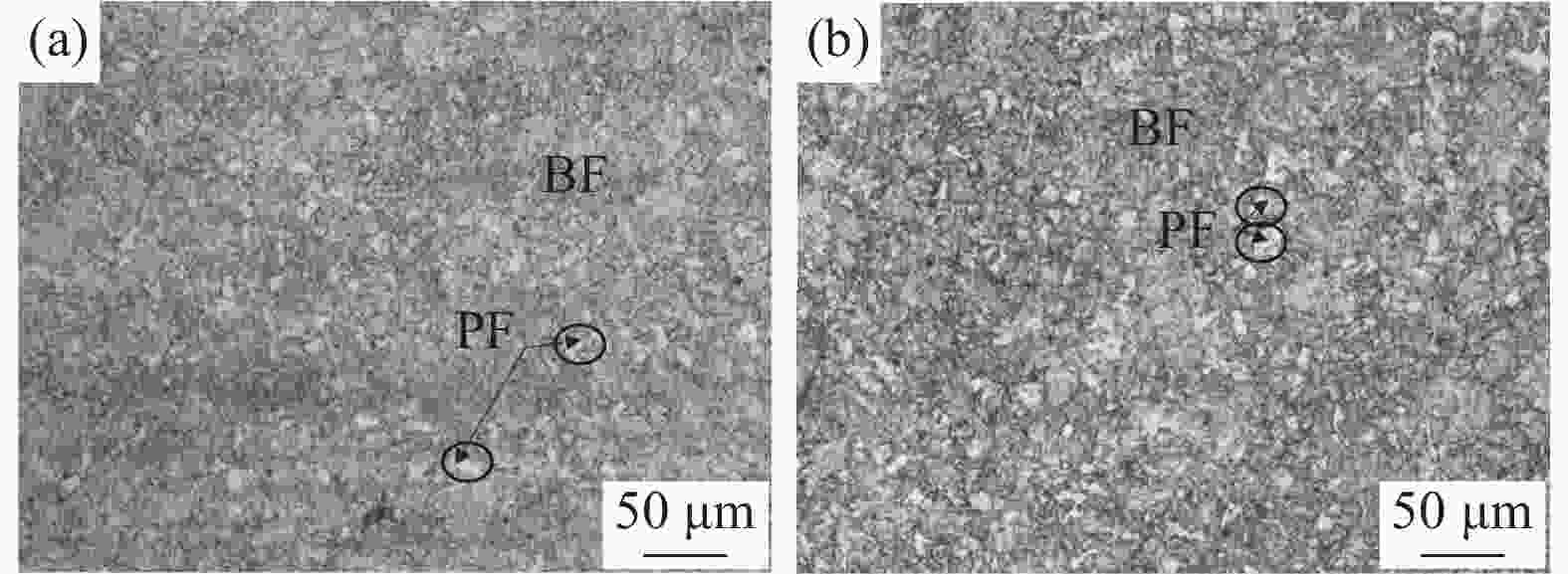
摘要: 为揭示Mg在低合金钢中的微合金化效果,以2.25Cr1Mo钢为研究对象,利用真空感应炉、450型双辊可逆轧机制备不同Mg含量的15 mm板材,采用OM、TEM等手段分析热处理后显微组织,以及原奥氏体晶粒特征,并对其力学性能进行了测定。研究结果表明:Mg加入2.25Cr1Mo钢中可细化其原奥氏体晶粒,增加热处理组织中多边形铁素体体积分数。2.25Cr1Mo钢全氧含量在
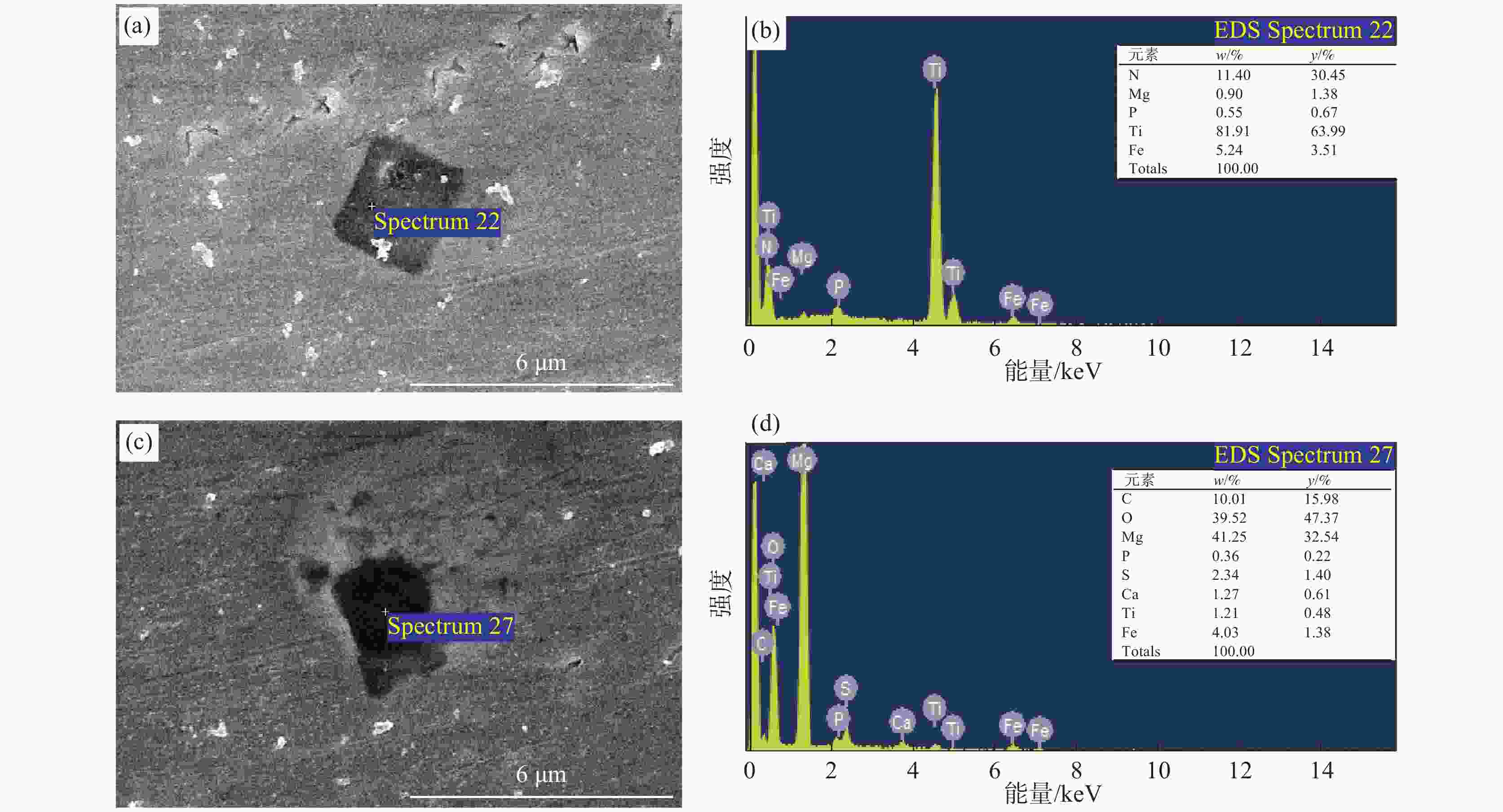
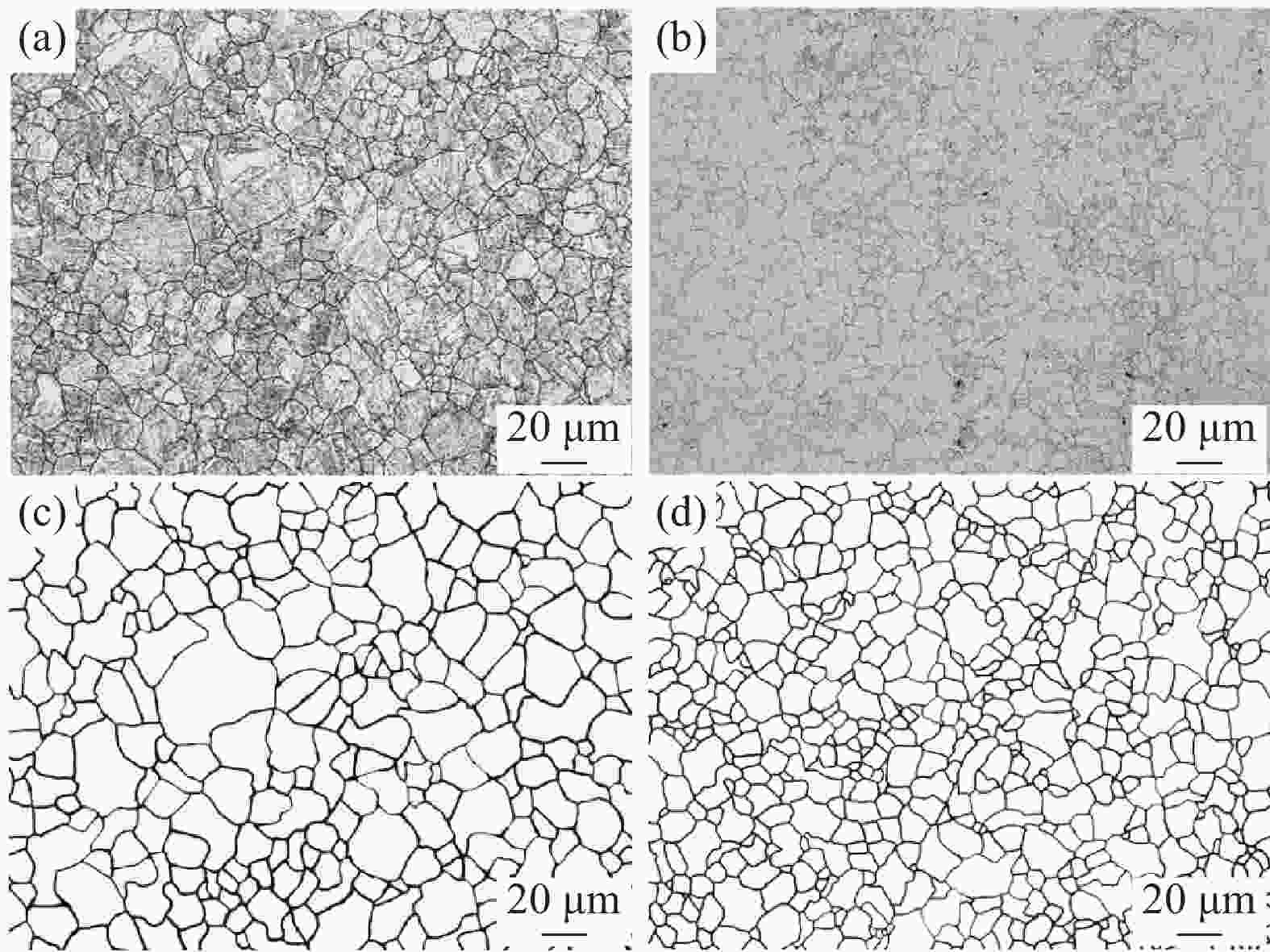
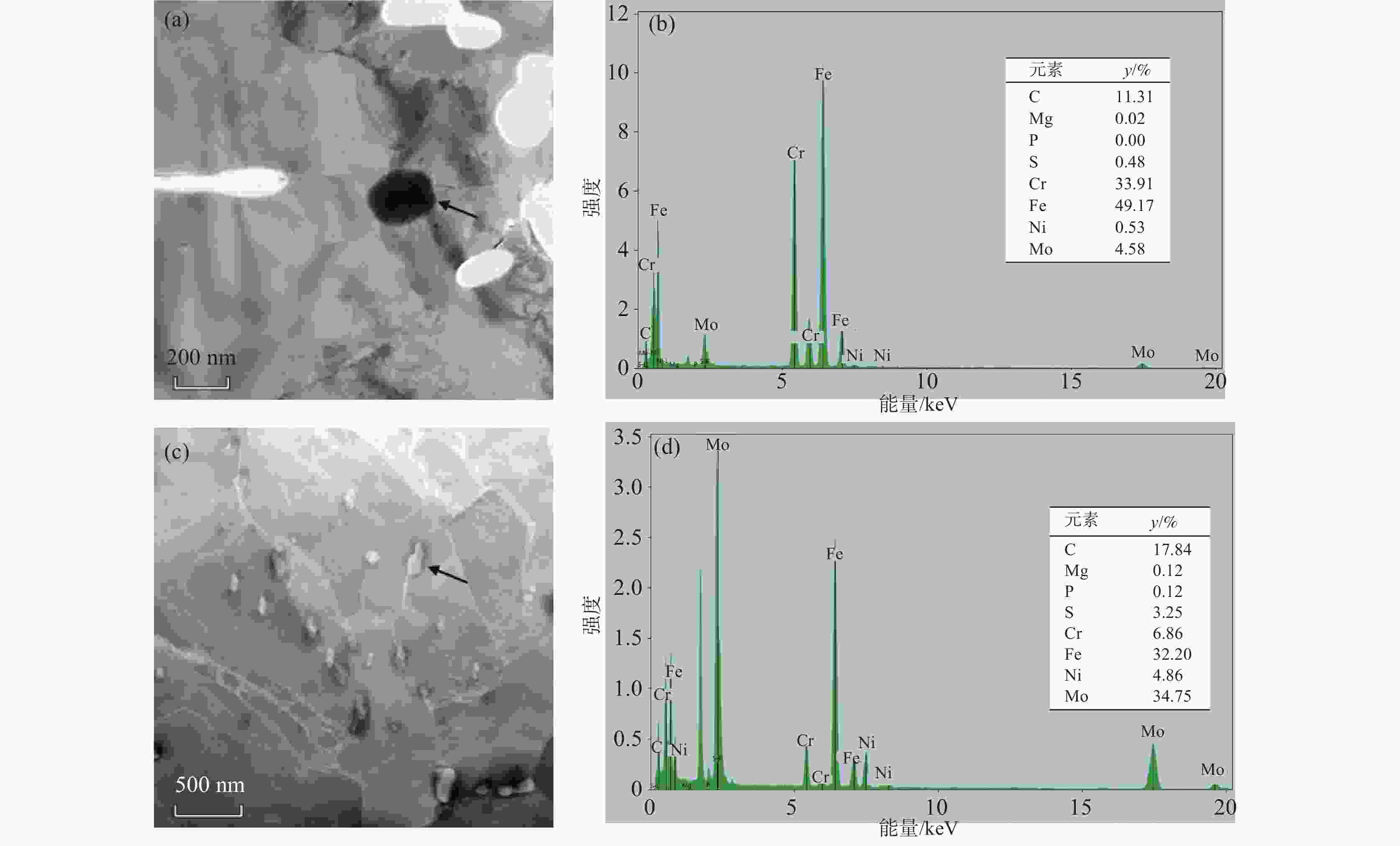
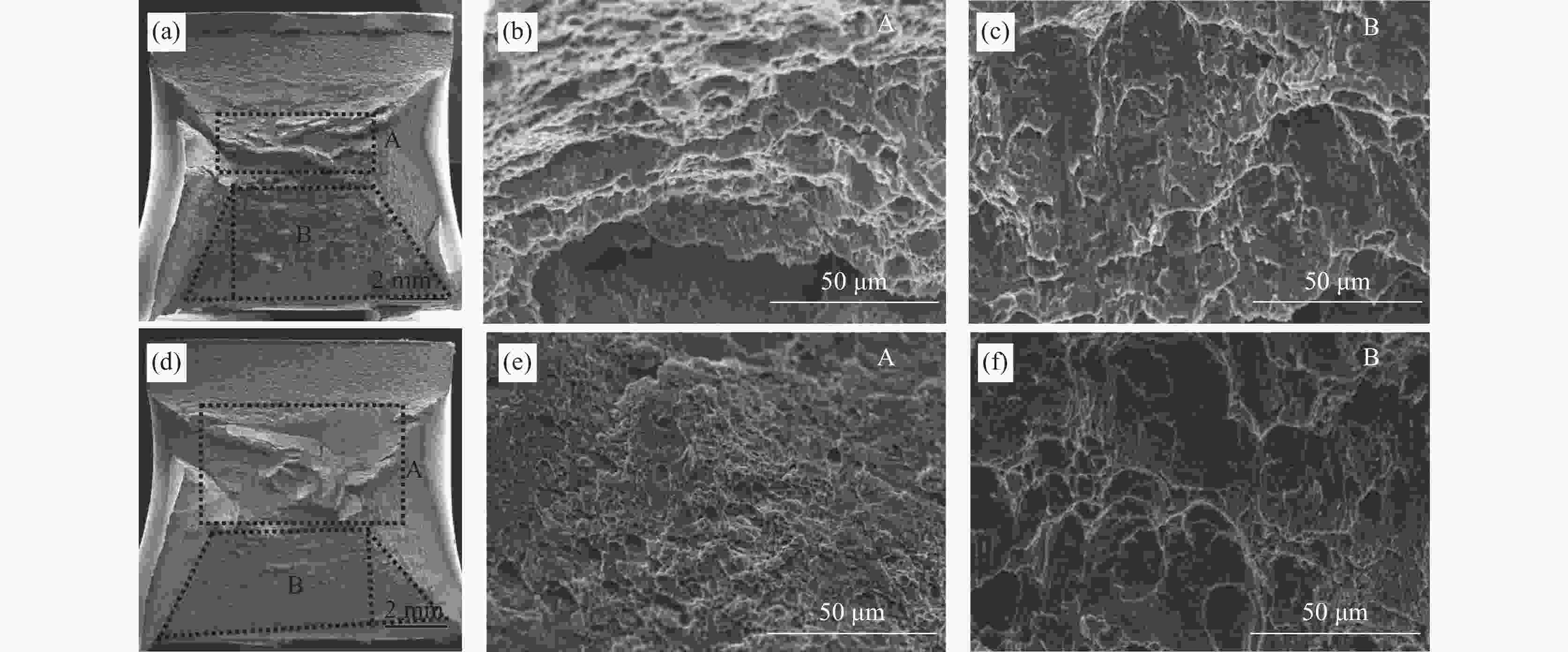
0.0003 %的低含量条件下,Mg会偏聚在碳化物中,诱使碳化物尺寸降低,数量增多,增强碳化物对奥氏体晶粒长大的钉扎作用,进而达到细化原奥氏体晶粒的效果。经0.005%Mg处理后,2.25Cr1Mo钢冲击韧性稍有提升,而显微硬度变化并不明显。Mg处理后使得钢中铁素体分数出现一定范围内的增加是改善其冲击韧性的重要原因。-
关键词:
- 2.25Cr1Mo钢 /
- Mg /
- 铁素体 /
- 奥氏体 /
- 冲击韧性
Abstract: In order to reveal the function of Mg micro-alloying in low micro-alloyed steel, the 2.25Cr1Mo with 15 mm thick steel plates containing different Mg content were prepared with vacuum induction furnace and rolled with double-stick reversible rolling mill. The characteristics of heat-treated microstructure, primary austenite grain, and mechanical properties were investigated with TEM, OM and so on. The results show that after adding Mg for the heat-treated microstructure, the primary austenite grain size is refined and the ferrite volume fraction is increased. When the total oxygen content of 2.25Cr1Mo steel is0.0003 %, Mg will segregate in the carbides, thereby reducing the size of carbides and increasing the amount of these compounds, which increases the pinning effect on austenite grain growth, and then refines the original austenite grain. After adding 0.005% Mg, the impact toughness of 2.25Cr1Mo steel is slightly improved, but the microhardness change is not obvious. The increase of ferrite content in steel after Mg treatment contribute to improving its impact toughness.-
Key words:
- 2.25Cr1Mo steel /
- Mg /
- ferrite /
- austenite /
- impact toughness
-
表 1 试验钢主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of the steels
% 试验钢序号 C Cr Mo Mn Ti Ni P S N O Mg S1 0.11 2.21 1.00 0.49 0.05 0.89 0.002 0.0044 0.0065 0.0005 S2 0.11 2.21 1.04 0.49 0.05 0.86 0.002 0.0017 0.0063 0.0003 0.005 -
[1] Liu Zhen, Ma Jin, Chen Derun. Local hear treatment of defective casting of 2.25Cr-1Mo alloy steel after rewelding[J]. Foundry Engineering, 2016,5:36-38. (刘振, 马进, 陈得润. 有缺陷的2.25Cr-1Mo合金钢铸件返修焊接后的局部热处理[J]. 铸造工程, 2016,5:36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3320.2016.05.016Liu Zhen, Ma Jin, Chen Derun. Local hear treatment of defective casting of 2.25Cr-1Mo alloy steel after rewelding[J]. Foundry Engineering, 2016, 5: 36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3320.2016.05.016 [2] Yoshino K, McMahon C J. The cooperative relation between temper embrittlement and hydrogen embrittlement in a high strength steel[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1974,5(2):363. doi: 10.1007/BF02644103 [3] Li Xiaobing, Dong Xin, Xing Weiwei, et al. Effect of alloying elements addition on the secondary tempering brittleness of Cr-Mo steels reviews[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 56(3): 1-10. (李小兵, 董鑫, 邢炜伟, 等. 合金元素对Cr-Mo钢第二类回火脆性影响研究综述[J]. 钢铁, 2021, 56(3): 1-10.Li Xiaobing, Dong Xin, Xing Weiwei, et al. Effect of alloying elements addition on the secondary tempering brittleness of Cr-Mo steels reviews[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 56(3): 1-10. [4] Qu Z, McMahon C J. The effects of tempering reactions on temper embrittlement of alloy steels[J]. Metall. Trans. A, 1983, 14: 1101-1108. [5] McMahon C J, Cianelli A K, Feng H C. The influence of Mo on P-induced temper embrittlement in Ni-Cr steel[J]. Metall. Trans. A, 1977, 8(7): 1055-1057. [6] Geng W T, Freeman A J, Olson G B. Influence of alloying additions on the impurity induced grain boundary embrittlement[J]. Solid State Commun., 2001,119:585. doi: 10.1016/S0038-1098(01)00298-8 [7] Zhang Dongbin, Wu Chengjian. Behavior of cerium in grain boundary segregation and its influence on equilibrium segregation of phosphorus at grain boundary in α-iron[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 1988,24(2):100. (张东彬, 吴承建. Ce在α-Fe晶界的偏聚及其对磷的晶界平衡偏聚的影响[J]. 金属学报, 1988,24(2):100.Zhang Dongbin, Wu Chengjian. Behavior of cerium in grain boundary segregation and its influence on equilibrium segregation of phosphorus at grain boundary in α-iron[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 1988, 24(2): 100. [8] Wang Haiyang, Gao Xueyun, Ren Huiping, et al. Density functional theory study on cerium occupying tendency and effecting mechanism in bcc α-Fe[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014,43(11):2739. (王海洋, 高雪云, 任慧平, 等. 稀土Ce在α-Fe中占位倾向与作用机理的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2014,43(11):2739.Wang Haiyang, Gao Xueyun, Ren Huiping, et al. Density functional theory study on cerium occupying tendency and effecting mechanism in bcc α-Fe[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43(11): 2739. [9] Jahazi M, Jonas J J. The non-equilibrium segregation of boron on original and moving austenite grain boundaries[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 335: 49-54. [10] Jones R B, Younas C M, Heard P J. The effect of microscale distribution of boron on the yield strength of C-Mn steels subjected to neutron irradiation[J]. Acta Metall., 2002, 50(17): 4395-4417. [11] Song S H, Guo M A, Shen D D, et al. Effect of boron on the hot ductility of 2.25Cr1Mo steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 360: 96-100. [12] Takahashi J, Kawakami K, Ushioda K, et al. Quantitative analysis of grain boundaries in carbon- and nitrogen added ferritic steels by atom probe tomography[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2012,66:207. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.10.026 [13] Han J C, Seolb J B, Jafari M, et al. Competitive grain boundary segregation of phosphorus and carbon governs delamination crack in a ferritic steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018,145:454. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2018.08.060 [14] Li Xiaobing, Dong Xin, Zhao Pengxiang, et al. Effect of Mg Addition on the temper embrittlement in 2.25Cr-1Mo steel doped with 0.056% P—Mg segregation behavior at grain boundary[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2021, 28(10): 1259-1267. [15] Wang Deyong, Qu Tianpeng. Development and prospect of Mg clean steel technology[J]. Steelmaking, 2020,36(5):1-13. (王德永, 屈天鹏. 镁洁净钢新技术发展与展望[J]. 炼钢, 2020,36(5):1-13.Wang Deyong, Qu Tianpeng. Development and prospect of Mg clean steel technology[J]. Steelmaking, 2020, 36(5): 1-13. [16] Li Xiaobing, Min Yi, Liu Chengjun, et al. Effect of Mg addition on the characterization of γ-α phase transformation during continuous cooling in low carbon steel[J]. Steel Research International, 2015,86(12):1530-1540. doi: 10.1002/srin.201400517 [17] Liu Ying, Liu Jianhua, He Yang, et al. Effect of Mg addition on solidification structure and inclusions in ALSI4130 steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2022,38(6):6-13. (刘颖, 刘建华, 何杨, 等. 镁处理对AISI4130钢组织及夹杂物的影响[J]. 炼钢, 2022,38(6):6-13.Liu Ying, Liu Jianhua, He Yang, et al. Effect of Mg addition on solidification structure and inclusions in ALSI4130 steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2022, 38(6): 6-13. [18] Li Yandong, Xing Weiwei, Li Xiaobing, et al. Effect of Mg addition on microstructure and properties of heat-affected zone in submerged arc welding of a Al-killed low carbon steel[j]. Materials, 2021, 14(9): 2445. [19] Sarma D S, Karasev A V, Jonsson P G. On the role of non-metallic inclusions in the nucleation of acicular ferrite in steels[J]. ISIJ International, 2009,49(7):1063-1074. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.49.1063 [20] Badu S S, Bhadeshia H K D H. Stress and the acicular ferrite transformation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1992,156(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/0921-5093(92)90410-3 [21] Bor H Y, Chao C G, Ma C Y. The influence of magnesium on carbide characteristics and creep behavior of the Mar-M247 superalloy[J]. Scr. Mater. , 1997, 38(2): 329-335. [22] Sakata K, Suito H. Grain-growth-inhibiting effects of primary inclusion particles of ZrO2 and MgO in Fe-10masspctNi alloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2000,31(4):1213-1223. doi: 10.1007/s11661-000-0117-z [23] Kojima A, Kiyose A, Uemori R, et al. Super high HAZ toughness technology with fine microstructure imparted by fine particles[J]. Nippon Steel Technical Research, 2004(90):2-6. [24] Tian Bo, Sun Ligen, Zhu Liguang. The behavior of pinned particles for Mg treated shipbuilding steel under high temperature[J]. Steelmaking, 2020,36(6):72-77. (田博, 孙立根, 朱立光. 高温条件下Mg处理船体钢钉扎粒子的作用行为[J]. 炼钢, 2020,36(6):72-77.Tian Bo, Sun Ligen, Zhu Liguang. The behavior of pinned particles for Mg treated shipbuilding steel under high temperature[J]. Steelmaking, 2020, 36(6): 72-77. [25] Ji Yongshuai, Li Yang, Jiang Zhouhua, et al. Process of adding magnesium oxide particles in preparation of iron and steel materials[J]. China Metallurgy, 2023,33(2):8-21. (鸡永帅, 李阳, 姜周华, 等. 外加镁系氧化物粒子在钢铁材料制备中的进展[J]. 中国冶金, 2023,33(2):8-21.Ji Yongshuai, Li Yang, Jiang Zhouhua, et al. Process of adding magnesium oxide particles in preparation of iron and steel materials[J]. China Metallurgy, 2023, 33(2): 8-21. [26] Han S Q, Zhao J Q, Wan R D, et al. Effect of microstructure on long-term aging stability of 2.25Cr-1Mo steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2020,45(2):11-18. -




 下载:
下载: