Molecular dynamics simulation study on the tensile behavior of FeC alloy
-
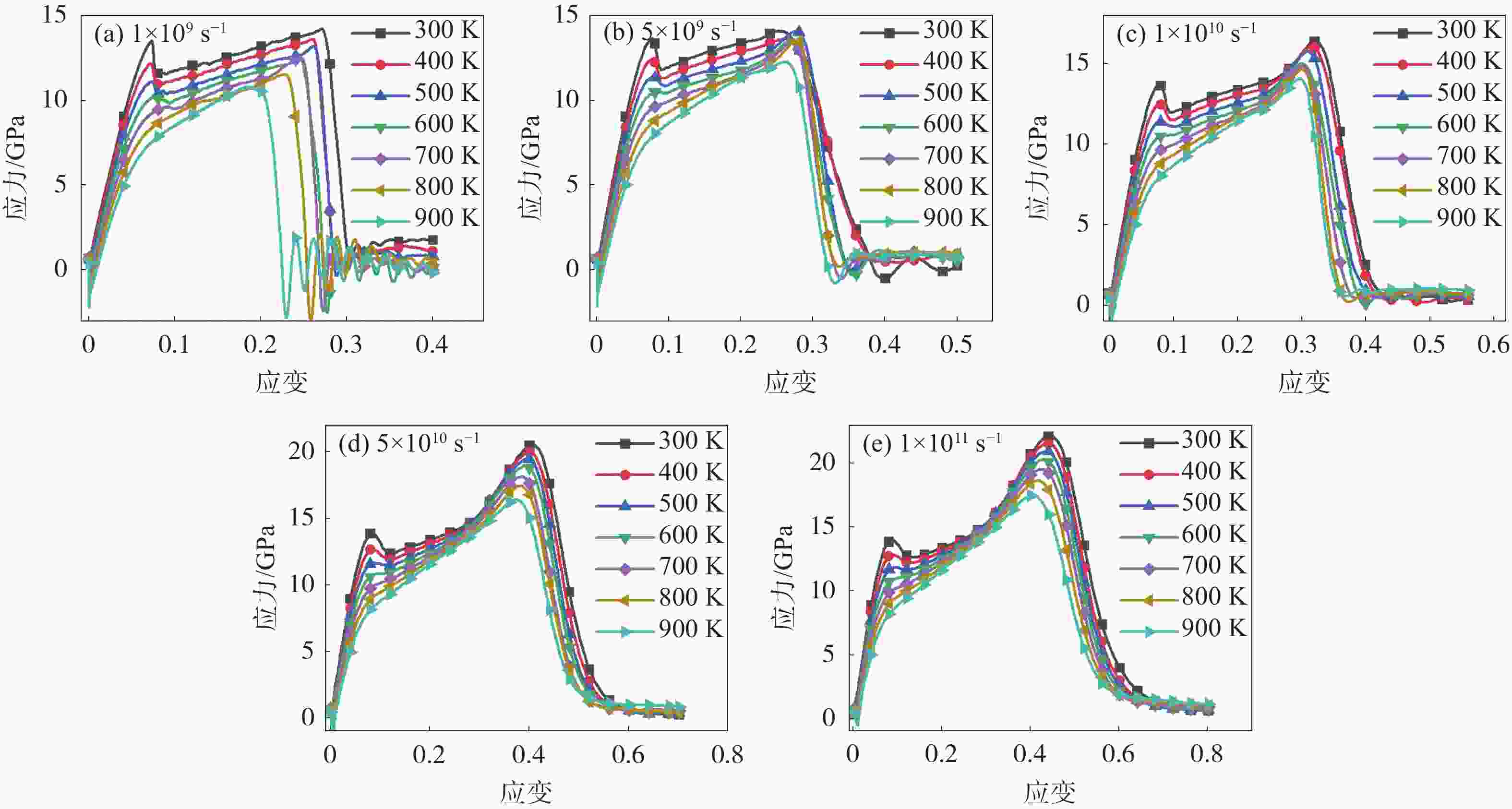
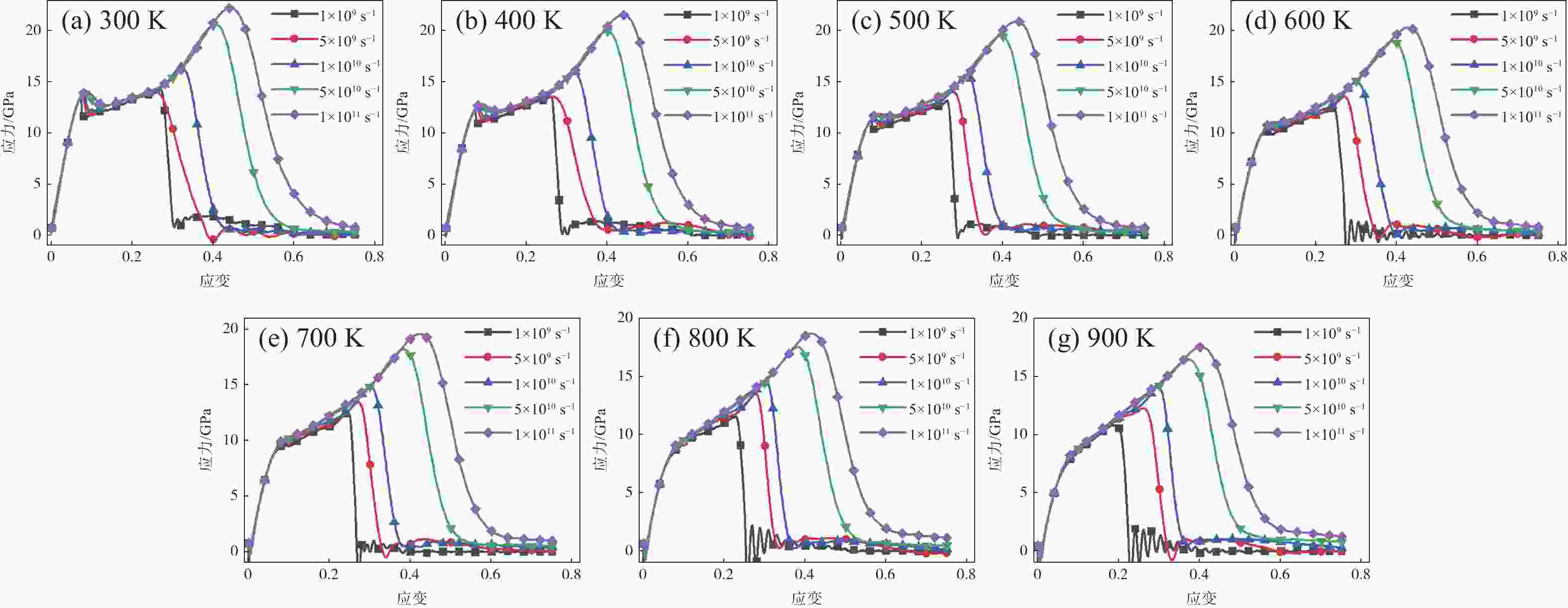
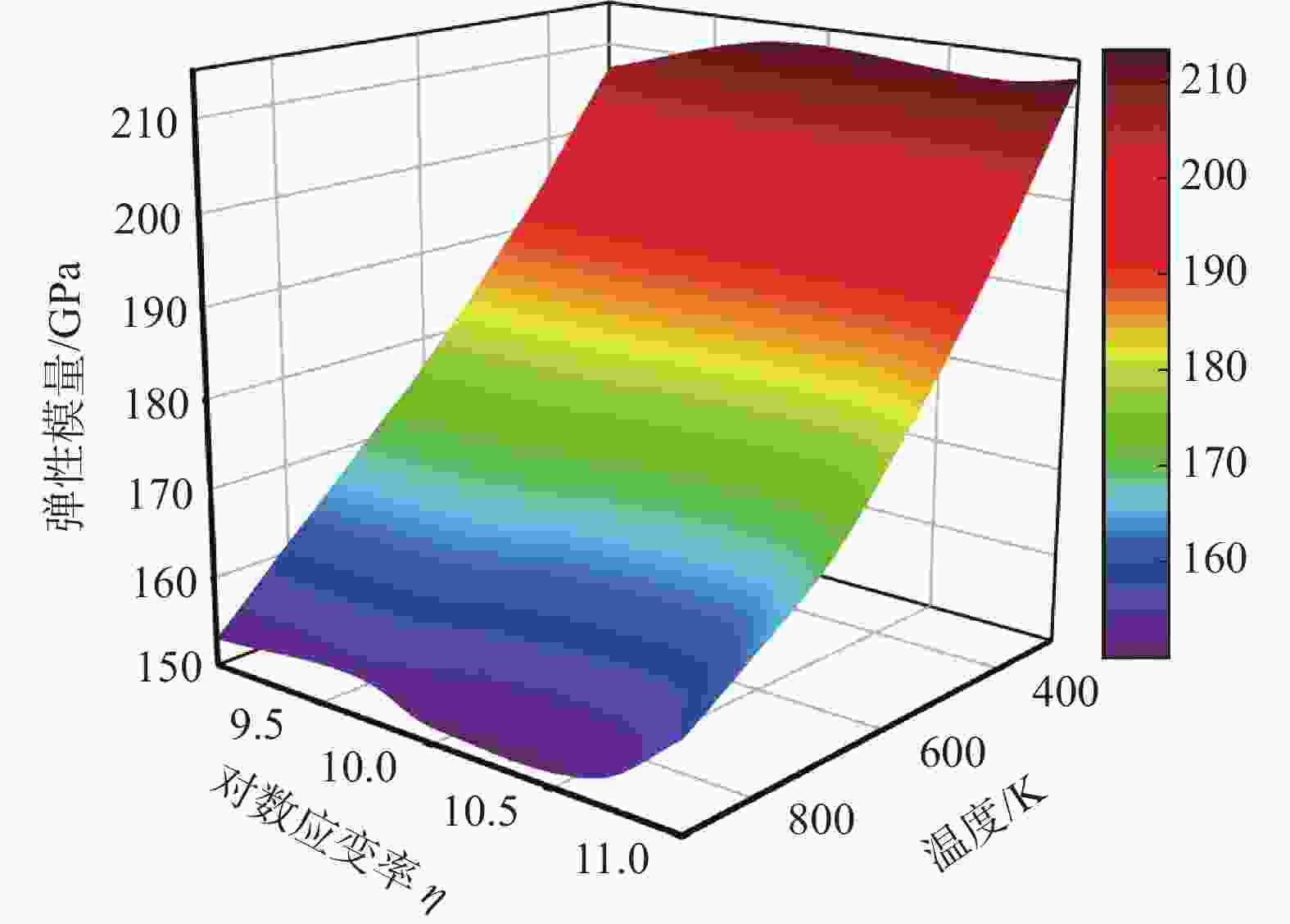
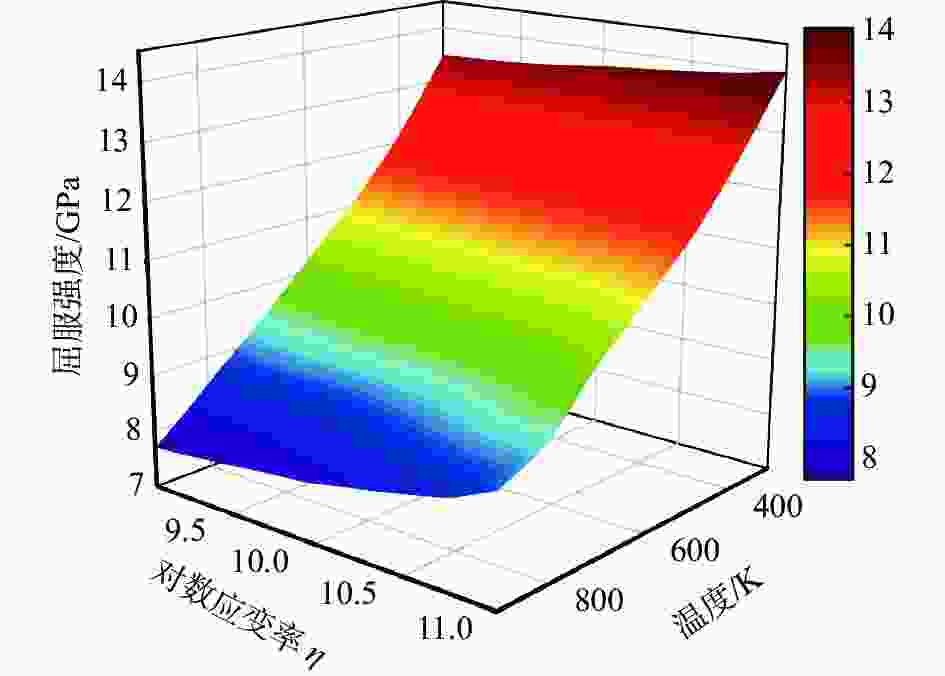
摘要: 为了探究温度和应变率对FeC合金微观力学性能的影响,运用分子动力学方法对FeC合金进行了拉伸性能的模拟,得到了不同温度、不同应变率工况下FeC合金的应力应变曲线,并对其进行了分析,利用MATLAB对数据进行处理,建立了关于温度和应变率的FeC合金弹性模量和屈服强度的数学预测模型。结果表明:弹性模量和屈服强度的仿真值与数学模型的预测值之间的绝对误差最大分别为2.680 GPa和0.079 GPa,相对误差最大分别为1.680%和0.737%,数学预测模型能在一定程度上对弹性模量和屈服强度进行有效的预测。Abstract: In order to investigate the effects of temperature and strain rate on the micro-mechanical properties of FeC alloys, molecular dynamics methods were used to simulate the tensile properties of FeC alloys. The stress-strain curves of FeC alloys at different temperatures and strain rates were obtained and analyzed, and the data was processed using MATLAB. A mathematical model was established to predict the elastic modulus and yield strength of FeC alloys calculated on the basis of temperature and strain rate. The results show that the maximum absolute errors between the simulation and the prediction values by the mathematical model of elastic modulus and yield strength are 2.680 GPa and 0.079 GPa, respectively. The maximum relative errors are 1.680% and 0.737%, respectively. The mathematical prediction model can effectively predict the elastic modulus and yield strength to a certain extent.
-
Key words:
- FeC alloy /
- mechanical properties /
- molecular dynamics /
- elastic modulus /
- yield strength
-
表 1 结果统计
Table 1. Statistic results
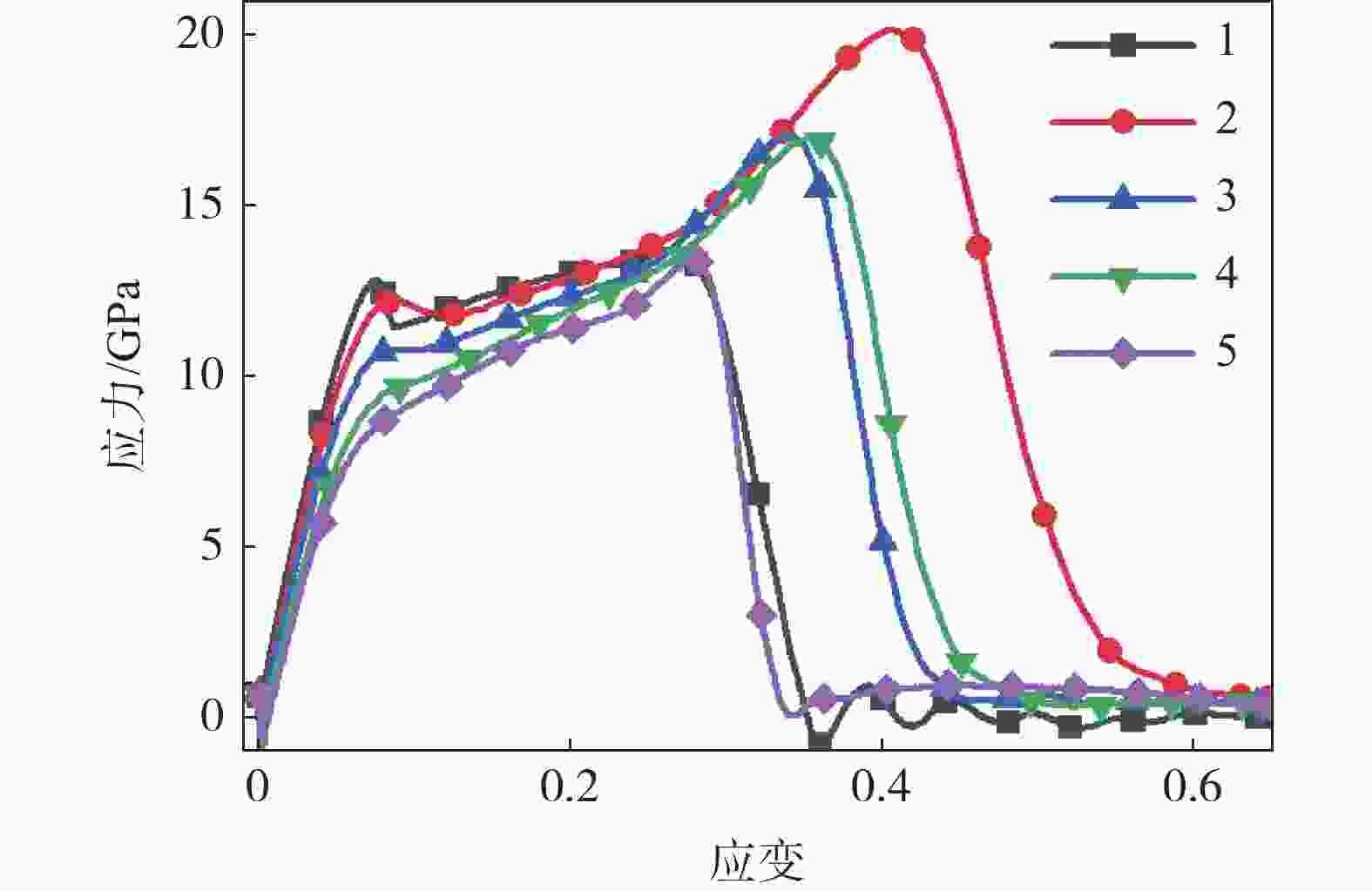
温度/K E/GPa Q/GPa 1×109 s−1 5×109 s−1 1×1010 s−1 5×1010 s−1 1×1011 s−1 1×109 s−1 5×109 s−1 1×1010 s−1 5×1010 s−1 1×1011 s−1 300 207.165 212.584 213.059 211.881 213.066 13.478 13.589 13.696 13.890 14.041 400 195.880 197.963 198.091 198.596 200.514 12.155 12.369 12.458 12.705 12.879 500 186.006 186.347 185.781 185.427 188.833 11.102 11.320 11.400 11.657 11.834 600 176.817 176.904 174.907 174.036 178.773 10.227 10.398 10.532 10.739 11.034 700 168.936 168.354 165.489 164.826 170.282 9.344 9.578 9.595 9.908 10.297 800 161.087 161.185 158.769 158.424 164.841 8.525 8.591 8.764 9.258 9.354 900 153.050 154.258 151.722 153.005 159.754 7.708 7.934 8.037 8.498 8.908 表 2 仿真条件
Table 2. Simulation conditions
组号 温度/K 应变率×10−9/s−1 1 360 4 2 450 60 3 580 20 4 730 30 5 810 6 表 3 误差分析
Table 3. Error analysis
组号 E/GPa E的相对误差/% Q/GPa Q的相对误差/% 预测值 仿真值 绝对误差 预测值 仿真值 绝对误差 1 203.395 204.518 −1.123 −0.549 12.811 12.806 0.005 0.039 2 192.23 190.738 1.492 0.782 12.205 12.233 −0.028 −0.229 3 176.21 176.098 0.112 0.064 10.793 10.714 0.079 0.737 4 162.192 159.512 2.680 1.680 9.538 9.524 0.014 0.147 5 160.003 160.439 −0.436 −0.272 9.218 9.199 0.019 0.207 -
[1] 叶天舟, 姚欢, 巫英伟, 等. FeCrAl合金拉伸力学性能分子动力学研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2023, 52(2): 777-784.Ye Tianzhou, Yao Huan, Wu Yingwei, et al. Molecular dynamics study on tensile mechanical properties of FeCrAl alloy[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2023, 52(2): 777-784. [2] Zhou Jikai, Zhu Qinghua. Molecular dynamics of temperature and strain rate effects of dynamic tensile mechanical properties of FeC alloy[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019,19(11):61-66. (周继凯, 朱清华. FeC 合金动态拉伸力学性能温度和应变率效应分子动力学[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019,19(11):61-66.Zhou Jikai, Zhu Qinghua. Molecular dynamics of temperature and strain rate effects of dynamic tensile mechanical properties of Fe-C alloy[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19( 11): 61-66 [3] Wu Qian, Wang Yong, Han Tao, et al.Molecular dynamics simulations of the effect of temperature and strain rate on the plastic deformation of body centred cubic iron nanowires[J].Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology, 2021, 143: 031007. [4] 曾 强, 王丽娟, 陈 韬, 等. 纳米孪晶与Fe 掺杂对SLM-Al 力学性能影响的分子动力学模拟[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2023, 52(1): 145-152.Zeng Qiang, Wang Lijuan, Chen Tao, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation on effect of nano-twin and Fe doping on mechanical roperties of SLM-Al[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2023, 52 (1): 145-152. [5] Zheng Wei, Han Junzhao, Duan Xing, et al. Mechanical properties of Al0.1CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy based on molecular dynamics study[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2022,51(9):3230-3235. [6] Wang Yuntian, Zeng Xiangguo, Yang Xin. Molecular dynamics simulation of effect of temperature on oid nucleation and growth of single crystal ron at a high strain rate[J]. Acta Phys. Sin, 2019,68(24):246102. (王云天, 曾祥国, 杨鑫. 高应变率下温度对单晶铁中孔洞成核与生长影响的分子动力学研究[J]. 物理学报, 2019,68(24):246102. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20190920Wang Yun -Tian, Zeng Xiang -Guo, Yang Xin. Molecular dynamics simulation of effect of temperature on oid nucleation and growth of single crystal ron at a high strain rate[J]. Acta Phys. Sin. 2019, 68(24): 246102 doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20190920 [7] Aidan P Thompson, H Metin Aktulga, Richard Berger, et al. LAMMPS - a flexible simulation tool for particle-based materials odeling at the atomic, meso, and continuum scales[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2022,271:108171. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2021.108171 [8] Zhang Chuntao, Zhu Hongjie, Zhu Li. Effect of interaction between corrosion and high temperature on mechanical properties of Q355 structural steel[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021,271:121605. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121605 [9] Derek J Hepburn, Graeme J Ackland. Metallic-covalent interatomic potential for carbon in iron[J]. Physical Review B, 78(16), 165115. [10] Zhu Lhshan, Zhao Shijin. Influence of Ni on Cu precipitation in Fe-Cu-Ni ternary alloy by an atomic study[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2014,23(6):193-198. -




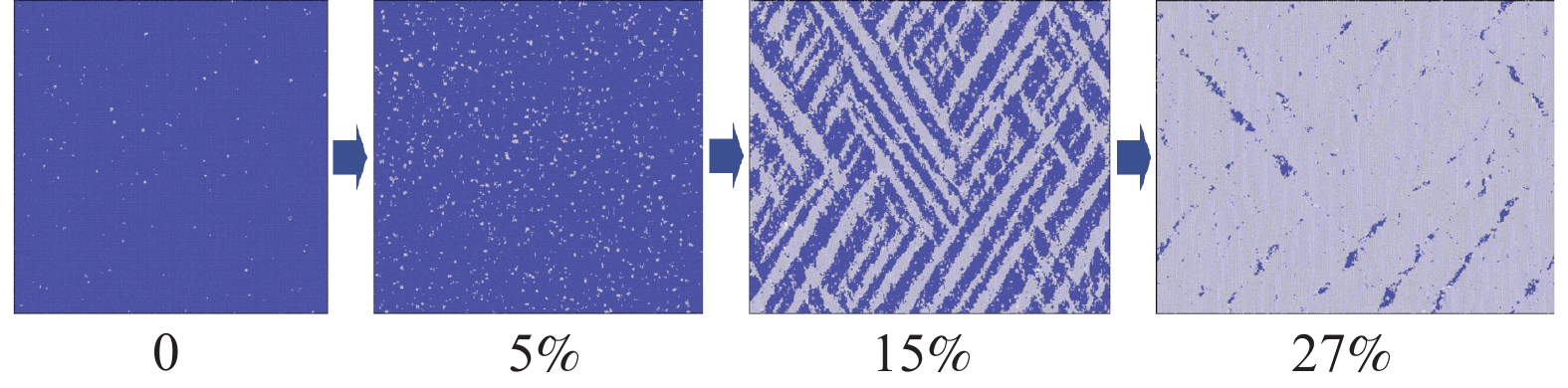
 下载:
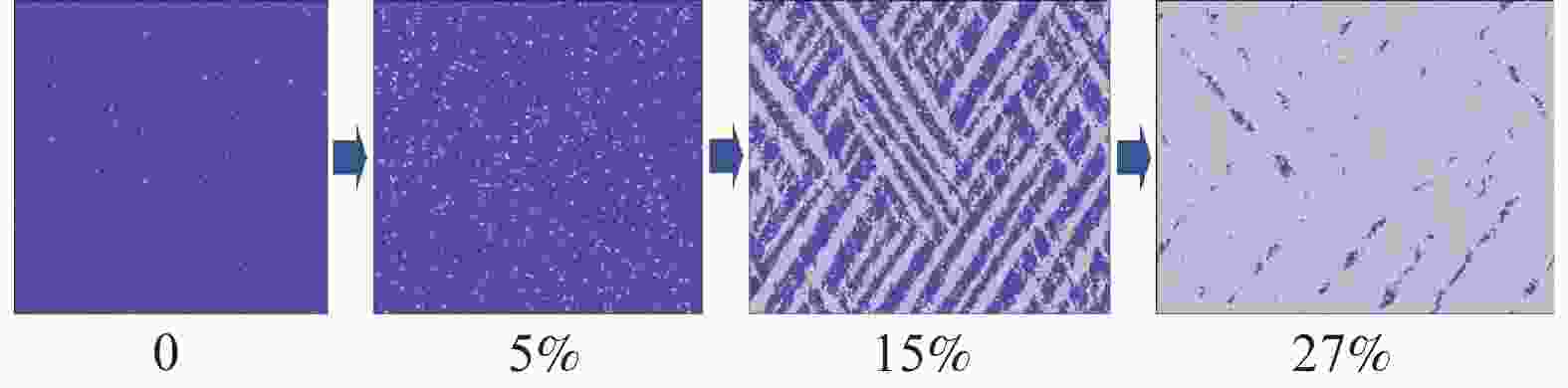
下载: