Study on mechanical properties of resistance spot welded joints with single pulse unequal thickness of 22MnB5/DP590
-
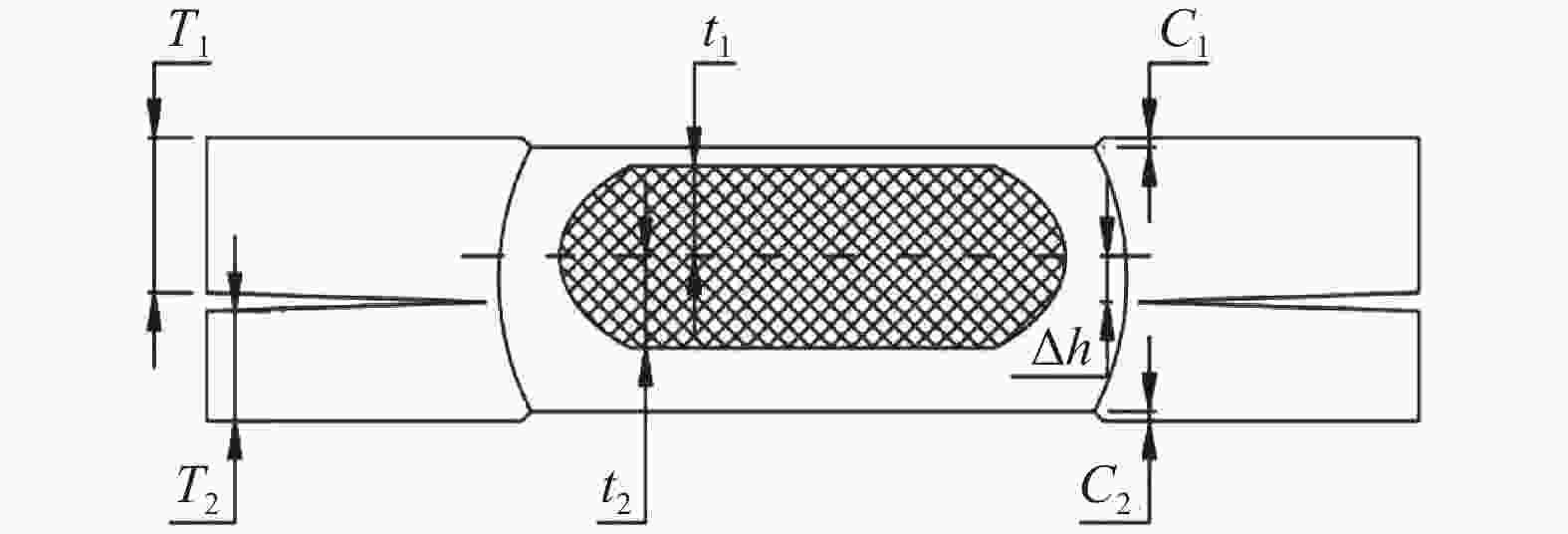
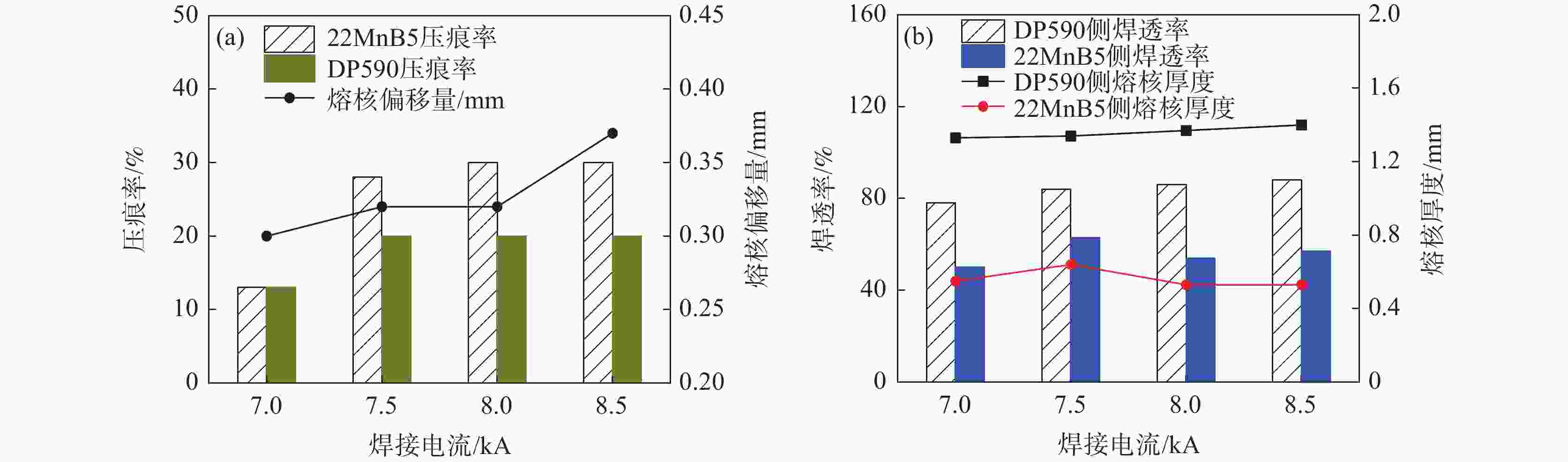
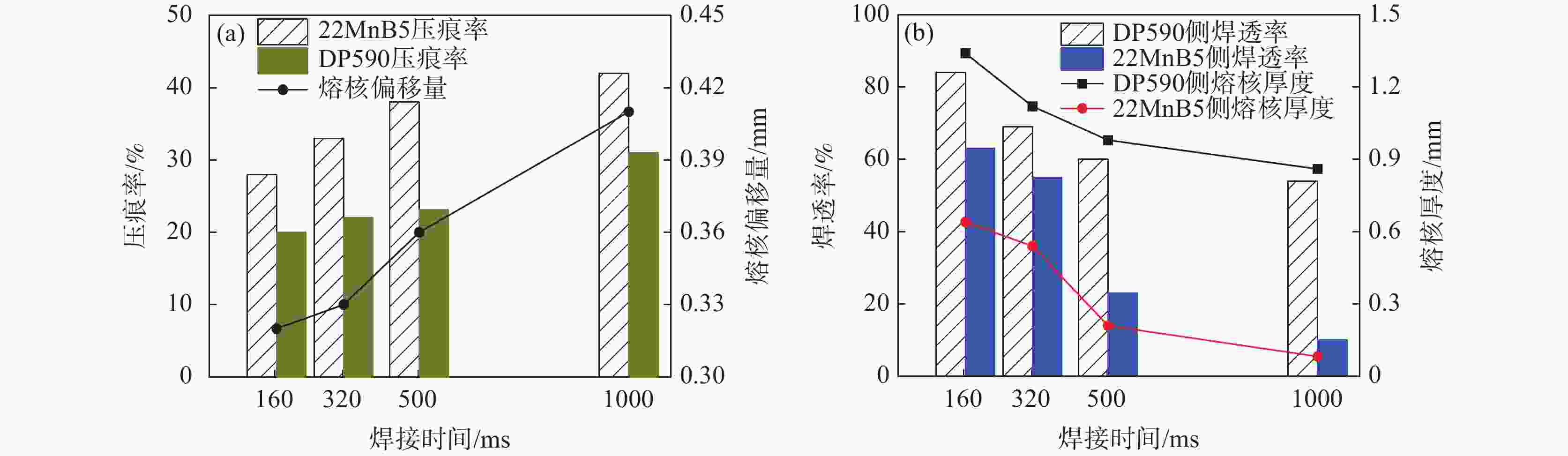
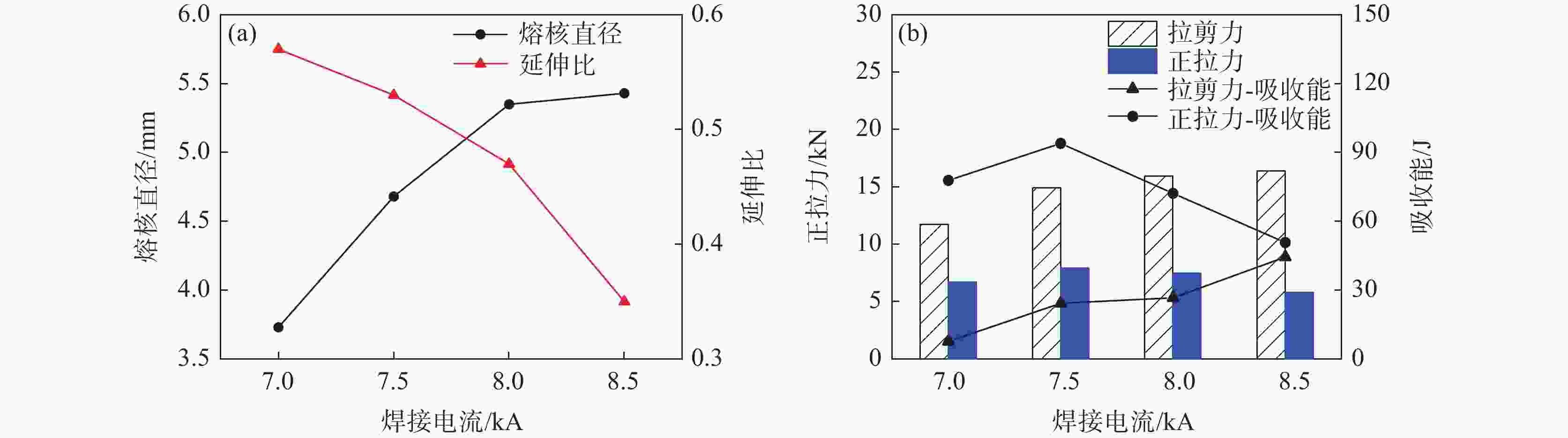
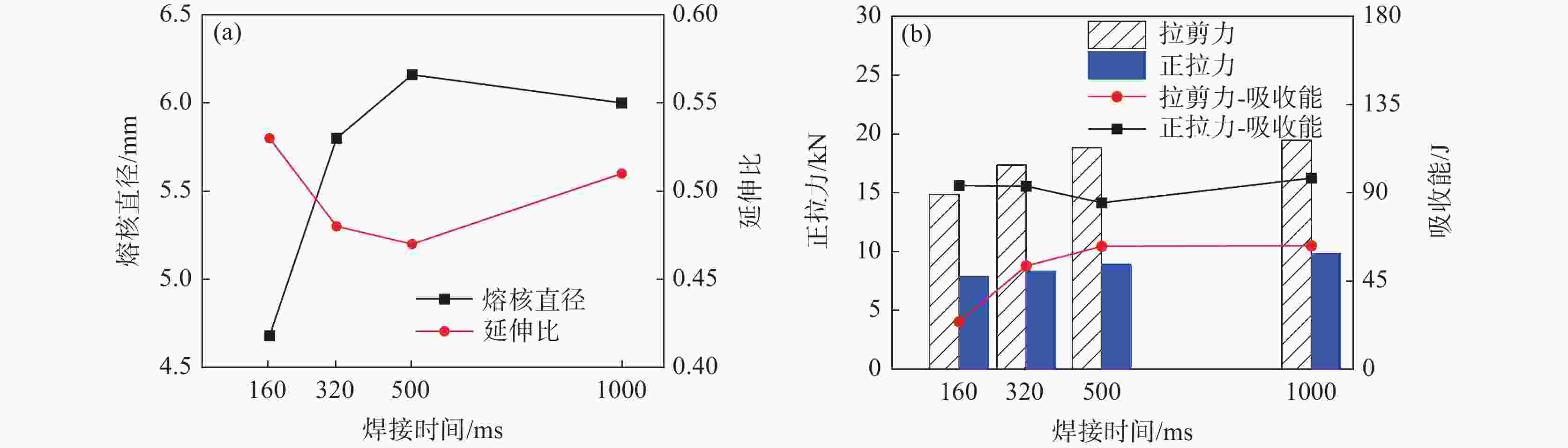
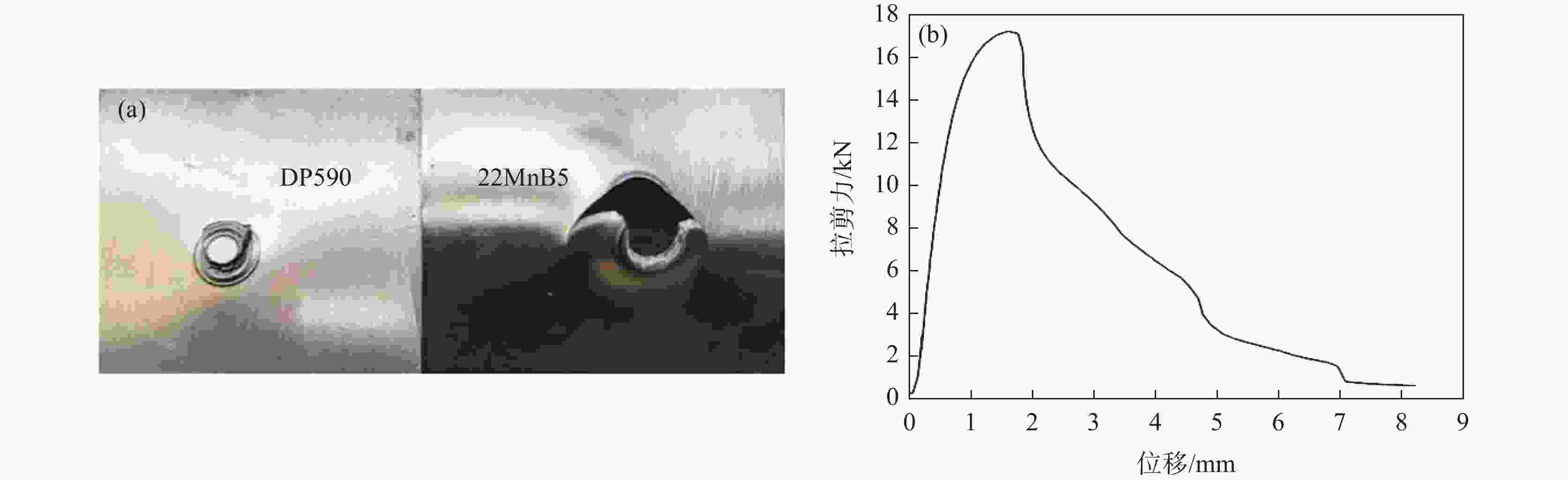
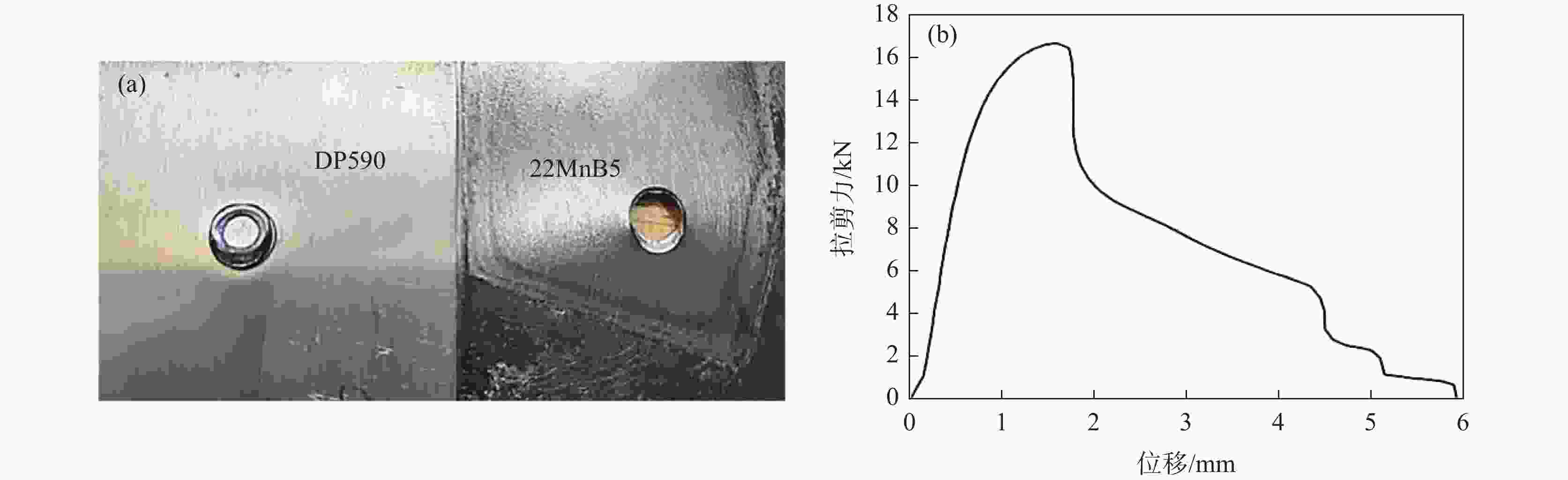
摘要: 采用单脉冲电阻点焊连接技术,研究不同的焊接电流和焊接时间条件下不等厚22MnB5/DP590点焊接头截面特征和拉伸性能,分析点焊接头显微硬度的变化规律。结果表明:焊接电流对母材焊透率和熔核厚度的影响不大。随焊接电流的增加,熔核向较厚DP590侧方向偏移,接头熔核直径和拉剪力增加。与焊接电流相比,焊接时间的增加对接头压痕率和熔核偏移量的影响严重;随焊接时间的增加,母材的焊透率和熔核厚度减小,焊接时间为
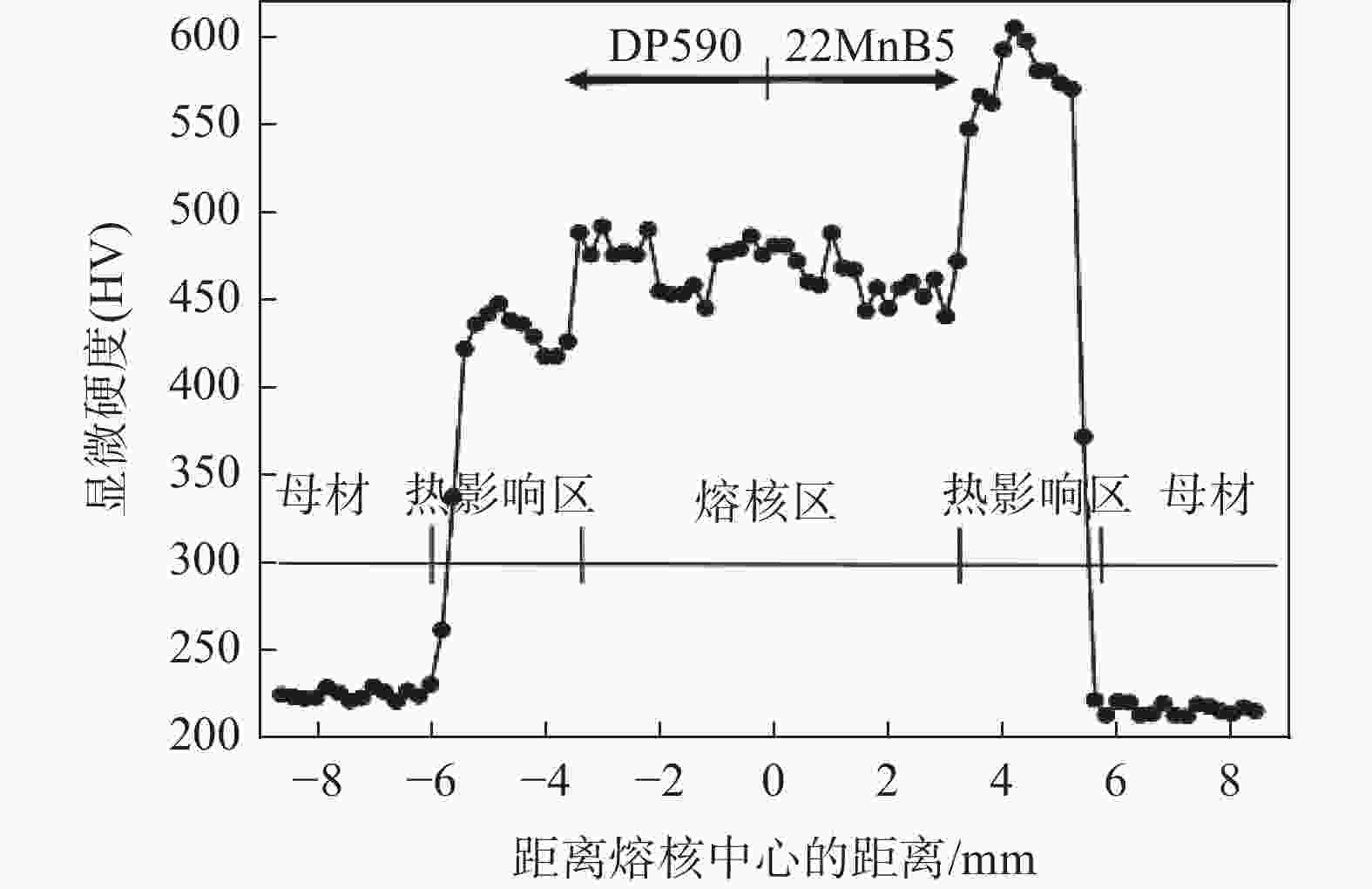
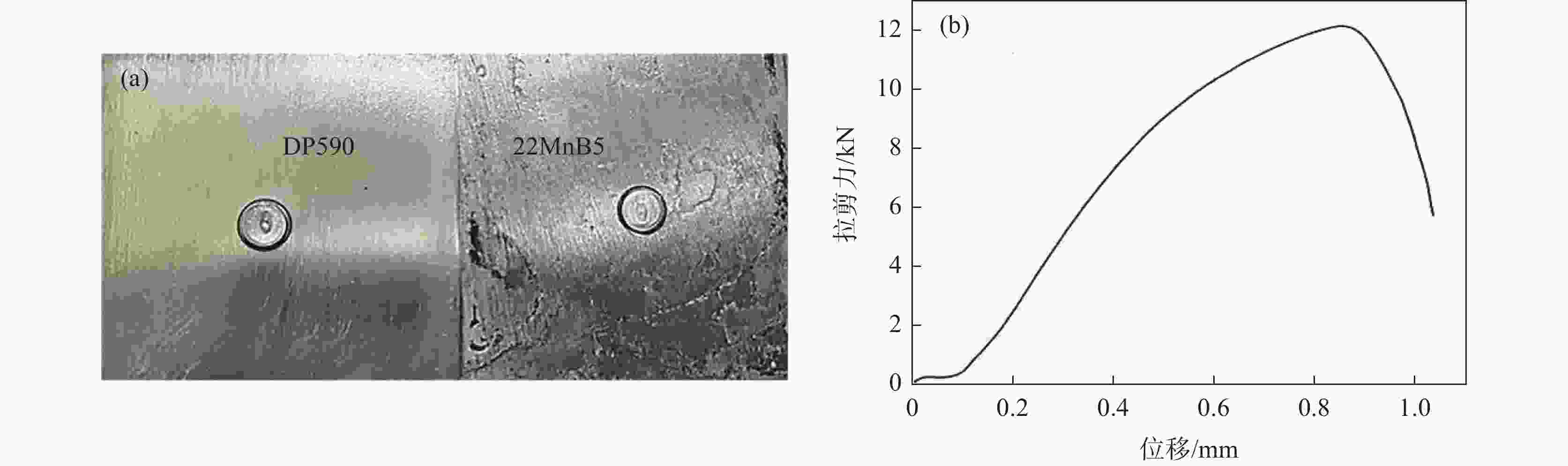
1000 ms时熔核直径减小,而拉剪力一直增加。点焊接头的显微硬度值由高到低分别为22MnB5侧热影响区→熔核区→DP590侧热影响区。在拉剪力作用下,接头拉伸断裂方式有界面断裂、部分界面断裂和熔核拔出断裂。并由此得出结论:在电极压力为3.8 kN的条件下,不等厚DP590/22MnB5的最佳点焊工艺为焊接电流为8.5 kA,焊接时间为160 ms。Abstract: In this paper, the single pulse resistance spot welding technology was used to study the section characteristics and tensile properties of 22MnB5/DP590 spot welding joints with varying thickness section under different welding current and welding time, and the variation of microhardness of spot welding joints was analyzed. The results show that the welding current has little effect on the penetration and core thickness of the base metal. With the increase of welding current, the weld core moves towards the thicker DP590 side, and both weld diameter and tensile shear of the joint increase. Compared with the welding current, prolonging welding time has significant effect on the indentation rate and core offset of the joint. With the increase of welding time, the penetration of the base metal and the thickness of the molten core decrease. The diameter of the molten core decreases when the welding time is1000 ms, but the tensile shear keeps increasing. The microhardness values of spot welded joints from high to low are as follows: 22MnB5 side heat affected zone → molten core zone →DP590 side heat affected zone. Under the action of tensile shear, the joint tensile fracture modes include interface fracture, partial interface fracture and core pulling out fracture. It is concluded that given 3.8 kN of welding force the optimum welding conditions for varying section of DP590/22MnB5 are 8.5 kA of welding current and 160 ms of welding time.-
Key words:
- 22MnB5 /
- DP590 /
- resistance spot welding /
- welding current /
- welding time /
- mechanical properties
-
表 1 DP590和22MnB5的化学成分
Table 1. The chemical compositions of DP590 and 22MnB5 steel
% 材料 C Si Mn P S Cr B Al Ti N Fe DP590 0.06 0.31 1.23 0.02 0.004 0.55 0.029 Bal. 22MnB5 0.22 0.23 1.2 0.013 0.001 0.2 0.0027 0.04 0.028 0.004 Bal. 表 2 单脉冲点焊工艺参数
Table 2. Welding parameters of single pulse spot welding process
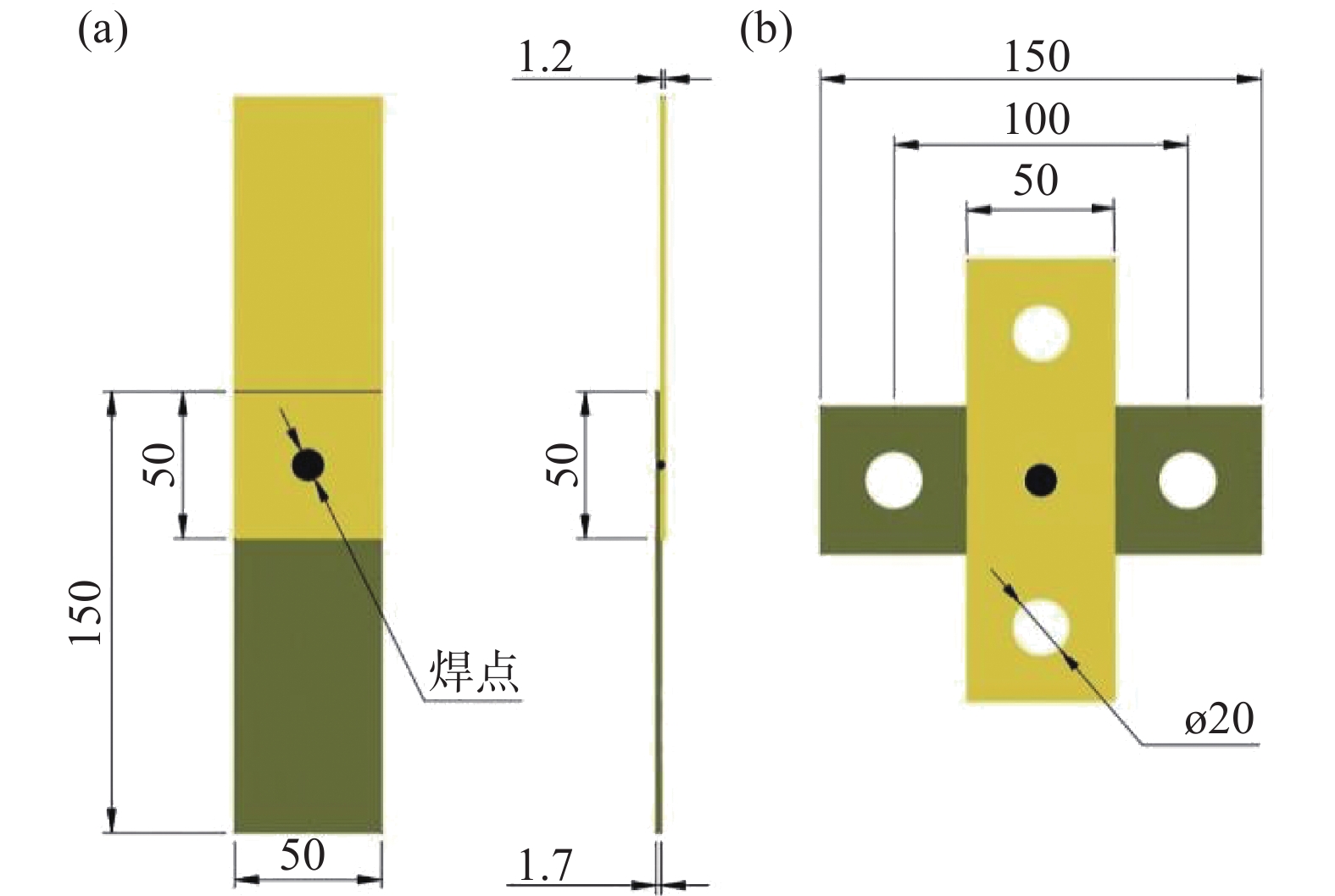
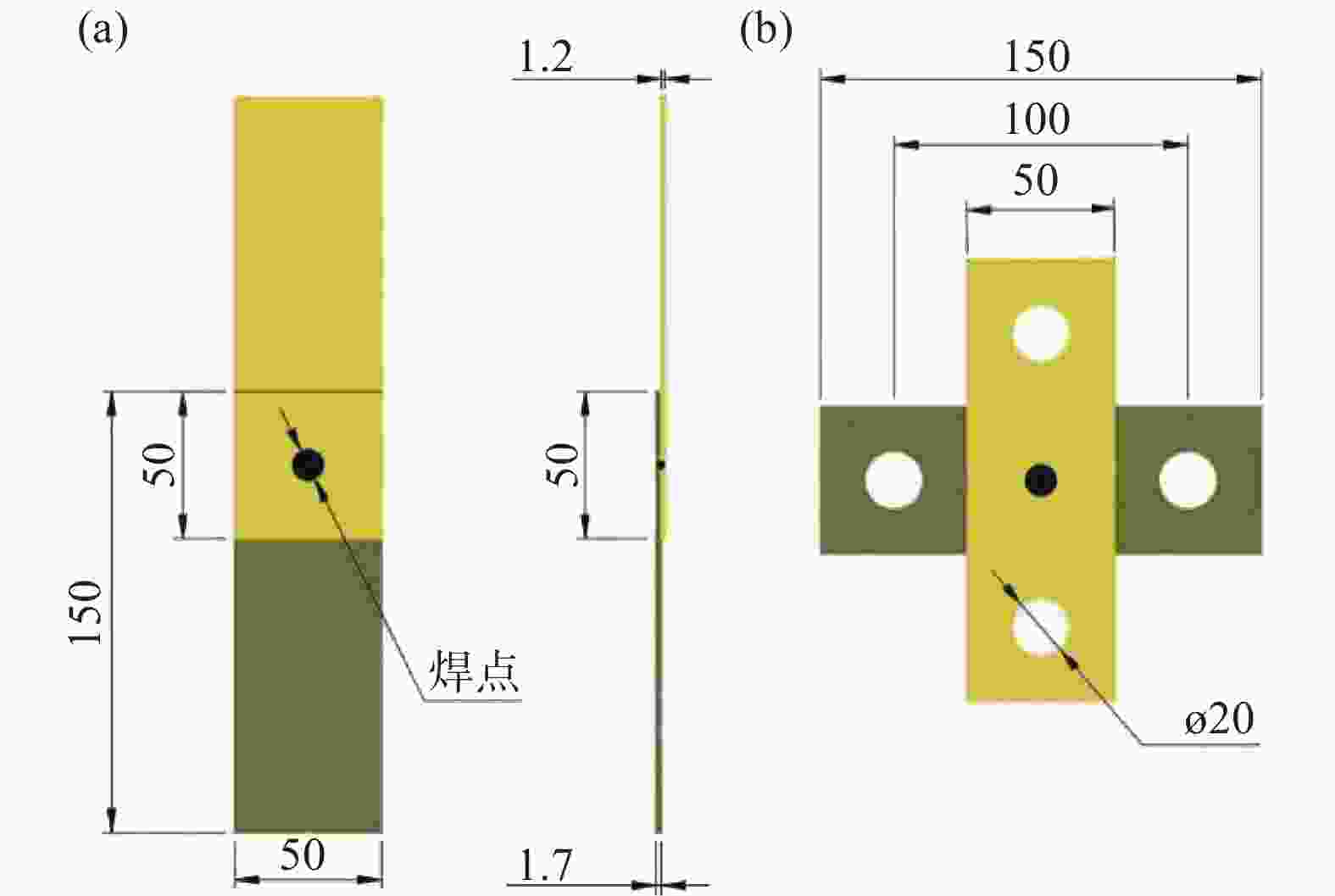
编号 焊接时间/ms 焊接电流/kA 电极压力/kN 保持时间/ms 1 160 7 3.8 400 2 160 7.5 3.8 400 3 160 8 3.8 400 4 160 8.5 3.8 400 5 320 7.5 3.8 400 6 500 7.5 3.8 400 7 1000 7.5 3.8 400 -
[1] Senuma T. Physical metallurgy of modern high strength steel sheets[J]. ISIJ International, 2001,41(6):520-532. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.41.520 [2] Dean T A.一种新工艺: 热冲压和冷模淬火[C]//第十届全国塑性工程学术年会、第三届国际塑性加工先进技术研讨会.南昌: 中国机械工程学会塑性工程分会, 2007:719-727.Dean T A. A novel process: hot stamping and cold die quenching[C]//The 10th National Plastic Engineering Academic Annual Conference and 3rd International Symposium on Advanced Technology for Plasticity. Nanchang: China Society for Technology of Plasticity, 2007: 719-727. [3] Çavuşoğlu O, Çavuşoğlu O, Yılmazoğlu A G, et al. Microstructural features and mechanical properties of 22MnB5 hot stamping steel in different heat treatment conditions[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020,9(5):10901-10908. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.07.043 [4] 梁雪波. 热成形硼钢22MnB5与镀锌钢HSLA350焊点宏/微观结构、力学性能及相关机理研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2016.Liang Xuebo. Study on macro/microstructure, mechanical properties and related mechanism of hot stamping boron steel 22MnB5 and galvanized steel HSLA350 RSW joint[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2016. [5] Sun Haoran, Miao Tieling. Traditional high strength steel and advanced high strength steel for automobile[J]. Metal World, 2010,(6):24-27. (孙浩然, 苗铁岭. 汽车用传统高强钢和先进高强钢[J]. 金属世界, 2010,(6):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6826.2010.06.010Sun Haoran, Miao Tieling. Traditional High Strength Steel and Advanced High Strength Steel for Automobile [J]. Metal World, 2010(06): 24-27+5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6826.2010.06.010 [6] Yuan Xinjian, Li Ci, Chen Jianbin, et al. Resistance spot welding of dissimilar DP600 and DC54D steels[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017,239:31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.08.012 [7] Wang Bin, Hua Lin, Wang Xiaokai, et al. Effects of electrode tip morphology on resistance spot welding quality of DP590 dual-phase steel[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 83(12):1-10. [8] Gao Xu, Wang Gengzhu. Study on fusion process of heterogeneous materials Fe-Ni spot welding[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2004,(8):42-44. (高旭, 王更柱. 异质材料铁-镍点焊熔合过程的研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2004,(8):42-44. doi: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.2004.08.019Gao Xu, Wang Gengzhu. Study on Fusion Process of Heterogeneous Materials Fe-Ni Spot Welding [J]. Hot Working Technology, 2004(8): 42-44. (in Chinese) doi: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.2004.08.019 [9] 顾萌. DP780/HC660不等厚异质高强钢电阻点焊接头组织与性能的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015.Gu Meng. Study on microstructure and properties of resistance spot welded joint of DP780/HC660 heterogeneous high strength steel with unequal thickness[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015. [10] Wang Xiaole, Zhu Zhengqiang, Zhao Xiang. Microstructure and properties of resistance spot welded joints of unequal thickness high strength steel H220YD/DP590GA[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2016,50(12):1889-1892. (王小乐, 朱政强, 赵翔. 不等厚高强度钢H220YD/DP590GA电阻点焊接头的组织和性能[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2016,50(12):1889-1892.Wang Xiaole, Zhu Zhengqiang, Zhao Xiang. Microstructure and Properties of Resistance Spot Welded Joints of Unequal Thickness High Strength Steel H220 YD/DP590 GA [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2016, 50(12): 1889-1892. [11] Thibaut Huin, Sylvain Dancette, Damien Fabrègue, et al. Investigation of the failure of advanced high strength steels heterogeneous spot welds[J]. Metals, 2016, 6(5):111. [12] Jung G S, Lee K Y, Lee J B, et al. Spot weldability of TRIP assisted steels with high carbon and aluminium contents[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2012,17(2):92-98. doi: 10.1179/1362171811Y.0000000081 [13] Vignesh Krishnan, Elayaperumal Ayyasamy, Velmurugan Paramasivam. Influence of resistance spot welding process parameters on dissimilar austenitic and duplex stainless steel welded joints[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part E Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering, 2021,235(1):12-23. [14] Zhao Dawei, Wang Yuanxun, Sheng Suning, et al. Multi-objective optimal design of small scale resistance spotwelding process with principal component analysis and response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2013,26(1):1-14. [15] Qiu Ranfeng, Li Jiuyong, Zhang Zhenwei, et al. Core migration in resistance spot welding of non-equal thickness stainless steel plate[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017,38(6):7-10. (邱然锋, 李久勇, 张振伟, 等. 非等厚不锈钢板电阻点焊的熔核偏移[J]. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,38(6):7-10. doi: 10.15926/j.cnki.issn1672-6871.2017.06.002Qiu Ranfeng, Li Jiuyong, Zhang Zhenwei, et al. Core Migration in Resistance Spot Welding of Non-equal Thickness Stainless Steel Plate [J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 38(06): 7-10+3. doi: 10.15926/j.cnki.issn1672-6871.2017.06.002 [16] 王蕾. 铝/钢异种金属电阻点焊焊接性及接头疲劳行为的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022.Wang Lei. Research on weldability and joint fatigue behavior of aluminum/steel dissimilar metal resistance spot welding[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022. -




 下载:
下载: