Numerical simulation of fluidized chlorination velocity of high titanium slag
-
摘要: 基于高钛渣和氯气物性参数,采用经典初始流化速度公式计算了高钛渣沸腾氯化的初始流化速度,并结合欧拉双流体模型建立了高钛渣沸腾氯化气固两相流的数学模型并开展数值计算,最后以数值模拟结果为依据对高钛渣沸腾氯化表观操作气速进行了预测。研究结果表明:以欧拉双流体模型结合Grace公式得到初始流化速度能够准确模拟出高钛渣氯化过程的气固两相流特征;依据沸腾氯化床层中高钛渣颗粒体积分数、床层截面速度和压力分布规律,确定高钛渣沸腾氯化的最佳表观操作气速为Grace计算公式得到的初始流化速度值的1.5倍。Abstract: Based on the physical parameters of high titanium slag and chlorine gas, the initial fluidization velocity of fluidized chlorination of high titanium slag was calculated by using the classical initial fluidization velocity formula. And the mathematical model of gas-solid two-phase flow of fluidized chlorination of high titanium slag was established by combining Euler two-fluid model. Finally, based on the numerical simulation results, the superficial gas velocity of fluidized chlorination of high titanium slag was predicted. The results show that the initial fluidization velocity obtained by Euler two-fluid model combined with Grace formula can accurately simulate the gas-solid two-phase flow characteristics of high titanium slag chlorination process. According to the volume fraction of high titanium slag particles in the fluidized chlorination bed, the velocity and pressure distribution of the cross section of the bed, the optimal superficial gas velocity for the fluidized chlorination of high titanium slag was determined to be 1.5 times the initial fluidization velocity obtained by Grace’s calculation formula.
-
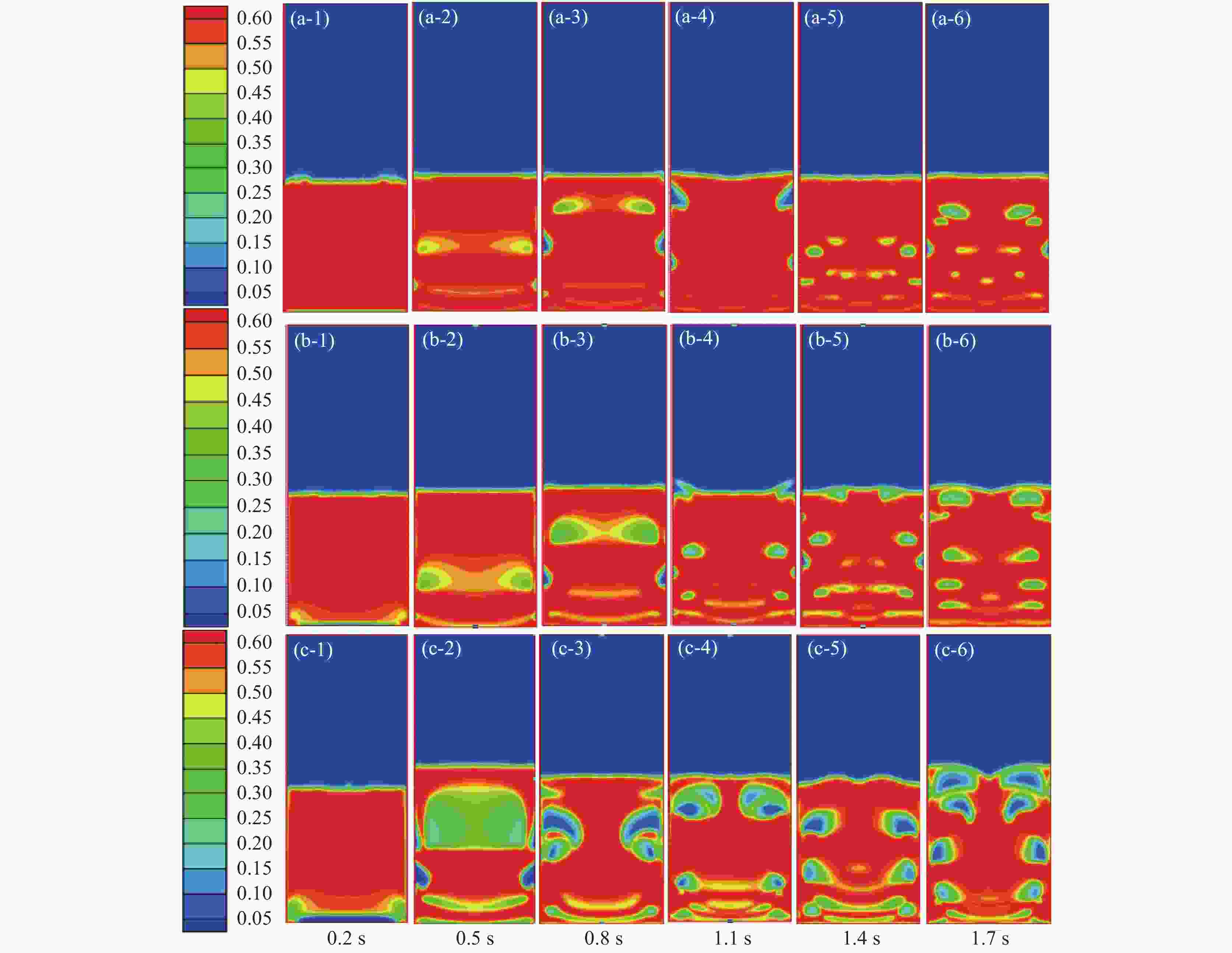
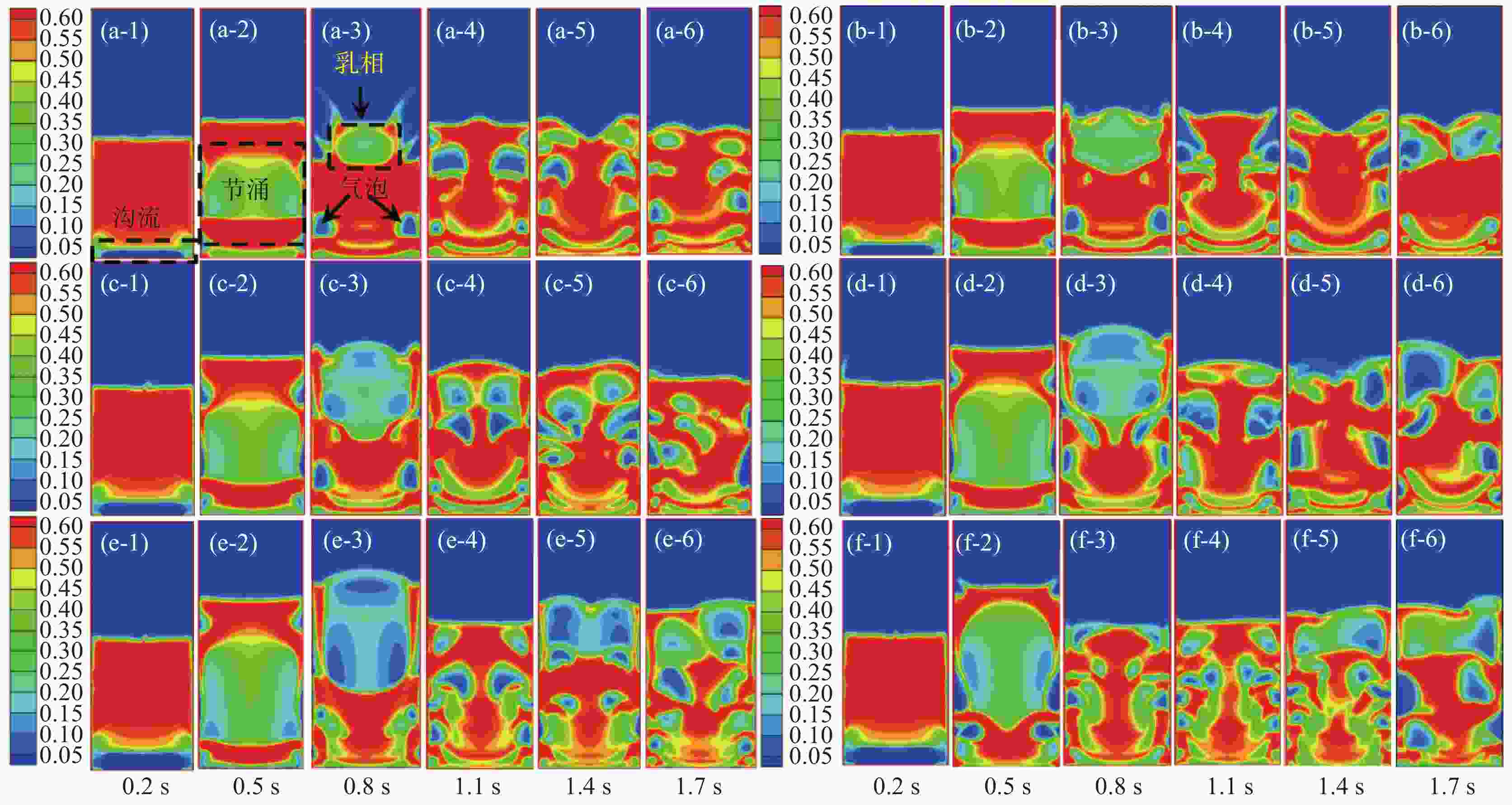
图 3 不同修正系数下固体颗粒体积分数云图
(a-1)~(a-6): 1.1倍初始流化速度(0.4675 m/s);(b-1)~(b-6): 1.2倍初始流化速度(0.51 m/s);(c-1)~(c-6): 1.3倍初始流化速度(0.5525 m/s);(d-1)~(d-6): 1.4倍初始流化速度(0.595 m/s);(e-1)~(e-6): 1.5倍初始流化速度(0.6375 m/s);(f-1)~(f-6): 1.1倍初始流化速度(0.68 m/s)
Figure 3. Volume fraction of solid particles under different correction coefficients
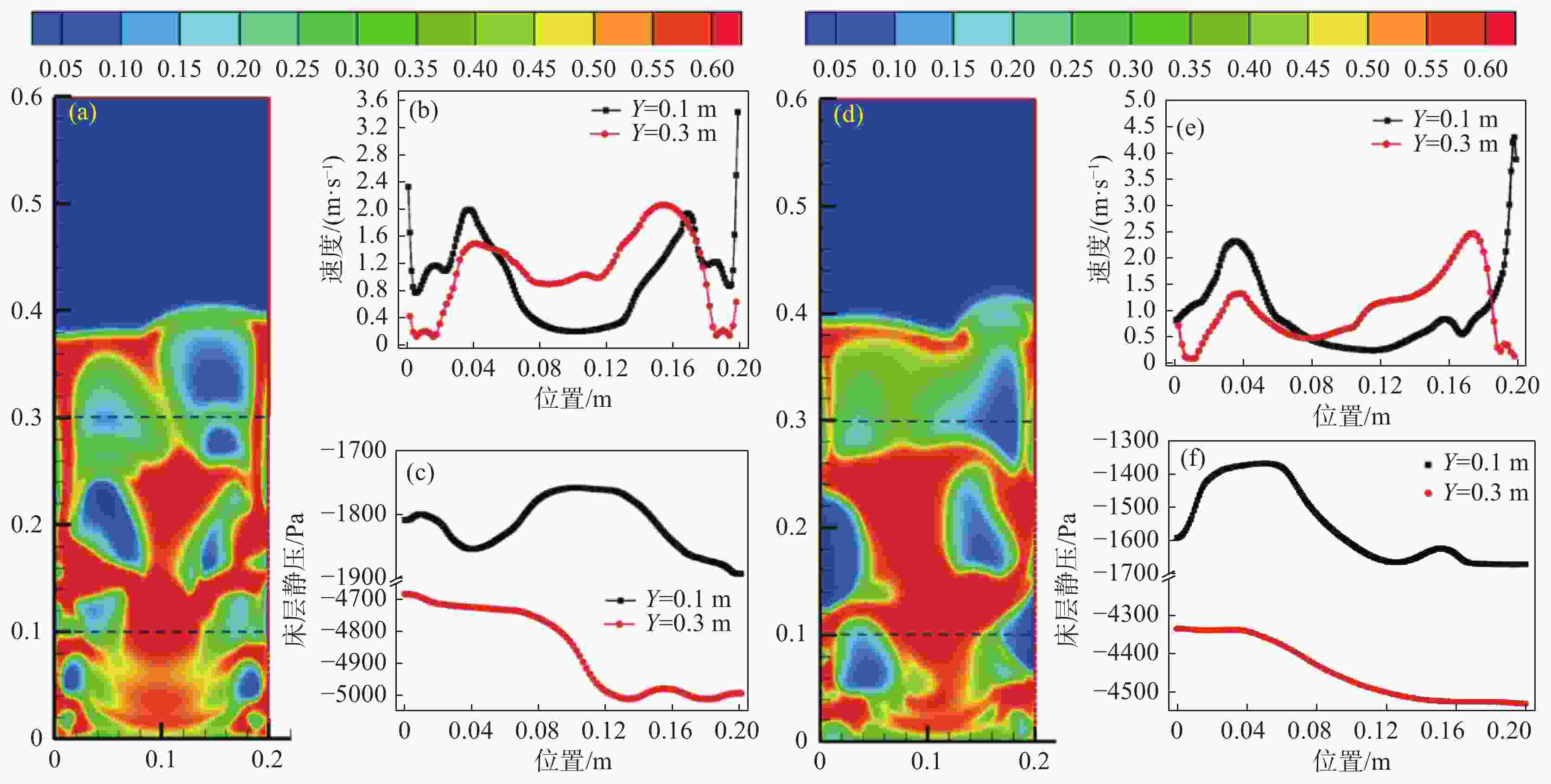
图 4 不同表观操作气速下,高钛渣体积分数和不同截面处速度和压力的关系
(a)表观操作气速为0.6375 m/s,沸腾氯化时间为1.7 s时的高钛渣体积分数云图;(b)图(a)中Y=0.1 m 和Y=0.3 m处高钛渣颗粒速度;(c)图(a)中Y=0.1 m 和Y=0.3 m处床层截面静压;(d) 表观操作气速为0.68 m/s,沸腾氯化时间为1.7 s时的高钛渣体积分数云图;(e)图(d)中Y=0.1 m 和Y=0.3 m处高钛渣颗粒速度;(f) 图(d)中Y=0.1 m 和Y=0.3 m处床层截面静压
Figure 4. Relationship between the volume fraction of high titanium slag and the velocity and pressure at different sections under different apparent operating gas velocities
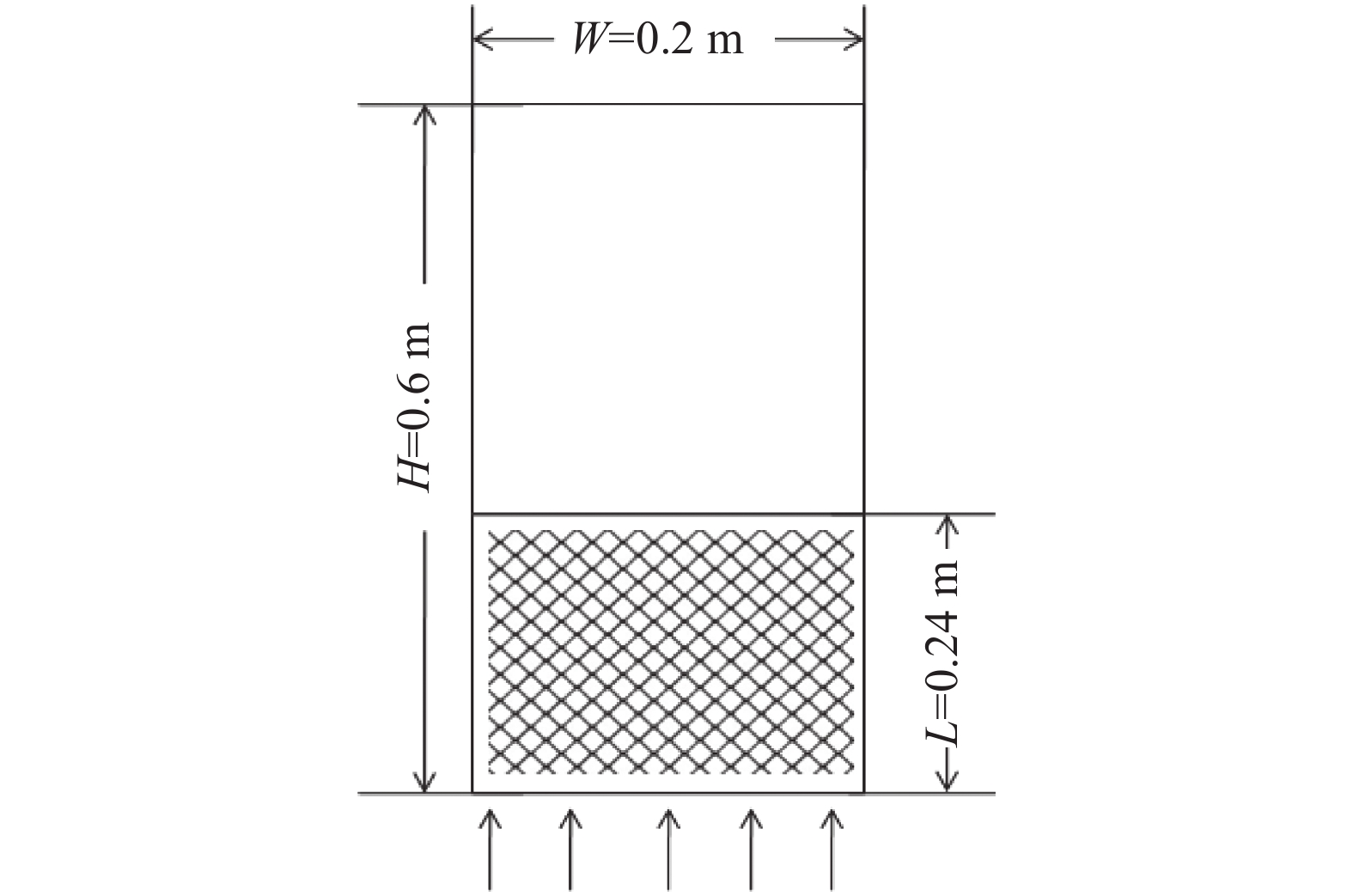
表 1 边界条件和模拟参数
Table 1. Boundary conditions and simulation model parameters
钛渣密度/(kg·m−3) 钛渣直径/m 初始体积分数 氯气密度/(kg·m−3) 初始静床高/m 床层空隙率 曳力模型 3810 5×10−4 0.7 2.95 0.24 0.61 Gidaspow 湍流模型 求解算法 内摩擦角/(°) 时间步长 时间步数 收敛标准 网格数目 RNG-k-ε Simple 30 10−4 30 000 0.0001 10 000 表 2 不同经验公式计算的高钛渣初始流化速度
Table 2. Initial fluidization velocity of high titanium slag calculated by different empirical formulas
m/s 经验计算公式 Grace公式 Wen-Yu 公式 Ergun公式 计算值 0.425 0.319 0.288 表 3 不同表观操作气速床层不同截面静压力分布和速度分布的期望与方差
Table 3. The expectation and variance of static pressure distribution and velocity distribution in different sections of different superficial gas velocity
表观操作气速/(m∙s-1) 床层位置/m 静压力分布 速度分布 期望(E) 方差(D) 期望(E) 方差(D) 0.6375 Y=0.1 − 1812.65 41.52 0.97 0.60 Y=0.3 − 4858.61 130.31 1.11 0.56 0.68 Y=0.1 − 1555.53 115.92 0.96 0.76 Y=0.3 − 4445.26 78.13 1.01 0.60 -
[1] Bordbar Hossein, Ali Akbar Yousefi, Hossein Abedini. Production of titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) from titanium ores: A review[J]. Polyolefins Journal, 2017,4(2):149-173. [2] Dai Yingjie, Wei Zhizhong, Wang Lijuan, et al. Study on impurity removal process of titanium tetrachloride produced by boiling chlorination[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(5): 40-44. (代应杰, 魏治中, 王丽娟, 等. 沸腾氯化生产四氯化钛除杂工艺探讨[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022, 43(05): 40-44.Dai Yingjie, Wei Zhizhong, Wang Lijuan, et al. Study on impurity removal process of titanium tetrachloride produced by boiling chlorination[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(5): 40-44. [3] Sun Kang. Titanium extraction metallurgy physical chemistry[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2001: 38-42. (孙康. 钛提取冶金物理化学 [M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2001: 38-42.Sun Kang. Titanium extraction metallurgy physical chemistry[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2001: 38-42. [4] Xiong Kun, Wen Shuming, Xie Meifang. Process mineralogy on titanium-rich slag in panzhihua[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2011(6):14-17. (熊堃, 文书明, 谢美芳. 攀枝花高钛渣的工艺矿物学[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2011(6):14-17.Xiong Kun, Wen Shuming, Xie Meifang. Process mineralogy on titanium-rich slag in panzhihua[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2011(6): 14-17. [5] Guo Musun, Li Hongzhong. Review and prospect of fluidization science and technology[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2012,64(1):52-62. [6] Linghu Changhong. Application and discussion of high titanium sludge from Yunnan in fluidizing chlorination[J]. Light Metals, 2002(6):48-50. (令狐昌鸿. 云南高钛渣在沸腾氯化中的应用与探讨[J]. 轻金属, 2002(6):48-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2002.06.014Linghu Changhong. Application and discussion of high titanium sludge from Yunnan in fluidizing chlorination[J]. Light Metals, 2002(6): 48-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1752.2002.06.014 [7] Wang Jialin, Yang Yibang, Lu Yingwen, et al. The process control study on large scale boiling chlorinating furnace without screen plate[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2017,46(4):77-80. (王佳林, 杨易邦, 陆应文, 等. 大型无筛板沸腾氯化炉工艺控制研究[J]. 云南冶金, 2017,46(4):77-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2017.04.017Wang Jialin, Yang Yibang, Lu Yingwen, et al. The process control study on large scale boiling chlorinating furnace without screen plate[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2017, 46(4): 77-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2017.04.017 [8] Kang Jungshin, Toru H Okabe. Thermodynamic consideration of the removal of iron from titanium ore by selective chlorination[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2014,45:1260-1271. doi: 10.1007/s11663-014-0061-8 [9] Chen Yifan, Tang Xiaoning, Liu Shaopu, et al.Thermodynamic analysis of preparation of titanium tetrachloride by boiling chlorination process[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2019, 9(5): 6-17. (陈一凡, 唐晓宁, 刘韶浦, 等. 沸腾氯化法制备四氯化钛过程热力学分析[J]. 有色金属工程, 2019, 9(5): 6-17.Chen Yifan, Tang Xiaoning, Liu Shaopu, et al.Thermodynamic analysis of preparation of titanium tetrachloride by boiling chlorination process[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2019, 9(5): 6-17. [10] Tian Jian, Zhang Xiang, Huang Jiyu, et al. Technical analysis and comprehensive utilization of chlorinated waste during the production of TiCl4 by fluidized bed chlorination[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2018,35(3):6-11. (田键, 张祥, 黄季宇, 等. 沸腾氯化生产TiCl4工艺分析及氯化废料的综合利用[J]. 钛工业进展, 2018,35(3):6-11.Tian Jian, Zhang Xiang, Huang Jiyu, et al. Technical analysis and comprehensive utilization of chlorinated waste during the production of TiCl4 by fluidized bed chlorination[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2018, 35(3): 6-11. [11] Ergun Sabri, Orning Ao Ao. Fluid flow through randomly packed columns and fluidized beds[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1949,41(6):1179-1184. [12] Wen C, Yu Y H. A generalized method for predicting the minimum fluidization velocity[J]. Aichc Journal, 1966,12(3):610-612. doi: 10.1002/aic.690120343 [13] Grace John R, Fariborz Taghipour. Verification and validation of CFD models and dynamic similarity for fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2004,139(2):99-110. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2003.10.006 [14] Mukesh Upadhyay, Ayeon Kim, Heehyang Kim, et al. An assessment of drag models in Eulerian–Eulerian CFD simulation of gas-solid flow hydrodynamics in circulating fluidized bed riser[J]. Chem Engineering, 2020,37(4):402-439. [15] Gidaspow Dimitri. Multiphase flow and fluidization: continuum and kinetic theory description[J]. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 1994,55(2):207-208. doi: 10.1016/0377-0257(94)80007-3 [16] Jin Yong. Fluidization engineering principles[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2001. (金涌. 流态化工程原理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2001.Jin Yong. Fluidization engineering principles[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2001. [17] Patil D J, Van S, Kuipers J. Critical comparison of hydrodynamic models for gas-solid fluidized beds-Part I: bubbling gas-solid fluidized beds operated with a jet[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005,60(25):57-72. [18] Zhu Kuisong. Liu Songli, Gou Shuyun, et al. Numerical simulation for fluidized chlorination cold model of high-titanium slag in Yunnan[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(2):30-36. (朱奎松, 刘松利, 芶淑云, 等. 云南高钛渣流态化氯化冷态模型数值模拟[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(2):30-36. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.02.005Zhu Kuisong. Liu Songli, Gou Shuyun, et al. Numerical simulation for fluidized chlorination cold model of high-titanium slag in Yunnan[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017, 38(2): 30-36. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.02.005 [19] El-Sadek M H, Fouad O A, Morsi M B, et al. Controlling conditions of fluidized bed chlorination of upgraded titania slag[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2019,72(2):423-427. doi: 10.1007/s12666-018-1493-7 -




 下载:
下载: