Study on powder metallurgical properties of molten salt electrolytic titanium powder
-
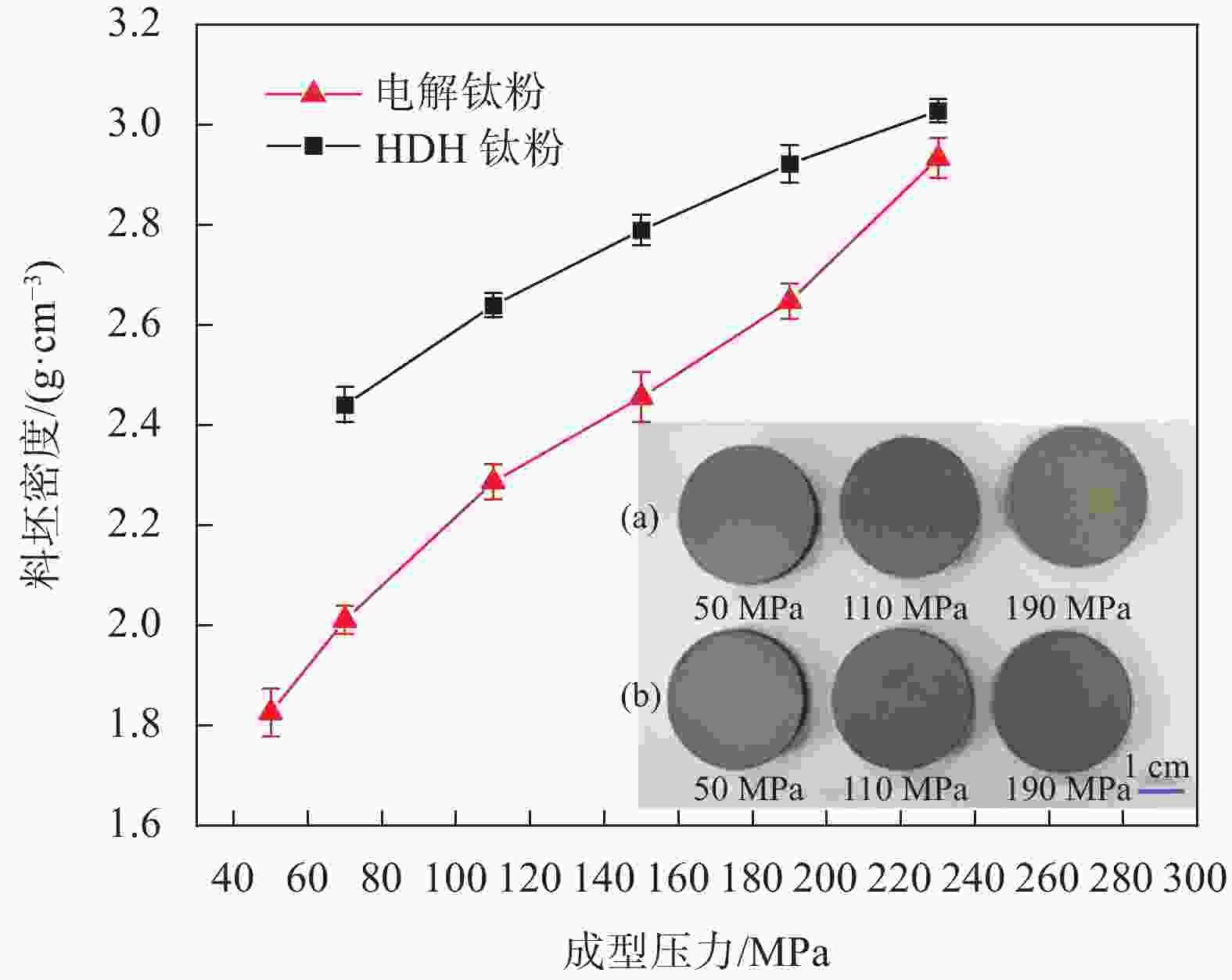
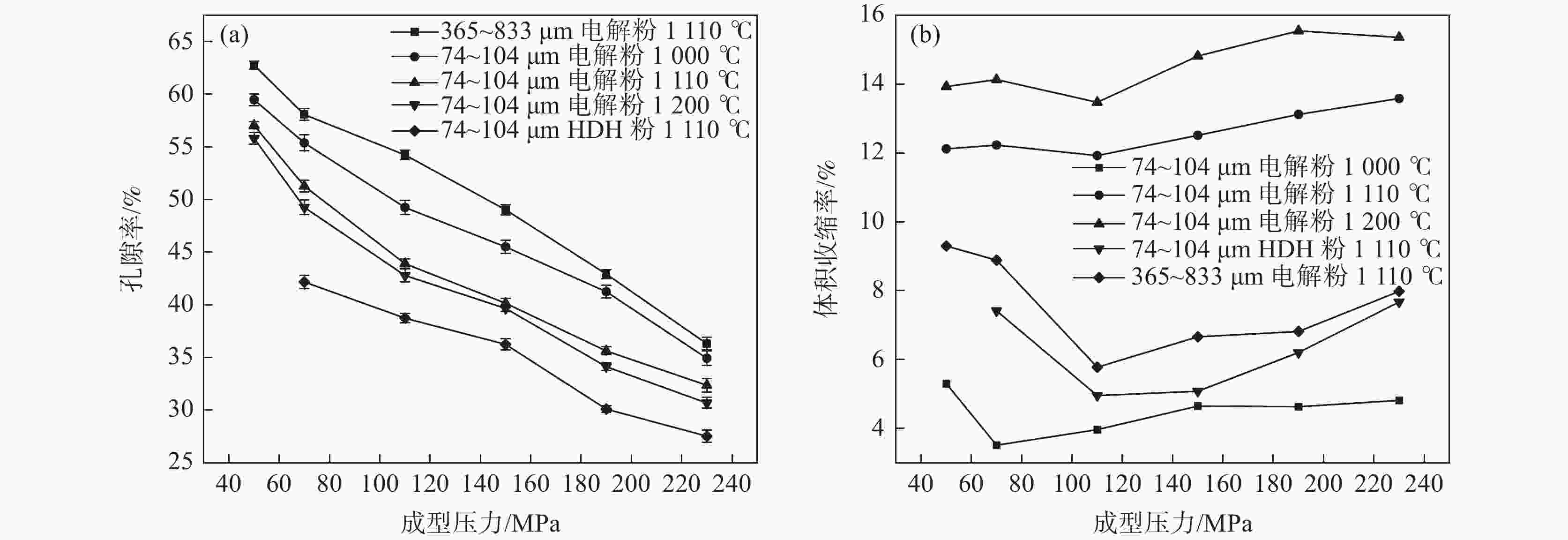
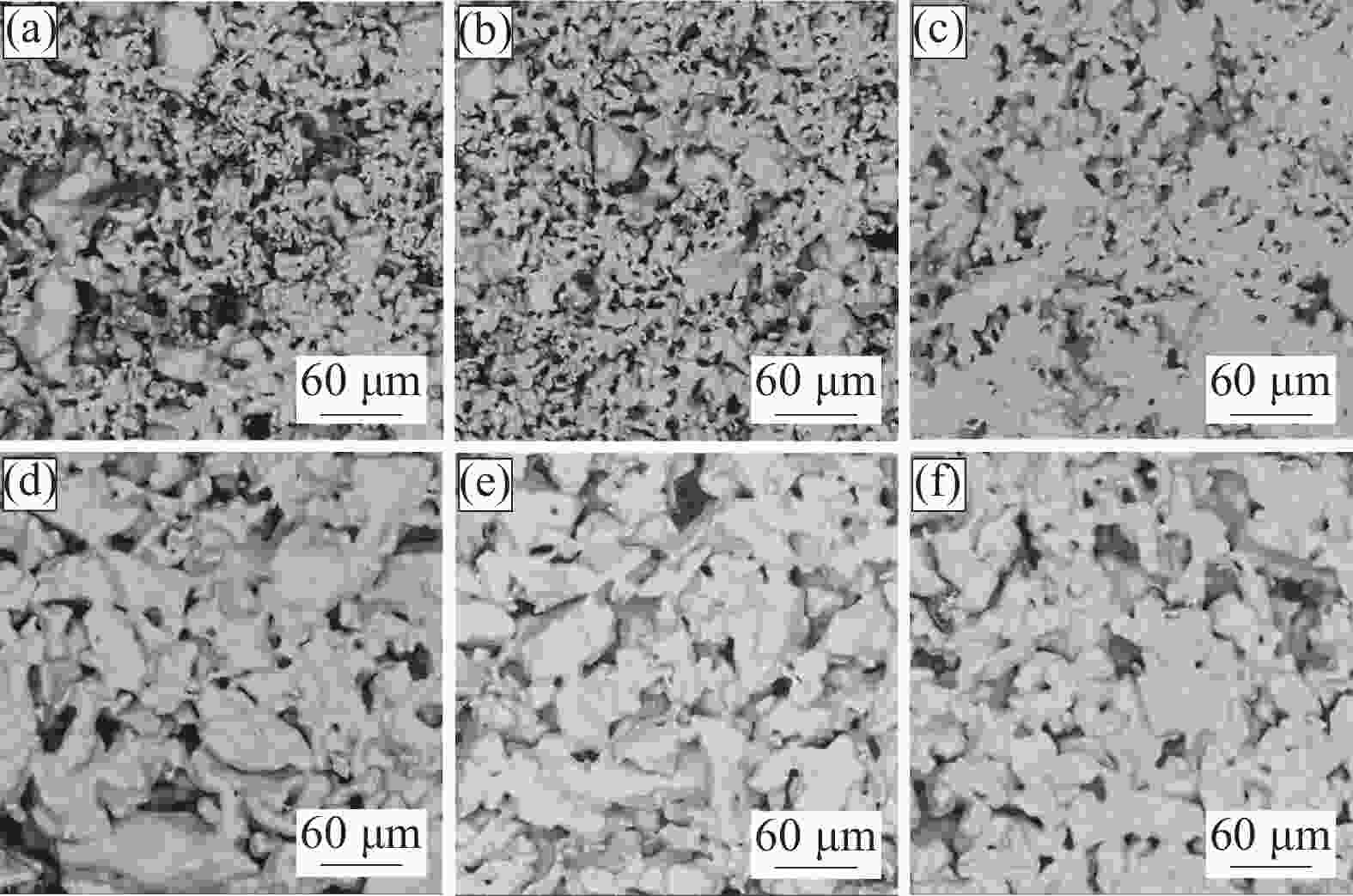
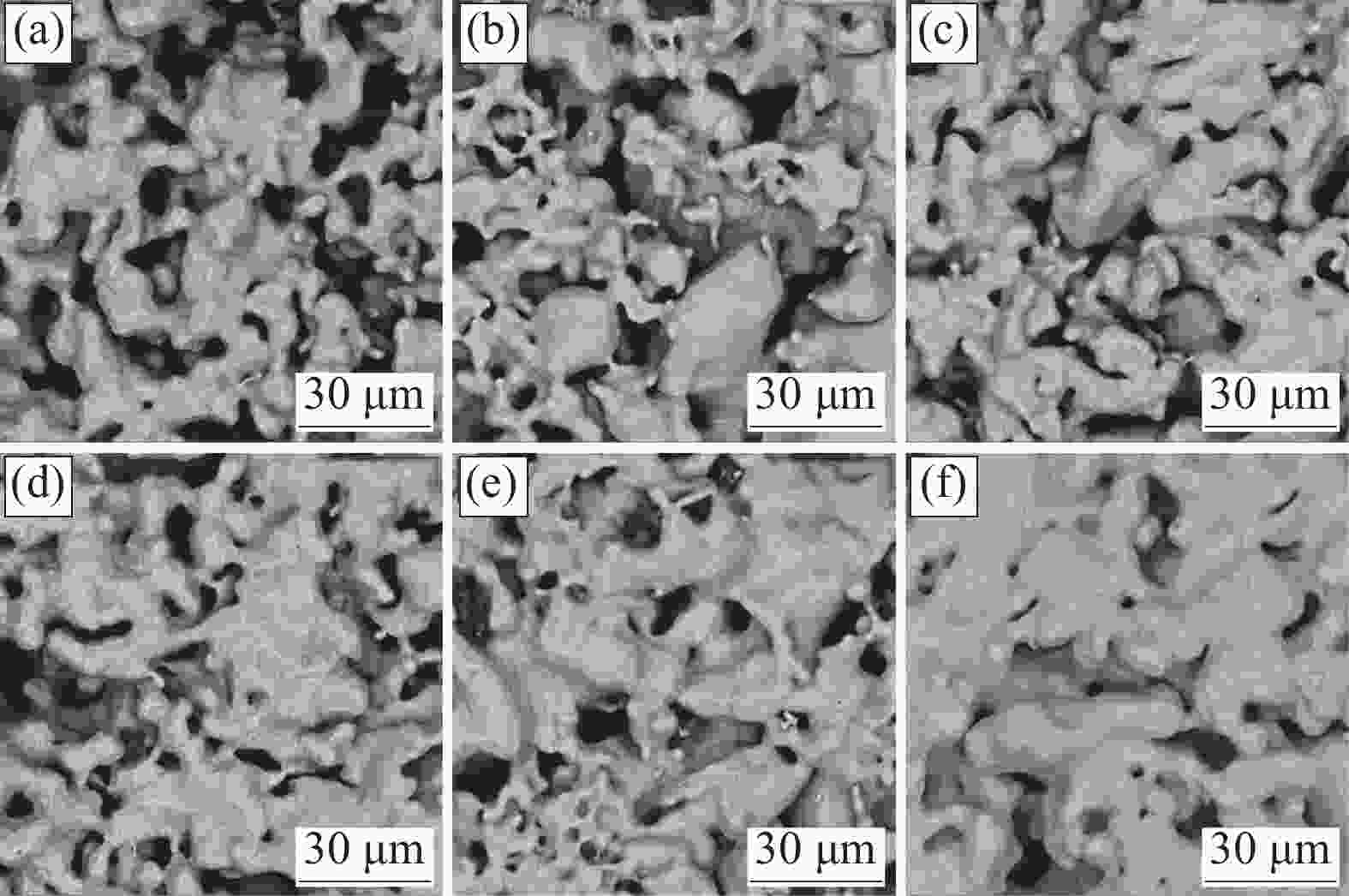
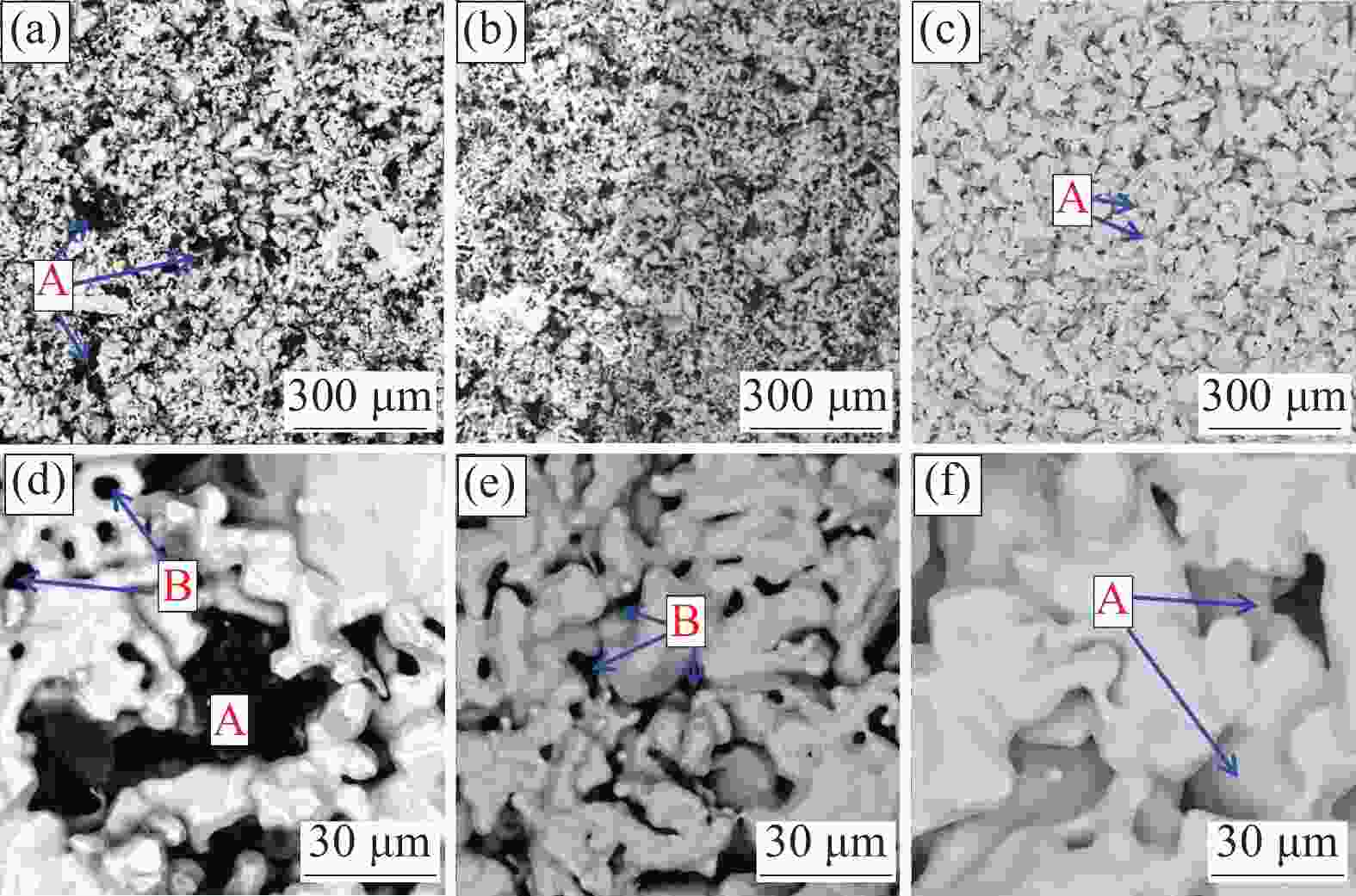
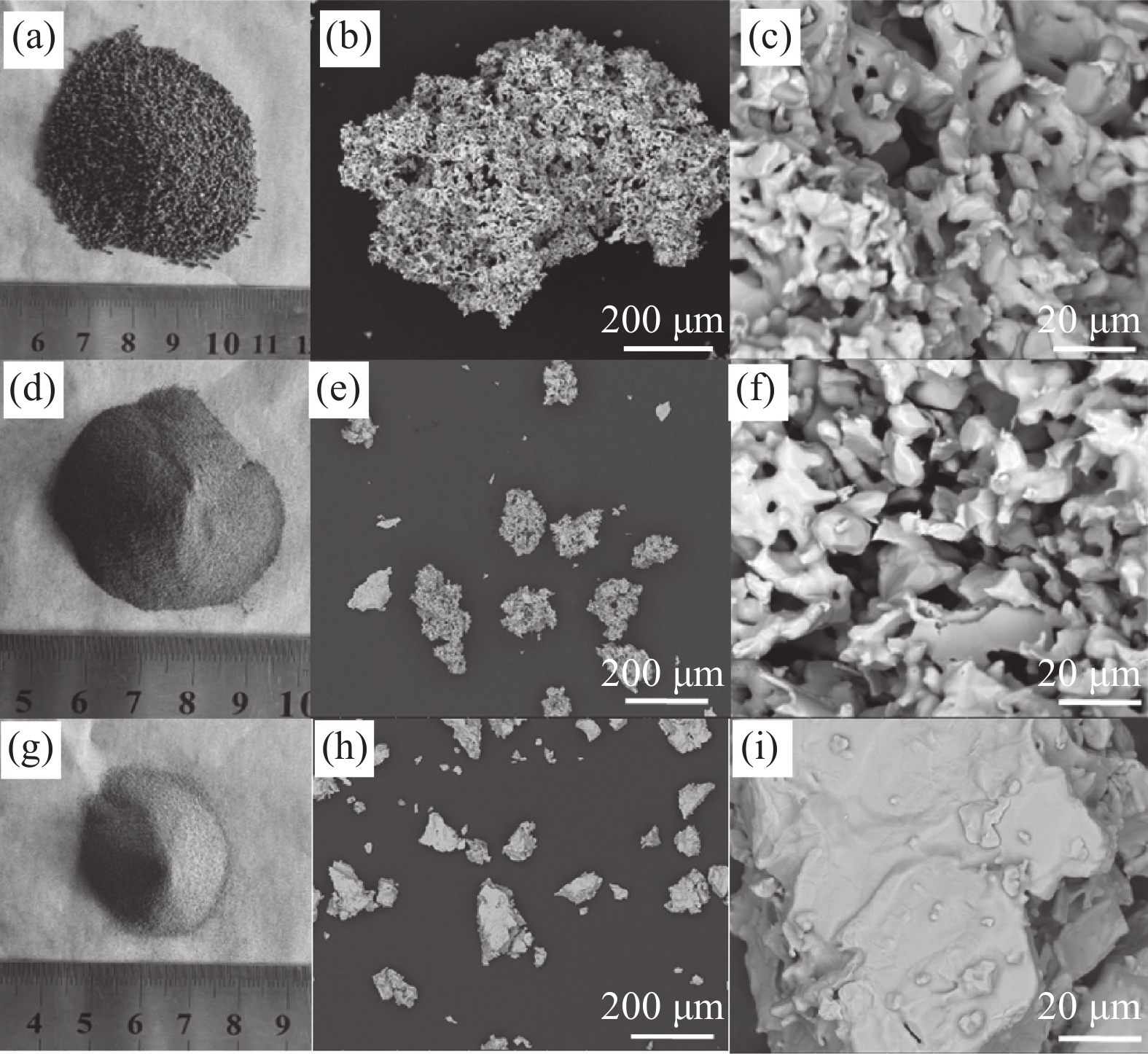
摘要: 以电解钛粉为原料,采用模压-烧结的方法制备多孔钛,对电解钛粉的成型和烧结特性进行了研究,最后针对制备的多孔钛的力学性能、孔结构、孔径分布及透气率等性能进行了表征。结果表明:随压制压力的增加,具有二次颗粒特征的电解钛粉颗粒间搭桥空间逐渐消失,可通过成型压力和烧结温度的调节获得不同孔隙率和力学强度的多孔钛。电解钛粉与氢化脱氢钛粉相比具有成型性能良好、更易发生烧结致密化、制件孔隙率高、透气率高、杨氏模量高等特点。使用粒径74~104 μm的电解钛粉在70~110 MPa成型、
1110 ℃烧结后的多孔钛,杨氏模量与人体松质骨接近,透气率和最大孔径满足烧结金属过滤元件(GBT6887-2019)TG035、TG020要求,在人体松质骨植入件以及过滤材料领域有应用前景。Abstract: Electrolytic titanium powder was utilized as the raw material for fabricating porous titanium through press-sintering technique. The forming and sintering characteristics were investigated. Then the mechanical properties, pore structure, pore size distribution and permeability of the prepared porous titanium were characterized. The results show that with the increase of pressing pressure, the bridging space between the particles of electrolytic titanium powder with secondary particle characteristics gradually disappears. Porous titanium powder with different porosity and mechanical strength can be obtained by adjusting the molding pressure and sintering temperature. Compared to HDH titanium powder, electrolytic titanium powder exhibits better molding performance, easier sintering densification, higher porosity, greater permeability, and a higher Young’s modulus. A porous titanium was obtained by using electrolytic titanium powder with a particle size of 74~104 μm at 70~110 MPa and then sintering it at1110 ℃, whose Young’s modulus is similar to that of human cancellous bone. The permeability and maximum pore diameter meet the requirements of TG035 and TG020 in the standard for sintered metal filtration elements (GBT6887-2019), indicating promising applications in the fields of human cancellous bone implants and filtration materials.-
Key words:
- porous titanium /
- electrolytic titanium powder /
- molding /
- sinter /
- mechanical property
-
表 1 钛粉化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of titanium powder
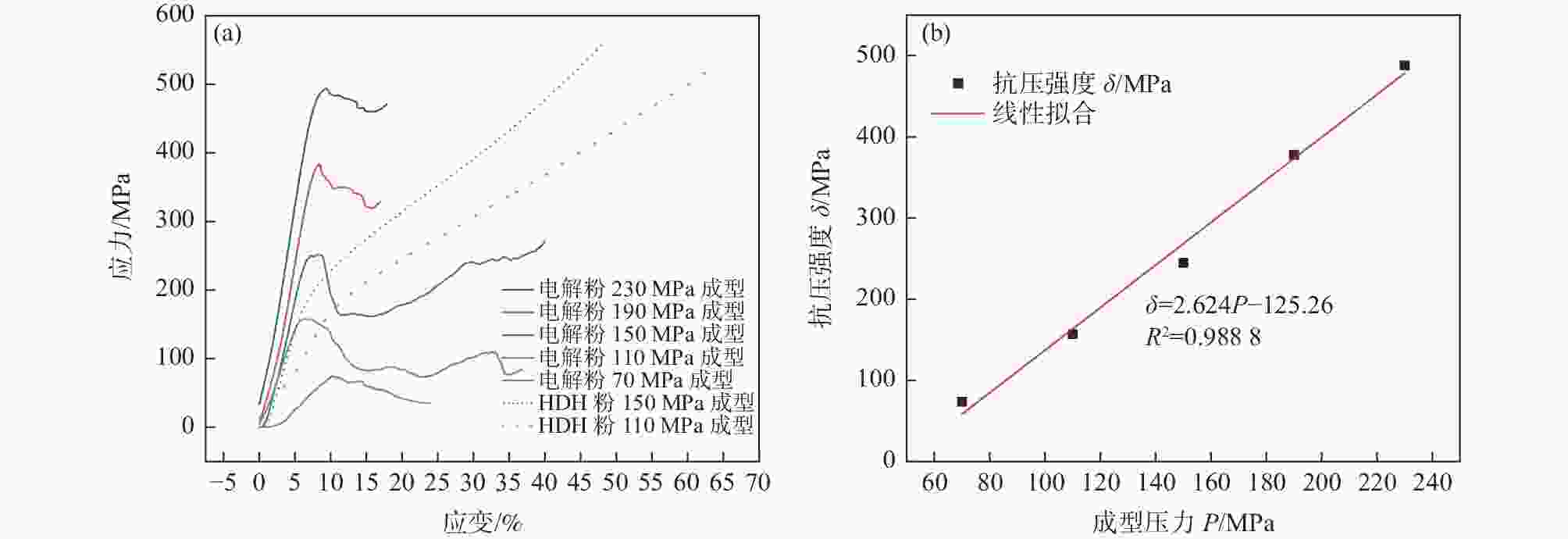
钛粉种类 粒径/μm 杂质含量/% Ni Cr Mn Na Ca Fe C N H O 电解粉 74~104 0.04 0.02 <0.01 0.02 0.02 0.04 <0.01 0.010 0.032 0.89 电解粉 365~833 <0.01 0.01 <0.01 0.02 0.01 <0.01 <0.01 0.007 0.005 0.78 HDH粉 74~104 0.02 0.01 <0.01 0.01 0.01 0.05 <0.01 0.010 0.022 0.12 表 2 不同成型压力的料坯
1100 ℃烧结后力学强度Table 2. Mechanical strength of billets sintered at
1100 ℃ under different forming pressures原料类型 成型压力/MPa 最大压缩力/kN 抗压强度/MPa 杨氏模量/GPa 电解
钛粉70 5.264 73.7 0.84 110 11.043 157 2.79 150 17.507 245 4.07 190 27.103 378 5.17 230 34.459 488 6.11 HDH
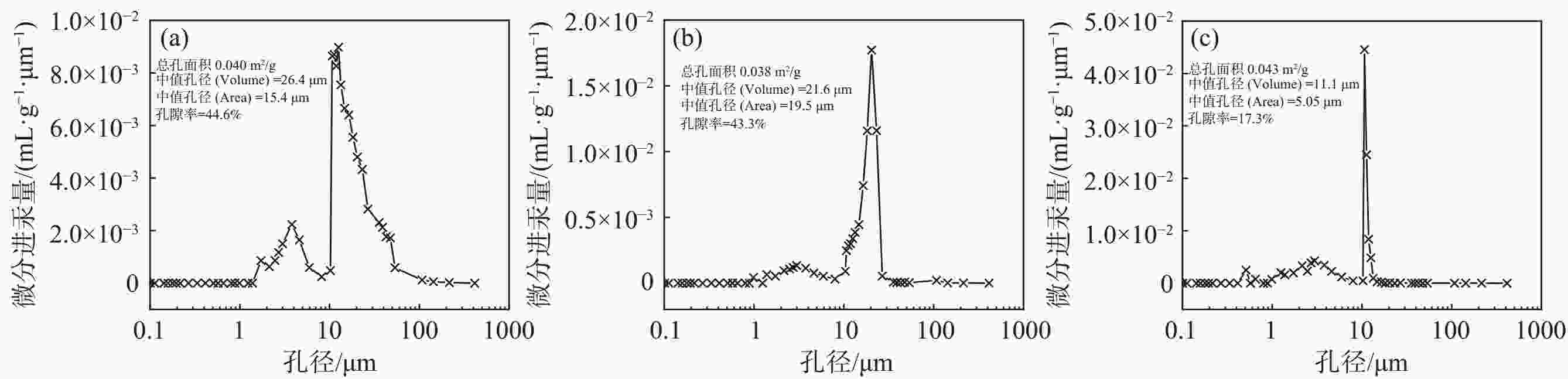
钛粉110 174.2 1.51 150 216.4 3.51 表 3 不同制备条件的钛粉孔隙率及孔径
Table 3. Porosity and pore size of titanium powder under different preparation conditions
原料
类型钛粉粒径/μm 制备条件 孔隙率
(质量-
体积)/%孔隙率
(压汞法)/%体积中值孔径
(压汞法)/μm成型压力/MPa 烧结温度/℃ 烧结时间/h 电解
钛粉365~833 110 1110 2 54.2 44.60 26.4 74~104 150 1110 2 40.1 25.91 11.2 74~104 110 1110 2 43.9 43.30 21.6 74~104 110 1200 2 42.1 9.75 10.7 74~104 190 1200 2 36.6 6.66 5.06 74~104 50 1200 2 55.8 68.82 172.5 HDH
钛粉74~104 110 1110 2 39.5 17.31 11.1 表 4 多孔钛的透气率及最大孔径
Table 4. Permeability and maximum pore size of porous titanium
样品
编号原料
类型粒径/μm 制备条件 透气率/
(m3·h−1·m−2·kPa−1)气泡最大孔径/μm 成型
压力/
MPa烧结
温度/
℃烧结
时间/
h1 电解粉 365~833 110 1110 2 292 68 2 电解粉 365~833 70 1110 2 472 92 3 电解粉 74~104 110 1110 2 207 44 4 HDH粉 74~104 110 1110 2 100 32 -
[1] Barbis D P, Gasior R M, Walker G P, et al. Titanium powders from the hydride-dehydride process[M]//Titanium Powder Metallurgy. Elsevier, 2015: 101-116. [2] Allaire, Entezarian, Tsantrizos. Method of production of metal and ceramic powders by plasma atomization: US,US5707419[P]. 1998-01-13. [3] Zou Yu, Liao Xianjie, Lai Qi, et al. Research status of preparation technology of spherical titanium powder for 3D printing[J]. Materials China, 2019,38(11):1093-1101. (邹宇, 廖先杰, 赖奇, 等. 3D打印用球形钛粉制备技术研究现状[J]. 中国材料进展, 2019,38(11):1093-1101. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.201808033Zou Yu, Liao Xianjie, Lai Qi, et al. Research status of preparation technology of spherical titanium powder for 3D printing[J]. Materials China, 2019, 38(11): 1093-1101. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.201808033 [4] Withers J C, Loutfy R O. Thermal and electrochemical process for metal production: US,US20050294872[P]. 2005-12-06. [5] Jiao Shuqiang, Zhu Hongmin. Novel metallurgical process for titanium production[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2011,21(9):2172-2175. [6] Jiao Shuqiang, Zhu Hongmin. Electrolysis of Ti2CO solid solution prepared by TiC and TiO2[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007,438:243-246. [7] Chen G Z, Fray D J, Farthing T W. Direct electrochemical reduction of titanium dioxide to titanium in molten calcium chloride[J]. Nature, 2000, 407:361-364. [8] Zhang Chao, Liu Na, Zhu Guofeng. Innovative clean titanium reduction process-USTB process[J]. Metal World, 2015(1):70-73. (张超, 刘娜, 朱国峰. 新型 USTB 法清洁钛提取技术[J]. 世界金属, 2015(1):70-73.Zhang Chao, Liu Na, Zhu Guofeng. Innovative clean titanium reduction process-USTB process[J]. Metal World, 2015(1): 70-73. [9] Wu Yinjiang, Liang Yongren. Progress in titanium powder and titanium powder metallurgy products[J]. Materials China, 2011(6):44-50. (吴引江, 梁永仁. 钛粉末及其粉末冶金制品的发展现状[J]. 中国材料进展, 2011(6):44-50.Wu Yinjiang, Liang Yongren. Progress in titanium powder and titanium powder metallurgy products[J]. Materials China, 2011(6): 44-50. [10] Wang Jianzhong, Ao Qingbo, Jing Peng, et al. Preparation and application of porous titanium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2022(5):51. (王建忠, 敖庆波, 荆鹏, 等. 多孔钛的制备及应用[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2022(5):51.Wang Jianzhong, Ao Qingbo, Jing Peng, et al. Preparation and application of porous titanium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2022(5): 51. [11] Li Changyi. Porous metal materials and their application in stomatology[J]. Journal of Oral Materials and Instruments, 2023,32(1):1-6. (李长义. 多孔金属材料及其在口腔医学中的应用[J]. 口腔材料器械杂志, 2023,32(1):1-6. doi: 10.11752/j.kqcl.2023.01.01Li Changyi. Porous metal materials and their application in stomatology[J]. Journal of Oral Materials and Instruments, 2023, 32(1): 1-6. doi: 10.11752/j.kqcl.2023.01.01 [12] Pan Zhicheng. Study on the morphology and properties of graded porous titanium prepared by TiH2 vacuum sintering[D]. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2023. (潘志铖. TiH2真空烧结制备梯度多孔钛形貌及性能研究[D]. 昆明:昆明理工大学, 2023.Pan Zhicheng. Study on the morphology and properties of graded porous titanium prepared by TiH2 vacuum sintering[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2023. [13] Peng Yuqing. Process and properties of ordered porous titanium prepared by sintering TiH 2[D]. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2023. (彭玉青. 烧结TiH2制备有序多孔钛工艺与性能研究[D]. 昆明:昆明理工大学, 2023.Peng Yuqing. Process and properties of ordered porous titanium prepared by sintering TiH 2[D]. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2023. [14] Qian M, Xu W, Brandt M, et al. Additive manufacturing and postprocessing of Ti-6Al-4V for superior mechanical properties[J]. MRS Bull, 2016, 41 (10): 775-783. [15] Trevisan F, Calignano F, Aversa A, et al. Additive manufacturing of titanium alloys in the biomedical field: processes, properties and applications[J]. J. Appl. Biomater Funct. Mater, 2018,16(2):57-67. [16] Laptev A, Vyal O, Bram M, et al. Green strength of powder compacts provided for production of highly porous titanium parts[J]. Powder Metallurgy, 2005, 48: 358-364. [17] Yan Beilei, Wang Jun, Yang Tao, et al. Synthesis of Ti powders with different morphologies via controlling the valence state of the titanium ion in KCl-NaCl molten salt[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2020,876:114496. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114496 [18] Zhu Fuxing, Qiu Kehui, Sun Zhaohui, et al. Electrochemical deposition of titanium ions in molten salts[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(4):12-18. (朱福兴, 邱克辉, 孙朝晖, 等. 熔盐电解中钛离子电化学沉积行为研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(4):12-18. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.04.003Zhu Fuxing, Qiu Kehui, Sun Zhaohui, et al. Electrochemical deposition of titanium ions in molten salts[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017, 38(4): 12-18. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.04.003 [19] Ashby M F, Evans A G, Fleck N A. Metal foams: A design guide [M]. Liu P S, Wang X S, Li Y X translated. Beijing: Metallurgy Industry Press, 2006: 15-16. [20] Liu Jie. Preparation and mechanical properties of porous titanium[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015. (刘杰. 多孔钛的制备及力学性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2015.Liu Jie. Preparation and mechanical properties of porous titanium[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015. [21] Heary R F, Parvathreddy N, Sampath S, et al. Elastic modulus in the selection of interbody implants[J]. Journal of Spine Surgery, 2017, 3(2): 163. -





 下载:
下载: