Characterization of surface properties of titanium dioxide by inverse gas chromatography
-
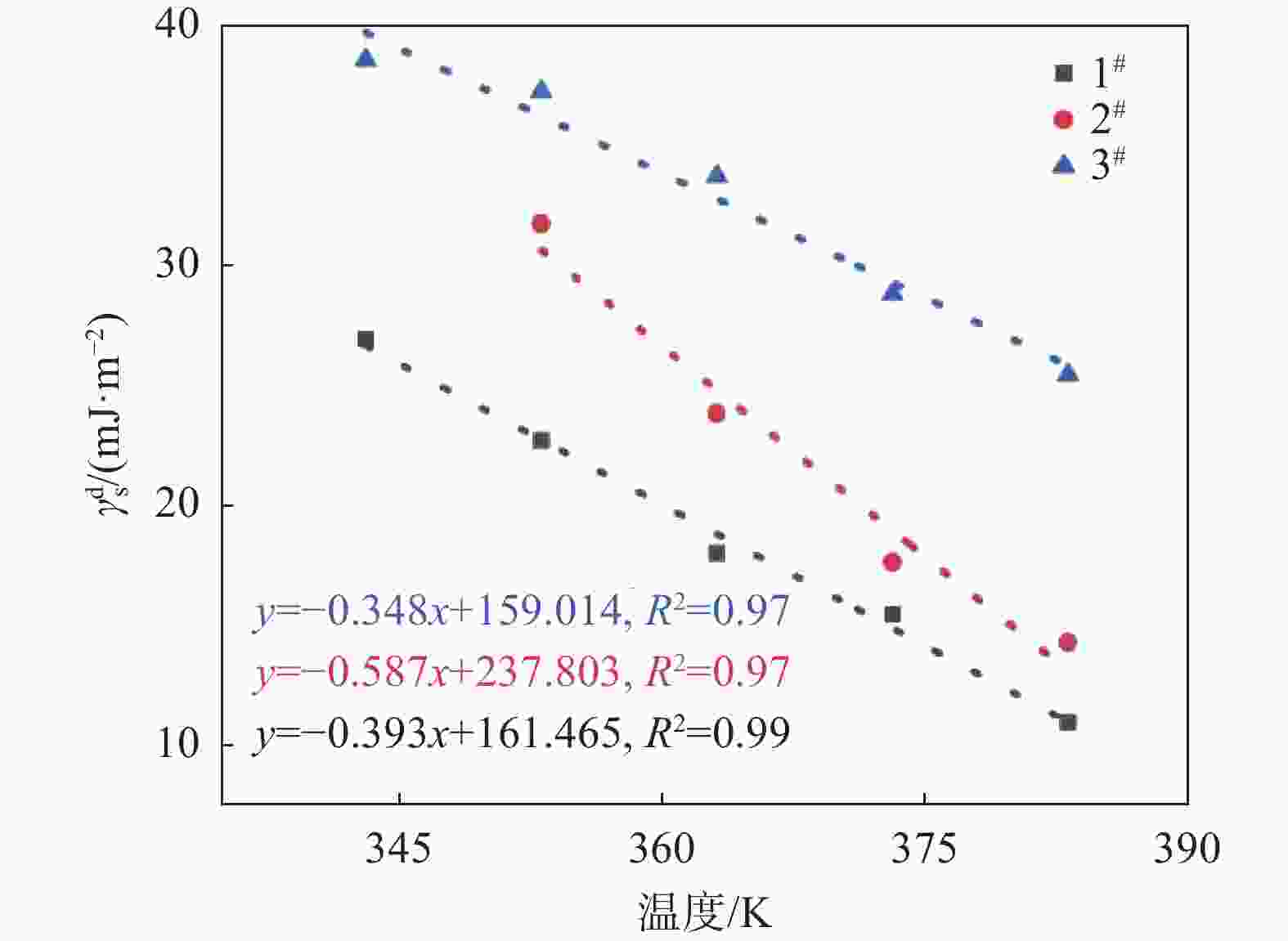
摘要: 采用反气相色谱法(IGC)测试了3种钛白粉的表面能和酸碱常数,研究有机表面处理对钛白粉表面性质的影响。通过不同温度下不同分子探针试验计算研究了样品的非极性表面能。结果表明:在同一温度下(测试温度范围内),随着包覆有机物的增加,样品的非极性表面能$ {\gamma }_{s}^{d} $减小;样品的$ {\gamma }_{s}^{d} $随着温度的升高而减小。同时通过以极性分子为探针分子计算研究表面能的酸碱分量,结果表明钛白粉表面呈两性偏酸性,有机处理剂与钛白表面羟基反应使得表面酸位点减少,酸性下降。但是过多地加入有机处理剂时,部分有机处理剂水解生成羟基未与钛白反应,反而增加样品表面酸性。Abstract: The surface energy and acid/base constants of three kinds of titanium dioxide (TiO2) were measured by inverse gas chromatography (IGC) to investigate the effect of organic treatment on the surface properties of TiO2. The non-polar surface energy of the samples were calculated by using different molecular probes at different temperatures. The results indicate that non-polar surface energy $ \gamma\mathrm{_s^d} $of TiO2 decreases with the increase of organic cladding amount at the same temperature (within the testing temperature range). As the temperature increases, $ \gamma\mathrm{_s^d} $of TiO2 decreases. Meanwhile, the acid-base component of surface energy was studied by using polar molecules as probe molecules, revealing that the surface of titanium dioxide is amphoacid. Since the surface of TiO2 presents acidic, the reaction between organic agents and the hydroxyl groups on the surface of TiO2 leads to the decrease in the surface acid sites and thus the surface acidity of TiO2. However, when excessive organic agent is added, some hydroxyl groups generated by organic agents hydrolyzation would not react with TiO2, resulting in the increment of TiO2 surface acidity.
-
Key words:
- TiO2 /
- surface properties /
- inverse gas chromatography (IGC) /
- organic agents
-
表 1 以非极性溶剂作为探针分子,钛白样品的吸附自由能
Table 1. ΔG of titanium dioxides while non-polar solvent acting as the probe molecule
探针
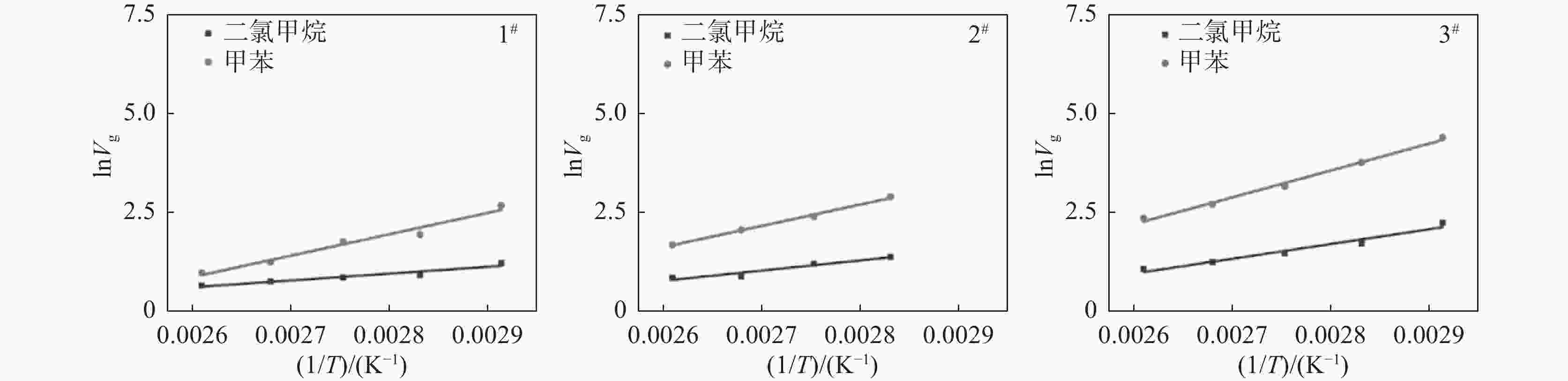
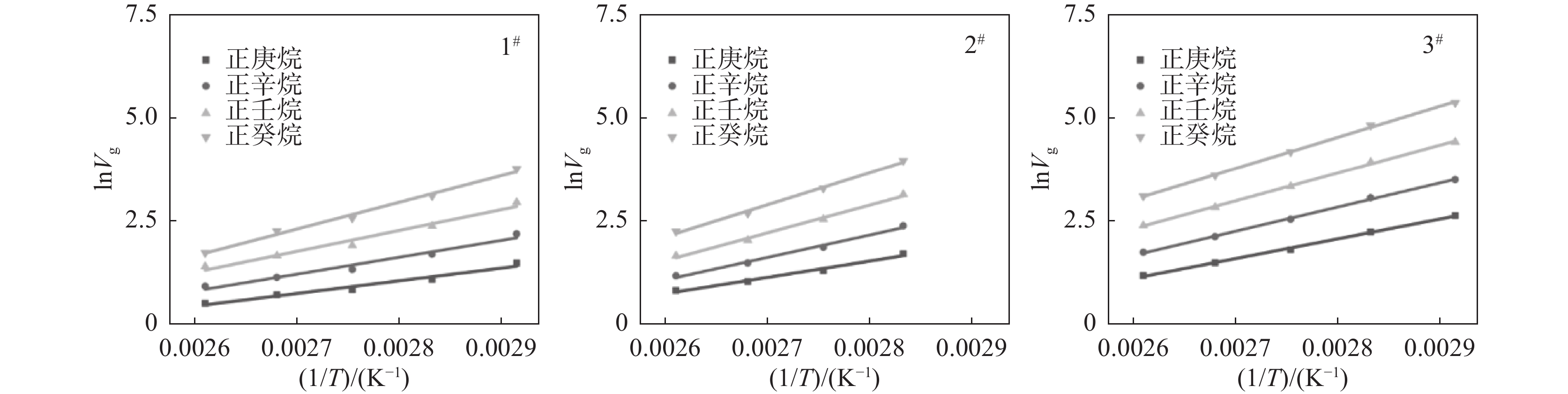
分子1# 2# 3# $ -\Delta G/ $(kJ·mol−1) $ {R}^{2} $ $ -\Delta G/ $(kJ·mol−1) $ {R}^{2} $ $ -\Delta G/ $(kJ·mol−1) $ {R}^{2} $ 正庚烷 25.6 0.968 33.0 0.984 39.9 0.998 正辛烷 34.1 0.970 45.3 0.992 48.9 0.999 正壬烷 42.1 0.975 56.1 0.994 56.5 0.999 正癸烷 54.1 0.991 64.89 0.995 63.1 0.999 表 2 以极性溶剂作为探针分子,钛白样品的吸附自由能
Table 2. $ \Delta G $ of titanium dioxides while polar solvent acting as the probe molecule
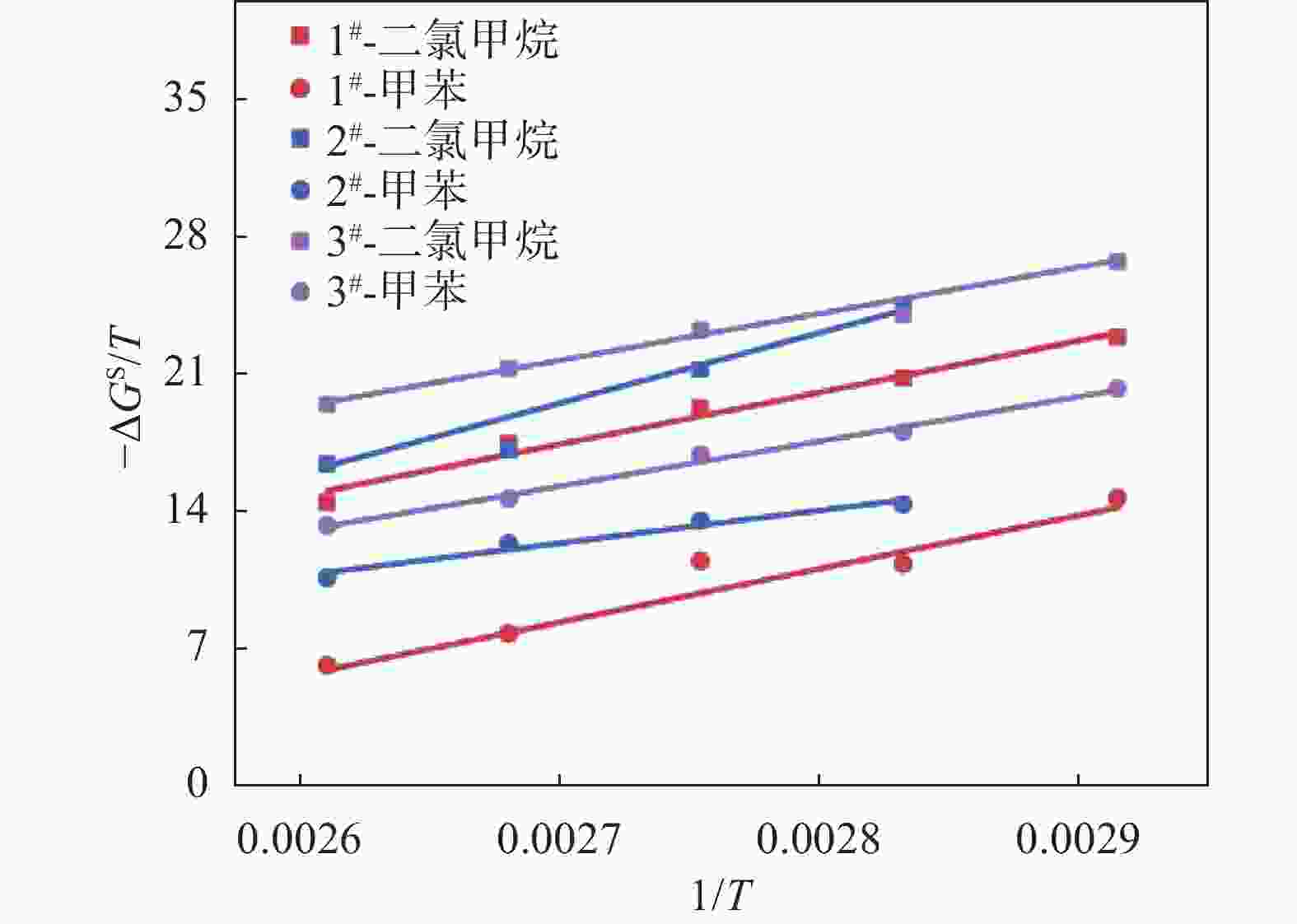
探针分子 1# 2# 3# $ -\Delta G/ $(kJ·mol−1) $ {R}^{2} $ $ -\Delta G/ $(kJ·mol−1) $ {R}^{2} $ $ -\Delta G/ $(kJ·mol−1) $ {R}^{2} $ 二氯甲烷 14.3 0.926 21.4 0.930 30.9 0.960 甲苯 44.9 0.968 44.6 0.995 56.2 0.993 表 3 不同温度下钛白粉样品的$ {\gamma }_{\mathrm{s}}^{\mathrm{d}} $
Table 3. The ${\gamma }_{\mathrm{s}}^{\mathrm{d}} $ of TiO2 samples at different temperatures
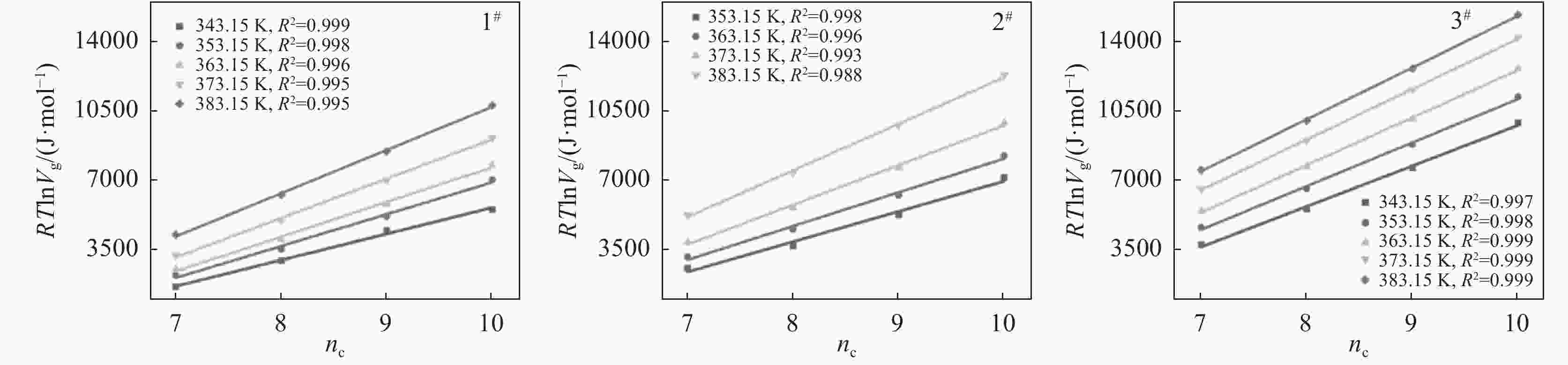
编号 $ {\gamma }_{\mathrm{s}}^{\mathrm{d}} $/(mJ·m−2) 383.15 K 373.15 K 363.15 K 353.15 K 343.15 K 1# 10.72 15.25 17.80 22.53 26.75 2# 14.08 17.44 23.65 31.58 3# 25.27 28.64 33.58 37.11 38.44 表 4 钛白样品表面的酸碱作用自由能
Table 4. $ \Delta {G}^{s} $ of acid-base interaction on the surface of TiO2 samples
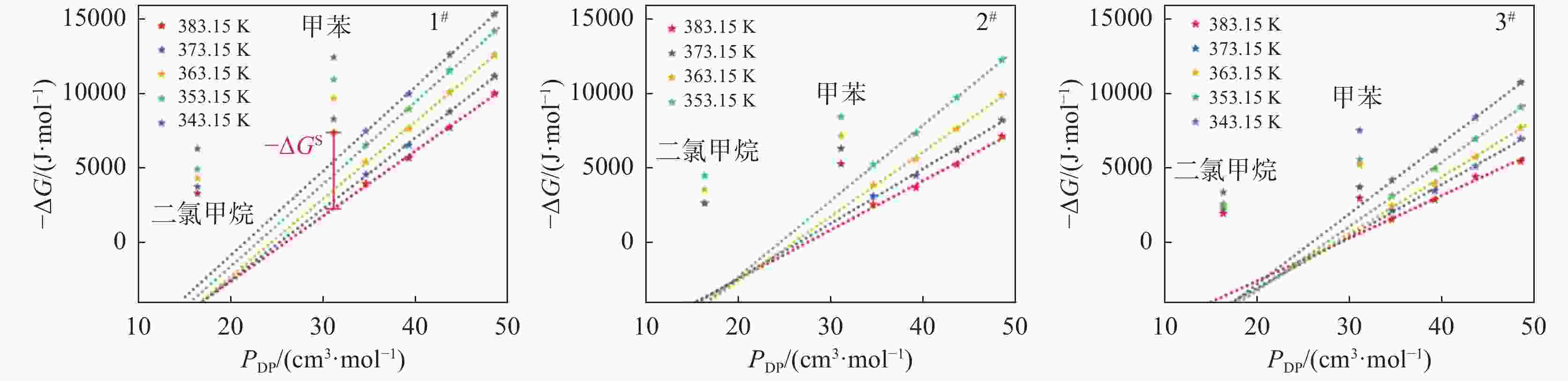
T/K 探针分子 $ -\Delta {G}^{\mathrm{s}} $/(kJ·mol−1) 1# 2# 3# 383.15 二氯甲烷 5.540 6.280 7.442 甲苯 2.357 4.071 5.083 373.15 二氯甲烷 6.509 6.385 7.934 甲苯 2.903 4.611 5.466 363.15 二氯甲烷 6.995 7.703 8.425 甲苯 4.168 4.907 6.132 353.15 二氯甲烷 7.333 8.611 8.478 甲苯 3.998 5.066 6.367 343.15 二氯甲烷 7.843 9.152 甲苯 5.038 6.946 表 5 钛白样品表面的酸碱性
Table 5. Surface acid/base characteristics of TiO2 samples
编号 $ {K}_{\mathrm{a}} $ $ {K}_{\mathrm{b}} $ $ {K}_{\mathrm{a}}/{K}_{\mathrm{b}} $ 1# 64.72 1.62 40.02 2# 39.52 2.1911 18.02 3# 54.28 1.45 37.31 -
[1] Cao Jingwen, Wang Qiang, Hu Dingkai, et al. Surface properties of fluorine-functionalized metal–organic frameworks based on inverse gas chromatography[J]. Langmuir, 2023,39(25):8737-8748. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c00735 [2] Bai Wenli, Pakdel Esfandiar, Li Quanxiang, et al. Inverse gas chromatography (IGC) for studying the cellulosic materials surface characteristics: A mini review[J]. Cellulose, 2023,30(6):3379-3396. doi: 10.1007/s10570-023-05116-9 [3] Yusuf K, Natraj A, Li K, et al. Inverse gas chromatography demonstrates the crystallinity-dependent physicochemical properties of two-dimensional covalent organic framework stationary phases[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2023,35(4):1691-1701. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c03448 [4] Jacob P N, Berg J C. Acid-base surface energy characterization of microcrystalline cellulose and two wood pulp fiber types using inverse gas chromatography[J]. Langmuir, 1994,10(9):3086-3093. doi: 10.1021/la00021a036 [5] Schultz J, Lavielle L, Martin C. The role of the interface in carbon fibre-epoxy composites[J]. Journal of Adhesion, 1987,23(1):45-60. doi: 10.1080/00218468708080469 [6] Dorris G M, Gray D G. Adsorption of n-alkanes at zero surface coverage on cellulose paper and wood fibers[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 1980,77(2):353-362. [7] Dong S, Brendlé M, Donnet J B. Study of solid surface polarity by inverse gas chromatography at infinite dilution[J]. Chromatographia, 1989,28:469-472. doi: 10.1007/BF02261062 [8] Flour C S, Eugène Papirer. Gas-solid chromatography: a quick method of estimating surface free energy variations induced by the treatment of short glass fibers[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 1983,91(1):69-75. [9] Brookman D J, Sawyer D T. Specific interactions affecting gas chromatographic retention for modified alumina columns[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1968,40(1):106-110. doi: 10.1021/ac60257a061 [10] Masato Ohta, Graham Buckton. The use of inverse gas chromatography to assess the acid–base contributions to surface energies of cefditoren pivoxil and methacrylate copolymers and possible links to instability[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2004,272:121-128. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2003.12.007 [11] Wu Guangzhao. Studies on the surface properties of modified-silica and its reinforcing effect on SBR[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2015. (吴广照. 改性白炭黑的表面性质对丁苯橡胶补强性能影响的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2015.Wu Guangzhao. Studies on the surface properties of modified-silica and its reinforcing effect on SBR[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2015. -




 下载:
下载: