Review of MXenes as electrocatalysts for hydrogen production
-
摘要: 基于可再生能源的电解水技术是生产“绿氢”的主要方法但受限于高电耗以及由此产生的高电力成本,电解水技术在大规模推广应用方面仍面临困难。降低电耗的途径在于开发高性能的电催化剂。MXenes是一种碳化物、氮化物和碳氮化物组成的二维材料,具有高导电性、大比表面积、高机械强度和优异的亲水性,是电催化剂的理想载体,被广泛应用于电解水制氢领域的研究。首先介绍了MXenes的基本组成与结构特征,其次总结分析了MXenes直接用于电解水制氢方面的研究成果,并阐述了其作为载体材料锚定高活性物质用于析氢和析氧反应的应用和进展,最后总结并展望了MXenes材料未来的发展前景。Abstract: Renewable energy-based water electrolysis is the main method of producing “green hydrogen”, but it still faces difficulties in large-scale application due to high power consumption and the resulting high cost of electricity. The way to reduce power consumption lies in the development of high-performance electrocatalysts. MXenes is a two-dimensional material composed of carbides, nitrides and carbon-nitrides with high electrical conductivity, large specific surface area, high mechanical strength and excellent hydrophilicity, which is an ideal carrier for electrocatalysts and has been widely used in the research in the field of hydrogen production by electrolysis of water. This paper firstly introduces the basic composition and structural characteristics of MXenes, summarizes and analyzes the research results on the direct use of MXenes in electrolysis of water for hydrogen production, and describes the application and progress of its use as a carrier material to anchor highly active substances for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reaction, and finally summarizes and looks forward to the future development prospects of MXenes materials.
-
Key words:
- MXenes /
- electrochemical water splitting /
- carrier /
- application
-
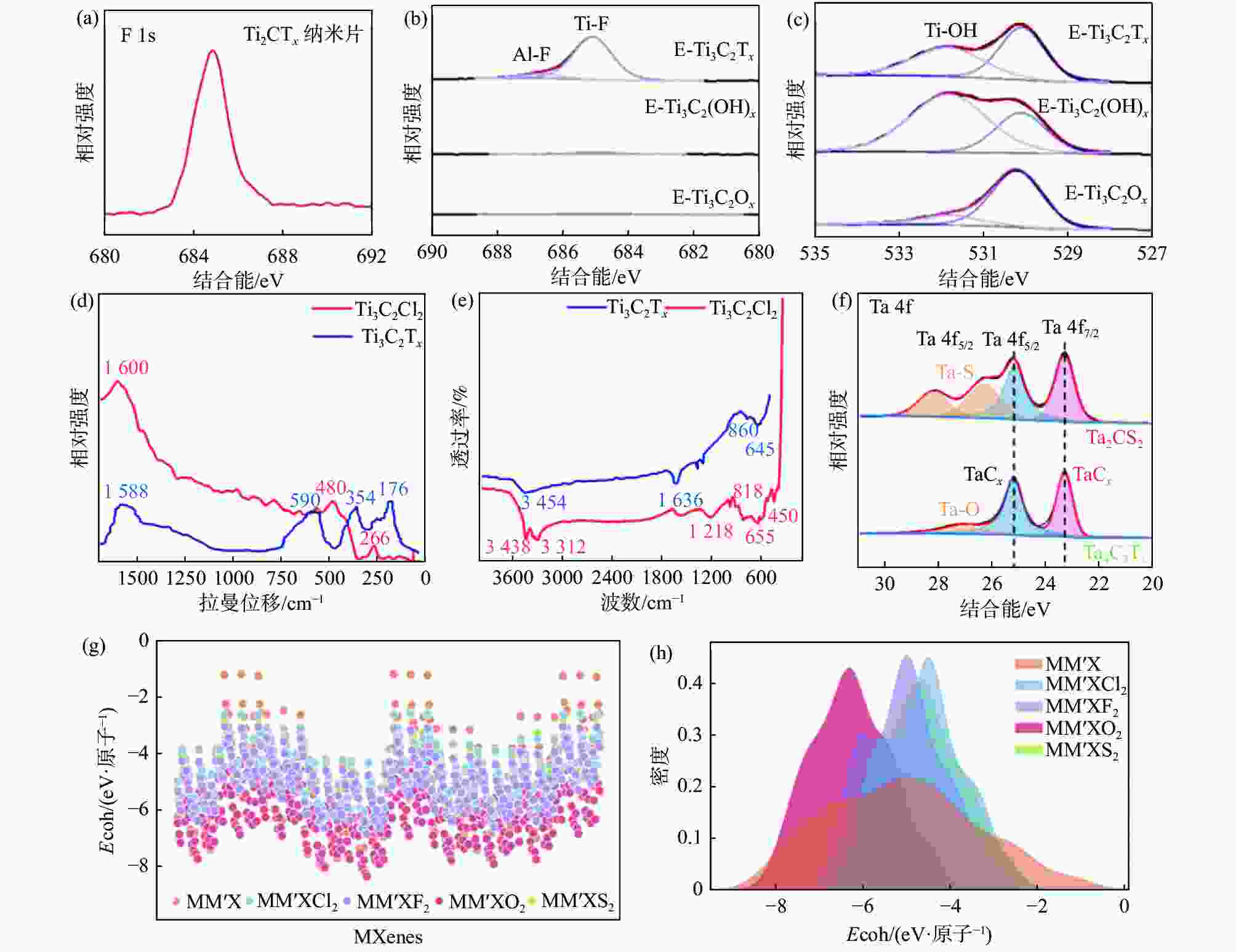
图 4 不同官能团MXenes的表征与理论计算
(a) Ti3C2Tx纳米片F 1s的XPS光谱[34]; Ti3C2Tx、Ti3C2(OH)x与Ti3C2Ox的XPS光谱:(b)F 1s与(c) O 1s[35];Ti3C2Cl2与Ti3C2Tx的(d)拉曼光谱与(e)傅里叶红外光谱[37]; (f) Ta2CS2与Ta4C3Tx在Ta 4f的XPS光谱[39];(g)不同官能团的归一化结合能与(h)相应的分布[40]
Figure 4. Characterization and theoretical calculations of MXenes with different functional groups
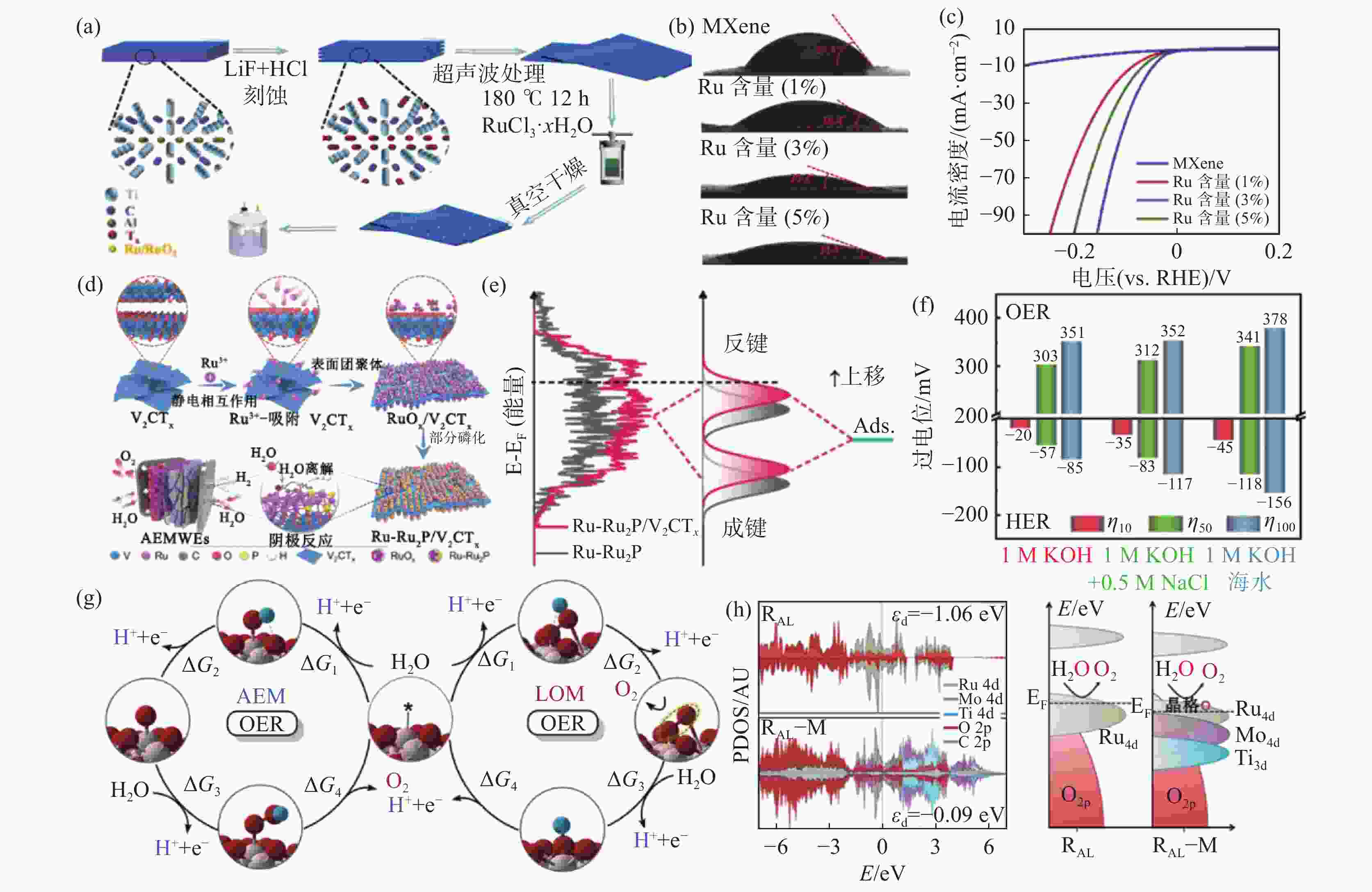
图 6 MXenes与贵金属化合物的形成、性能与理论计算
(a) Ru-RuO2/Ti3C2Tx催化剂的合成示意[47]; (b) Ti3C2Tx、Ru-RuO2/Ti3C2Tx与水的接触角测试[47]; (c) Ti3C2Tx与不同Ru负载量下Ru-RuO2/Ti3C2Tx的HER极化曲线[47]; (d) Ru-Ru2P/Ti3C2Tx催化剂的合成示意与其在AEMWE的应用[48];(e) Ru-Ru2P与Ru-Ru2P/Ti3C2Tx催化剂Ru 3d轨道的投影态密度(PDOS)[48]; (f) RuO2-Ti3C2/NF在10、50与100 mA/cm2电流密度下不同电解质中的HER与OER过电位[49]; (g)析氧反应(OER)中的吸附氧化机制(AEM)和晶格氧化机制(LOM)[50];(h) RuO2与RuO2-Mo2TiC2Tx催化剂的投影态密度(PDOS)[50]
Figure 6. Formation, properties and theoretical calculations of MXenes and precious metal compounds
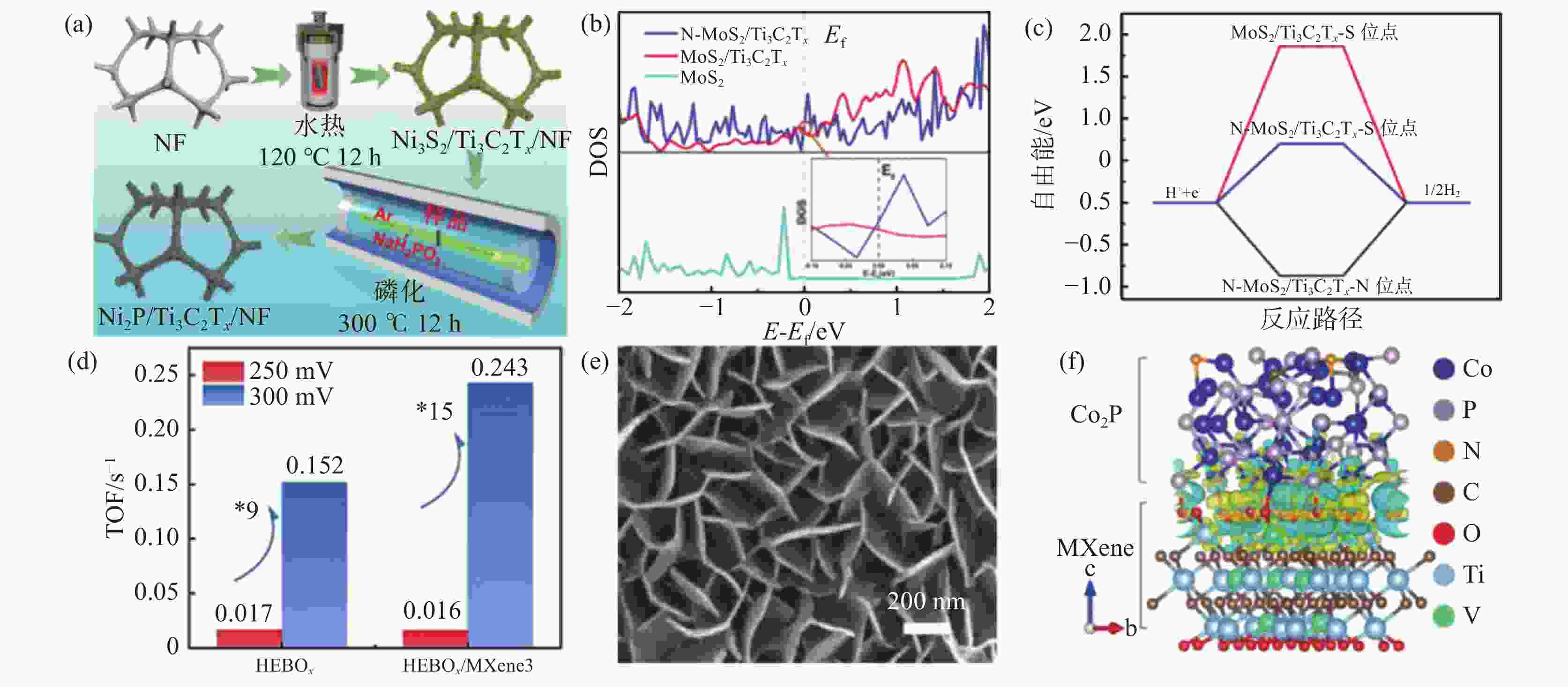
图 7 MXenes与过渡金属化合物的形成、表征与理论计算
(a) Ni2P/Ti3C2Tx/NF合成示意[51]; (b) N-MoS2/Ti3C2Tx、MoS2/Ti3C2Tx与MoS2的态密度(DOS)[52];(c) N-MoS2/Ti3C2Tx与MoS2/Ti3C2Tx在S与N位点的氢吸附吉布斯自由能台阶图[52]; (d) FeCoNiMnBOx与FeCoNiMnBOx/Ti3C2Tx的TOF[53]; (e) NiCo-LDH/Ti3C2Tx/NF的SEM图[54]; (f) Co2P与MXenes界面产生的电荷密度差分(黄色代表电子积累,蓝色代表电子损失)[55]
Figure 7. Formation, characterization and theoretical calculations of MXenes and transition metal compounds
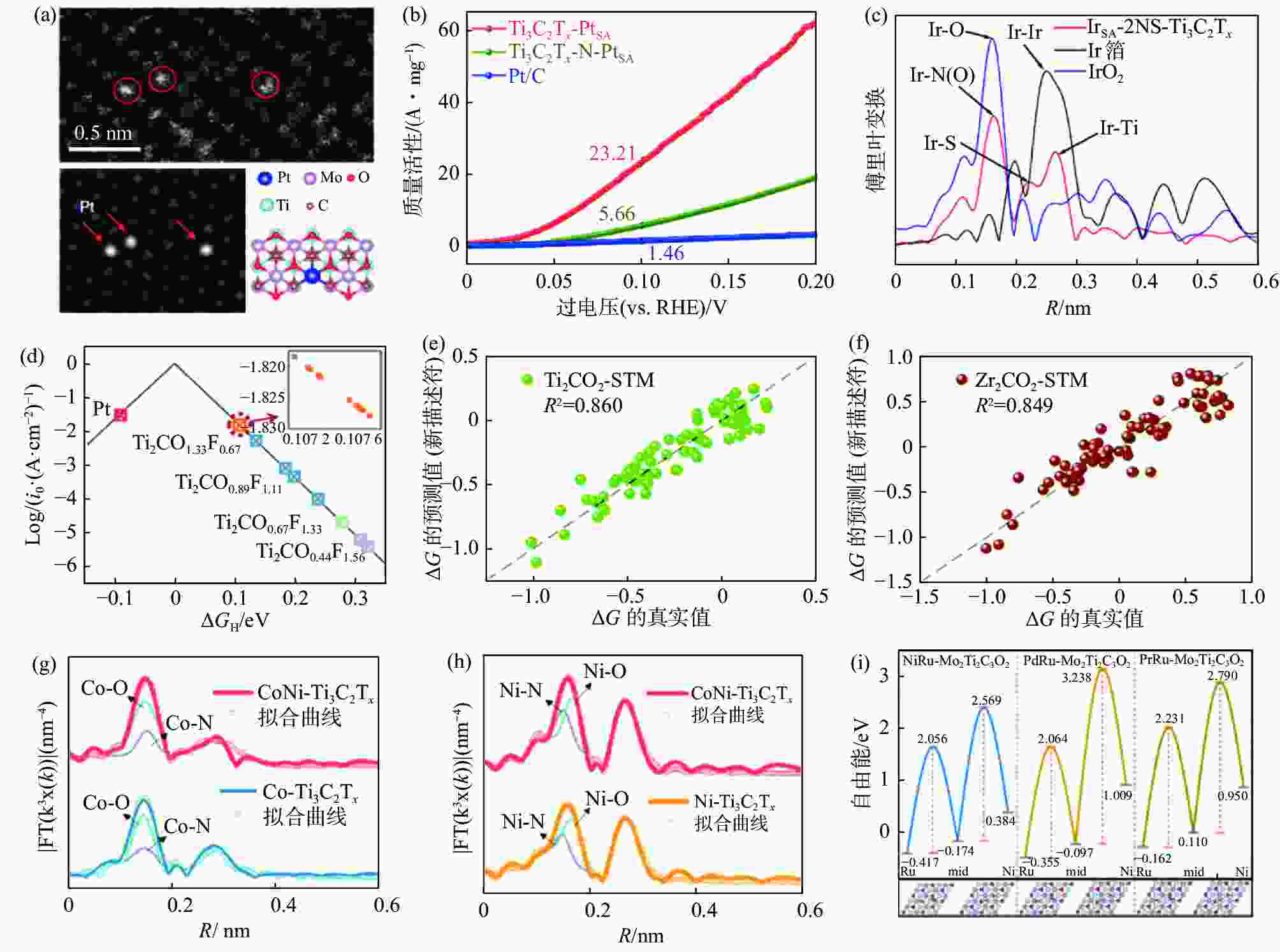
图 8 MXenes与单/双原子催化剂的表征与理论计算
(a) PtSA-Mo2TiC2Tx的HAADF-STEM放大图像及其相应的模拟图像[58]; (b) PtSA-Ti3C2Tx、最近报道的MXenes基与Pt基催化剂质量活性比较[59]; (c) Ir-2 NS-Ti3C2Tx、Ir箔和IrO2的EXAFS谱的傅里叶变换[60]; (d)不同F/O比下Ti2CTx的交换电流密度i0与∆GH的火山图[61]; 新描述符预测∆GH用于(e)Ti2CO2-STM与(f)Zr2CO2-STM[62]; (g) CoNi-Ti3C2Tx与Co-Ti3C2Tx的EXAFS谱的傅里叶变换[63]; (h) CoNi-Ti3C2Tx与Ni-Ti3C2Tx的EXAFS谱的傅里叶变换[63]; (h) Ru与Ni、Pd、Pt分别负载于Mo2Ti2C3O2时*OH迁移的动态能垒[64]
Figure 8. Characterization and theoretical calculations of MXenes and single/double atom catalysts
表 1 MXenes直接用于电解水催化性能的对比
Table 1. Comparison of catalytic properties of MXenes directly used for electrolysis of water
电催化剂 电解液 电解液浓度/(mol·L−1) 应用 过电位@10 mAcm−2/mV 塔菲尔斜率/(mV·dec−1) 参考
文献Ti3C2Tx KOH 1 HER 188 110 [25] Ti3C2Tx KOH 1 OER 330 91 [25] Ti3C2Tx nanofibers H2SO4 0.5 HER 169 97 [26] Ti2CTx H2SO4 0.5 HER 609 124 [27] Mo2CTx H2SO4 0.5 HER 283 82 [27] V4C3Tx H2SO4 0.5 HER >700 236 [28] Nb4C3Tx KOH 1 HER 398 122.2 [29] Ti2CFx H2SO4 0.5 HER 170 100 [34] Ti3C2(OH)x H2SO4 0.5 HER 217 88.5 [35] Ti3C2Ox H2SO4 0.5 HER 190 60.7 [35] Ti3C2Cl2 KOH 1 HER 259 92 [37] Ti3C2Cl2 KOH 1 OER 150 48 [37] Ta2CS2 KOH 1 HER 73 61.1 [42] Ta2CS2 KOH 1 OER 243 66.9 [42] N-Ti3C2Tx H2SO4 0.5 HER 198 92 [41] N-Ti2CTx H2SO4 0.5 HER 215 67 [42] P-Mo2CTx H2SO4 0.5 HER 186 [43] 表 2 MXenes作催化剂载体用于电解水催化性能的对比
Table 2. Comparison of catalytic performance of MXenes as catalyst carriers for water electrolysis
电催化剂 电解液 电解液浓度/(mol·L−1) 应用 过电位(@10 mAcm−2)/mV 塔菲尔斜率/(mV·dec−1) 参考文献 Ru-RuO2/Ti3C2Tx KOH 1 HER 43 52.1 [47] Ru-Ru2P/V2CTx H2SO4 0.5 HER 37 61.3 [48] Ru-Ru2P/V2CTx KOH 1 HER 21 31.4 [48] RuO2-Ti3C2/NF KOH 1 HER 20 45.8 [49] RuO2-Ti3C2/NF KOH+ NaCl 1+0.5 HER 35 45.8 [49] RuO2-Ti3C2/NF KOH+海水 1 HER 45 45.8 [49] RuO2-Mo2TiC2Tx H2SO4 0.5 OER 222 50.4 [50] Ni2P/Ti3C2Tx/NF KOH 1 HER 135 86.6 [51] N-MoS2/Ti3C2Tx KOH 1 HER 80 100 [52] FeCoNiMnBOx/Ti3C2Tx KOH 1 OER 268 39.8 [53] NiCo-LDH/Ti3C2Tx/NF KOH 1 HER 123 86.6 [54] Ti2VC2Tx@MOF-Co2P KOH 1 HER 114 93.1 [56] Ti2VC2Tx@MOF-Co2P KOH 1 OER 246 28.18 [55] PtSA-Mo2TiC2Tx H2SO4 0.5 HER 30 30 [58] PtSA- Ti3C2Tx H2SO4 0.5 HER 38 45 [59] Ir-2NS-Ti3C2Tx H2SO4 0.5 HER 57.7 25.1 [60] Ir-2NS-Ti3C2Tx KOH 1 HER 40.9 50.5 [60] CoNi-Ti3C2Tx KOH 1 HER 31 33.0 [63] CoNi-Ti3C2Tx KOH 1 OER 241 79.8 [63] -
[1] Cui Yanglansen, Cao Zhenjiang, Zhang Yongzheng, et al. Single-atom sites on MXenes for energy conversion and storage[J]. Small Science, 2021,1(6):2100017. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202100017 [2] Cheng Yan, Gong Juhui, Cao Bo, et al. Ultrafine VN nanodots induced generation of abundant cobalt single-atom active sites on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube for efficient hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022,68:646-657. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.11.035 [3] Liu Min, Yao Zhendong, Gu Jing, et al. Issues and opportunities facing hydrolytic hydrogen production materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023,461:141918. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.141918 [4] Chen Chao, Li Jinzhou, Lü Zepeng, et al. Recent strategies to improve the catalytic activity of pristine MOFs and their derived catalysts in electrochemical water splitting[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023,48(78):30435-30463. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.04.241 [5] Chen Jieli, Gao Xiaohong, Li Jing, et al. Progress in MXene-based catalysts for oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Electron, 2024,2(1):e17. doi: 10.1002/elt2.17 [6] Aggarwal Priyanka, Sarkar Debasish, Awasthi Kamlendra, et al. Functional role of single-atom catalysts in electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution: current developments and future challenges[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2022,452:214289. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214289 [7] Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5696): 666-669. [8] Naguib Michael, Barsoum Michel W, Gogotsi Yury. Ten years of progress in the synthesis and development of MXenes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021,33(39):2103393. doi: 10.1002/adma.202103393 [9] Naguib Michael, Mashtalir Olha, Carle Joshua, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides[J]. ACS Nano, 2012,6(2):1322-1331. doi: 10.1021/nn204153h [10] Wen Yangyang, Rufford Thomas E, Chen Xingzhu, et al. Nitrogen-doped Ti3C2T x MXene electrodes for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. Nano Energy, 2017,38:368-376. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.06.009 [11] Lu Ming, Li Haojie, Han Wenjuan, et al. 2D titanium carbide (MXene) electrodes with lower-f surface for high performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2019,31:148-153. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2018.05.017 [12] Hu Feiyue, Wang Xiaohan, Bao Shen, et al. Tailoring electromagnetic responses of delaminated Mo2TiC2T x MXene through the decoration of Ni particles of different morphologies[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022,440:135855. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135855 [13] Lü Zepeng, Fei Jinshuai, You Yang, et al. Synergism and anion-cation dual chemical substitution in heterostructure sprouted on MXene enable high-efficiency and stable overall water splitting[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023,147:207-216. [14] Ma Wansen, Liu Dong, Gao Feiyu, et al. P-doped MoS2/Ni2P/ Ti3C2T x heterostructures for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline media[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022,105(10):6096-6104. doi: 10.1111/jace.18622 [15] Lü Zepeng, Ma Wansen, Dang Jie, et al. Induction of Co2P growth on a MXene (Ti3C2T x)-modified self-supporting electrode for efficient overall water splitting[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2021,12(20):4841-4848. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c01345 [16] Lü Zepeng, Ma Wansen, Wang Meng, et al. Co-Constructing interfaces of multiheterostructure on MXene (Ti3C2T x)‐modified 3d self-supporting electrode for ultraefficient electrocatalytic her in alkaline media[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021,31(29):2102576. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202102576 [17] Naguib Michael, Mochalin Vadym N, Barsoum Michel W, et al. 25th anniversary article: MXenes: a new family of two-dimensional materials[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(7): 992-1005. [18] Anasori Babak, Lukatskaya Maria R, Gogotsi Yury. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017,2(2):1-17. [19] Pang Jinbo, Mendes Rafael G, Bachmatiuk Alicja, et al. Applications of 2d MXenes in energy conversion and storage systems[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019,48(1):72-133. doi: 10.1039/C8CS00324F [20] Gogotsi Yury, Anasori Babak. The rise of MXenes[J]. ACS Nano, 2019,13(8):8491-8494. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b06394 [21] Wang Limeng, Li Yaru, Ren Yongpeng, et al. Research progress of MXene-based materials in electrocatalysis[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023,40(9):4917-4931. (王利萌, 李亚如, 任永鹏, 等. MXene基材料在电催化领域的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023,40(9):4917-4931.Wang Limeng, Li Yaru, Ren Yongpeng, et al. Research progress of MXene-based materials in electrocatalysis[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(9): 4917-4931. [22] Soomro Razium A, Zhang Peng, Fan Baomin, et al. Progression in the oxidation stability of MXenes[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023,15(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00977-4 [23] VahidMohammadi Armin, Rosen Johanna, Gogotsi Yury. The world of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides (MXenes)[J]. Science, 2021,372(6547):eabf1581. doi: 10.1126/science.abf1581 [24] Hantanasirisakul Kanit, Gogotsi Yury. Electronic and optical properties of 2d transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes)[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018,30(52):1804779. doi: 10.1002/adma.201804779 [25] Sharma Piyush, Kainth Shagun, Pandey Om Prakash, et al. Customized synthesis of 2d Ti3C2 MXene for improved overall water splitting[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2023,6(23):21788-21802. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c03986 [26] Yuan Wenyu, Cheng Laifei, An Yurong, et al. MXene nanofibers as highly active catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018,6(7):8976-8982. [27] Seh Zhi Wei, Fredrickson Kurt D, Anasori Babak, et al. Two-dimensional molybdenum carbide (MXene) as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2016,1(3):589-594. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00247 [28] Tran Minh H, Schäfer Timo, Shahraei Ali, et al. Adding a new member to the MXene family: synthesis, structure, and electrocatalytic activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction of V4C3T x[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018,1(8):3908-3914. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.8b00652 [29] Tan Yuanbo, Zhu Zhenye, Zhang Xueting, et al. Nb4C3T x (MXene) as a new stable catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021,46(2):1955-1966. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.10.046 [30] Wang Xiaoxu, Wang Changxin, Ci Shinan, et al. Accelerating 2d MXene catalyst discovery for the hydrogen evolution reaction by computer-driven workflow and an ensemble learning strategy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020,8(44):23488-23497. doi: 10.1039/D0TA06583H [31] Zheng Jingnan, Sun Xiang, Qiu Chenglong, et al. High-throughput screening of hydrogen evolution reaction catalysts in MXene materials[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020,124(25):13695-13705. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c02265 [32] Sun Xiang, Zheng Jingnan, Gao Yijing, et al. Machine-learning-accelerated screening of hydrogen evolution catalysts in MBenes materials[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020,526:146522. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146522 [33] Zhang Mengling, Lu Qingjie, Lu Qiang, et al. Influence of surface end-groups on hydrogen production from electrolyzed water in MXene materials[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2023,54(1):1229-1236. (张萌玲, 卢清杰, 卢强, 等. 表面端基对MXene材料电解水制氢的影响[J]. 功能材料, 2023,54(1):1229-1236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2023.01.033Zhang Mengling, Lu Qingjie, Lu Qiang, et al. Influence of surface end-groups on hydrogen production from electrolyzed water in MXene materials[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2023, 54(1): 1229-1236. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2023.01.033 [34] Li Shuang, Tuo Ping, Xie Junfeng, et al. Ultrathin MXene nanosheets with rich fluorine termination groups realizing efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Nano Energy, 2018,47:512-518. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.03.022 [35] Jiang Yanan, Sun Tao, Xie Xi, et al. Oxygen-functionalized ultrathin Ti3C2T x MXene for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. ChemSusChem, 2019,12(7):1368-1373. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201803032 [36] Gao Guoping, Mullane Anthony PO’, Du Aijun. 2D MXenes: a new family of promising catalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017,7(1):494-500. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b02754 [37] Sarfraz Bilal, Taqi Muhammad Mehran, Baig Mutawara Mahmood, et al. HF free greener Cl-terminated MXene as novel electrocatalyst for overall water splitting in alkaline media[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2022,46(8):10942-10954. doi: 10.1002/er.7895 [38] Zhao Qian, Zhu Qizhen, Miao Jiawei, et al. 2D MXene nanosheets enable small-sulfur electrodes to be flexible for lithium–sulfur batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2019,11(17):8442-8448. doi: 10.1039/C8NR09653H [39] Wu Tong, Pang Xin, Zhao Siwei, et al. One-step construction of ordered sulfur-terminated tantalum carbide MXene for efficient overall water splitting[J]. Small Structures, 2022,3(3):2100206. doi: 10.1002/sstr.202100206 [40] Abraham B Moses. Fusing machine learning strategy with density functional theory to hasten the discovery of 2d MXene based catalysts for hydrogen generation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6(12):4948-4954. doi: 10.1039/C7TA10374C [41] Le Thi Anh, Bui Quoc Viet, Tran Ngoc Quang, et al. Synergistic effects of nitrogen doping on MXene for enhancement of hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019,7(19):16879-16888. [42] Yoon Yeoheung, Tiwari Anand P, Lee Minhe, et al. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity by chemical nitridation of two-dimensional titanium carbide MXene for hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6(42):20869-20877. doi: 10.1039/C8TA08197B [43] Qu Guoxing, Zhou Yang, Wu Tianli, et al. Phosphorized MXene-phase molybdenum carbide as an earth-abundant hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018,1(12):7206-7212. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.8b01642 [44] Ding Bo, Ong Wee-Jun, Jiang Jizhou, et al. Uncovering the electrochemical mechanisms for hydrogen evolution reaction of heteroatom doped M2C MXene (M = Ti, Mo)[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020,500:143987. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143987 [45] Zubair Muhammad, Hassan Muhammad Muneeb Ul, Mehran Muhammad Taqi, et al. 2D MXenes and their heterostructures for HER, OER and overall water splitting: a review[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022,47(5):2794-2818. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.10.248 [46] Li Jinzhou, Hou Chengzhen, Chen Chao, et al. Collaborative interface optimization strategy guided ultrafine RuCo and MXene heterostructure electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting[J]. ACS Nano, 2023,17(11):10947-10957. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c02956 [47] Shi Xintong, Du Mingxuan, Jing Hongmei, et al. Bold innovation of noble metal support system: Ru-RuO2/MXene@CC for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction in water electrolysis[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023,679:132638. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132638 [48] Nguyen Thanh Hai, Tran Phan Khanh Linh, Tran Duy Thanh, et al. Ru-Ru2P hetero-cluster promoted V2CT x sheets-based electrocatalyst enables industrial-level AEM water electrolysis[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2024,343:123517. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123517 [49] Zhang Yi, Zhang Zhaohui, Yu Zhiran, et al. Ruthenium oxide nanoparticles immobilized on Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets for boosting seawater electrolysis[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023,15(50):58345-58355. [50] Tiwari Jitendra N, Umer Muhammad, Bhaskaran Gokul, et al. Atomic layers of ruthenium oxide coupled with Mo2TiC2T x MXene for exceptionally high catalytic activity toward water oxidation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023,339:123139. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123139 [51] Lü Zepeng, Wang Meng, Liu Dong, et al. Synergetic effect of Ni2P and MXene enhances catalytic activity in the hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2021,60(3):1604-1611. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03072 [52] Liu Dong, Lü Zepeng, Dang Jie, et al. Nitrogen-doped MoS2/Ti3C2T x heterostructures as ultra-efficient alkaline her electrocatalysts[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2021,60(13):9932-9940. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c01193 [53] Li Xinglong, He Huan, Yu Yihang, et al. Boosting oxygen evolution reaction by synergistically coupling amorphous high-entropy borate feconimnbox with MXene[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2024,645:158838. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.158838 [54] Liu Xinyu, Wang Min, Ji Shan, et al. Adjusting surface electron density of heterostructured NiCo LDH/MXene/NF material to improve its electrocatalytic performance in hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024,67:192-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.04.171 [55] Li Jinzhou, Chen Chao, Lü Zepeng, et al. Constructing heterostructures of ZIF-67 derived C, N doped Co2P and Ti2VC2T x MXene for enhanced OER[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023,145:74-82. [56] Li Jinzhou, Chen Chao, Dang Jie. Study on the electrocatalytic performance of MXene/cobalt phosphide composites for hydrogen production[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(2):48-54. (李金洲, 陈超, 党杰. MXene/磷化钴复合材料电催化制氢性能研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(2):48-54.Li Jinzhou, Chen Chao, Dang Jie. Study on the electrocatalytic performance of MXene/cobalt phosphide composites for hydrogen production[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(2): 48-54. [57] Qiao Botao, Wang Aiqin, Yang Xiaofeng, et al. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeO x[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2011,3(8):634-641. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1095 [58] Zhang Jinqiang, Zhao Yufei, Guo Xin, et al. Single platinum atoms immobilized on an MXene as an efficient catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2018,1(12):985-992. doi: 10.1038/s41929-018-0195-1 [59] Zhang Jiangjiang, Wang Erqing, Cui Shiqiang, et al. Single-atom Pt anchored on oxygen vacancy of monolayer Ti3C2T x for superior hydrogen evolution[J]. Nano Letters, 2022,22(3):1398-1405. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c04809 [60] Lin Wujun, Lu Yingrui, Peng Wei, et al. Atomic bridging modulation of Ir–N, S co-doped MXene for accelerating hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022,10(18):9878-9885. doi: 10.1039/D2TA00550F [61] Gu Yitao, Wei Bo, Legut Dominik, et al. Single atom-modified hybrid transition metal carbides as efficient hydrogen evolution reaction catalysts[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021,31(43):2104285. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202104285 [62] Wang Changxin, Wang Xiaoxu, Zhang Tianyao, et al. A descriptor for the design of 2d MXene hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalysts[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022,10(35):18195-18205. doi: 10.1039/D2TA02837A [63] Zhao Xin, Li Wanpeng, Cao Yanhui, et al. Dual-atom Co/Ni electrocatalyst anchored at the surface-modified Ti3C2T x MXene enables efficient hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions[J]. ACS Nano, 2024,18(5):4256-4268. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c09639 [64] Xi Qing, Xie Fangxia, Sun Zijun, et al. NiRu–Mo2Ti2C3O2 as an efficient catalyst for alkaline hydrogen evolution reactions: the role of bimetallic site interactions in promoting volmer-step kinetics[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2024,26(8):7166-7176. doi: 10.1039/D3CP05892A [65] Li Pengkun, Zhu Jinguo, Handoko Albertus D, et al. High-throughput theoretical optimization of the hydrogen evolution reaction on MXenes by transition metal modification[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6(10):4271-4278. doi: 10.1039/C8TA00173A -




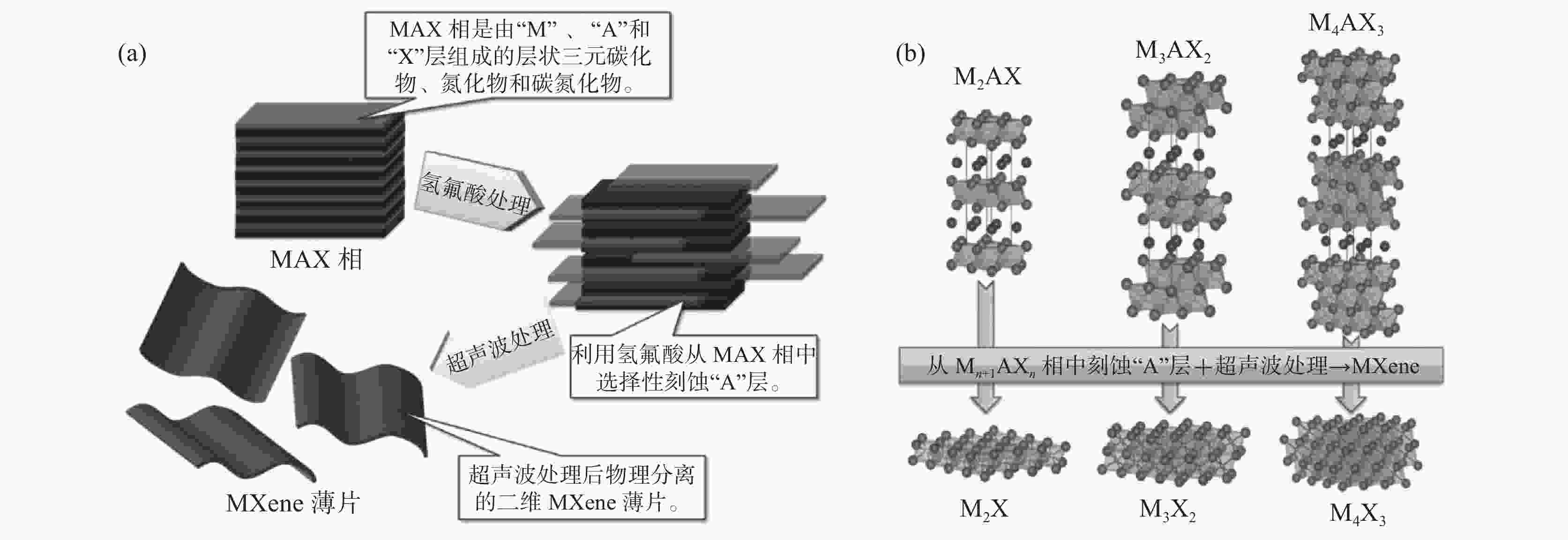
 下载:
下载: