Research on TIG welding organizational and performance of TC4 forge alloy
-
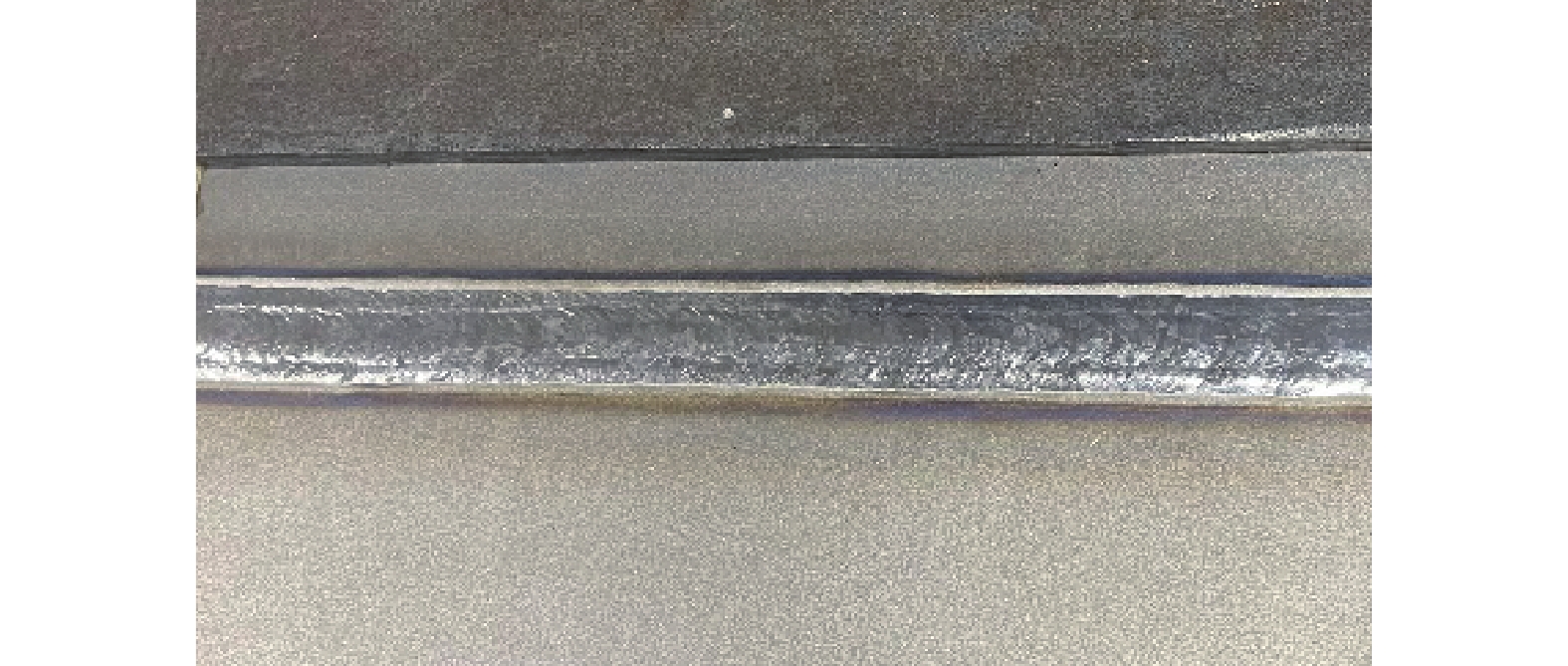
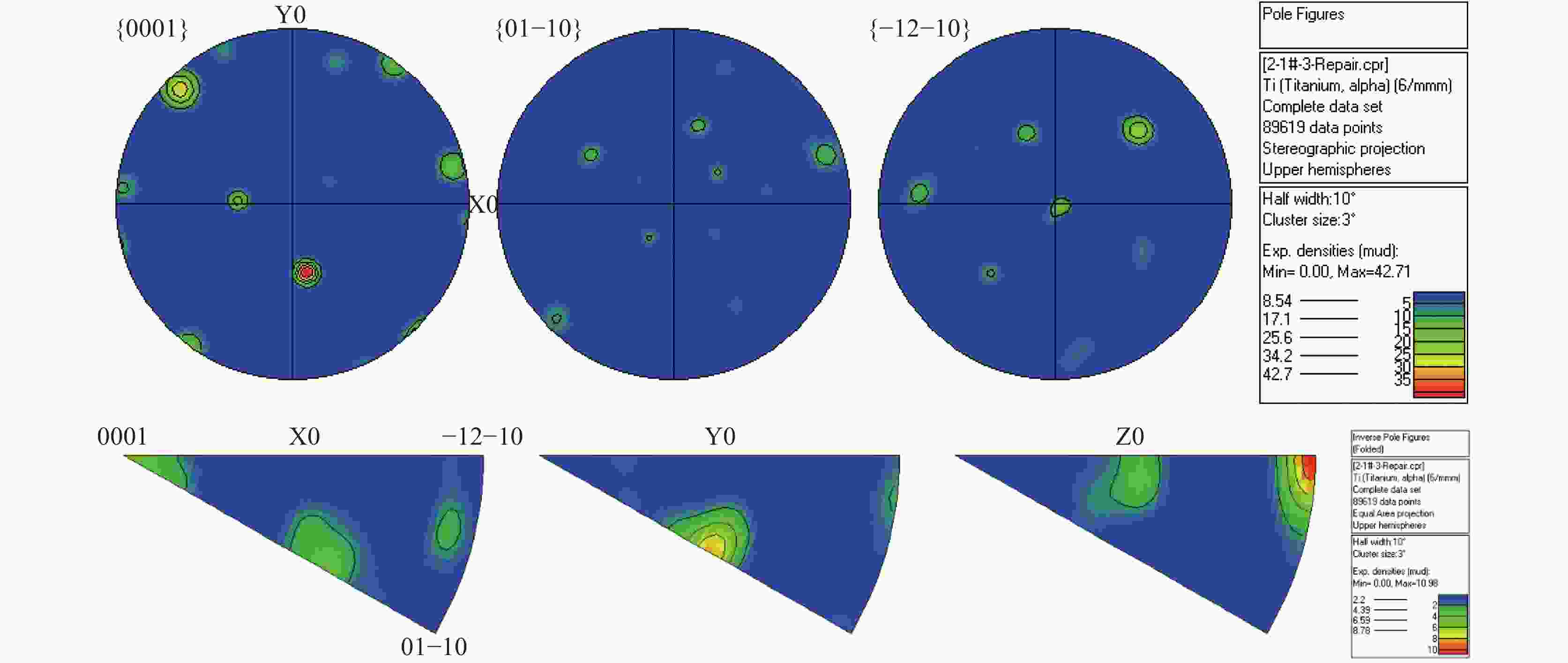
摘要: 采用非熔化极钨极氩弧焊(TIG)对厚度14 mm的TC4锻态钛合金板材进行多层多道对接焊接试验,研究了焊接接头的金相组织、晶体取向、力学性能。结果表明:TC4钛合金焊接接头焊缝成形美观,焊核区组织多为柱状晶和细长针状马氏体α′相,热影响区为(α+β)+α′相,母材区为(α+β)相。对应于晶体取向关系,焊核区晶粒交错分布按不同物相呈现一定择优取向,其中打底焊位置晶粒取向更多沿<111>与<001>方向,而母材晶粒取向分布不均匀。焊接件的抗拉强度和断后延伸率分别为982 MPa和6.0%,低于母材,弯曲试验均产生裂纹或断裂。从焊缝中心到母材,接头硬度值呈现先降低后升高的变化趋势,其中焊核区盖面焊层的显微硬度略低于打底焊层。Abstract: TC4 forged titanium plates with a thickness of 14 mm were multi-layer and multi-pass butt welded by non-melting tungsten inert gas welding (TIG), and the metallographic structure, crystal orientation and mechanical properties of the joints were investigated. The results show that the weld seams of TC4 titanium alloy welding joints are nicely formed, and the welding zone microstructure is mainly composed of columnar crystal and elongated acicular martensite α' phase. The microstructure of heat-affected zone is (α+β)+α′ phase, and base metal microstructure is (α+β) phase. Corresponding to the crystal orientation relationship, the grain interlacing distribution in the welding zone shows a certain preferred orientation according to different phases, among which the <111> and <001> direction is more preferred for the grain orientation at the bottom welding position, while the grain orientation distribution of base metal is not uniform. The tensile strength and elongation after fracture of the welding joint are 982 MPa and 6.0%, respectively, which are lower than those of the base metal, and all the bending tests produce cracks or fractures. The joint hardness first decreases and then increases from welding zone center to base metal, with the microhardness of the welding zone cover weld layer is slightly lower than that in the bottom weld layer.
-
Key words:
- titanium alloy /
- TIG welding /
- microstructure /
- EBSD /
- mechanical properties
-
表 1 TC4钛合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of TC4 alloy
% Al V Fe C N H O Ti 5.5~6.75 3.5~4.5 0.30 0.08 0.05 0.015 0.20 余量 表 2 焊接工艺参数
Table 2. Welding parameters
板厚/mm 焊缝层
道数焊接
电流/A焊接
电压/V焊接速度/(mm·min−1) 气体流量/(L·min−1) 14 12~15 110 17~18 60~120 18~20 表 3 ERTi6Al4V钛合金焊丝的化学成分
Table 3. Chemical composition of ERTi6Al4V alloy
% Ti Al V Fe O C N H 余量 5.5~6.75 3.5~4.5 0.25 0.18 0.05 0.05 0.012 表 4 TC4钛合金接头晶粒分析结果
Table 4. Grain analysis results of TC4 welding joint
位置 Area/µm² D/µm Major/µm GOS/° 位置 Area/µm² D/µm Major/µm GOS/° 盖面焊 13.80 3.18 5.06 0.97 打底焊 22.76 3.49 4.99 0.86 填充焊 14.02 3.32 4.92 0.92 母材区 35.66 5.03 6.29 2.70 表 5 拉伸性能
Table 5. Tensile mechanical properties
试样编号 抗拉强度σb /MPa 断后延伸率δ/% 断裂位置 焊接件-1 988 6.0 焊缝 焊接件-2 975 5.5 焊缝 母材-1 1021 14.0 标距内 母材-2 1035 15.5 标距内 -
[1] Li Qiuze, Shan Wei, Zhang Yingchun, et al. Technological development and prospect of China`s high speed EMU bogies[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2023(2):14-35. (李秋泽, 单巍, 张英春, 等. 中国高速动车组转向架技术发展及展望[J]. 机车电传动, 2023(2):14-35.Li Qiuze, Shan Wei, Zhang Yingchun, et al. Technological development and prospect of China`s high speed EMU bogies[J]. Electric Drive for Locomotives, 2023(2): 14-35. [2] Duan Shihui, Xu Shifeng, Li Lidong, et al. Research on key technology of bogies of railway rapid freight car[J]. Rolling Stock, 2022,60(4):6. (段仕会, 徐世锋, 李立东, 等. 铁路快捷货车转向架关键技术研究[J]. 铁道车辆, 2022,60(4):6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2022.04.013Duan Shihui, Xu Shifeng, Li Lidong, et al. Research on key technology of bogies of railway rapid freight car[J]. Rolling Stock, 2022, 60(4): 6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7602.2022.04.013 [3] Guo F, Wu S C, Liu J X, et al. Fatigue life assessment of bogie frames in high-speed railway vehicles considering gear meshing[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2020, 132:105353. [4] Feng Shengrong, Ming Zhu, Bai Guanshun, et al. Microstructure and properties of TA15 titanium alloy fabricated by wire and arc additive manufacturing[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2023,46(4):101-105. (丰生荣, 明珠, 柏关顺, 等. 电弧增材制造TA15钛合金的组织与性能研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2023,46(4):101-105.Feng Shengrong, Ming Zhu, Bai Guanshun, et al. Microstructure and properties of TA15 titanium alloy fabricated by wire and arc additive manufacturing[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2023, 46(4): 101-105. [5] Chen Caina, Zeng Zhi, Zhang Yao, et al. Effect of thermal isostatic pressing on microstructure and properties of TB6 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2023,52(7):110-112. (陈彩娜, 曾志, 张耀, 等. 热等静压工艺对TB6钛合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2023,52(7):110-112.Chen Caina, Zeng Zhi, Zhang Yao, et al. Effect of thermal isostatic pressing on microstructure and properties of TB6 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2023, 52(7): 110-112. [6] Zhang Le, Liu Yingying, Shi Xiaonan, et al. Microstructure and tensile properties of TC18 titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2017,38(6):54-60. (张乐, 刘莹莹, 史晓楠, 等. TC18钛合金的显微组织及拉伸性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2017,38(6):54-60.Zhang Le, Liu Yingying, Shi Xiaonan, et al. Microstructure and tensile properties of TC18 titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2017, 38(6): 54-60. [7] Zhao Xiaolong, Wang Bin, Gong Shuili, et al. Study on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded joint of 2 mm thick TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017(9):3. (赵晓龙, 王彬, 巩水利, 等. 2.0mm厚TC4钛合金激光焊接接头组织与力学性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017(9):3.Zhao Xiaolong, Wang Bin, Gong Shuili, et al. Study on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded joint of 2 mm thick TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017(9): 3. [8] Pramod Kumar, Sinha A. Effect of heat input in pulsed Nd: YAG laser welding of titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) on microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Neurosurgical Sciences, 2019,63(3):673-689. [9] Mou Gang, Hua Xueming, Xu Xiaobo, et al. Comparative study on welding procedure and performance of 8 mm thick TC4 titanium alloy with TIG and MIG[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2020,50(4):7. (牟刚, 华学明, 徐小波, 等. 8mm厚TC4钛合金TIG, MIG焊接工艺及性能对比研究[J]. 电焊机, 2020,50(4):7.Mou Gang, Hua Xueming, Xu Xiaobo, et al. Comparative study on welding procedure and performance of 8 mm thick TC4 titanium alloy with TIG and MIG[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2020, 50(4): 7. [10] Lu Xin. Microstructures and defect analysis of TC4 titanium alloy joints by the TIG welding[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(4):7. (陆鑫. TC4钛合金TIG焊接头组织及缺陷分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(4):7. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.04.013Lu Xin. Microstructures and defect analysis of TC4 titanium alloy joints by the TIG welding[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39(4): 7. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.04.013 [11] Gao Xiaogang, Dong Junhui, Han Xu. Effect of microstructure on properties of TIG welded joint for TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Welding & Joining, 2016(7):5. (高晓刚, 董俊慧, 韩旭. TC4钛合金TIG焊接头组织对性能的影响[J]. 焊接, 2016(7):5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2016.07.006Gao Xiaogang, Dong Junhui, Han Xu. Effect of microstructure on properties of TIG welded joint for TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Welding & Joining, 2016(7): 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2016.07.006 [12] Wei Zhixiang, Li Guoxuan, Wang Yueyong, et al. Microstructure and properties of TC4 titanium alloy produced by TIG arc additive manufacturing[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2021,11(10):7. (魏志祥, 李国选, 汪月勇, 等. TIG电弧增材制造TC4钛合金的组织与性能[J]. 有色金属工程, 2021,11(10):7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2021.10.003Wei Zhixiang, Li Guoxuan, Wang Yueyong, et al. Microstructure and properties of TC4 titanium alloy produced by TIG arc additive manufacturing[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2021, 11(10): 7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2021.10.003 [13] Wang Xuyang, Quan Yinzhu, Li Ju, et al. Microstructure and texture evolution in linear friction welded TC11 titanium alloy joint[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2023,47(5):692-700. (王旭扬, 权银洙, 李菊, 等. TC11钛合金线性摩擦焊接头组织及织构演变机制[J]. 稀有金属, 2023,47(5):692-700.Wang Xuyang, Quan Yinzhu, Li Ju, et al. Microstructure and texture evolution in linear friction welded TC11 titanium alloy joint[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2023, 47(5): 692-700. -





 下载:
下载: