Microstructures, properties and high-temp oxidation behaviors of Ti-45Al-8Nb-xHf alloys
-
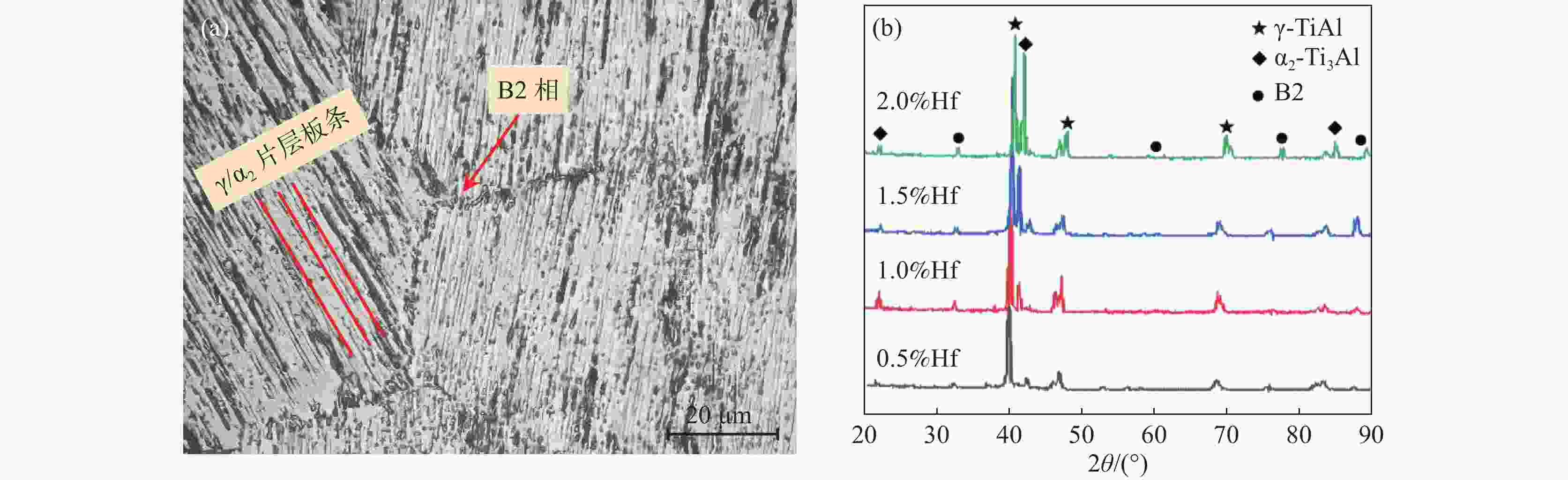
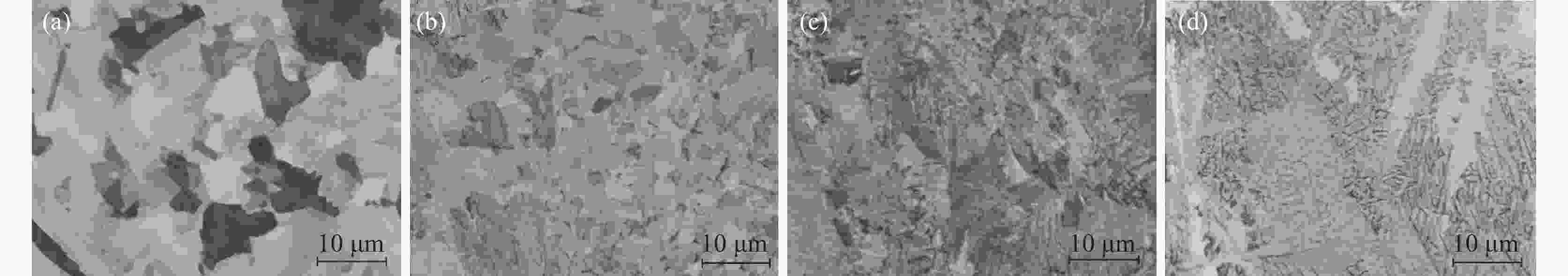
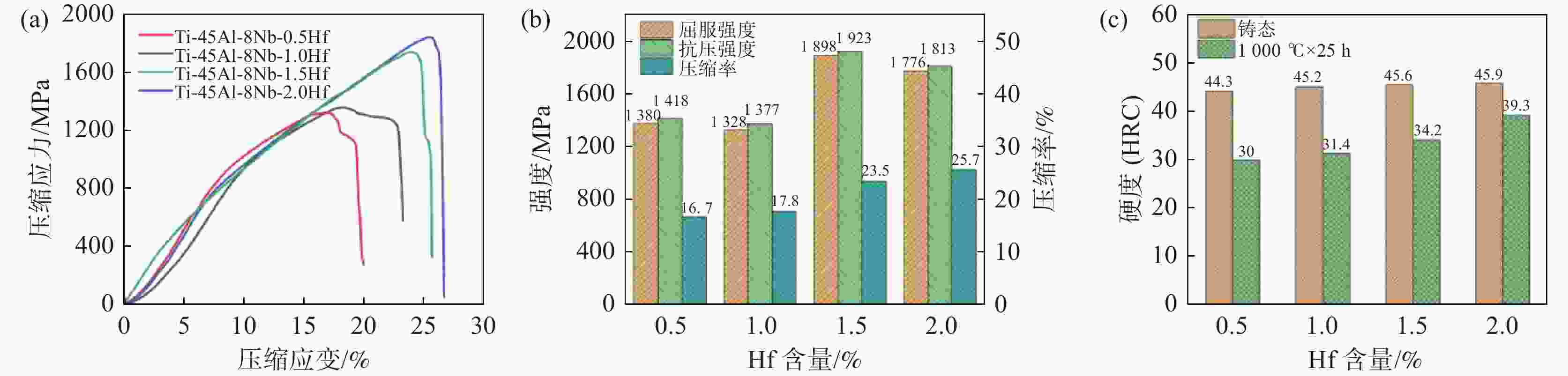
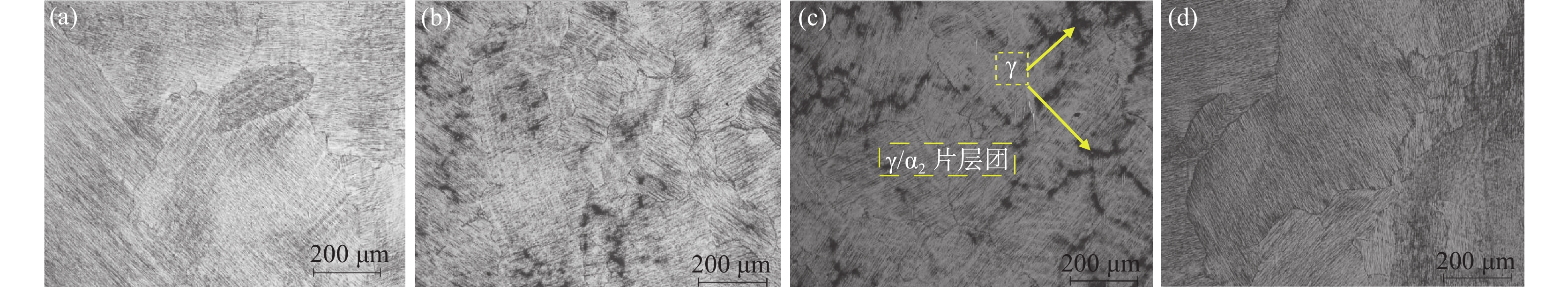
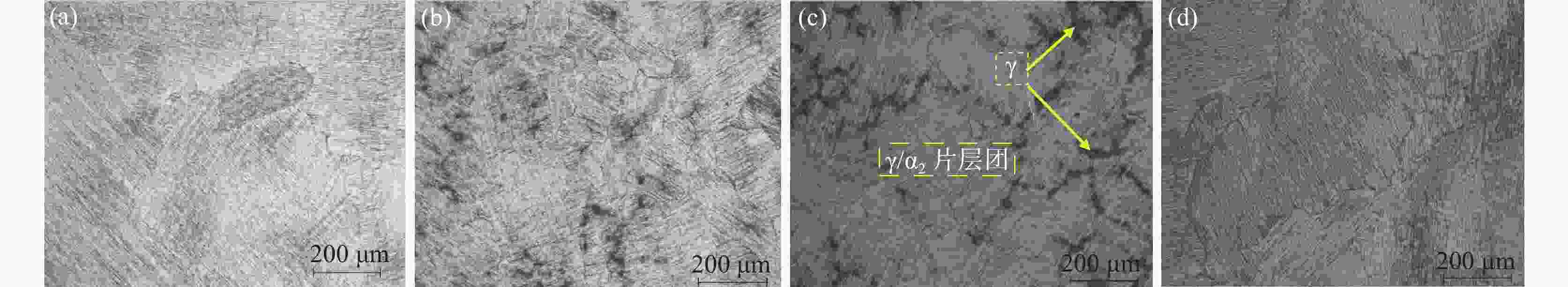
摘要: 采用氩气保护真空感应熔炼工艺制备了Ti-45Al-8Nb-xHf (x=0.5、1.0、1.5、2) 合金,利用金相显微镜(OM)、扫描电镜(SEM)、能谱仪 (EDS)、X射线衍射仪(XRD)、万能试验机等研究了合金显微组织、压缩性能和抗氧化性能。结果表明,Hf元素含量的增加能够保持和细化合金显微组织,延缓高温下组织的转变,使合金抗压强度和压缩率分别提高到1923 MPa和25.7%,升幅30%以上,具有显著强化效应。合金在
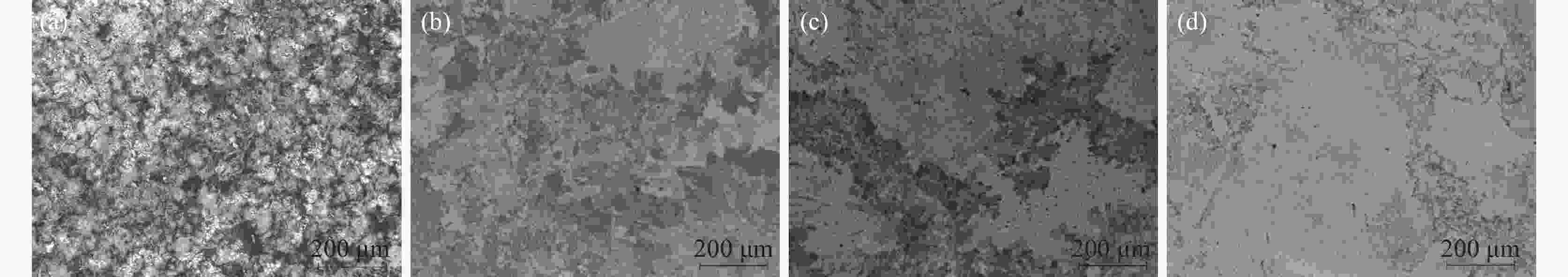
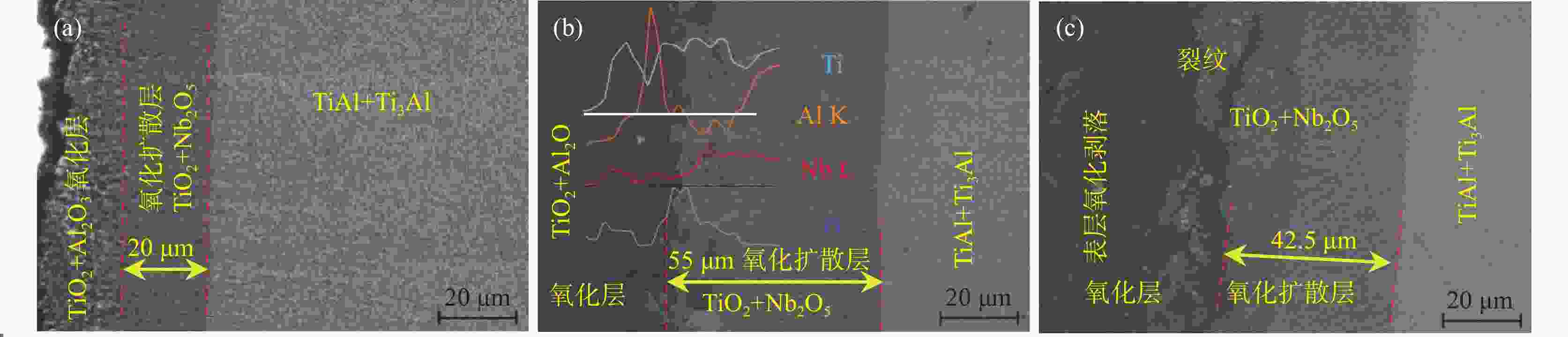
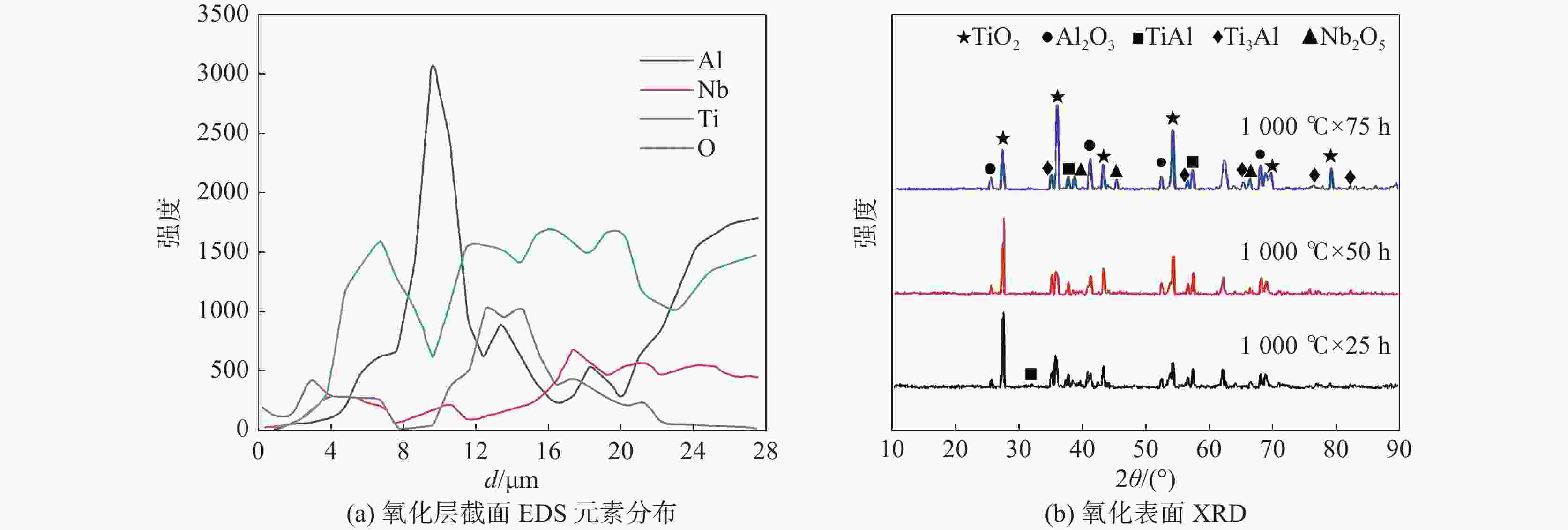
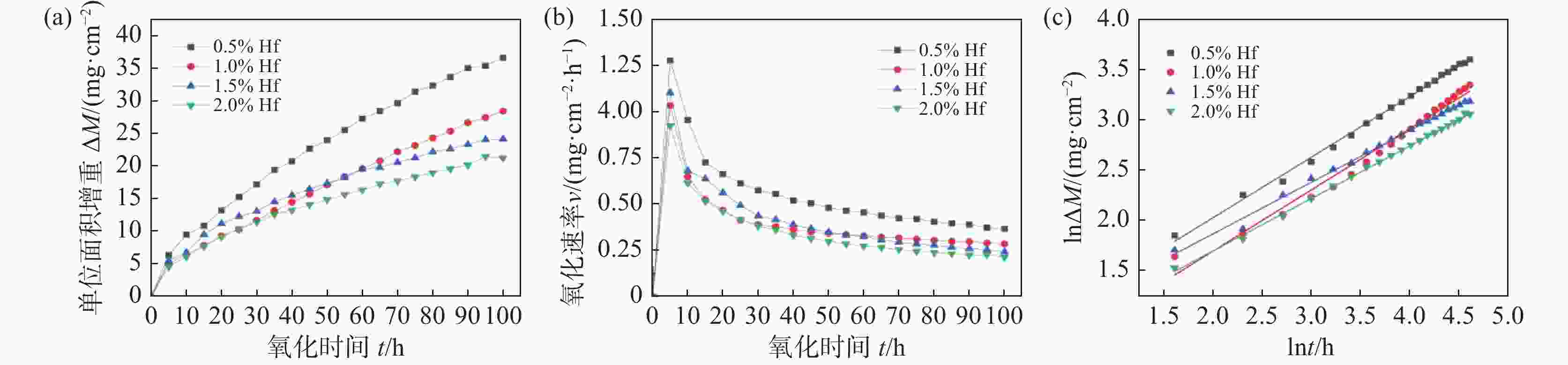
1000 ℃氧化时具有稳定TiO2+Nb2O5的氧化亚层,以平直界面氧化生长,氧化扩散层尺寸稳定小于85 μm,氧化质量呈线性变化,氧化速率曲线下降并最终达到稳定氧化阶段。适量Hf的添加有利于强化合金的力学性能和高温抗氧化性能。-
关键词:
- Ti-45Al-8Nb-xHf /
- 力学性能 /
- 显微组织 /
- 抗氧化性
Abstract: Ti-45Al-8Nb-xHf (x=0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2) alloys were prepared by argon-protected vacuum induction melting process, and the microstructure, compressive properties and antioxidant properties of the alloys were investigated by using optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy spectrum spectrometry (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and universal testing machine. The results show that the increase of Hf element content can maintain and refine the microstructure of the alloys, delay the transformation of the tissue at high temperature, and increase the compressive strength and compression ratio of the alloys to1923 MPa and 25.7%, respectively, with an increase of more than 30%, which has a significant strengthening effect. The alloys have a stable TiO2+Nb2O5 oxide sublayer when oxidized at1000 ℃, which grows by oxidation at a flat interface, the size of the oxide diffusion layer is stable less than 85 μm, the oxidized quality changes linearly, and the oxidation rate curve decreases and finally reaches the stable oxidation stage. The addition of appropriate amount of Hf is conducive to strengthening the mechanical properties of the alloys and high-temperature oxidation resistance.-
Key words:
- Ti-45Al-8Nb-xHf /
- mechanical properties /
- microstructure /
- oxidation resistance
-
表 1 TiAl基多元合金铸锭化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of test alloys with different Hf contents
% Al Nb xHf Ti 45.0 8.0 0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 Bal. 表 2 合金
1000 ℃氧化动力学参数Table 2. Kinetic parameters of oxidation at
1000 ℃合金 n kn R2 t/h Ti-45Al-8Nb-0.5Hf 1.659 0.602 0.9963 0~100 Ti-45Al-8Nb-1.0Hf 1.640 0.609 0.9772 0~100 Ti-45Al-8Nb-1.5Hf 1.944 0.522 0.9947 0~100 Ti-45Al-8Nb-2.0Hf 1.914 0.514 0.9985 0~100 -
[1] Chen Yuyong, Wu Jingxi. Research and advances in processing, working, microstructure, properties and industrial application of β-solidifying TiAl alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titaniun, 2021,42(6):1-16. (陈玉勇, 吴敬玺. β相凝固TiAl合金的制备、加工、组织、性能及工业应用研究进展[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(6):1-16. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.06.001Chen Yuyong, Wu Jingxi. Research and advances in processing, working, microstructure, properties and industrial application of β-solidifying TiAl alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titaniun, 2021, 42(6): 1-16. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.06.001 [2] Zhu Dongdong, Yan Jiangfei, Jin Yuliang, et al. Pressure-induced excellent corrosion resistance of Ti-45Al-8Nb alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2024,355:135446. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2023.135446 [3] Chandran Anju, Ganesan Hariprasath, Cyron Christian J. Studying the effects of Nb on high-temperature deformation in TiAl alloys using atomistic simulations[J]. Materials & Design, 2024,237:112596. [4] Cao Jun, Sun Tielong, Guo Zhichao, et al. Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility in high Nb-TiAl by Si alloying[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024,177:128-132. [5] Guo Yingchao, Liang Yongfeng, Sun Dingbang, et al. Refinement and enhancement of high-Nb TiAl alloy via in-situ precipitation of Ti2AlC and TiB2 nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024,29:1052-1065. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.01.122 [6] Imayev V M, Ganeev A A, Trofimov D M, et al. Effect of Nb, Zr and Zr+Hf on the microstructure and mechanical properties of β-solidifying γ-TiAl alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021,817:141388. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141388 [7] Jack Nelson, Mohammad Ghadyani, Claire Utton, et al. A study of the effects of Al, Cr, Hf, and Ti additions on the microstructure and oxidation of Nb-24Ti-18Si silicide based alloys[J]. Materials, 2018,11(9):1579-1579. doi: 10.3390/ma11091579 [8] Guo Fangyu, Holec David, Wang Jianchuan, et al. Impact of V, Hf and Si on oxidation processes in Ti-Al-N: Insights from ab initio molecular dynamics[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2020,381:125125. [9] Takeshi Nagase, Mitsuharu Todai, Wang Pan, et al. Design and development of (Ti, Zr, Hf)-Al based medium entropy alloys and high entropy alloys[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022,276:12-15. [10] Xiang Henggao, Chen Yang, Qi Zhixiang, et al. Mechanical behavior of TiAl alloys[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2023,66(9):2457-2480. doi: 10.1007/s11431-022-2186-9 [11] Huang Feng, Liang Sicheng, Hu Shangxing, et al. Status and progress in strengthening and toughening of TiAl alloy[J]. Specal Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2023,43(11):1441-1446. (黄锋, 梁思诚, 胡尚兴, 等. TiAl合金强韧化研究现状与进展[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2023,43(11):1441-1446.Huang Feng, Liang Sicheng, Hu Shangxing, et al. Status and progress in strengthening and toughening of TiAl alloy[J]. Specal Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2023, 43(11): 1441-1446. [12] Wang Zite, Zheng Gong, Qi Zixiang, et al. Structures, microstructures, properties, and applications of TiAl alloys[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2023,68:3259-3274. (王子特, 郑功, 祁志祥, 等. TiAl合金结构、组织、性能与应用[J]. 科学通报, 2023,68:3259-3274. doi: 10.1360/TB-2023-0037Wang Zite, Zheng Gong, Qi Zixiang, et al. Structures, microstructures, properties, and applications of TiAl alloys[J]. Chin Sci Bull, 2023, 68: 3259-3274. doi: 10.1360/TB-2023-0037 [13] Feng Lihan, Li Bo, Li Qiang, et al. Enhancement of mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of TiAl alloy with addition of Nb and Mo alloying elements[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2024,316:129148. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2024.129148 [14] Tian Shiwei, Zhang Tengkun, Zeng Shangwu, et al. Cyclic oxidation kinetics and thermal stress evolution of TiAl alloys at high temperature[J]. Metals, 2023,14(1):28. doi: 10.3390/met14010028 [15] Liu Renci, Wang Peng, Cao Ruxin, et al. Influence of thermal exposure at 700 oC on the microstructure and morphology in the surface of β-solidifying γ-TiAl alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2022,58(8):1003-1012. (刘仁慈, 王鹏, 曹如心, 等. 700 ℃热暴露对 β 凝固 γ-TiAl合金表面组织及形貌的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2022,58(8):1003-1012.Liu Renci, Wang Peng, Cao Ruxin, et al. Influence of thermal exposure at 700 oC on the microstructure and morphology in the surface of β-solidifying γ-TiAl alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2022, 58(8): 1003-1012. [16] Birks Nell. Introduction to the high temperature oxidation of meatals[M]. 2nd edition. Cambridge University, 2009: 101-157. [17] Jin Xuchen, Ye Peihao, Ji Hongrui, et al. Oxidation resistance of powder metallurgy Ti–45Al–10Nb alloy at high temperature[J]. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2022,29(12):2232-2240. doi: 10.1007/s12613-021-2320-4 [18] Lai Xuping, Li Tianfang, Liu Rui, et al. Effect of Nb, Hf and Zr on oxidation resistance of γ-TiAl alloy[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(Z1): 374-377. (赖旭平, 李天方, 刘瑞, 等. 元素Nb、Hf、Zr对γ-TiAl合金抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(Z1): 374-377.Lai Xuping, Li Tianfang, Liu Rui, et al. Effect of Nb, Hf and Zr on oxidation resistance of γ-TiAl alloy[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(Z1): 374-377. [19] Wang Yanjing, Li Fei. Study on the high-temperature oxidation resistance of Ti-45Al-8(Nb, Hf, Y)-0.2B alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016,45(1):132-136. (王艳晶, 李菲. Ti-45Al-8(Nb, Hf, Y)-0.2B合金高温抗氧化性研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016,45(1):132-136.Wang Yanjing, Li Fei. Study on the high-temperature oxidation resistance of Ti-45Al-8(Nb, Hf, Y)-0.2B alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(1): 132-136. -




 下载:
下载: