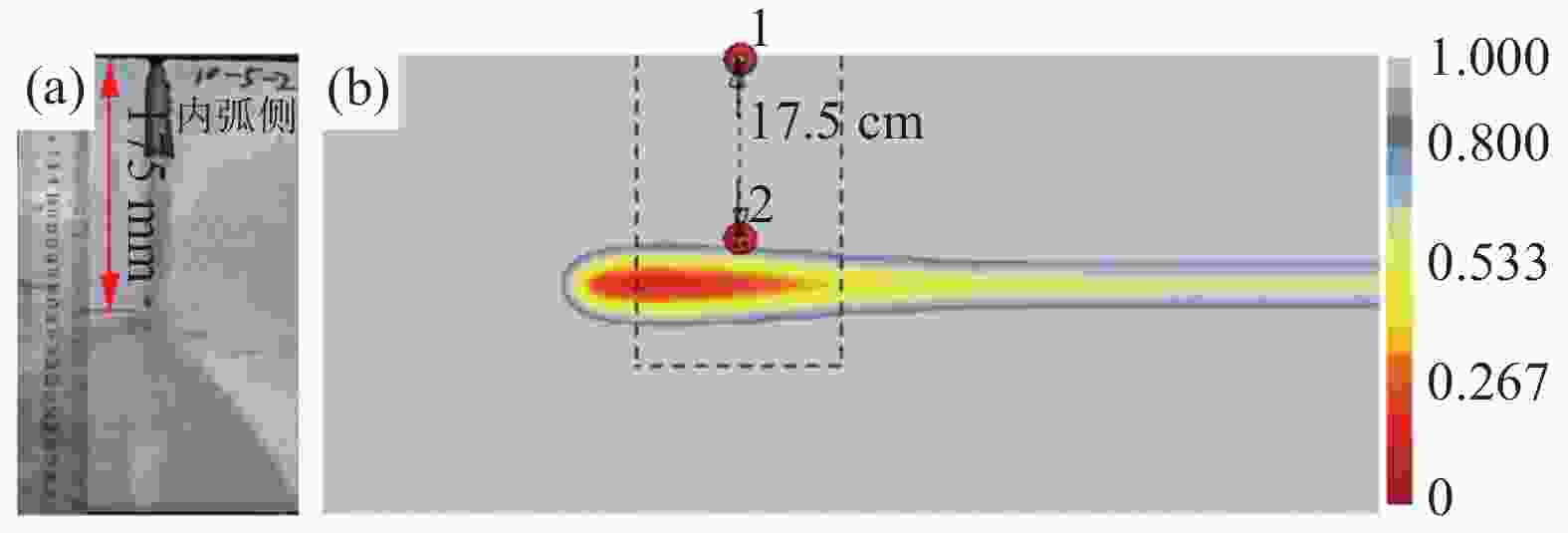
Numerical simulation of solidification process for Q345R thick slab continuous casting
-
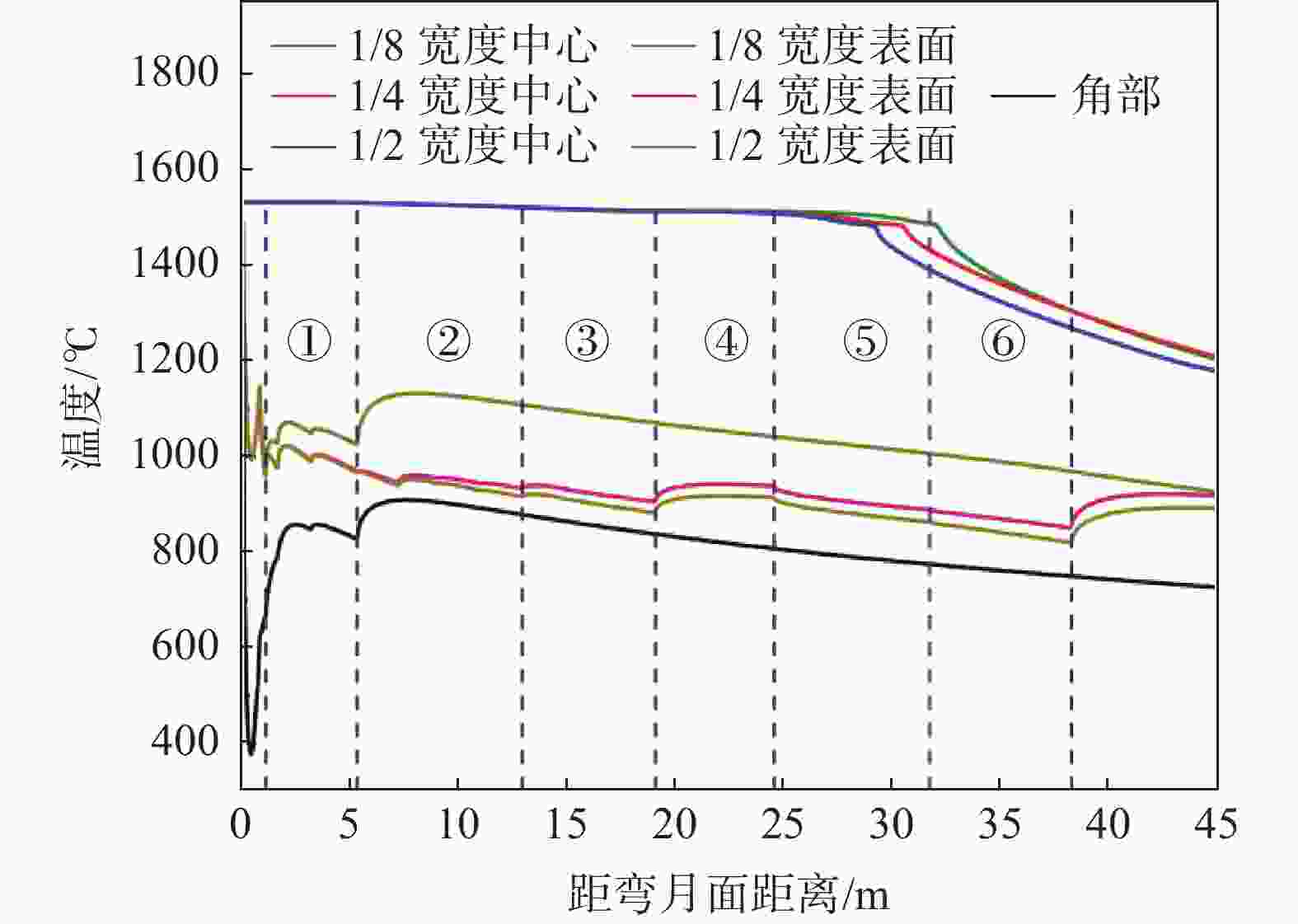
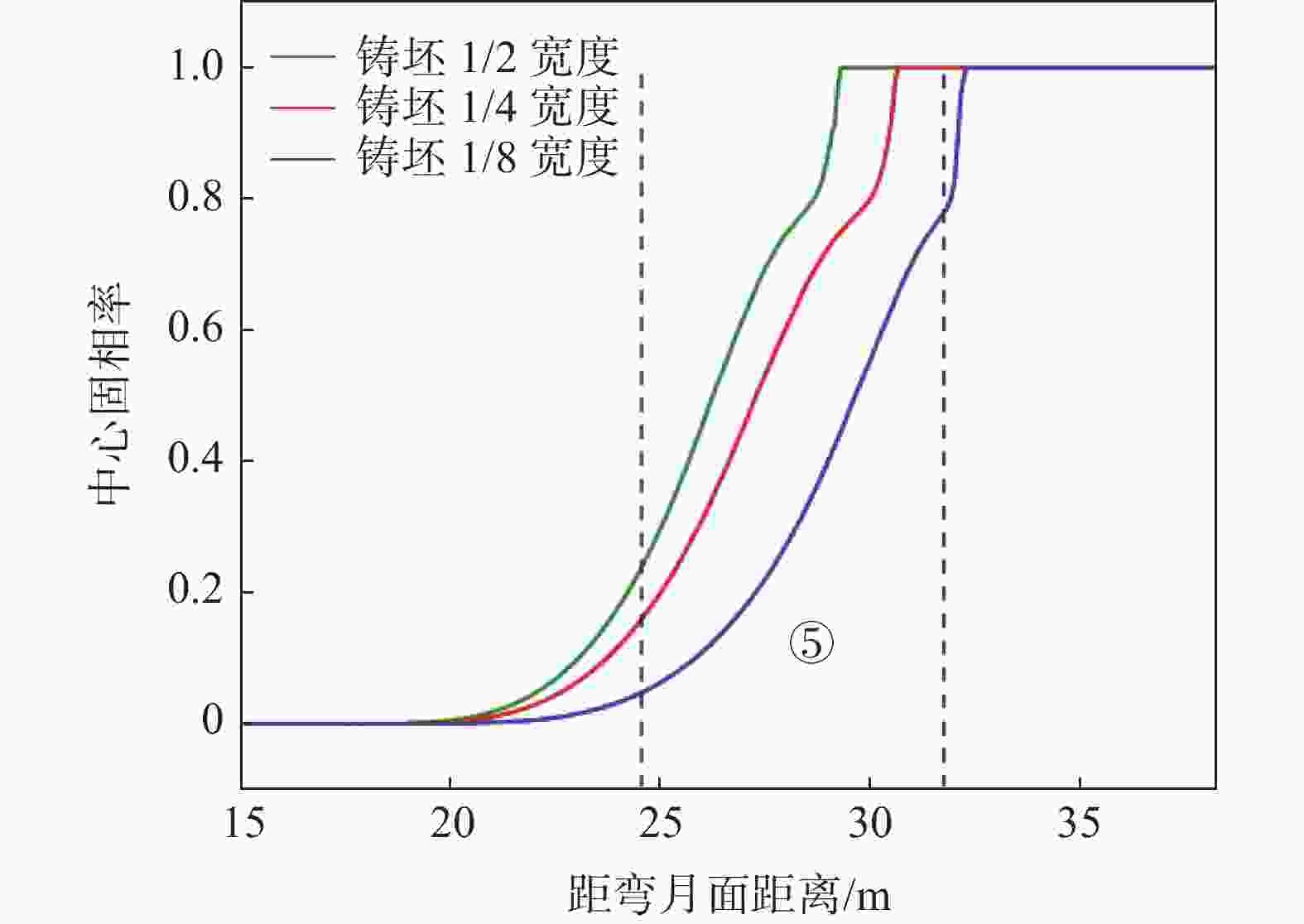
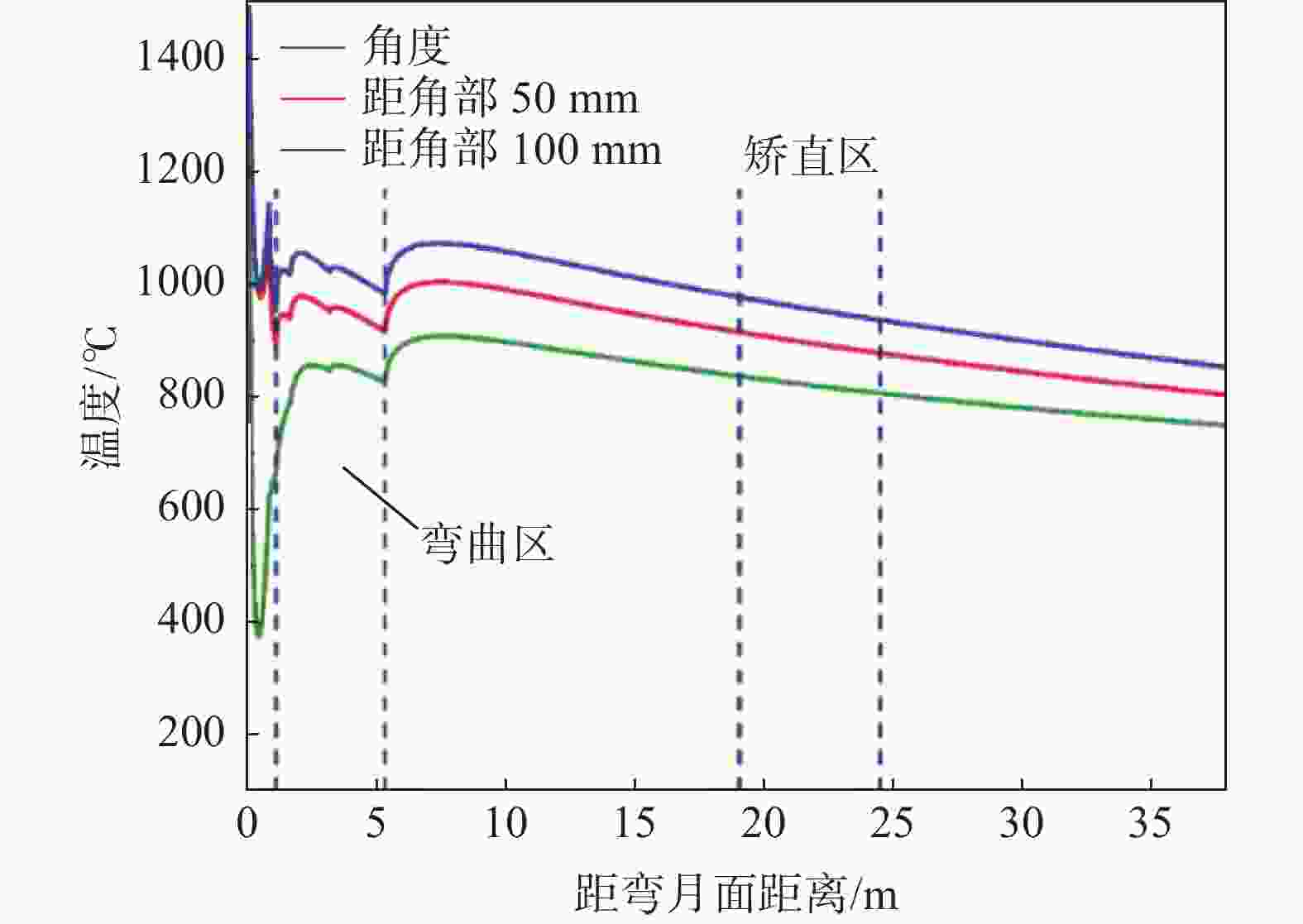
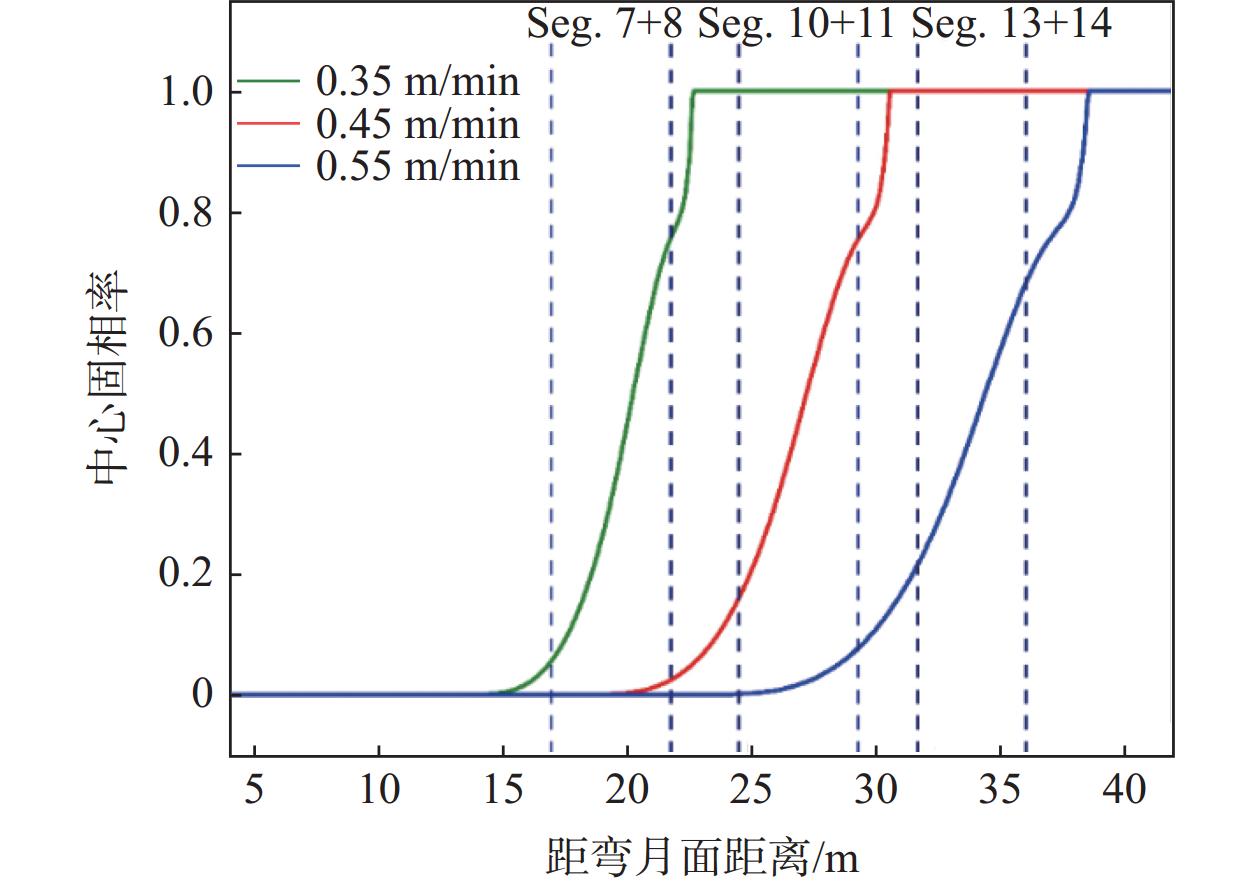
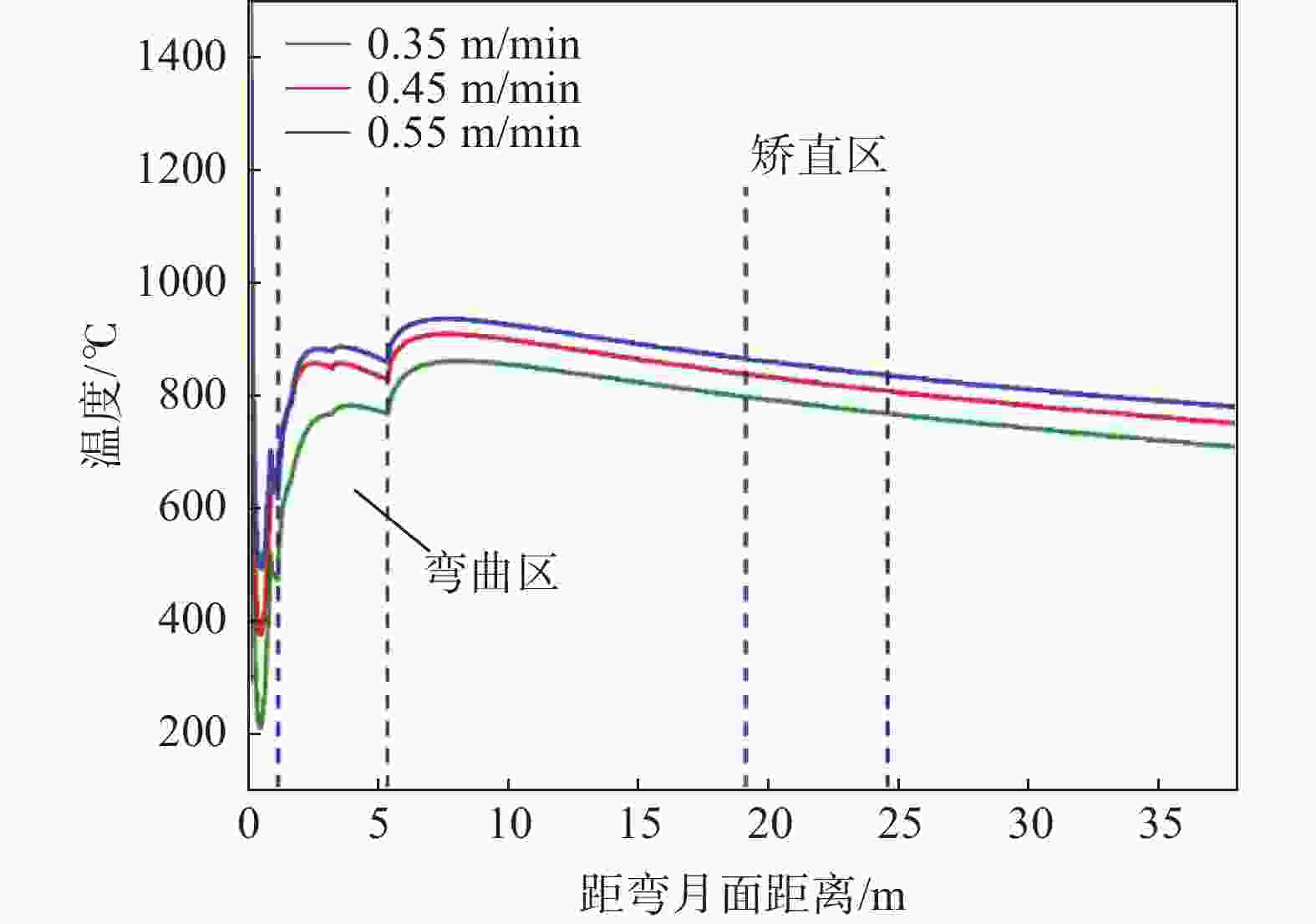
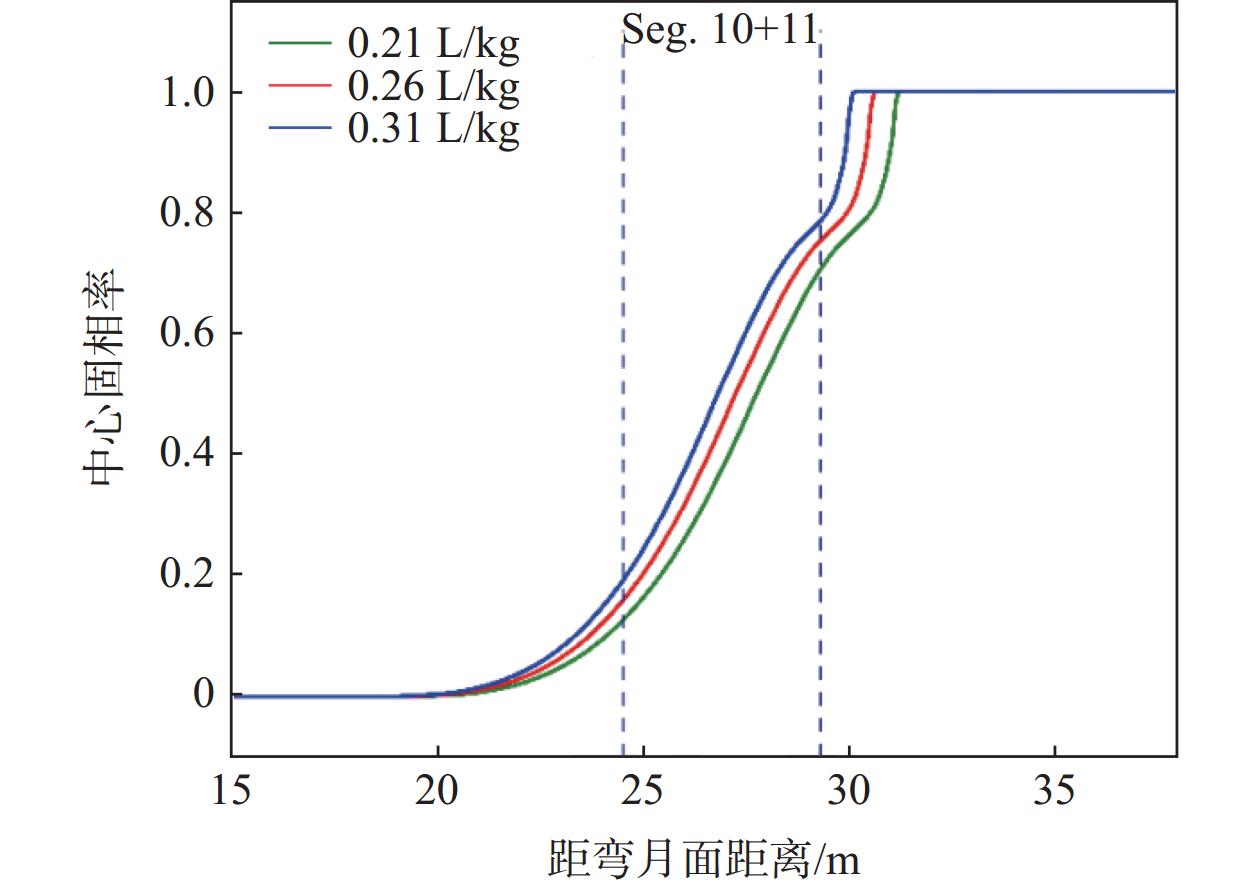
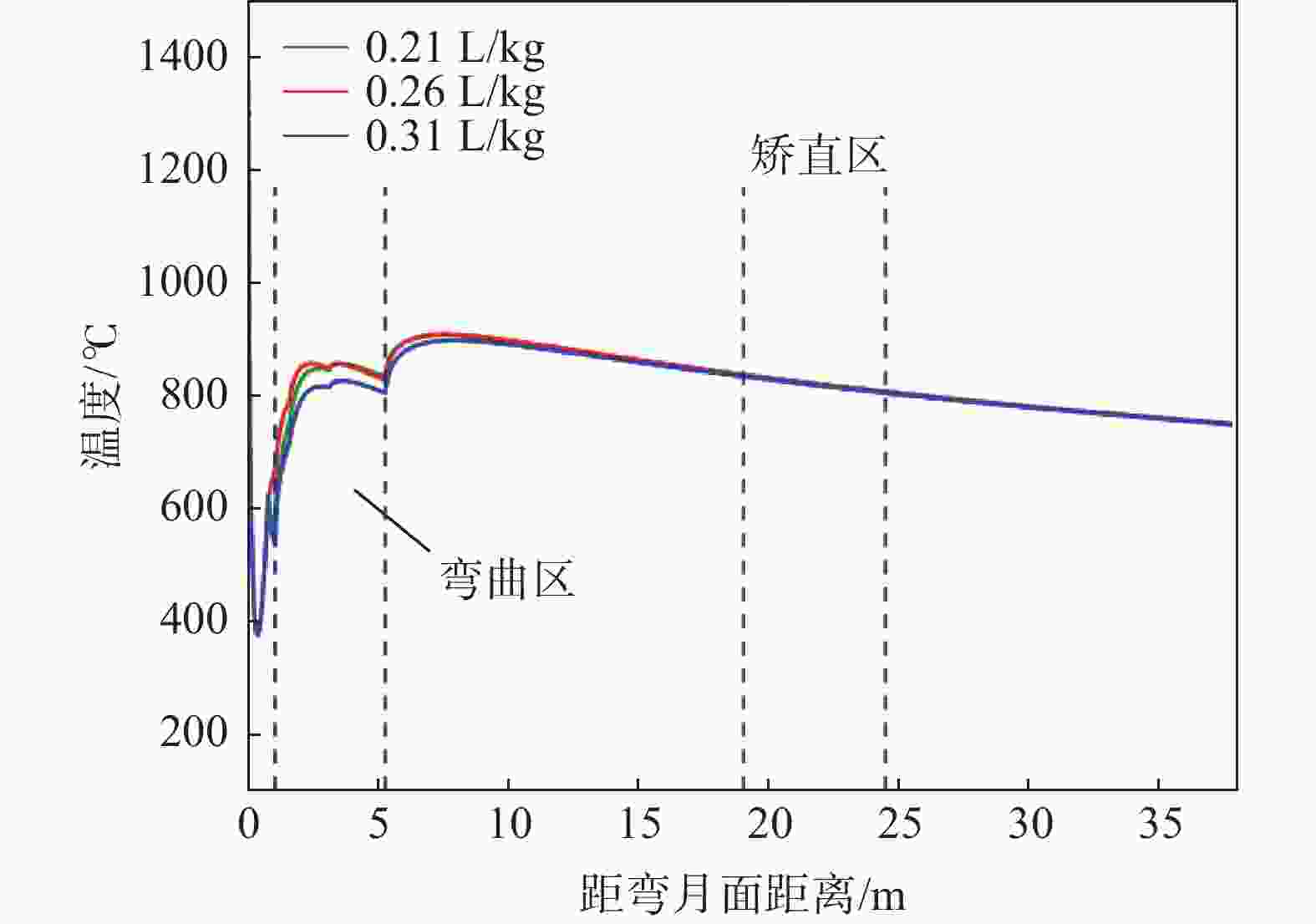
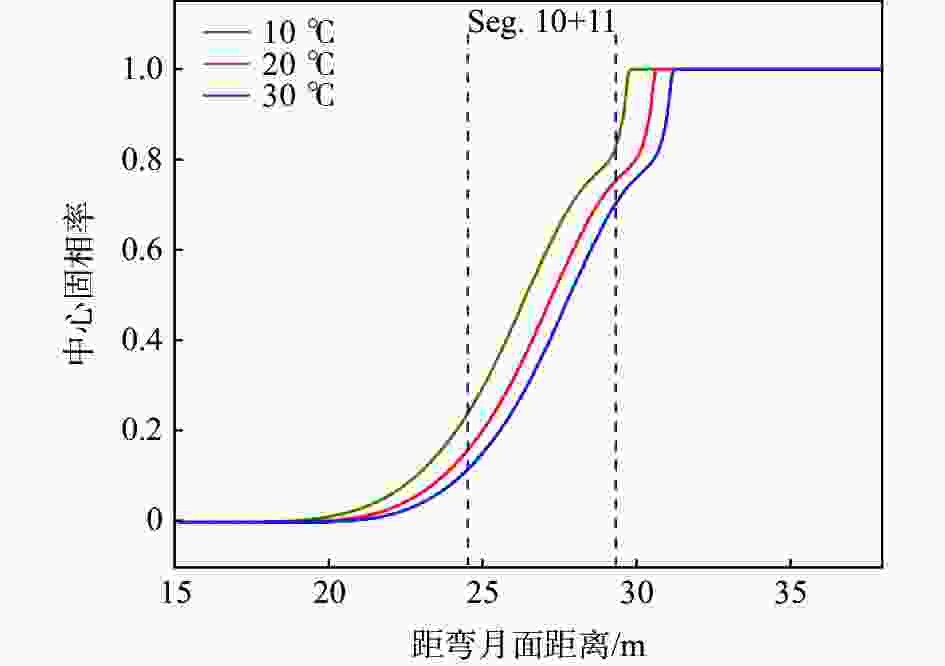
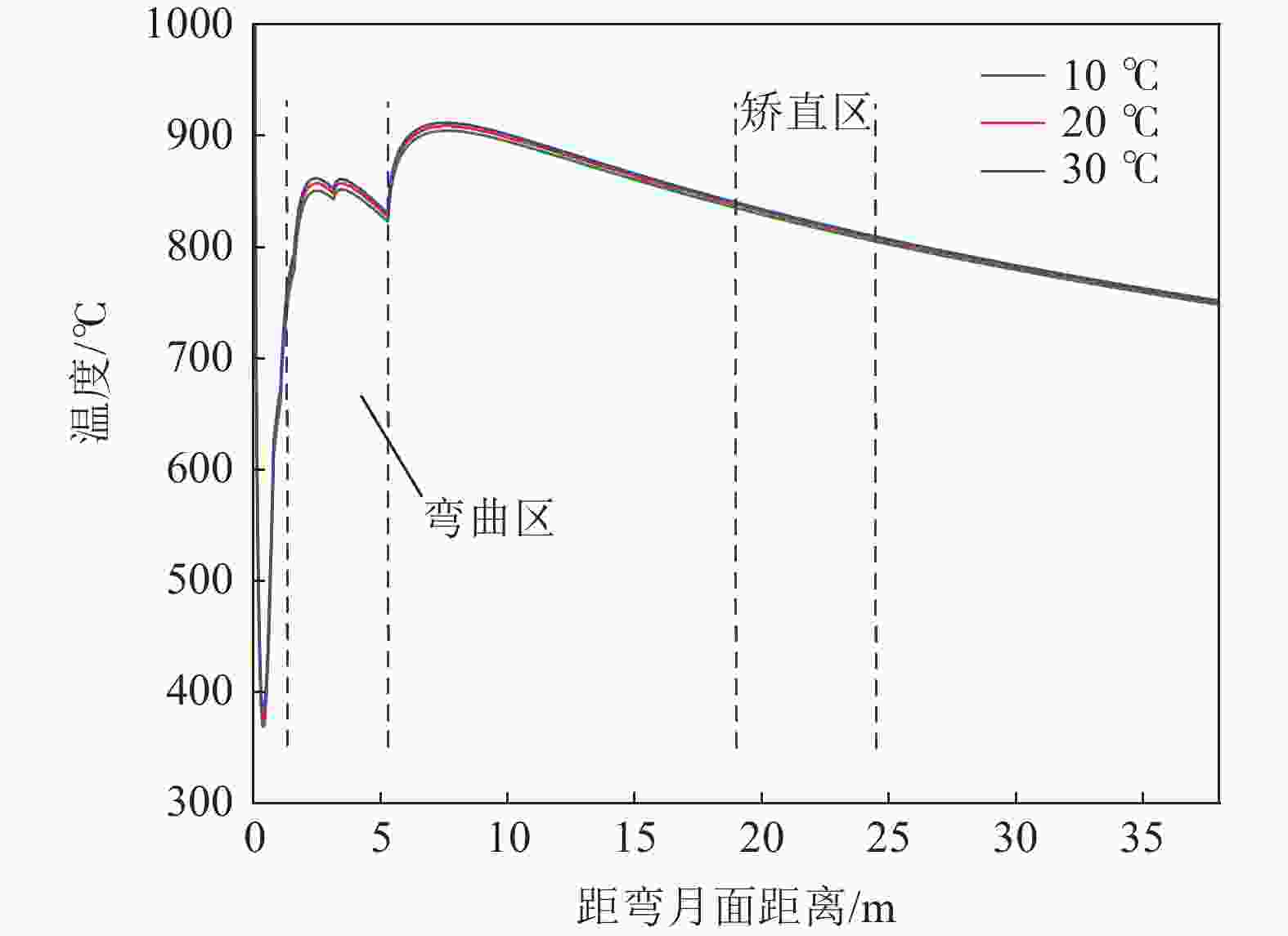
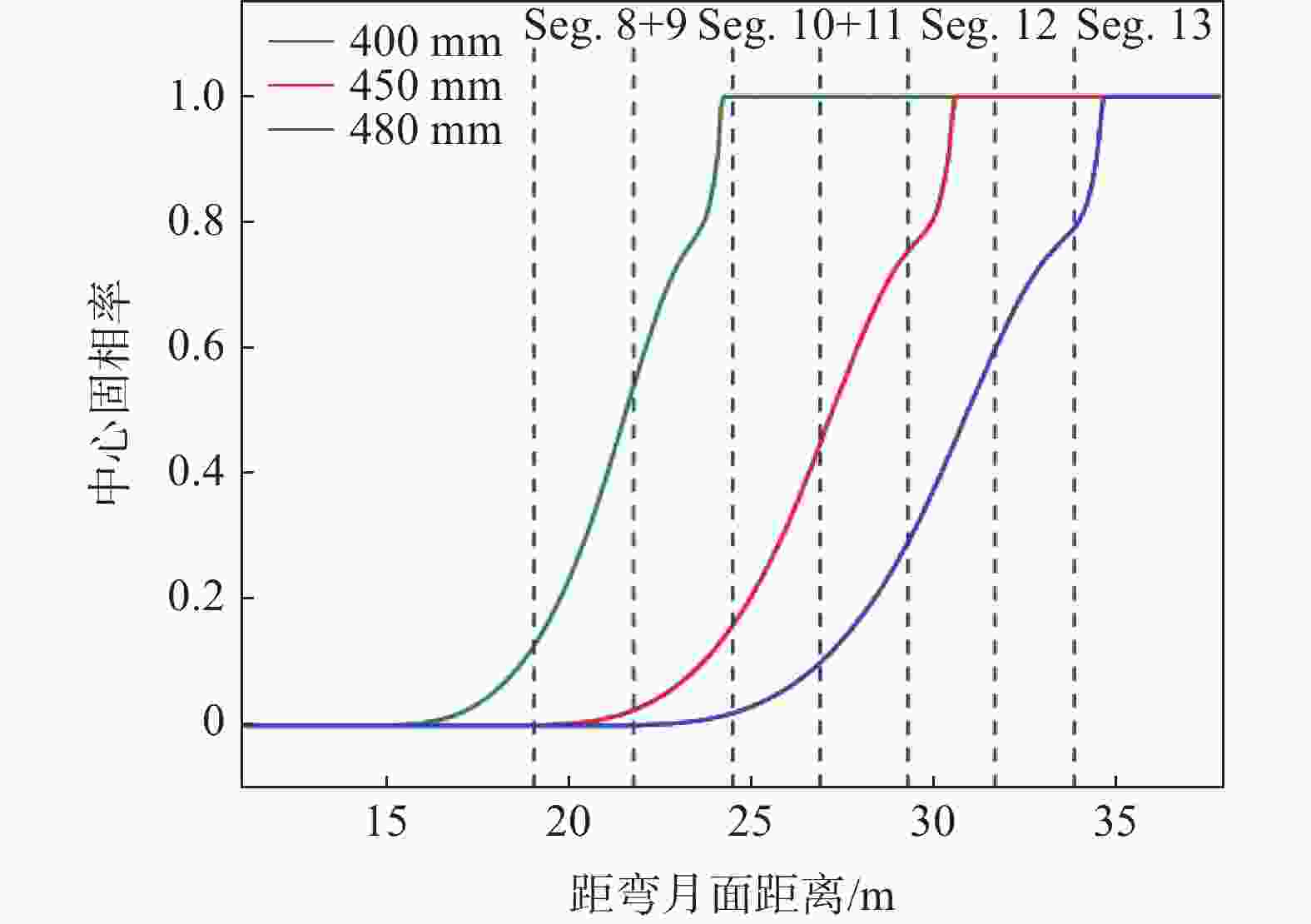
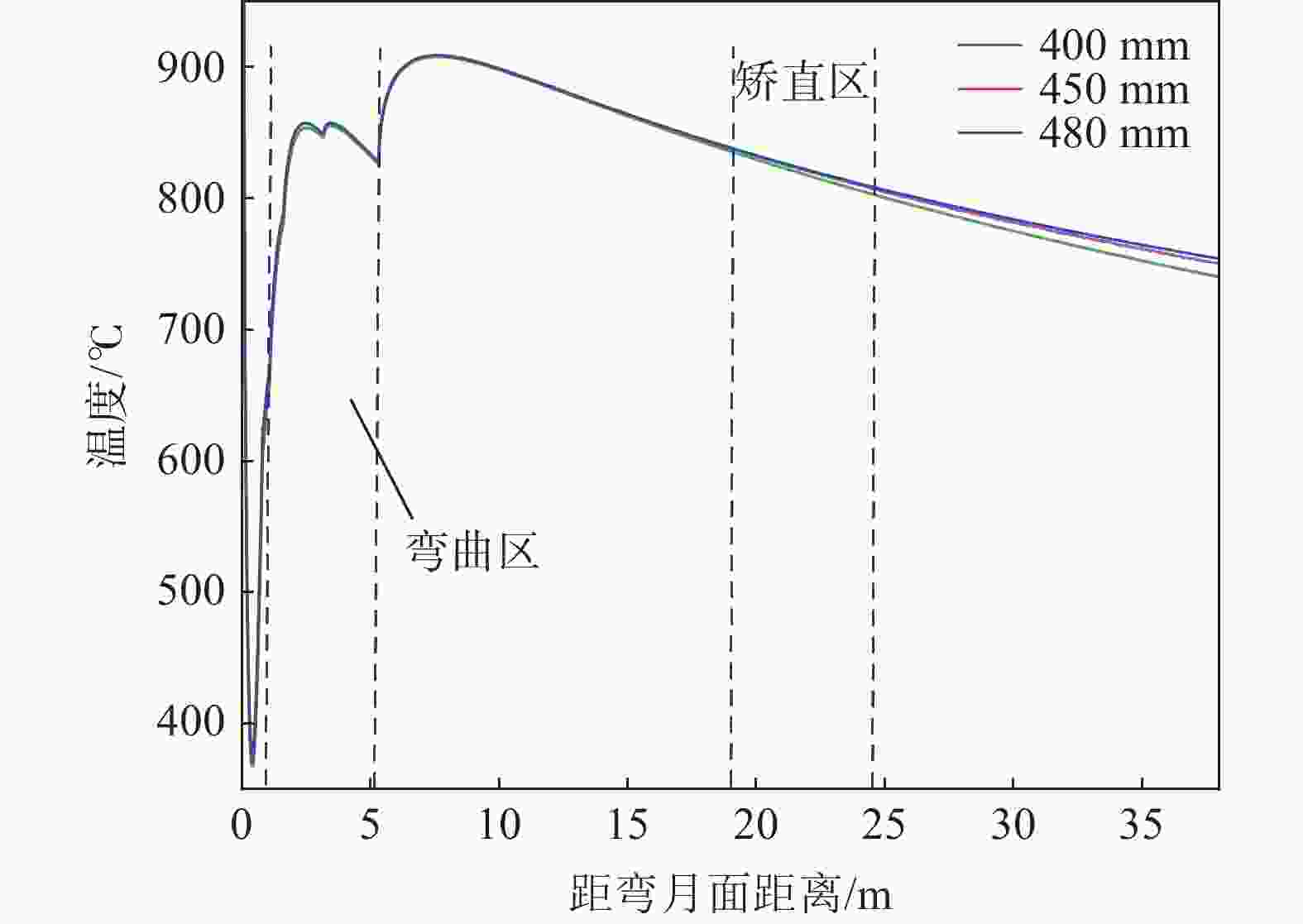
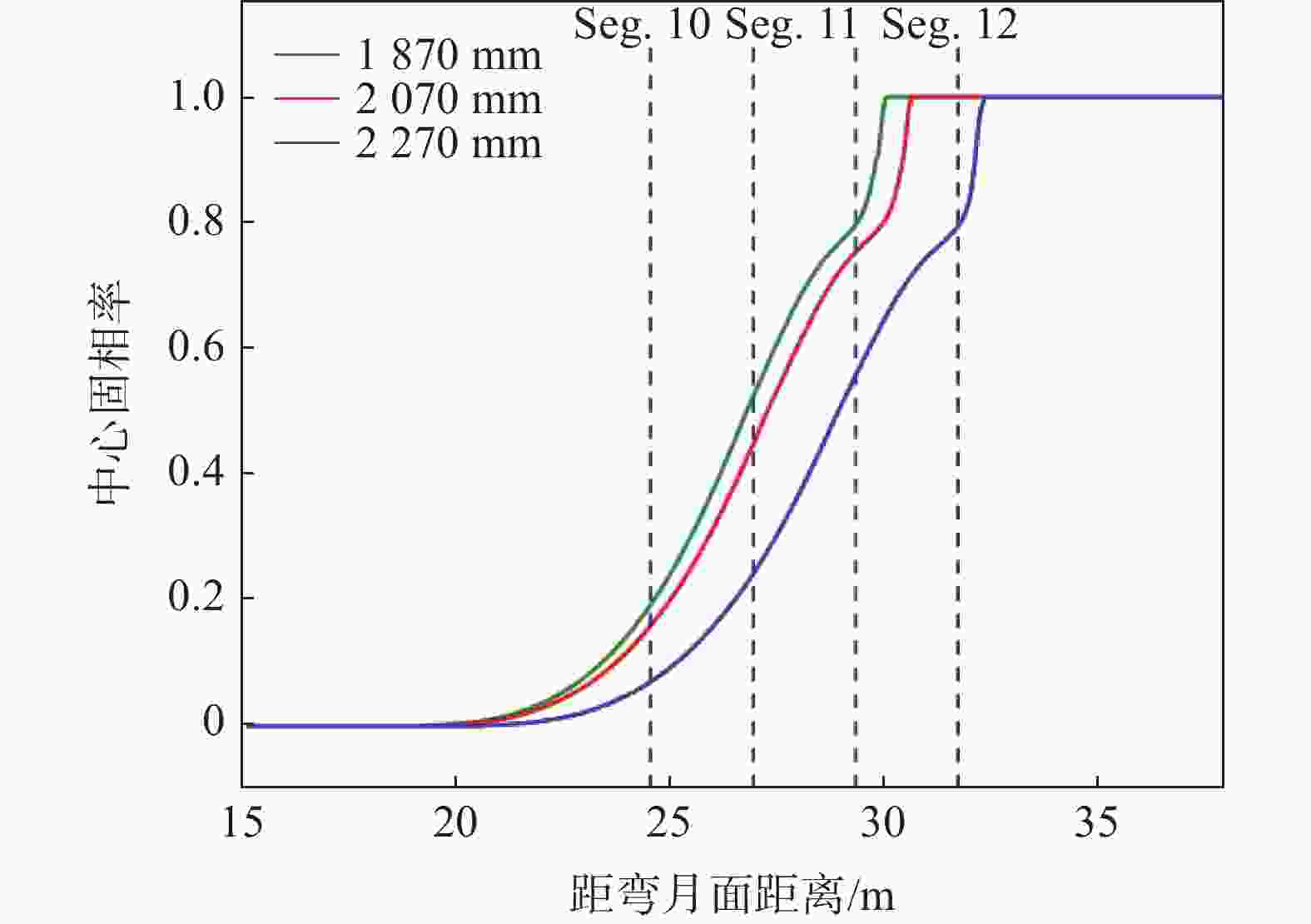
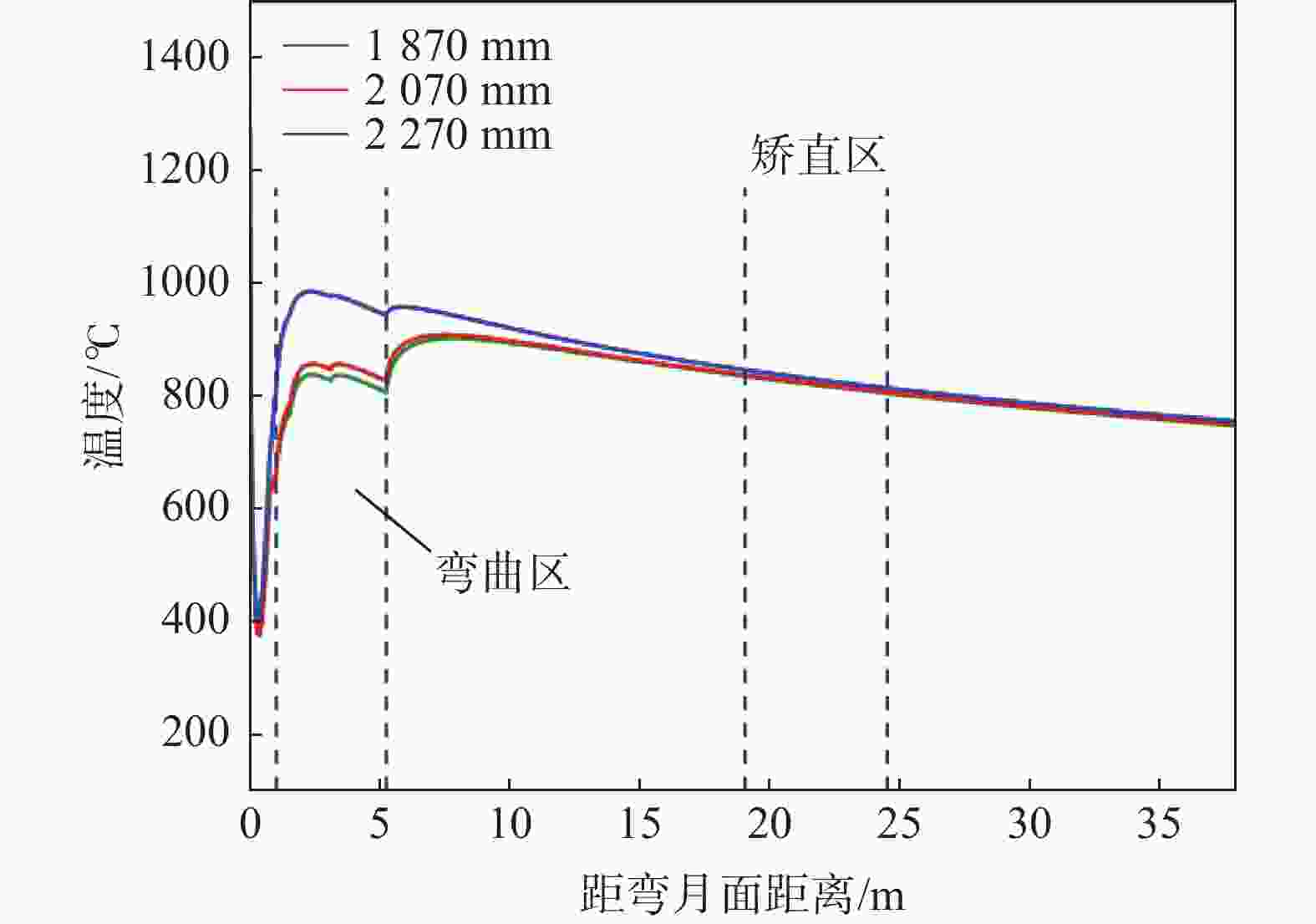
摘要: 为改善湘钢Q345R厚板坯铸坯质量,建立了凝固传热模型,采用射钉试验对模型进行验证和修正。通过数值模拟的方法,对现有的生产工艺进行了评价,并分别研究了拉速、比水量、过热度以及铸坯厚度和宽度对压下位置和压下区间的影响规律,同时研究了其对铸坯角部温度的影响规律。对模拟结果进行分析,理论上得到生产该钢种时合理的连铸工艺参数及铸坯规格,其工艺参数为:断面为450 mm×2 270 mm,拉速为0.55 m/min,过热度为15~25 ℃,二冷比水量为0.26 L/kg。矫直区为Seg.8~9,轻压下区为Seg.13~15。Abstract: In order to improve the quality of Xianggang Q345R thick slab casting billet, a solidification heat transfer model was established and was verified and corrected by nail shooting experiment. Through numerical simulation, the existing production process was evaluated, and the influence of casting speed, cooling water, superheat, thickness and width of casting billet on the pressing position and pressing interval were studied respectively, and their influence on the corner temperature of the casting billet was studied. The simulation results are analyzed, and the reasonable continuous casting process parameters and billet specifications during the production of the steel grade are obtained as follows: the cross-section is 450 mm×2 270 mm, the tensile speed is 0.55 m/min, the superheat is 15~25 ℃, and the specific water volume of secondary cooling is 0.26 L/kg, the straightening zone is Seg.8~9, and the light pressure area is Seg.13~15. With these casting parameters applied, the center segregation of the slab and the crack defects in the corners can be effectively controlled.
-
表 1 结晶器参数
Table 1. The technical parameters of mould
有效
高度/mm宽面
水量/(L·min−1)窄面
水量/(L·min−1)进出口
水温差/ ℃900 6000 1000 5 表 2 二冷区参数
Table 2. The technical parameters of secondary cooling zone
二冷分区 扇形段 区长度/mm 冷却水量/(L·min−1) 内外弧中部 内外弧边部 1区 足辊 267 181.6① 45.0② 2区 弯曲段上部 540 86.7 25.9 3区 弯曲段中部 1548 75.5 22.6 4区 弯曲段下部 2142 59.0 17.6 5区 弧形段1段 1902 42.9 0 6区 弧形段2段 1902 11.6 0 7区 弧形段3段 1902 10.5 0 8区 弧形段4段 1914 9.4 0 9区 弧形段5段 2027 7.0 0 10区 弧形段6段 2027 7.9 0 11区 弧形段7段 2077 7.9 0 12区 矫直8~9段 5461 5.1 0 13区 水平10~12段 7190 12.9 0 14区 水平13~15段 6550 12.9 0 注:二冷区各段冷却水进水温度为30 ℃;①为1区宽面,②为1区窄面。 表 3 Q345R钢的主要化学成分
Table 3. The main chemical composition of Q345R steel
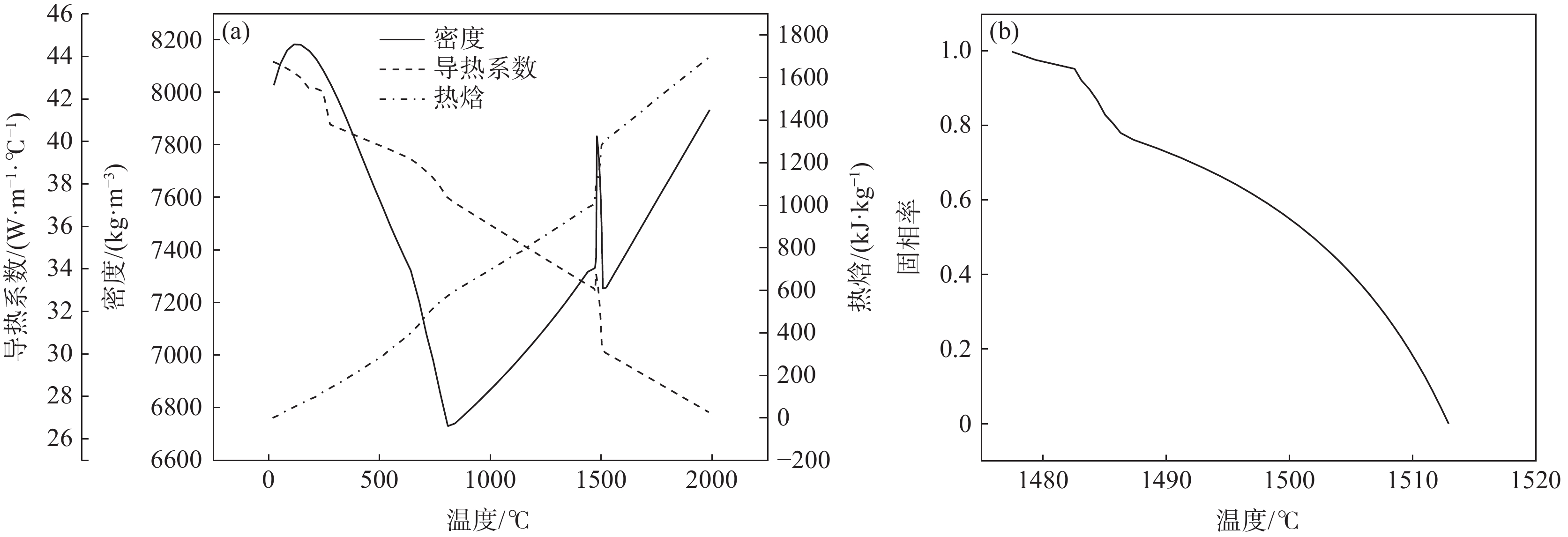
% C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Al Cu Ti Nb 0.13 0.27 1.52 0.012 0.0002 0.21 0.16 0.025 0.12 0.016 0.037 表 4 Q345R板坯射钉试验结果
Table 4. The nail shooting experiment results of Q345R slab
钢种 拉速/(m·min−1) 射钉位
置/m坯壳厚
度/mm综合凝固系数
k/(mm·min−1/2)凝固末端
位置/mQ345 R 0.45 26.92 175 25.70 34.60 -
[1] Zhao Lei. Research and analysis on properties of Q345R vessel steel [J]. Physics Examination and Testing, 2012, 30(1): 5-7,16. (赵蕾, Q345R压力容器板性能分析与研究[J]. 物理测试, 2012, 30(1): 5-7,16.Zhao Lei. Research and analysis on properties of Q345R vessel steel [J]. Physics Examination and Testing, 2012, 30(1): 5-7,16. [2] Cai Kaike, Wu Yuanzeng. Mathematical model of solidified heat transfer of continuous ingot slab[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Iron and Steel Technology, 1982(3):1-11. (蔡开科, 吴元增. 连续铸锭板坯凝固传热数学模型[J]. 北京钢铁学院学报, 1982(3):1-11.Cai Kaike, Wu Yuanzeng. Mathematical model of solidified heat transfer of continuous ingot slab[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Iron and Steel Technology, 1982(3): 1-11. [3] Li Jie. Study on soft reduction process theory and central segregation of pressure vessel steel wide slab[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2022. (李杰. 压力容器钢宽板坯轻压下工艺理论及中心偏析研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2022.Li Jie. Study on soft reduction process theory and central segregation of pressure vessel steel wide slab[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2022. [4] Wang Lu, Sun Yanhui, Niu Apeng, et al. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and solidification in X80 slab continuous casting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(6):143-149. (王璐, 孙彦辉, 牛阿朋, 等. X80板坯传热凝固数值模拟[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(6):143-149. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.06.023Wang Lu, Sun Yanhui, Niu Apeng, et al. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and solidification in X80 slab continuous casting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39(6): 143-149. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.06.023 [5] Gao Xiangzhou, Yang Shufeng, Li Jingshe, et al. Numerical simulation of solidification process for wide and thick slab[J]. Foundry Technology, 2015,36(3):678-683. (高向宙, 杨树峰, 李京社, 等. 宽厚板坯连铸凝固过程数值模拟[J]. 铸造技术, 2015,36(3):678-683.Gao Xiangzhou, Yang Shufeng, Li Jingshe, et al. Numerical simulation of solidification process for wide and thick slab[J]. Foundry Technology, 2015, 36(3): 678-683. [6] Wang Zhenming, Zhao Jing, Wang Yulong, et al. Research on central segregation control of 400 mm ultra-thick slab[J]. Continuous Casting, 2019,44(6):47-50. (王臻明, 赵晶, 王玉龙, 等. 400 mm特厚板坯中心偏析控制的研究[J]. 连铸, 2019,44(6):47-50.Wang Zhenming, Zhao Jing, Wang Yulong, et al. Research on central segregation control of 400 mm ultra-thick slab[J]. Continuous Casting, 2019, 44(6): 47-50. [7] Li Yaoguang. Simulation study of macroscopic transmission phenomenon and central segregation in continuous casting process[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2022. (李曜光. 连铸过程宏观传输现象及中心偏析的模拟研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2022.Li Yaoguang. Simulation study of macroscopic transmission phenomenon and central segregation in continuous casting process[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2022. [8] Zhou Guotao, Chen Jin, Huang Biaocai, et al. Numerical simulation of solidification and heat transfer of Q355B slab during continuous casting[J]. Continuous Casting, 2023(2):43-51. (周国涛, 陈金, 黄标彩, 等. Q355B板坯连铸凝固传热行为数值模拟[J]. 连铸, 2023(2):43-51.Zhou Guotao, Chen Jin, Huang Biaocai, et al. Numerical simulation of solidification and heat transfer of Q355B slab during continuous casting[J]. Continuous Casting, 2023(2): 43-51. [9] Lally B, Biegler L, Henein H. Finite difference heat-transfer modeling for continuous casting[J]. Metallurgical Transactions B, 1990,21(4):761-770. doi: 10.1007/BF02654255 [10] Tieu A K, Kim I S. Simulation of the continuous casting process by a mathematical model[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1997,39(2):185-192. doi: 10.1016/0020-7403(96)00052-5 [11] Sheng Yiping, Kong Xiangdong, Yang Yongli. Study on thermal boundary conditions in the mold for continuous casting[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2007(13):1615-1618. (盛义平, 孔祥东, 杨永利. 连铸结晶器传热边界条件研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2007(13):1615-1618. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2007.13.025Sheng Yiping, Kong Xiangdong, Yang Yongli. Study on thermal boundary conditions in the mold for continuous casting[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2007(13): 1615-1618. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2007.13.025 [12] Jing C, Wang X, Jiang M. Study on solidification structure of wheel steel round billet using FE-CA coupling modle[J]. Steel Research International, 2011,82(10):1173-1179. doi: 10.1002/srin.201000303 [13] Wang Xinhua. Ferrous metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007. (王新华. 钢铁冶金—炼钢学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007.Wang Xinhua. Ferrous metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007. [14] Su Cheng, Dong Fang. High temperature plasticity of micro-alloyed Q345B in slab continuous casting process[J]. Iron & Steel, 2012,47(08):65-69, 80. (宿成, 董方. 合金Q345B板坯连铸的高温塑性[J]. 钢铁, 2012,47(8):65-69, 80.Su Cheng, Dong Fang. High temperature plasticity of micro-alloyed Q345B in slab continuous casting process[J]. Iron & Steel, 2012, 47(08): 65-69, 80. [15] Cheng Xuhui. The optimization of cooling process of slab continuous casting in straightening zone[D]. Dalian: Northeastern University, 2018. (程旭辉. 板坯连铸矫直区冷却工艺优化[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2018.Cheng Xuhui. The optimization of cooling process of slab continuous casting in straightening zone[D]. Dalian: Northeastern University, 2018. -




 下载:
下载: