Effects of solidification structure on MnS in heavy rail steel bloom
-
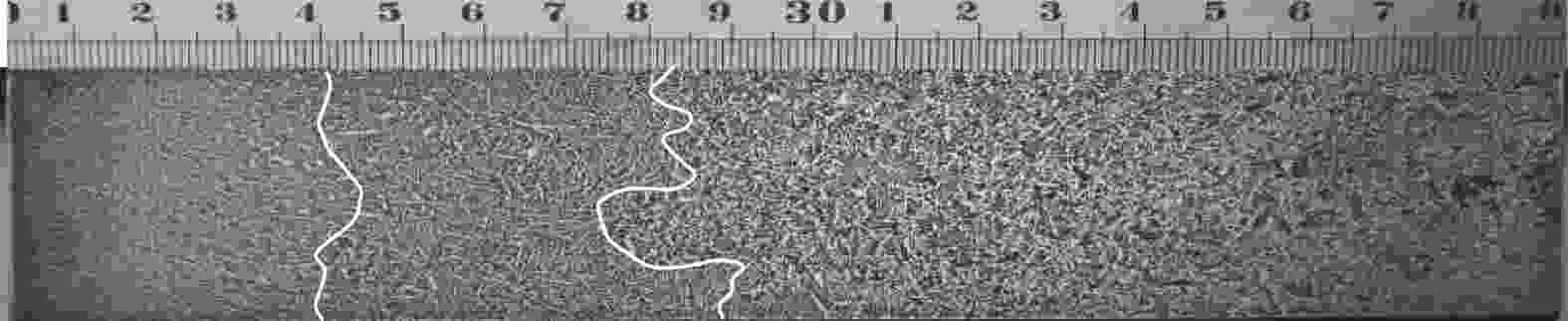
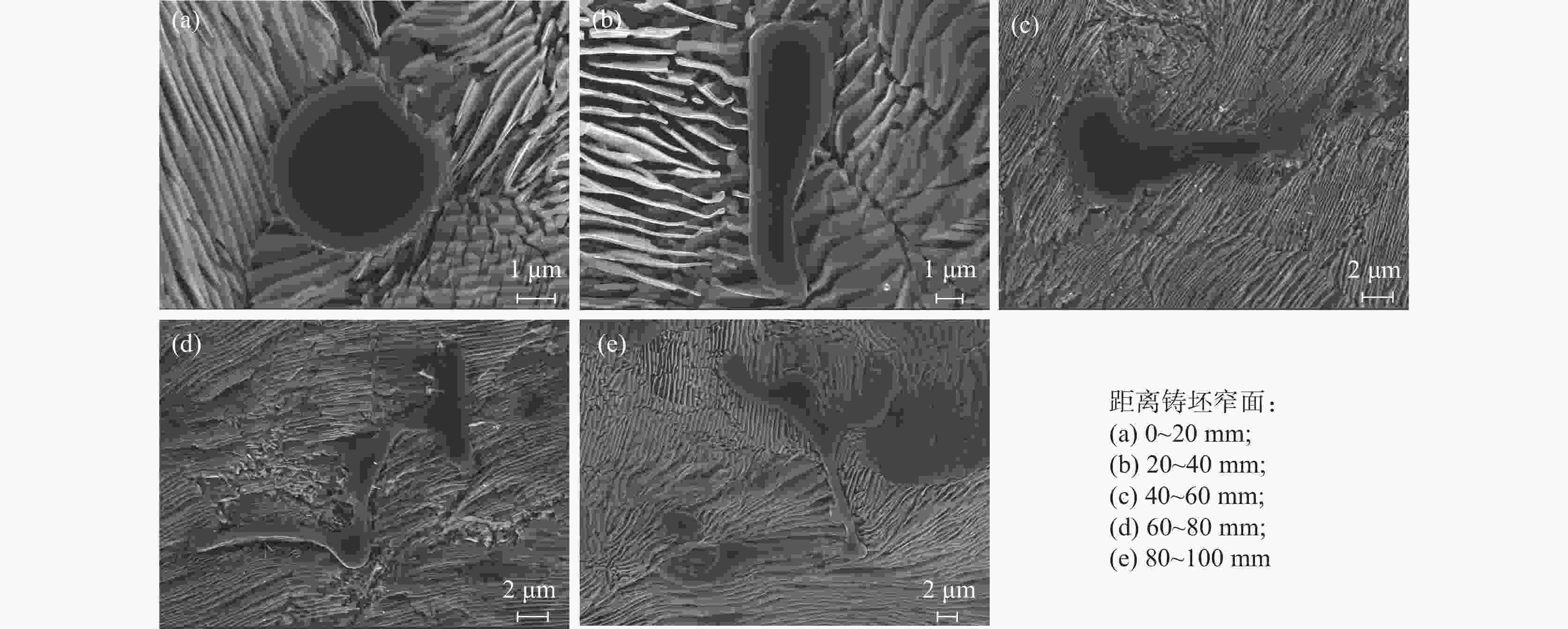
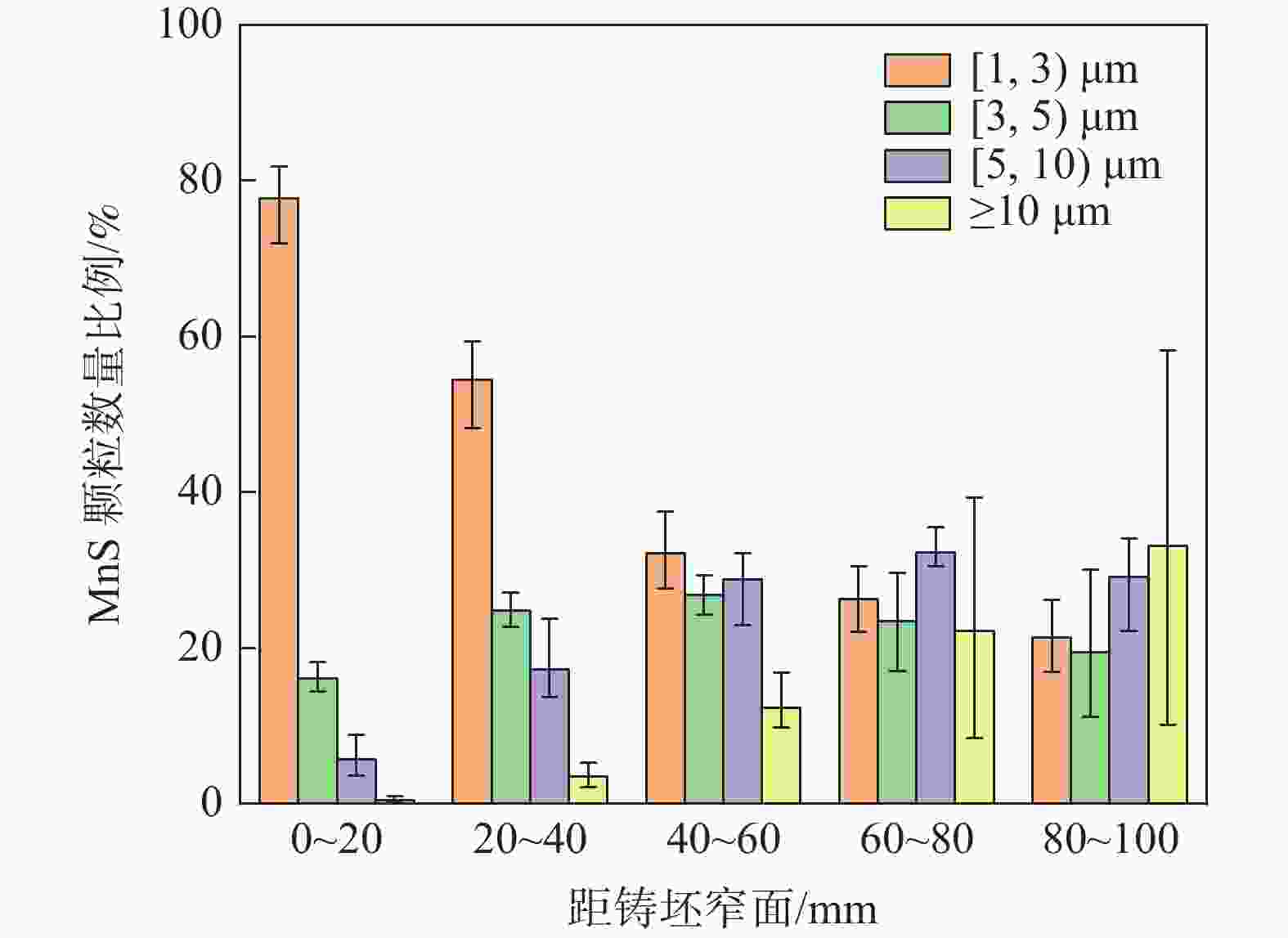
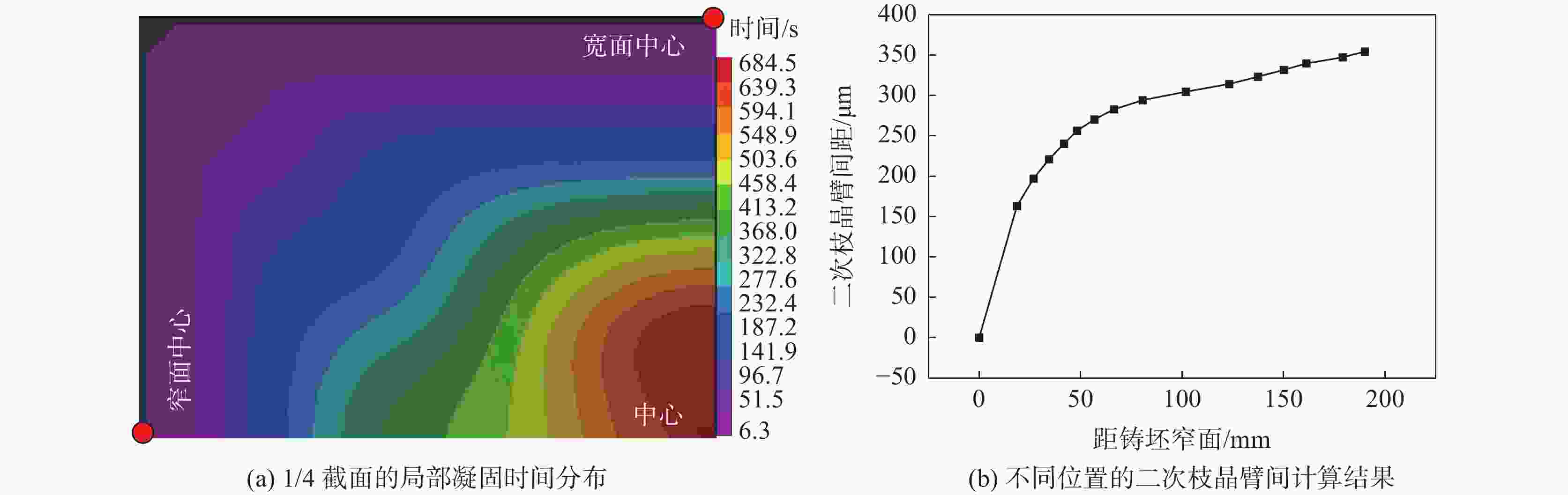
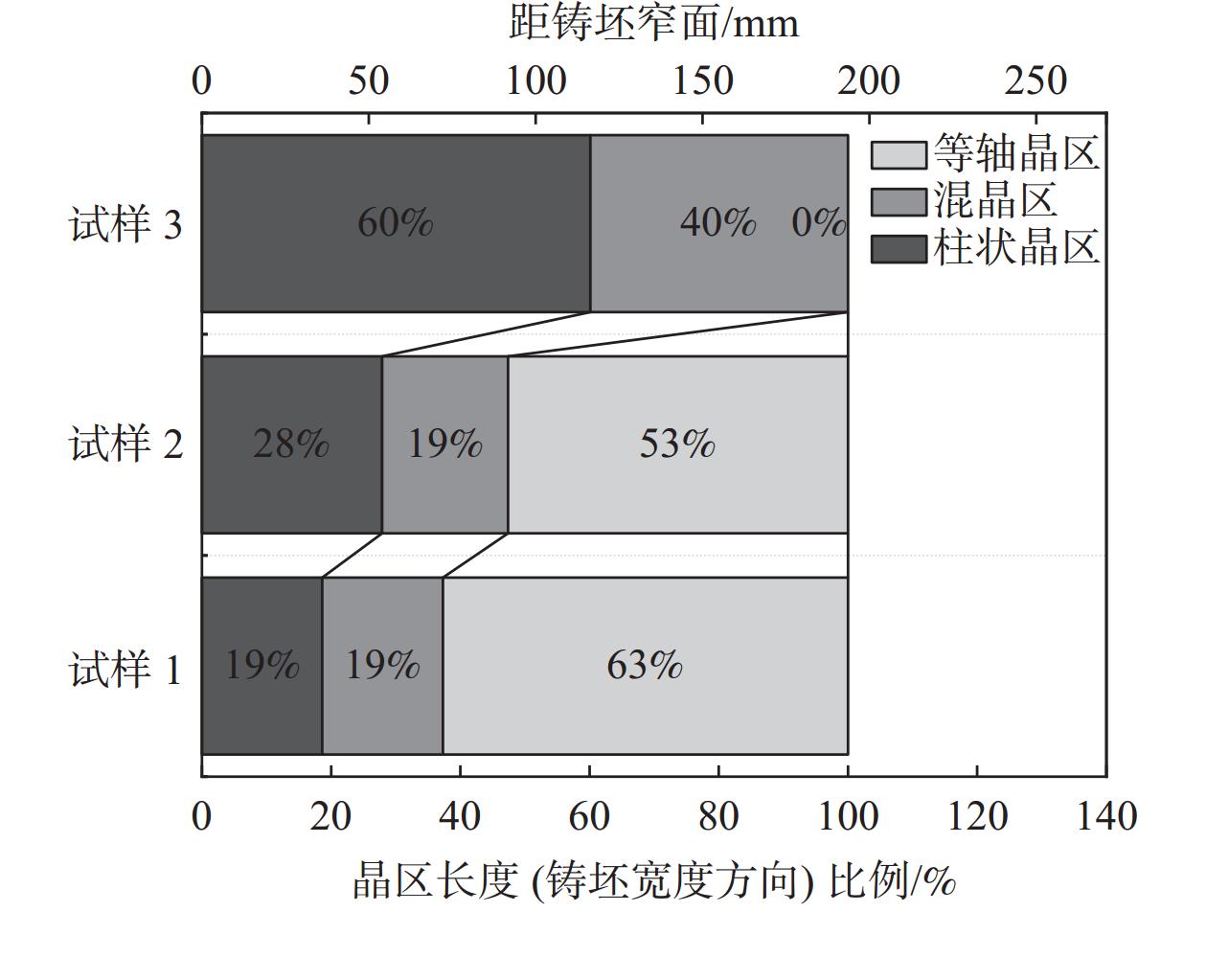
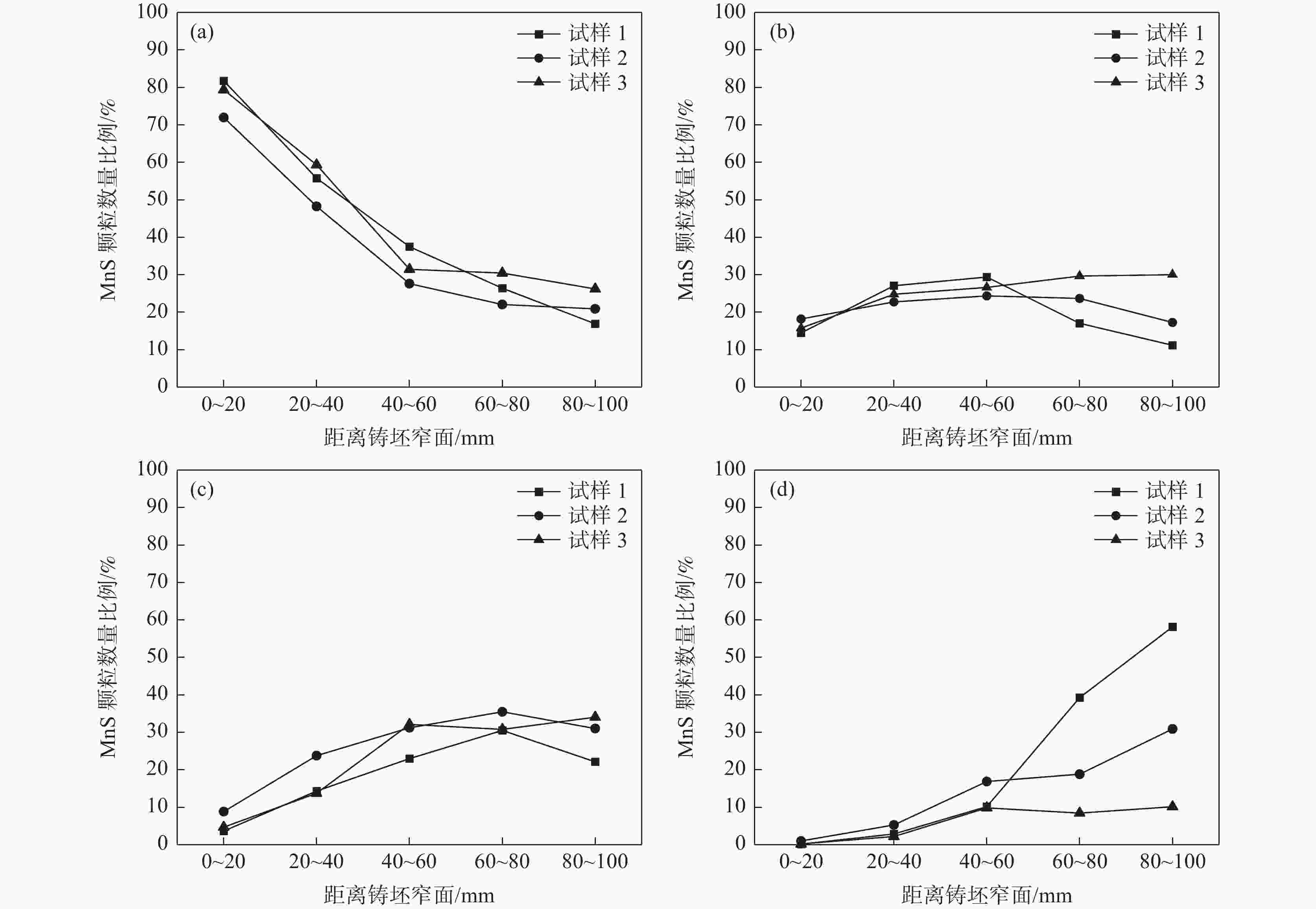
摘要: 采用电化学腐刻与Aspex扫描相结合,检测了重轨钢铸坯不同位置的MnS尺寸形貌,研究了凝固组织对MnS的影响。结果表明,凝固组织由混晶转变为粗大等轴晶时,3~5 μm的MnS颗粒数量比例降低,而≥10 μm的颗粒数量比例则明显增大。从距离铸坯窄面40 mm推移至100 mm,凝固组织类型转变越明显则≥10 μm的MnS颗粒数量比例增加越多:凝固组织发生明显转变时,其比例增加48.02%,凝固组织未发生类别转变时,其比例增加0.31%。通过连铸强化冷却等缩短局部凝固时间的工艺调控,可以促进MnS细小化控制。Abstract: The sizes and microstructures of MnS at different positions of the heavy rail steel bloom were measured by electro-chemical etching and Aspex scanning, and the effect of solidification structure on MnS was studied. The results show that when the solidification structure transforms from mixed-crystal to coarse equiaxed grain, the quantitative proportion of MnS particles with the size range of 3-5 μm decreases, and the quantitative proportion of particles with sizes larger than 10 μm increases significantly. While the distance from the narrow surface of the bloom changed from 40 mm to 100 mm, the solidification structure transformed more obviously, and the larger increment of the quantitative proportion of MnS particles with sizes over 10 μm was obtained: if the solidification structure transformed obviously, the quantitative proportion was increased by 48.02%, and if the solidification structure did not transform, the quantitative proportion was increased by 0.31%. It means MnS particles can be refined by adopting processes to shorten the local solidification time, such as strengthening cooling during continuous casting.
-
Key words:
- heavy rail steel /
- continuous casting billet /
- solidification structure /
- MnS
-
表 1 U75 V重轨钢主要化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of U75V heavy rail steel
% C Si Mn P S V 0.76 0.65 0.90 0.015 0.010 0.08 表 2 连铸关键工艺对比
Table 2. Comparison of the key continuous casting parameters
项目 M-EMS F-EMS 过热
度/ ℃二冷比水量/
(L·kg−1)拉速/
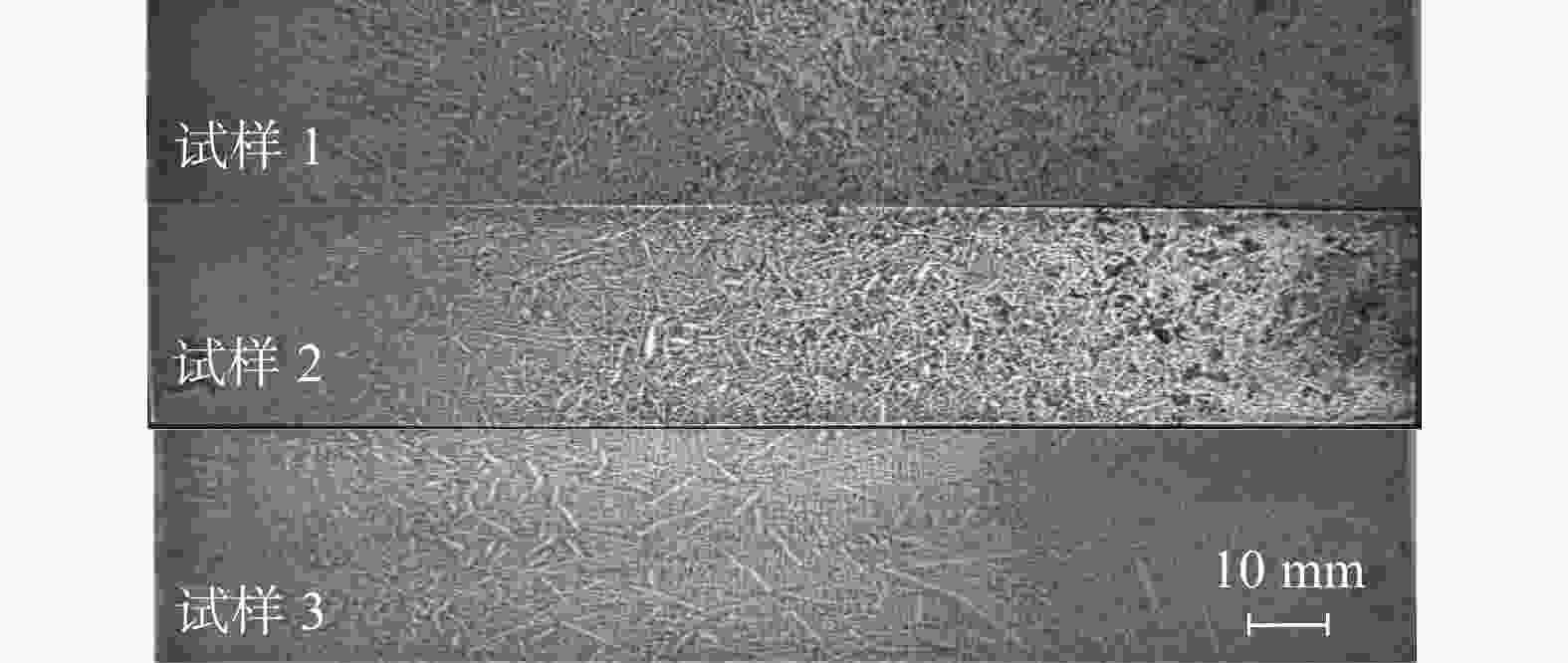
(m·min−1)试样1
(典型工艺)强 无 20~25 0.23~0.24 0.64~0.65 试样2 中 中 0.26~0.27 试样3 弱 中 30~35 0.30~0.31 0.68~0.70 -
[1] Li Bo, Zhang Zhonghua, Liu Huasong, et al. Characteristics and evolution of the spot segregations and banded defects in high strength corrosion resistant tube steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019,55(6):762-772. (李博, 张忠铧, 刘华松, 等. 高强耐蚀管钢点状偏析及带状缺陷的特征与演变[J]. 金属学报, 2019,55(6):762-772. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00557Li Bo, Zhang Zhonghua, Liu Huasong, et al. Characteristics and evolution of the spot segregations and banded defects in high strength corrosion resistant tube steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019, 55(6): 762-772. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00557 [2] Cai Zhaozhen, Zhu Miaoyong. Microsegregation of solute elements in solidifying mushy zone of steel and it’s effect on longitudinal surface crack of continuous casting strand[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009,45(8):949-955. (蔡兆镇, 朱苗勇. 钢凝固两相区溶质元素的微观偏析及其对连铸坯表面纵裂纹的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2009,45(8):949-955. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2009.08.009Cai Zhaozhen, Zhu Miaoyong. Microsegregation of solute elements in solidifying mushy zone of steel and it’s effect on longitudinal surface crack of continuous casting strand[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45(8): 949-955. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2009.08.009 [3] Li Ping, Wang Lei, Zhou Qingfeng. Formation reasons and countermeasures of cementite network in the center of 82B wire rods[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2014,26(9):33-36. (李平, 王雷, 周青峰. 82B中心网状渗碳体产生原因及改善方法[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2014,26(9):33-36.Li Ping, Wang Lei, Zhou Qingfeng. Formation reasons and countermeasures of cementite network in the center of 82B wire rods[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2014, 26(9): 33-36. [4] Ji Yuan. Segregation of billet castings and its heredity effect on the hot-rolled products[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018. (纪元. 连铸还偏析及其铸轧遗传性研究[D]. 北京:北京科技大学, 2018.Ji Yuan. Segregation of billet castings and its heredity effect on the hot-rolled products[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018. [5] Fang Qing. Numerical analysis of flow, heat transfer, solute transport behavior and solidification structure in continuously cast bloom[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2018. (方庆. 大方坯连铸过程流动、传热、传质行为及凝固组织的模拟研究[D]. 武汉:武汉科技大学, 2018.Fang Qing. Numerical analysis of flow, heat transfer, solute transport behavior and solidification structure in continuously cast bloom[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2018. [6] An Hanghang. Solidification mechanism and key control technology of macro segregation in continuously cast high-carbon steel blooms[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018. (安航航. 高碳钢大方坯凝固机理与宏观偏析关键控制技术研究[D]. 北京:北京科技大学, 2018.An Hanghang. Solidification mechanism and key control technology of macro segregation in continuously cast high-carbon steel blooms[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018. [7] Hu Jie. Failure cause analysis of s-shaped fracture of thermit welded joint in heavy haul railway[J]. Railway Engineering, 2017(3):125-128. (胡杰. 重载铁路钢轨铝热焊接头S形断裂失效原因分析[J]. 铁道建筑, 2017(3):125-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2017.03.33Hu Jie. Failure cause analysis of s-shaped fracture of thermit welded joint in heavy haul railway[J]. Railway Engineering, 2017(3): 125-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2017.03.33 [8] Ding Wei, Zhang Xianliang, Zhao Guo, et al. Formation mechanism and prevention methods of defects in overheat area at rail flash-butt welding joint[J]. Railway Engineering, 2015(11):96-99. (丁韦, 张宪良, 赵国, 等. 钢轨闪光焊接头过热区缺陷的形成机理及预防方法[J]. 铁道建筑, 2015(11):96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2015.11.28Ding Wei, Zhang Xianliang, Zhao Guo, et al. Formation mechanism and prevention methods of defects in overheat area at rail flash-butt welding joint[J]. Railway Engineering, 2015(11): 96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2015.11.28 [9] Zhang Xuewei, Zhang Lifeng, Yang Wen, et al. Nucleation and growth dynamics analysis of MnS particles during solidification process in heavy rail steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017,29(9):724-731. (张学伟, 张立峰, 杨文, 等. 凝固过程重轨钢中MnS粒子形核与长大动力学分析[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2017,29(9):724-731.Zhang Xuewei, Zhang Lifeng, Yang Wen, et al. Nucleation and growth dynamics analysis of MnS particles during solidification process in heavy rail steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017, 29(9): 724-731. [10] Qi Jianghua, Wu Jie, Suo Jinping, et al. Formation reason of large MnS in hectometer high speed heavy rail steel[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 2011,39(3):22-24. (齐江华, 吴杰, 索进平, 等. 百米高速重轨钢中大型MnS夹杂的形成原因[J]. 钢铁研究, 2011,39(3):22-24.Qi Jianghua, Wu Jie, Suo Jinping, et al. Formation reason of large MnS in hectometer high speed heavy rail steel[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 2011, 39(3): 22-24. [11] Zhang Xuewei, Zhang Lifeng, Yang Wen, et al. Thermodynamics and dynamics of MnS inclusions precipitation during solidification process in heavy rail steels[J]. Iron & Steel, 2016,51(9):30-39. (张学伟, 张立峰, 杨文, 等. 重轨钢中MnS析出热力学和动力学分析[J]. 钢铁, 2016,51(9):30-39.Zhang Xuewei, Zhang Lifeng, Yang Wen, et al. Thermodynamics and dynamics of MnS inclusions precipitation during solidification process in heavy rail steels[J]. Iron & Steel, 2016, 51(9): 30-39. [12] Li Hongguang, Chen Tianming, Chen Liang, et al. Analysis and research on the segregation of A-type inclusion in rail steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(2):143-149. (李红光, 陈天明, 陈亮, 等. 钢轨A类非金属夹杂的析出分析研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(2):143-149. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.02.025Li Hongguang, Chen Tianming, Chen Liang, et al. Analysis and research on the segregation of A-type inclusion in rail steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017, 38(2): 143-149. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.02.025 [13] Li Hongguang, Ji Cheng, Jiang Dongbin, et al. Formation mechanism and control of semi-macro-segregation in rail steel bloom[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021,56(6):59-66. (李红光, 祭程, 姜东滨, 等. 重载钢轨钢连铸大方坯半宏观偏析形成机制与控制[J]. 钢铁, l, 2021,56(6):59-66.Li Hongguang, Ji Cheng, Jiang Dongbin, et al. Formation mechanism and control of semi-macro-segregation in rail steel bloom[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 56(6): 59-66. [14] Liu Yang, Wang Xinhua. Effect of electromagnetic stirring at secondary cooling area on central segregation of a continuously cast slab[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2007(6):582-585, 590. (刘洋, 王新华. 二冷区电磁搅拌对连铸板坯中心偏析的影响[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2007(6):582-585, 590.Liu Yang, Wang Xinhua. Effect of electromagnetic stirring at secondary cooling area on central segregation of a continuously cast slab[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2007(6): 582-585, 590. [15] Wang Biao, Xie Zhi, Jia Guanglin, et al. Parameter determination and effects on center segregation of F-EMS[J]. Iron & Steel, 2007(3):18-21. (王彪, 谢植, 贾光霖, 等. 凝固末端电磁搅拌参数确定及其对中心偏析的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2007(3):18-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2007.03.005Wang Biao, Xie Zhi, Jia Guanglin, et al. Parameter determination and effects on center segregation of F-EMS[J]. Iron & Steel, 2007(3): 18-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2007.03.005 [16] Lu Lu, Lu Kaiyi. Influence of controlling molten steel superheat on technology of concasting and quality of billet[J]. Special Steel, 2008(5):50-51. (鲁路, 鲁开嶷. 钢液过热度控制对连铸工艺和铸坯质量的影响[J]. 特殊钢, 2008(5):50-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2008.05.018Lu Lu, Lu Kaiyi. Influence of controlling molten steel superheat on technology of concasting and quality of billet[J]. Special Steel, 2008(5): 50-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2008.05.018 [17] Yang Wu, Qiu Shengtao, Tao Hongbiao, et al. Effect of decreasing superheat temperature on solidification structure of billet[J]. Iron & Steel, 2010,45(2):45-48. (杨武, 仇圣桃, 陶红标, 等. 降低过热度对方坯凝固组织的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2010,45(2):45-48.Yang Wu, Qiu Shengtao, Tao Hongbiao, et al. Effect of decreasing superheat temperature on solidification structure of billet[J]. Iron & Steel, 2010, 45(2): 45-48. [18] Yi Bo. Control superheat of molten steel and promote quality and output of continuously cast slab[J]. China Metallurgy, 2008(10):43-45. (依波. 控制钢液过热度提高连铸坯质量与产量[J]. 中国冶金, 2008(10):43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9356.2008.10.011Yi Bo. Control superheat of molten steel and promote quality and output of continuously cast slab[J]. China Metallurgy, 2008(10): 43-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9356.2008.10.011 [19] Xia Yunjin, Fan Dingdong, Li Jie. Mathematical simulation on the heat transfer and solidification process of secondary cooling in bloom steel continuous casting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2014,14(2):217-222. (夏云进, 范鼎东, 李杰. 大方钢坯连铸二冷区传热与凝固过程数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2014,14(2):217-222.Xia Yunjin, Fan Dingdong, Li Jie. Mathematical simulation on the heat transfer and solidification process of secondary cooling in bloom steel continuous casting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2014, 14(2): 217-222. [20] Luo Sen. Study and application of on-line solidification and heat transfer model for 360 mm×450 mm bloom continuous casting[D]. Shengyang: Northeastern University, 2008. (罗森. 360 mm×450 mm大方坯连铸在线凝固传热模型的研究与应用[D]. 沈阳:东北大学, 2008.Luo Sen. Study and application of on-line solidification and heat transfer model for 360 mm×450 mm bloom continuous casting[D]. Shengyang: Northeastern University, 2008. -




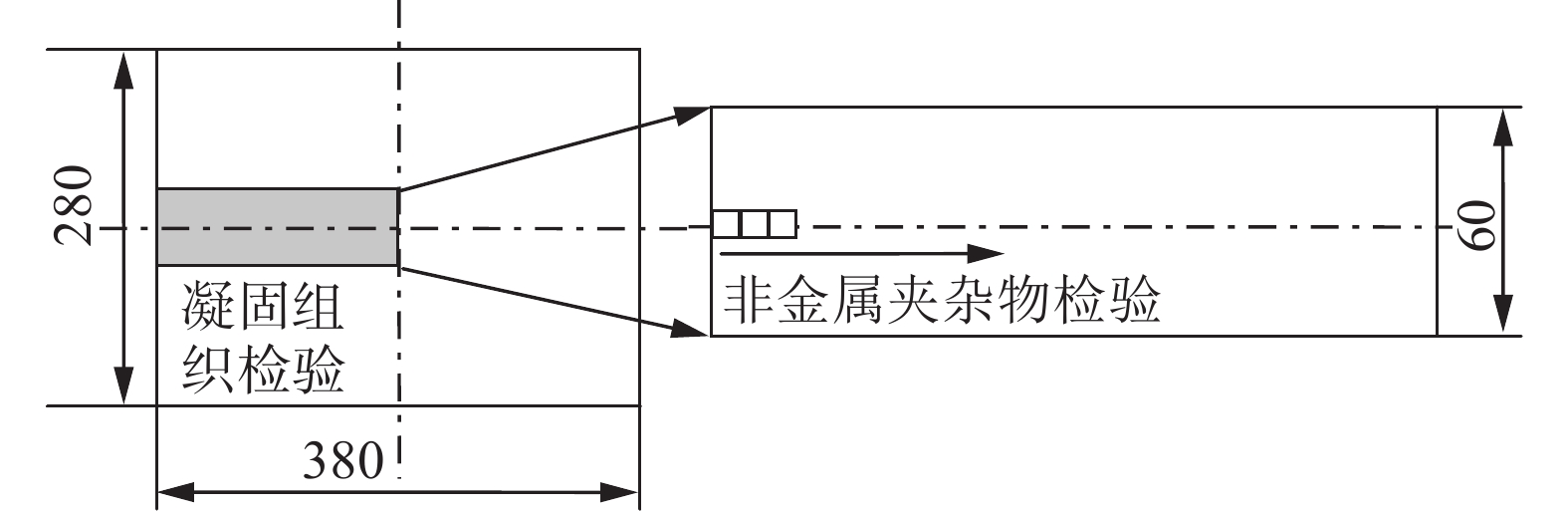
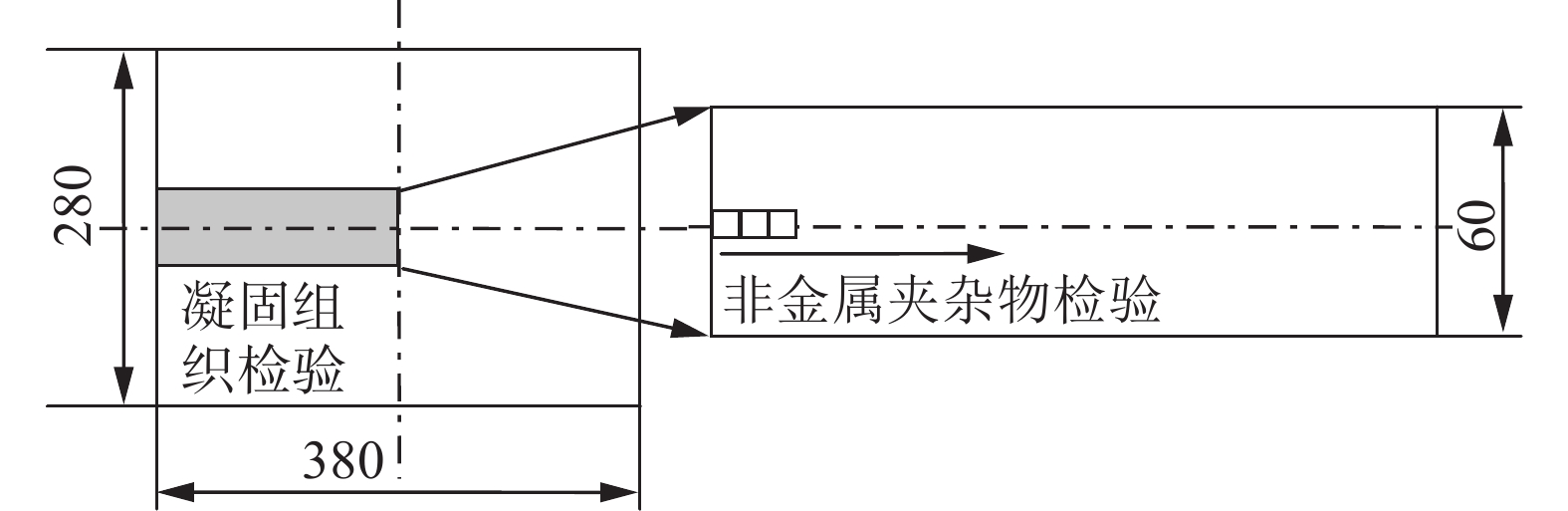
 下载:
下载: