Preparation of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode material from vanadium tailings
-
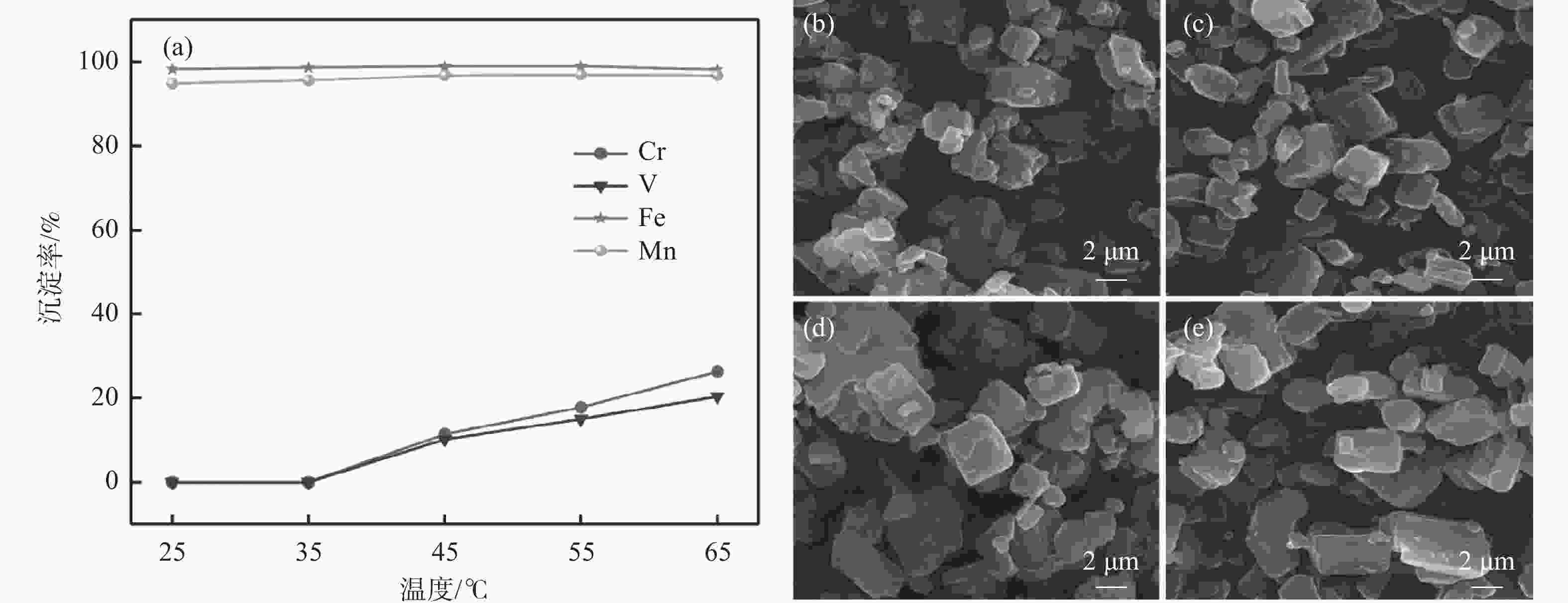
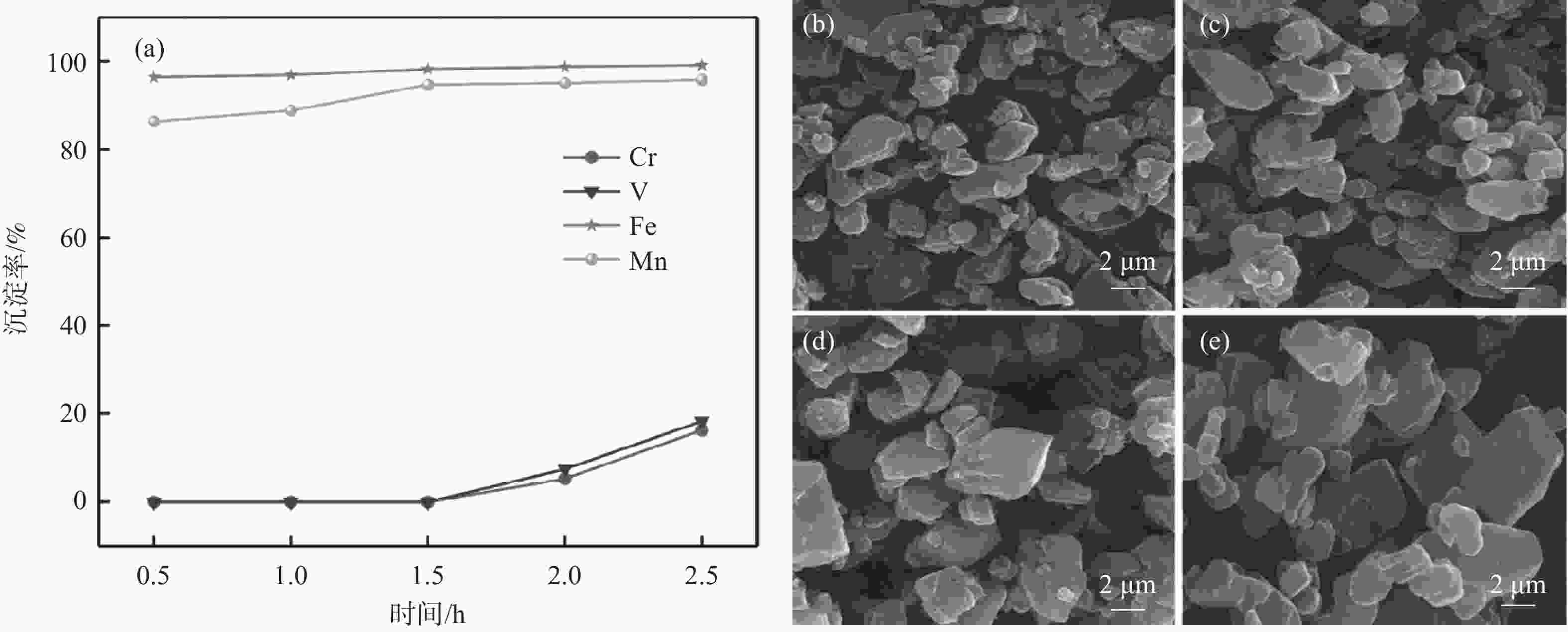
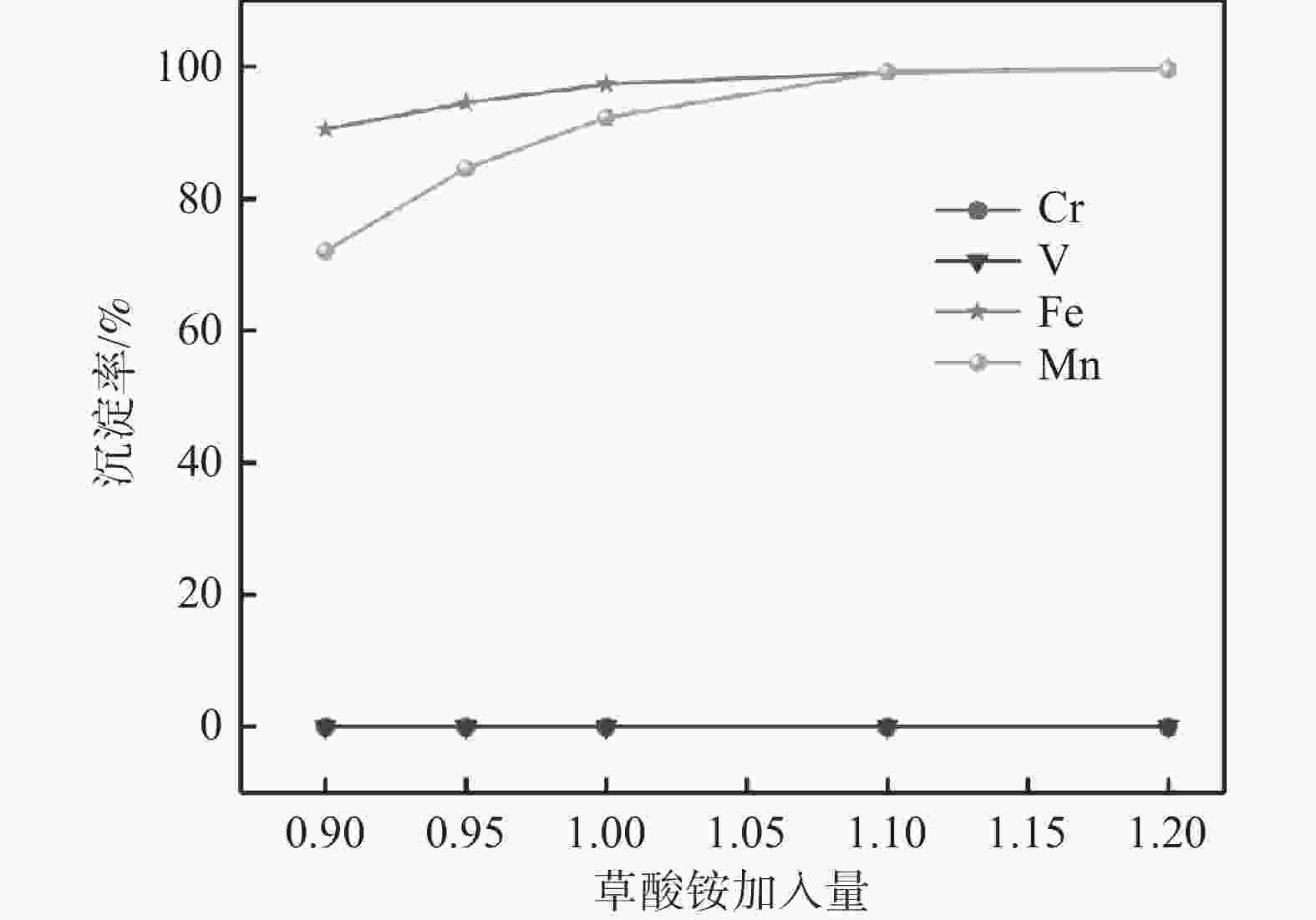
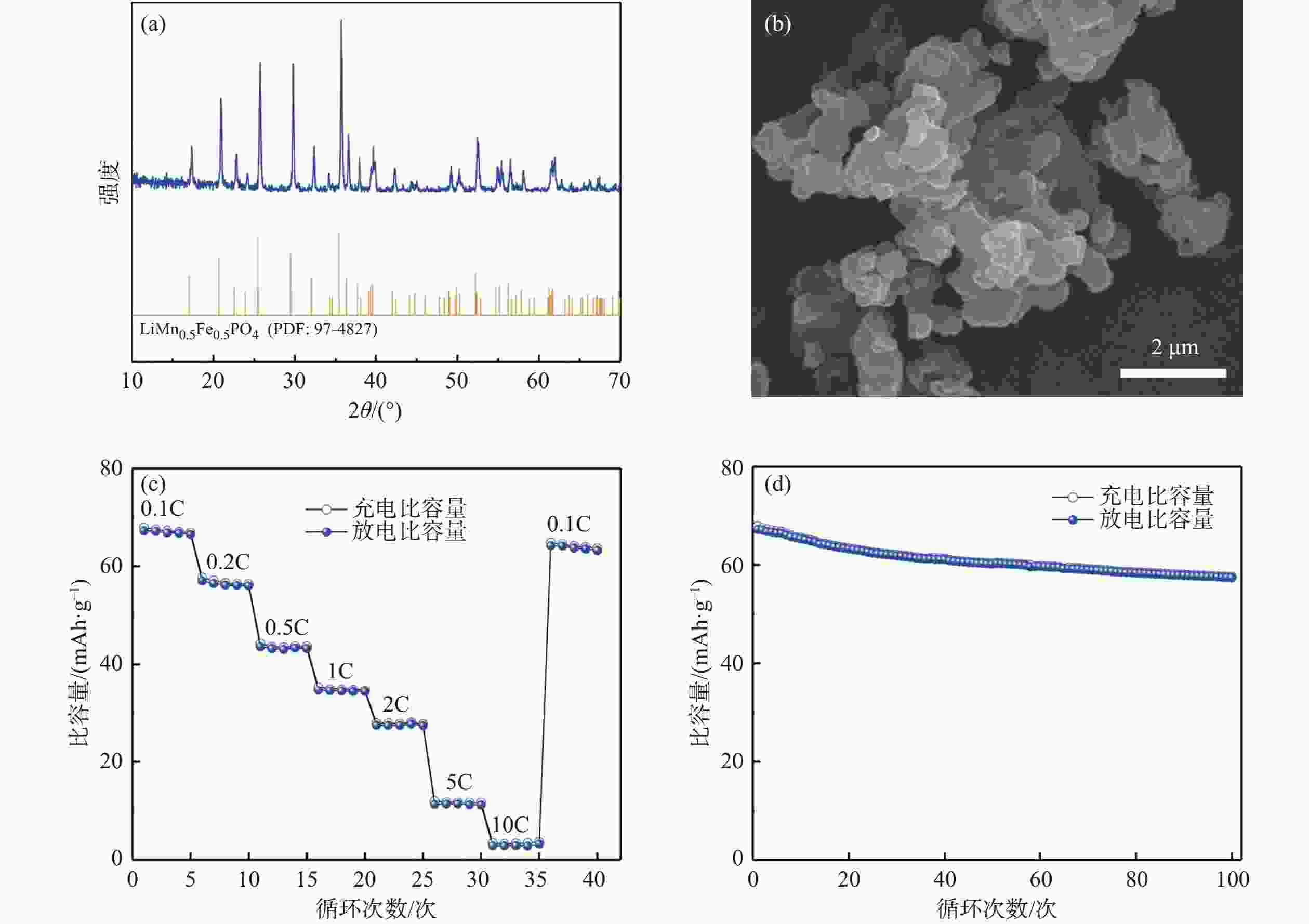
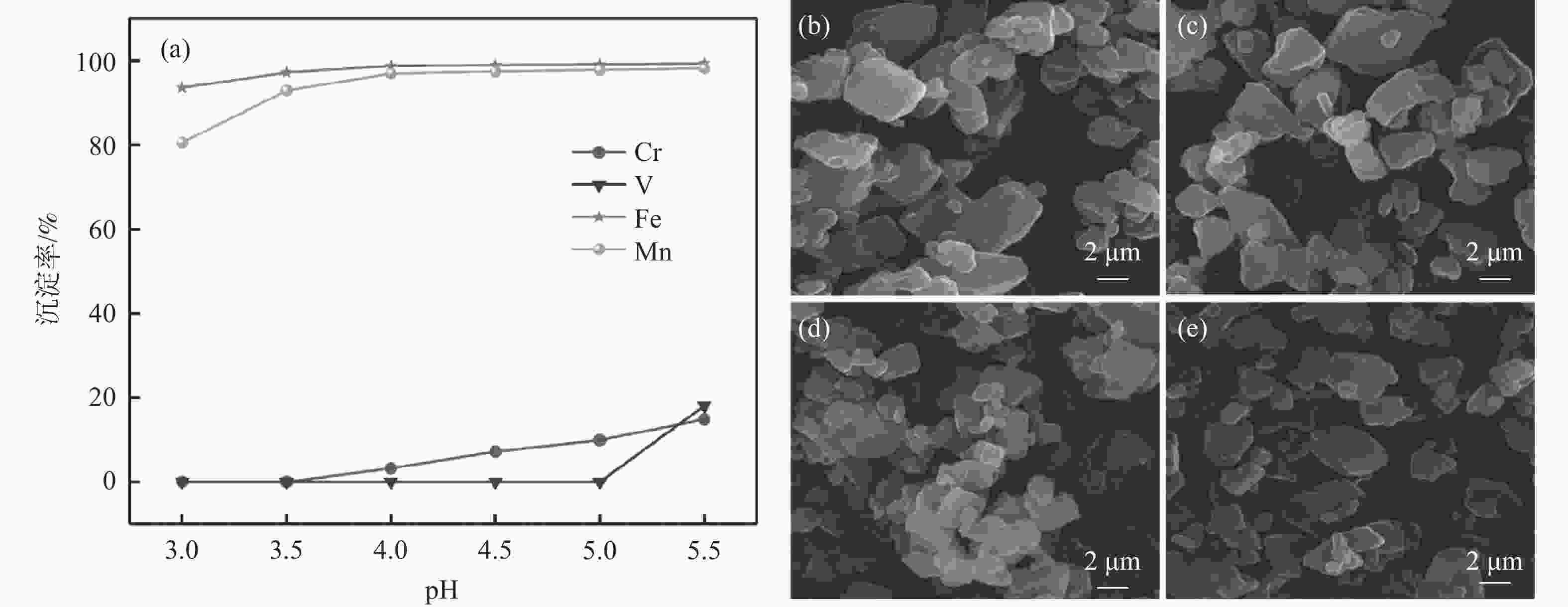
摘要: 以钒渣提钒过程中产生的富含铁锰的浸出液为原料,通过共沉淀法制备了二水草酸铁锰Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4∙2H2O,以此为前驱体,通过高温固相法成功合成了磷酸锰铁锂LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4正极材料,实现了钒渣浸出液中铁锰资源的综合利用。结果表明,在初始pH值为3.5,温度25 ℃,反应时间90 min,草酸铵加料量为理论值的1.1倍,加料方式为正加的条件下,铁和锰的沉淀率分别为99.5%和99.4%,与其他杂质实现深度分离,Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4·2H2O的纯度达99.97%,且粒径较小,分散性良好。可将其作为合成磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的前驱体,为磷酸锰铁锂的工业化生产提供了思路。Abstract: Using the iron-manganese-rich leaching solution generated during vanadium extraction from vanadium slag was used as the raw material, and ferromanganese oxalate dihydrate Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4∙2H2O was prepared by co-precipitation, and lithium ferromanganese iron phosphate LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 anode material was successfully synthesized by the high-temperature solid-phase method using this precursor, which achieved the comprehensive utilization of the iron-manganese resources in the vanadium slag leaching solution. The results showed that under the conditions of initial pH 3.5, temperature 25 ℃, reaction time 90 min, ammonium oxalate addition 1.1 times of the theoretical value, and the addition mode of positive addition, the precipitation efficiency of Fe and Mn were 99.5% and 99.4%, respectively. The depth separation from other impurities was achieved, and the purity of Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4·2H2O reached 99.97% with small particle sizes and good dispersion. It can be used as a precursor for synthesizing lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials, which provides the idea for the industrial production of lithium iron manganese phosphate.
-
表 1 溶液中主要元素及其含量
Table 1. Major elemental contents in the solution
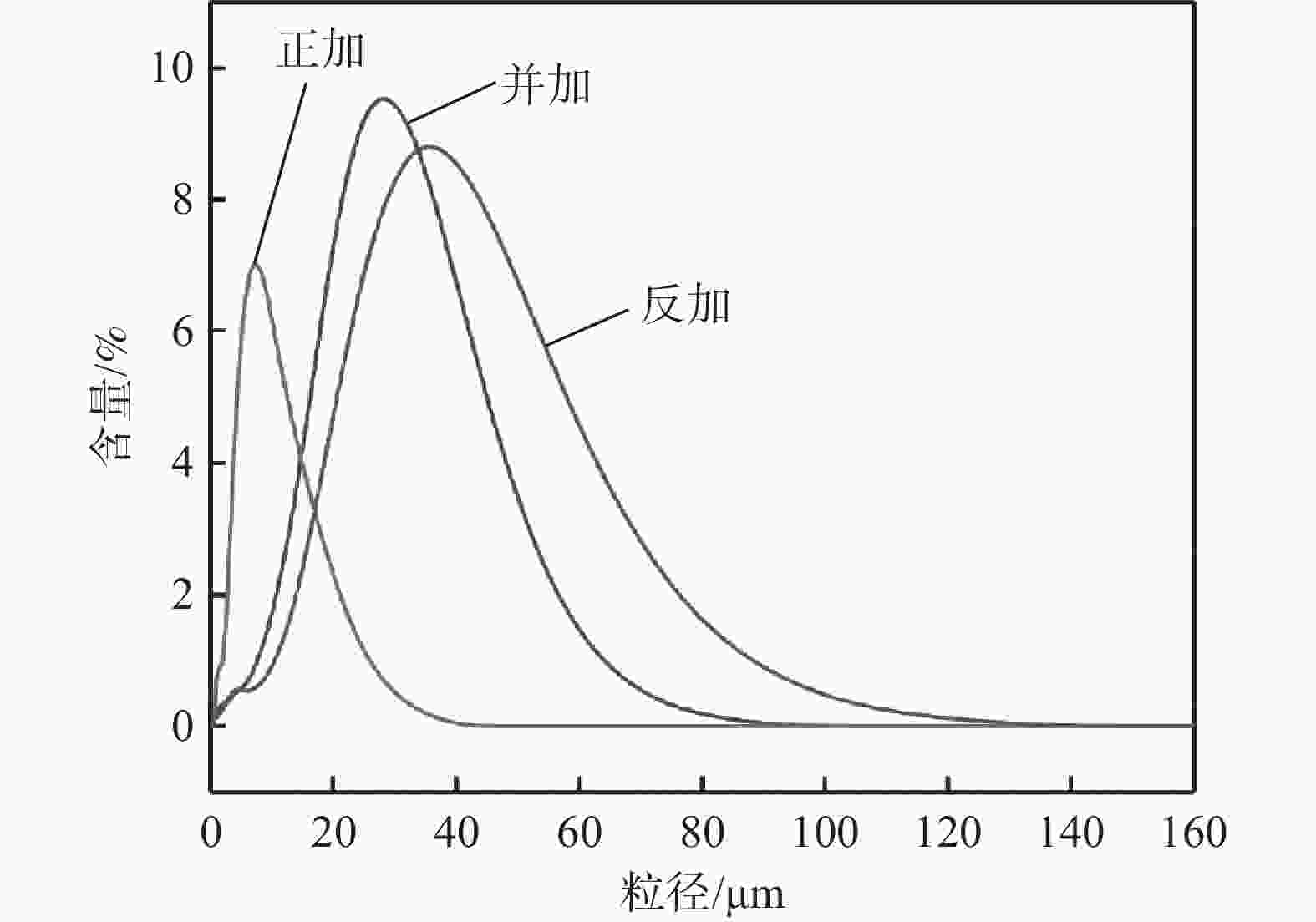
g·L−1 Fe Mn V Cr 25.21 5.13 0.26 0.24 表 2 不同加料方式共沉淀产物的粒度
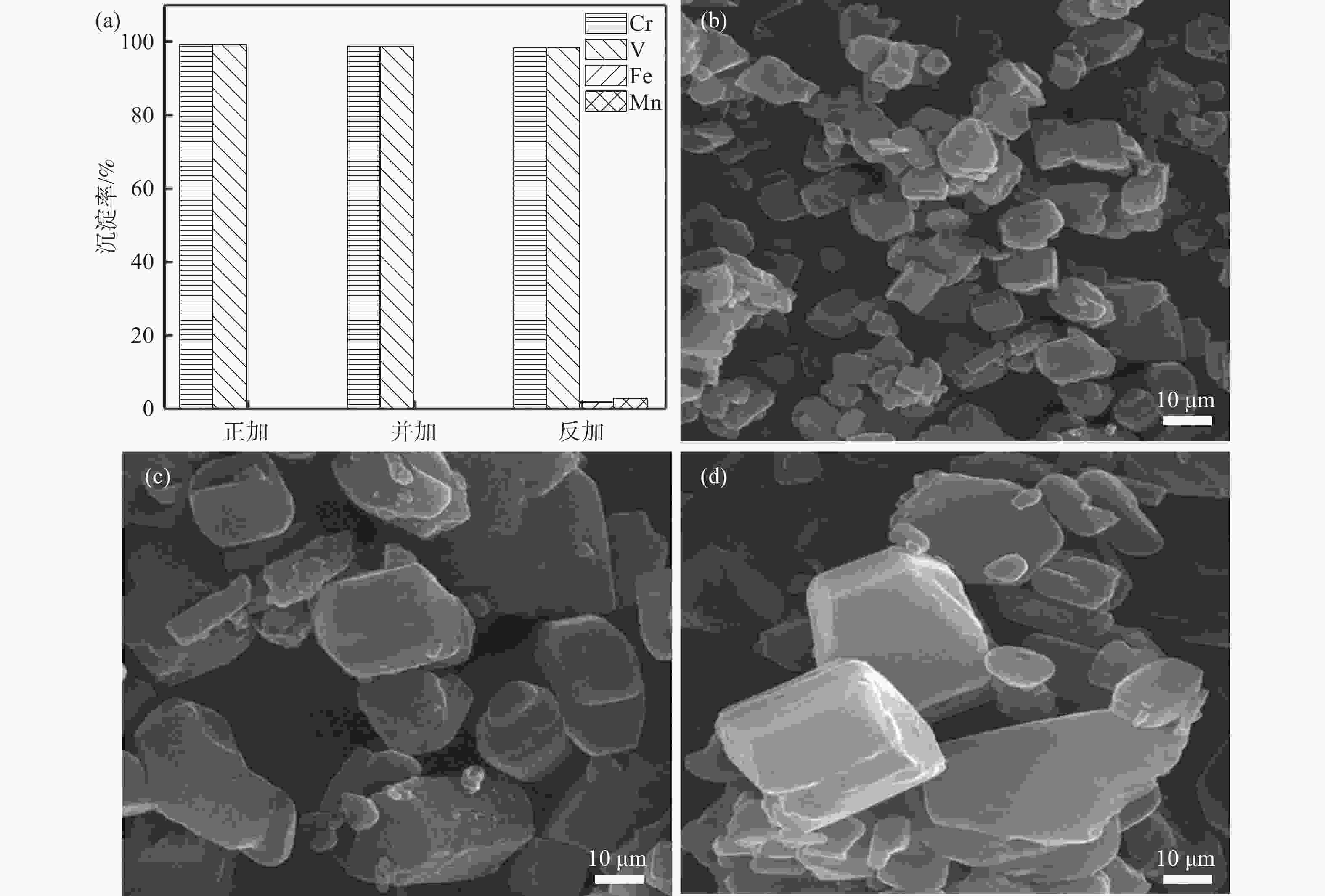
Table 2. Particle sizes of co-precipitation products with different addition methods
加料方式 D10/μm D50/μm D90/μm 正加 2.89 7.57 17.32 并加 10.57 26.66 46.31 反加 12.14 41.87 62.46 表 3 沉淀产物的组成
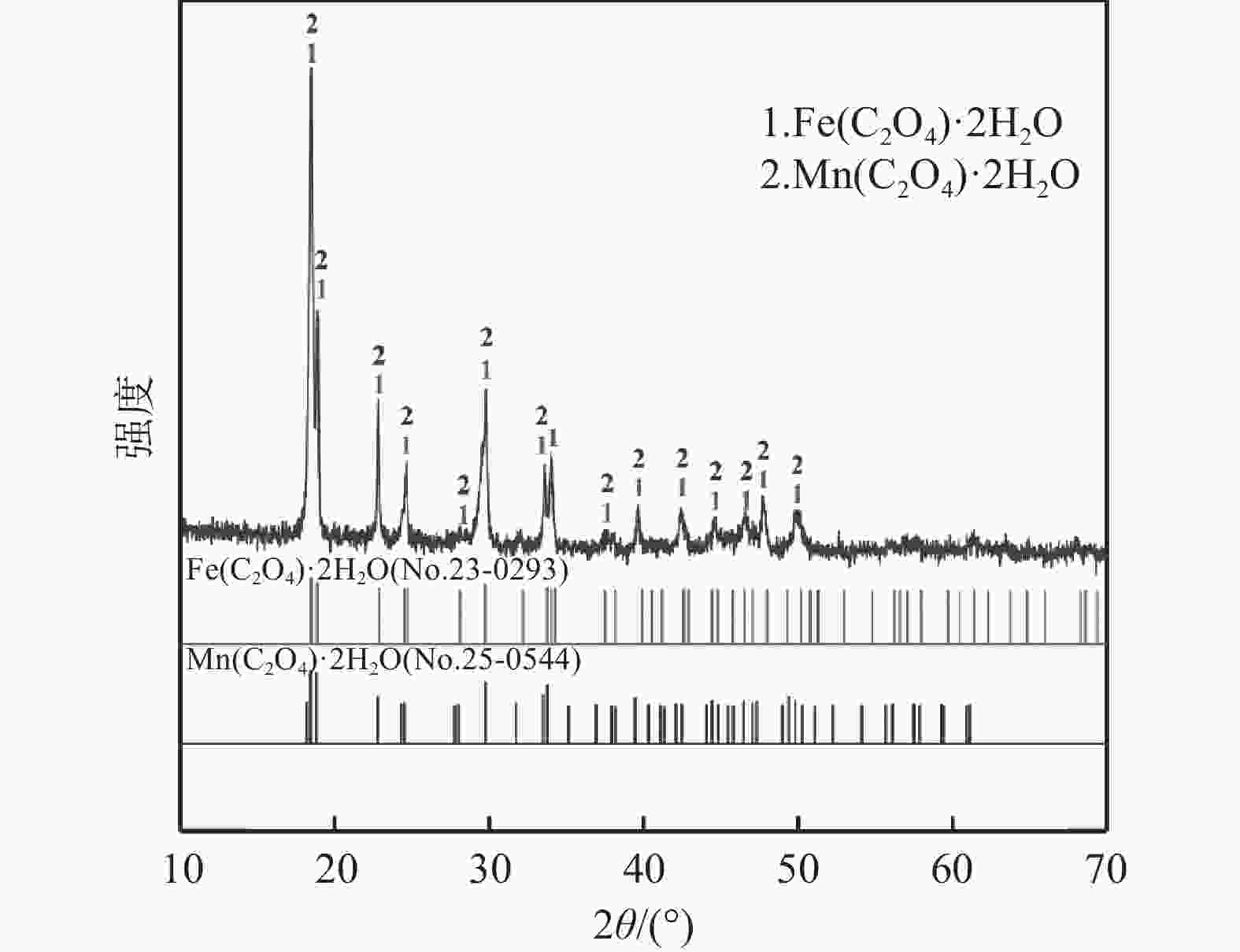
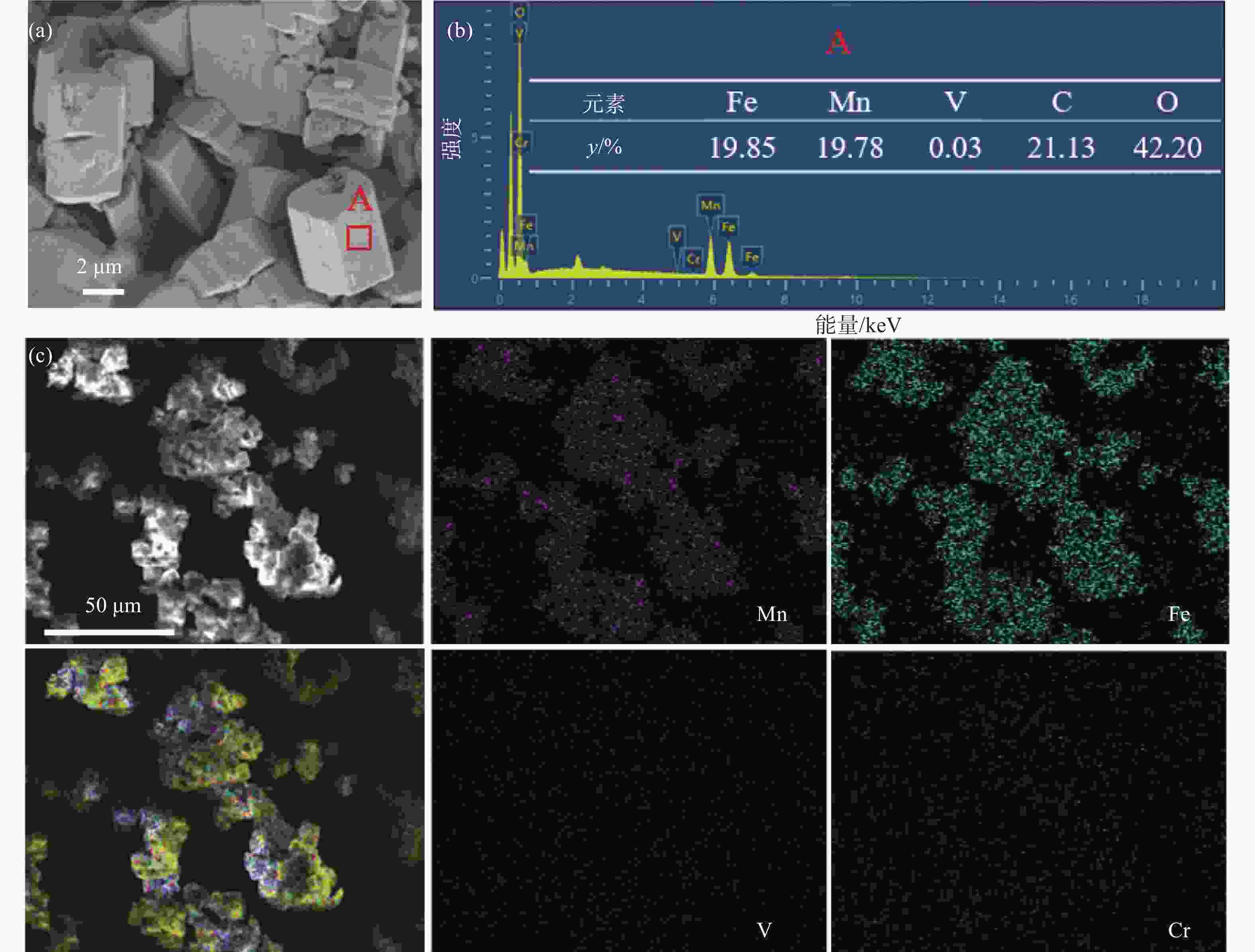
Table 3. Compositions of the precipitation product
% Fe Mn V Cr 49.94 50.03 0.03 <0.01 -
[1] Schmuch Richard, Wagner Ralf, Hörpel Gerhard, et al. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2018,3(4):267-278. doi: 10.1038/s41560-018-0107-2 [2] Wang Yanqiang, Ke Junxiong, Wang Biao, et al. Research progress of ferromanganese phosphate precursors[J]. Chemical Management, 2023(25):138-141. (王彦强, 柯君雄, 王镖, 等. 磷酸锰铁前驱体的研究进展[J]. 化工管理, 2023(25):138-141.Wang Yanqiang, Ke Junxiong, Wang Biao, et al. Research progress of ferromanganese phosphate precursors[J]. Chemical Management, 2023(25): 138-141. [3] Franky E, Lora Bedoya, Victoria Salgado, et al. Stable V-doped LiMnPO4/C cathode material for Li-ion batteries produced by a fast and facile microwave-assisted synthesis[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023,938:53-61. [4] Said Oukahou, Mohammad Maymoun, Abdelali Elomrani, et al. Enhancing the electrochemical performance of olivine LiMnPO4 as cathode materials for Li-ion batteries by Ni-Fe codoping[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(9): 10591-10603. [5] Du Hao, Kang Yuqiong, Li Chenglei, et al. Easily recyclable lithium-ion batteries: Recycling-oriented cathode design using highly soluble LiFeMnPO4 with a water-soluble binder[J]. Battery Energy, 2023,2(4):20230011. [6] Li Jing, Qin Yuanbin, Ning Xiaohui, et al. Improved preparation of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials by high-temperature solid-phase method[J]. Materials Guide, 2020,34(16):16001-16005. (李晶, 秦元斌, 宁晓辉, 等. 改进高温固相法制备磷酸锰铁锂正极材料[J]. 材料导报, 2020,34(16):16001-16005. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19070270Li Jing, Qin Yuanbin, Ning Xiaohui, et al. Improved preparation of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials by high-temperature solid-phase method[J]. Materials Guide, 2020, 34(16): 16001-16005. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19070270 [7] Liu Hongyu, Ren Li, Li Jiashen, et al. Iron-assisted carbon coating strategy for improved electrochemical LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 cathodes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016,212:800-807. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.07.049 [8] Zhu Bo, Wang Yajing, Wang Yanming, et al. Synthesis of LiMn1- xFe xPO4 nanosheets by solvothermal method and their electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Artificial Crystals, 2016,45(7):1826-1831. (朱波, 王雅静, 汪燕鸣, 等. 溶剂热法合成LiMn1- xFe xPO4纳米片及其电化学性能[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2016,45(7):1826-1831. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2016.07.020Zhu Bo, Wang Yajing, Wang Yanming, et al. Synthesis of LiMn1-xFexPO4 nanosheets by solvothermal method and their electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Artificial Crystals, 2016, 45(7): 1826-1831. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2016.07.020 [9] Lü Wei, Cai Wenlong, Wang Tuan, et al. Thermodynamic equilibrium theory-guided design and synthesis of Mg-doped LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4/C cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023,9(1):619-627. [10] Yue Yang, Sun Miaomiao, Yu Wenhao, et al. Recovering Fe, Mn and Li from LiMn1- xFe xPO4 cathode material of spent lithium-ion battery by gradient precipitation[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2023,36:1016-1026. [11] Wang Zhenghao, Chen Liang, Yang Ke, et al. Exploration of a novel vanadium source for the synthesis of a Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode of sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024,12(5):1973-1983. [12] Wang Zhenghao, Chen Liang, Qin Zhifeng, et al. A green and efficient route for simultaneous recovery of low valence of vanadium and chromium, titanium and iron from vanadium slag[J]. Resources, Conservation Recycling, 2022,178:106046. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.106046 [13] Yin Rentao, Chen Liang, Qin Zhifeng, et al. A novel complexation method for separation and recovery of low valence vanadium, iron and chromium from sulfuric acid solution[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022,373:133640. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133640 [14] Wang Zhenghao, Chen Liang, Yin Rentao, et al. Preparation of vanadyl sulfate electrolyte for vanadium flow battery from vanadium slag using calcium salt precipitation, sodium carbonate leaching and solvent extraction[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2023,222:106146. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2023.106146 [15] Zhou Weihua, Li Zhenqin, Duan Meng, et al. Study on complexation and iron removal in vanadium slag leach solution[J]. Iron and Steel Vanadium and Titanium, 2016,37(5):20-24. (周维华, 李振溱, 段猛, 等. 钒渣浸出液中络合除铁的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(5):20-24. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.05.004Zhou Weihua, Li Zhenqin, Duan Meng, et al. Study on complexation and iron removal in vanadium slag leach solution[J]. Iron and Steel Vanadium and Titanium, 2016, 37(5): 20-24. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.05.004 [16] Ding Dong, Yuta Maeysohi, Masaaki Kubota, et al. A facile way to synthesize carbon-coated LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/reduced graphene oxide sandwich-structured composite for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019,2(3):1727-1733. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.8b01821 [17] Yu Songmin, Jin Hongbo, Yang Minghu, et al. Fluorine-doped modified LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode materials and their electrochemical properties[J]. Advances in Chemical Engineering, 2023,43(1):302-309. (于松民, 金洪波, 杨明虎, 等. 氟掺杂改性LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4正极材料及其电化学性能[J]. 化工进展, 2023,43(1):302-309.Yu Songmin, Jin Hongbo, Yang Minghu, et al. Fluorine-doped modified LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode materials and their electrochemical properties[J]. Advances in Chemical Engineering, 2023, 43(1): 302-309. [18] Li Gang, Dai Zhongjia, Yang Wensheng, et al. Influence of precursor particle size on the performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 lithium ternary material[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2020,44(2):145-148. (李刚, 戴仲葭, 杨文胜, 等. 前驱体粒径对锂电三元材料LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2性能的影响[J]. 电源技术, 2020,44(2):145-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2020.02.001Li Gang, Dai Zhongjia, Yang Wensheng, et al. Influence of precursor particle size on the performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 lithium ternary material[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2020, 44(2): 145-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2020.02.001 [19] Yang Hao, Fu Cuimei, Sun Yijian, et al. Fe-doped LiMnPO4@C nanofibers with high Li-ion diffusion coefficient[J]. Carbon, 2020,158:102-109. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.11.067 [20] Lin Chengliang, Zhao Meiju, Yuan Yunquan, et al. Research on the performance regulation of LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4-based hybrid cathode materials[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2023,48(1):45-50. (蔺成良, 赵美菊, 袁云泉, 等. LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4基混合正极材料性能调控研究[J]. 电源技术, 2023,48(1):45-50.Lin Chengliang, Zhao Meiju, Yuan Yunquan, et al. Research on the performance regulation of LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4-based hybrid cathode materials[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2023, 48(1): 45-50. [21] Kosova Nina, Podgornova Olga, Gutakovskii Anton. Different electrochemical responses of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 prepared by mechanochemical and solvothermal methods[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,742:454-465. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.242 [22] Deng Yuanfu, Yang Chunxiang, Zou Kaixiang, et al. Recent advances of Mn-rich LiFe1- yMn yPO4 (0.5 ≤ y ≤ 1.0) cathode materials for high energy density lithium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017,7(13):10-16. [23] Xiao F P, Ding B, Lai O M, et al. High performance LiMn1- xFe xPO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) synthesized via a facile polymer[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017,160(6):918-926. [24] Wei Xiang, Yan Junzhong, Jun Yiji, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis, evolution, and electrochemical performance of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 nanostructures[J]. Physical chemistry chemical physics, 2019,17(28):29-37. [25] Zhou Xue, Xie Ye, Deng Yuanfu, et al. The enhanced rate performance of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C cathode material via synergistic strategies of surfactant-assisted solid state method and carbon coating[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014,3(3):996-1004. -




 下载:
下载: